ELISA Kits
Showing 301–450 of 3623 results
-
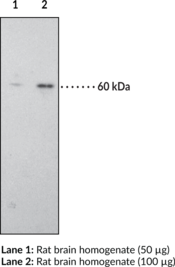
The CB1 receptor is a G-protein coupled receptor that binds the active component of cannabis, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. This antibody has been raised against the C-terminal (amino acids 461-472) intracellular region of the human CB1 receptor and can be used for western blotting.{6749,6747} Human and rat CB1 receptors exhibit 97.3% homology at the amino acid level over the complete protein, and 100% homology within the peptide sequence used to make this antibody.{6629,6628} This peptide exhibits no homology with the CB2 receptor. Based on the amino acid sequence, the CB1 receptor has a molecular weight of approximately 52,800.{6628} The CB1 receptor and the splice variant CB1a are localized mainly in the brain, whereas the CB2 receptor is localized predominantly in peripheral tissues, including the spleen and hemopoietic cells.{6629,6628,6726,6727}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006590 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
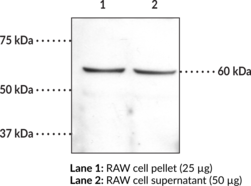
The CB1 receptor and the splice variant CB1a are localized mainly in the brain.{6628,6726,6724} The CB1 receptor is a G-protein coupled receptor that binds the active component of cannabis, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol. Human and rat CB1 receptors exhibit 97.3% homology at the amino acid level over the complete protein, and 100% homology within the peptide sequence used to make this antibody.{6629,6628} This peptide exhibits no homology with the CB2 receptor. Based on the amino acid sequence, the CB1 receptor has a molecular weight of approximately 52,800.{6628} The CB1 receptor and the splice variant CB1a are localized mainly in the brain, whereas the CB2 receptor is localized predominantly in peripheral tissues, including the spleen and hemopoietic cells.{6629,6628,6726,6724} Cayman’s CB1 Receptor Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot and immunohistochemistry applications. The antibody recognizes the N-terminal extracellular region of the CB1 receptor at 40 kDa from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:101500 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
The CB2 receptor is localized predominantly in peripheral tissues, including the spleen and hemopoietic cells.{6724} · The CB1 and CB2 receptors are G-protein coupled receptors that bind the active component of cannabis, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, as well as anandamide which is an endogenous CB receptor ligand. This antibody has been raised against a sequence between the N-terminus and the first transmembrane domain of the protein of the human CB2 receptor.{6724} It can be used for western blotting and immunohistochemistry applications. Conserved amino acids between the CB1 and CB2 receptors in this region are minimal.{6727} Human and murine CB2 receptors exhibit 82% homology at the amino acid level over the complete protein.{6727} The CB2 receptor is localized predominantly in peripheral tissues, including the spleen and hemopoietic cells.{6724}
Brand:CaymanSKU:101550 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
The central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors are G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) that bind the active component of cannabis, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol, as well as anandamide which is an endogenous CB receptor ligand. This antibody has been raised against a sequence between the N-terminal and the first transmembrane domain of the protein of the human CB2 receptor.{6724} Conserved amino acids between the CB1 and CB2 receptors in this region are minimal.{6727} Human and mouse CB2 receptors exhibit 82% homology at the amino acid level over the complete protein.{6727} The CB2 receptor is localized predominantly in peripheral tissues, including the spleen and hemopoietic cells.{6724}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010712 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
CCL2 also known as the monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) is a chemokine and more particularly an C-C chemokine. Initially discovered in 1983, it is a monomeric polypeptide of 73 amino acids (13 kDa). It belongs to a family composed at least of members (MCP-1, -2, -3, and -4). CCL-2 is produced by the immune-cells (monocyte/macrophages) and non-immune cells (endothelial cells-fibroblast-myocyte). The main function of the CCL2 is the chimiotactism and more particularly the regulation of the migration and the infiltration of monocytes, memory T lymphocytes, and natural killer (NK) cells on an infection site. CCL2 is involved in many diseases like HIV-1 pathogenesis, cancer, cardiovascular disease, or diabetes. [Bertin Catalog No. A05415]
Brand:CaymanSKU:23621 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
CD146, also known as the melanoma cell adhesion molecule (MCAM), is an adhesion molecule and type 1 transmembrane glycoprotein with roles in vascular homeostasis, cell migration, and neuronal differentiation and is encoded by MCAM in humans.{58076,58077} It is comprised of a signal sequence, an extracellular domain containing five immunoglobulin-like (Ig-like) domains, a hydrophobic transmembrane domain, and a cytosolic domain composed of an ezrin, radixin, moesin (ERM) protein complex binding motif and a double leucine motif for epithelial basolateral targeting. Alternative splicing of MCAM produces two isoforms that differ in length of their cytosolic domain, CD146 short (shCD146) and CD146 long (lgCD146), that contain one or two protein kinase C (PKC) phosphorylation sites, respectively.{58078} LgCD146 is expressed on endothelial cells, smooth muscle cells (SMCs), and pericytes where it is localized to tight junctions, as well as in mononuclear cells, mesenchymal stromal cells, and trophoblasts.{58076} It induces stabilization of capillary-like structures in a Matrigel™ assay. Cayman’s CD146 Long Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32202 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Revealing the molecular signals involved in B and T cell activation is critical to the future discovery of therapeutics that can augment cell-mediated immune responses to disease.{12747,12749,12748} CD150 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is involved in signal transduction of antigen specific responses in B and T cells. It is expressed by activated B cells isolated from tonsils and peripheral blood, B cells in germinal centers and mantle zone of lymph nodes, immature thymocytes, and CD45RO+CD45RA- subpopulation of T cells.{12746,12772} This antibody has been used to detect CD150 in neoplastic cells from diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Hodgkin’s disease, hairy cell leukemia, and some tumors of ectodermal origin.{12771}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004804 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
CD20 is a non-glycosylated protein encoded by MS4A1 in humans.{59585} It is comprised of four transmembrane domains, a single intracellular loop, and two extracellular loop domains with both the N and C-termini located in the cytosol. CD20 is a general B cell marker that is expressed from the late pre-B lymphocyte stage but is not expressed by pro-B lymphocytes and is lost in terminally differentiated plasma cells and plasmablasts. It forms supramolecular complexes with CD53, CD81, and CD82, as well as MHCII, CD40, B cell receptors, and C-terminal Src kinase-binding protein (CBP) to contribute to signal transduction. MS4A1 expression is variable in B cell malignancies, with the lowest expression found in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and the highest expression found in patients with diffuse large B cell lymphoma (DLBCL) or hairy cell lymphomas. MS4A1 expression is enriched on IFN-γ-inducible T-box transcription factor-expressing B cells in blood isolated from patients with multiple sclerosis.{59586} Cayman’s CD20 (C-Term) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32222 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
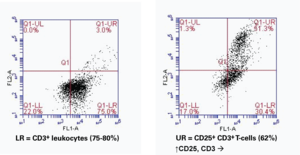
Interleukin-2 (IL-2) elicits its effects by binding to a multi-subunit cell-surface receptor that is inducible by various mitogens.{18182,18183,18184} The highest affinity for IL-2 is achieved when all 3 subunits (IL-2Rα or CD25, IL-2Rβ or CD122, and IL-2Rγ or CD132) are expressed together forming a heterotrimeric complex{6128}. CD25 is inducible in T-cells by antigen, mitogen or antibodies bound to the T-cell receptor CD3.{18183,18185} Binding of IL-2 to IL-2R on NK cells results in their conversion to LAK cells, which release several other cytokines (TNF, INF-γ, and GM-CSF).{6128,6349} Activated T-cells will respond to IL-2 by proliferating and secreting cytokines and cytolytic molecules. Activated B cells will proliferate and secrete antibodies.{11282}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10339 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
CD27 is a type II homodimeric transmembrane glycoprotein (Mr = 55 kDa) and a member of the nerve growth factor/tumor necrosis receptor superfamily.{13302,13303} The antigen was identified on medullar thymocytes, mature T lymphocytes (CD45RA+CD45RO- T-cell subpopulation), memory B cells, plasma, and NK cells. This antibody is well suited for immunohistochemical detection of CD27 in B cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004837 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
The CD3 antigen is a specific T-cell marker expressed on thymocytes and mature T-lymphocytes. The CD3 complex contains CD3g (Mr = 26 kDa), CD3d (Mr = 21 kDa), and CD3e (Mr = 20 kDa).{16550} CD3 is detected on the surface membrane or in the cytoplasm of T-cells from peripheral blood, depending on the state of cell differentiation. In addition to detection of T-cells from peripheral blood, the CD3 antibody can be used for detection of reactive T-cells in lymphoid infiltrates in tissues and neoplastic T-cells in non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas of T-cell lineage.{12060,16551}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10231 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
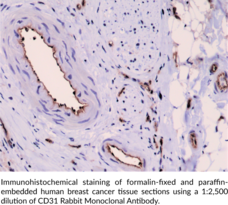
CD31, also known as platelet endothelial cell adhesion molecule (PECAM-1), is a vascular cell adhesion molecule and member of the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily of glycoproteins.{54427} It is a transmembrane glycoprotein that contains a large extracellular domain with Ig homology domains and glycosaminoglycan binding sites, a membrane-spanning region, and a cytoplasmic domain containing multiple phosphorylation sites.{54427,54428} CD31 is expressed on a variety of cells, including endothelial cells, monocytes, neutrophils, and platelets, among others.{54427} It forms homophilic interactions, which allow it to aggregate at endothelial cell-cell junctions where it regulates vascular permeability.{54428} Tyrosine phosphorylation at sites on the CD31 cytoplasmic domain, including at immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitory motifs (ITIMs), recruits cytoplasmic proteins, leading to downstream signaling with either inhibitory or activating effects.{54429} CD31 also has roles in integrin-mediated adhesion, leukocyte recruitment, angiogenesis, and inflammation.{54428,54430,54431} High levels of CD31+ circulating cells positively correlate with C-reactive protein (CRP) levels and the Framingham risk score for hard coronary artery disease, while low levels on circulating cells negatively correlate with the Framingham risk score.{54432} A mutation in PECAM1, the gene encoding CD31, is associated with atherosclerotic cerebral infarction.{54433} Cayman’s CD31 Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes CD31 at approximately 130 kDa from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32201 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
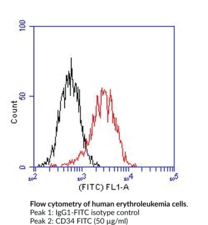
CD34 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein (Mr = 116 kDa). The antigen is expressed on stem cells and early hematopoietic progenitor cells, bone marrow stromal cells, endothelial cells, embryonic fibroblasts, and neurons.{13306,13307} This anti-CD34 monoclonal antibody can be used for the differential staining of acute leukemia cells.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004835 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
This CD34 monoclonal antibody recognizes an extracellular carbohydrate epitope of CD34.{15992} CD34 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein (Mr = 104-120 kDa) expressed on stem cells, early hematopoietic progenitor cells, bone marrow stroma cells, endothelial cells, embryonic fibroblasts, and neurons.{13306,13307} CD34 analysis can be used for the differential identification of acute leukemias as well as routine analysis of cultured stem cell lines.
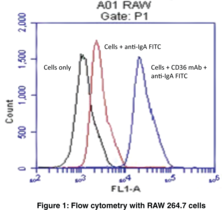
Brand:CaymanSKU:10208 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
CD36 is a type-B scavenger receptor that is necessary for the formation of foam cells and thereby atherosclerotic lesions.{7719,9800,9801,9795} This membrane glycoprotein can internalize fatty acids which activate PPARγ and stimulate further expression of CD36.{9798,8499} This positive feedback loop combined with the murine CD36 knock-out studies reinforces the importance of CD36 in lipid metabolism. Additionally, CD36 is needed for the phagocytosis of P. falciparum infected erythrocytes, retinal pigment epithelial cell photoreceptor fragments, and post-apoptotic monocytes and neutrophils.{9794,9310,9793,9791} CD36 expression has been monitored during hematopoietic cell differentiation and may be an indicator of tumor spreading in lymphocytic leukemia.{9797} Positive controls include cells from adipose and heart tissue, platelets, and macrophages. Cayman Chemical’s CD36 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone JC63.1) is recommended for flow cytometry on CD36-containing cells of murine, rat, and human origin. The antibody can also be used to antagonize CD36-mediated cellular activity. Functional blocking inhibits CD36 binding of oxLDL (macrophages) and prevents foam cell formation of macrophages.
Brand:CaymanSKU:188150 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
CD36 is a type-B scavenger receptor that is necessary for the formation of foam cells and thereby atherosclerotic lesions.{7719,9800,9801,9795} This membrane glycoprotein can internalize fatty acids which activate PPARγ and stimulate further expression of CD36.{9798,8499} This positive feedback loop combined with the murine CD36 knock-out studies reinforces the importance of CD36 in lipid metabolism. Additionally CD36 is needed for the phagocytosis of P. falciparum infected erythrocytes, retinal pigment epithelial cell photoreceptor fragments and post-apoptotic monocytes and neutrophils.{9794,9310,9793,9791} CD36 expression has been monitored during hematopoietic cell differentiation and may be an indicator of tumor spreading in lymphocytic leukemia.{9797} Positive controls include adipose and heart tissue, platelets, and macrophages. Cayman’s CD36 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone JC63.1) (azide free) can be used for flow cytometry, functional blocking, and immunocytochemistry applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009893 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
CD36 is a type-B scavenger receptor that is necessary for the formation of foam cells and thereby atherosclerotic lesions.{7719,9800,9801,9795} This membrane glycoprotein can internalize fatty acids which activate PPARγ and stimulate further expression of CD36.{9798,8499} This positive feedback loop combined with the murine CD36 knock-out studies reinforces the importance of CD36 in lipid metabolism. Additionally CD36 is needed for the phagocytosis of P. falciparum infected erythrocytes, retinal pigment epithelial cell photoreceptor fragments and post-apoptotic monocytes and neutrophils.{9794,9310,9793,9791} CD36 expression has been monitored during hematopoietic cell differentiation and may be an indicator of tumor spreading in lymphocytic leukemia.{9797} Positive controls include adipose and heart tissue, platelets, and macrophages. Cayman’s CD36 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone JC63.1) (azide free) can be used for flow cytometry, functional blocking, and immunocytochemistry applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009893 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
CD36 is a type-B scavenger receptor that is necessary for the formation of foam cells and thereby atherosclerotic lesions.{7719,9800, 9801,9795} This membrane glycoprotein can internalize fatty acids which activate proliferator-activated receptor γ and stimulate further expression of CD36.{9798,8499} This positive feedback loop combined with the murine CD36 knock-out studies reinforces the importance of CD36 in lipid metabolism. Additionally CD36 is needed for the phagocytosis of P. falciparum infected erythrocytes, retinal pigment epithelial cell photoreceptor fragments and post-apoptotic monocytes and neutrophils.{9794,9310,9793,9791} CD36 expression has been monitored during hematopoietic cell differentiation and may be an indicator of tumor spreading in lymphocytic leukemia.{9797} Positive controls include adipose and heart tissue, platelets, and macrophages. Cayman’s CD36 Monoclonal FITC Antibody (Clone JC63.1) can be used for flow cytometry and immunofluorescence applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009870 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
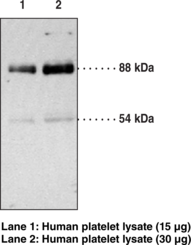
CD36 is a type-B scavenger receptor that is necessary for the formation of foam cells in atherosclerotic lesions.{7719,9800,9801,9795} This membrane glycoprotein can internalize fatty acids which activate PPARγ and stimulate further expression of CD36.{9798,8499} This positive feedback loop combined with the murine CD36 knock-out studies reinforces the importance of CD36 in lipid metabolism. Additionally CD36 is needed for the phagocytosis of P. falciparum infected erythrocytes, retinal pigment epithelial cell photoreceptor fragments, and post-apoptotic monocytes and neutrophils.{9794,9310,9793,9791} CD36 expression has been monitored during hematopoietic cell differentiation and may be an indicator of tumor spreading in lymphocytic leukemia.{9797} This transmembrane glycoprotein is detected by immunoblotting at 88 kDa or 54 kDa depending on the degree of glycosylation of the receptor in your sample. Positive controls include adipose and heart tissue, platelets, and macrophages.
Brand:CaymanSKU:100011 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
CD37 is a type III transmembrane glycoprotein (Mr = 40-52 kDa). The leukocyte-specific protein CD37 is a member of the tetraspanin superfamily, originally described as a cell surface glycoprotein expressed on mature human B cells, but not on pro-B cells or plasma cells.{13049,13050} T cells and monocytes express CD37 at low levels. In humans, CD37 expression is restricted to B and T lymphocytes, monocytes, macrophages, neutrophils, dendritic cells, and certain leukocyte-derived malignant cells. CD37 is not expressed by NK cells, platelets, or erythrocytes.{13048} CD37 monoclonal antibody is recommended for immunophenotyping of B cell neoplasia (B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia, hairy cell leukemia, and B cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas). Human, rat, and murine CD37 sequences have been identified.{13051,13052}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004718 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
CD4 is a transmembrane glycoprotein present on the surface of a majority of thymocytes and T cell subpopulations, which recognize antigens presented by MHC class II molecules. The CD4 antigen is also found on monocytes, dendritic cells, tissue macrophages, and granulocytes. CD4+ T lymphocytes are presented by functional T-helper cells and CD4+CD25+ regulatory (suppressor) T cells. Estimation of CD4+ T cell level could be used for immunological status monitoring.{12087}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004599 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
CD4, a transmembrane glycoprotein, is present on the surface of a majority of thymocytes and T cell subpopulations, which recognize antigens presented by MHC class II molecules. The CD4 antigen is also found on monocytes, dendritic cells, tissue macrophages and granulocytes. CD4+ T lymphocytes are presented by functional T-helper cells and CD4+CD25+ regulatory (suppressor) T cells. Estimation of CD4+ T cell level could be used for immunological status monitoring.{12087}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010530 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
CD44 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein and cell adhesion molecule belonging to the cartilage link protein family with roles in cell-cell and cell-matrix interactions, signal transduction, and cell migration.{55241,55242,55243} It is comprised of an N-terminal extracellular globular domain with a link domain that binds to the extracellular matrix component hyaluronan (HA) and other glycosaminoglycans, a membrane-proximal stem structure, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain that facilitates interactions with cytoskeleton-associated proteins.{55241,55244} The stem structure of CD44 can be modified via inclusion of variant exons between amino acid residues 222 and 223, resulting in several variant (CD44v) isoforms with the shortest and most prevalent isoform, known as the standard isoform (CD44s) or hematopoietic isoform (CD44H), having no exon insertions at this position.{55241,55245,55246} CD44 is expressed in a variety of cell types, including endothelial and epithelial cells, fibroblasts, and leukocytes.{55242} Binding of CD44 to HA is induced in T cells and monocytes upon antigen recognition and activation by inflammatory stimuli, respectively.{55247} The interaction between CD44 and HA mediates T cell rolling and recruitment of leukocytes to sites of inflammation. Several CD44 isoforms are expressed in tumor cells, including CD44v6, the overexpression of which is associated with tumor differentiation and lymph node metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).{55248,55249} Cayman’s CD44 Extracellular Domain Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32214 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
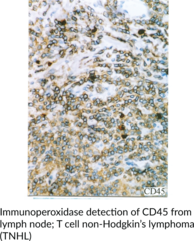
CD45 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is encoded by the PTPRC gene in humans and is abundantly expressed on nucleated hematopoietic cells.{49671} It contains an extracellular region that binds to glycoproteins and exists in various isoforms in a cell type-, differentiation state-, and activation state-dependent manner.{49671,49676} CD45 also contains two highly conserved cytoplasmic protein tyrosine phosphatase domains that regulate intracellular signaling.{49671} CD45 functions as a negative or positive regulator of antigen receptor signaling in T and B cells through dephosphorylation of Src family kinases in a cell type- and differentiation state-dependent manner.{49676} It also dephosphorylates JAK kinases, inhibiting cytokine and chemokine signaling in leukocytes. Mutations in PTPRC are associated with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) in mice and humans.{49672,49673,49674} The number of CD45+ cells is increased in postmortem brain from patients with Alzheimer’s disease.{49675} Increased levels of the CD45 isoform CD45RO have been found on CD19+ lamina propria B cells isolated from patients with Crohn’s disease.{49676} Fluorescently labeled versions of CD45 have commonly been used as a pan leukocyte marker in flow cytometry. Cayman’s CD45 (C-Term) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32236 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
CD45 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that is encoded by the PTPRC gene in humans and is abundantly expressed on nucleated hematopoietic cells.{49671} It contains an extracellular region that binds to glycoproteins and exists in various isoforms in a cell type-, differentiation state-, and activation state-dependent manner.{49671,49676} CD45 also contains two highly conserved cytoplasmic protein tyrosine phosphatase domains that regulate intracellular signaling.{49671} CD45 functions as a negative or positive regulator of antigen receptor signaling in T and B cells through dephosphorylation of Src family kinases in a cell type- and differentiation state-dependent manner.{49676} It also dephosphorylates JAK kinases, inhibiting cytokine and chemokine signaling in leukocytes. Mutations in PTPRC are associated with severe combined immunodeficiency (SCID) in mice and humans.{49672,49673,49674} The number of CD45+ cells is increased in postmortem brain from patients with Alzheimer’s disease.{49675} Increased levels of the CD45 isoform CD45RO have been found on CD19+ lamina propria B cells isolated from patients with Crohn’s disease.{49676} Fluorescently labeled versions of CD45 have commonly been used as a pan leukocyte marker in flow cytometry. Cayman’s CD45 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone BRA-55) can be used for flow cytometry, Western blot, immunocytochemistry, and immunohistochemistry applications. The antibody recognizes CD45 at 170-220 kDa from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004597 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
This monoclonal antibody is labeled with fluorescein and intended for direct labeling of human CD5-expressing cells. CD5 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein (Mr = 67 kDa), expressed on mature T-cells, the majority of thymocytes and B1a-subpopulation of B-cells.{17365} CD5 is a marker of lymphocytes in autoimmune disorders (rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosis), B-cell chronic leukemia, T-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia, small lymphocytic, and mantle cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Enough antibody for 100 x 3 µg tests is provided per vial.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10232 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
CD74 is a non-polymorphic type II integral membrane protein. It has a short N-terminal cytoplasmic tail of 28 amino acids, followed by a single 24 amino acid transmembrane region and an approximately 150 amino acid lumenal domain.{15683} The CD74 chain is thought to function mainly as a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II chaperone, which promotes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) exit of MHC class II molecules, directs them to endocytic compartments, prevents peptide binding in the ER, and contributes to peptide editing in the MHC class II compartment. Class II MHC and invariant chain expression was believed to be restricted to classical antigen-presenting cells (APC); however, during inflammation, other cell types, including mucosal epithelial cells, have also been reported to express class II MHC molecules.{15684} Experiments that investigate cell-surface CD74 are complicated by the fact that CD74 remains on the cell surface for a very short time. The surface half-life of CD74 was calculated to be fewer than 10 minutes.{15685} CD74 however has also recently been shown to have a role as an accessory-signalling molecule because of its macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF).{15685} The restricted expression of CD74 by normal tissues and its very rapid internalization make CD74 an attractive therapeutic target for both cancer and immunologic diseases.{15686}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011432 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
CD74 is a non-polymorphic type II integral membrane protein. It has a short N-terminal cytoplasmic tail of 28 amino acids, followed by a single 24 amino acid transmembrane region and an approximately 150 amino acid lumenal domain.{15683} The CD74 chain is thought to function mainly as a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II chaperone, which promotes endoplasmic reticulum (ER) exit of MHC class II molecules, directs them to endocytic compartments, prevents peptide binding in the ER, and contributes to peptide editing in the MHC class II compartment. Class II MHC and invariant chain expression was believed to be restricted to classical antigen-presenting cells (APC); however, during inflammation, other cell types, including mucosal epithelial cells, have also been reported to express class II MHC molecules.{15684} Experiments that investigate cell-surface CD74 are complicated by the fact that CD74 remains on the cell surface for a very short time. The surface half-life of CD74 was calculated to be fewer than 10 minutes.{15685} CD74 however has also recently been shown to have a role as an accessory-signalling molecule because of its macrophage migration-inhibitory factor (MIF).{15685} The restricted expression of CD74 by normal tissues and its very rapid internalization make CD74 an attractive therapeutic target for both cancer and immunologic diseases.{15686}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011432 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
CD8 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein that functions as a T cell receptor (TCR) co-receptor.{53531} It exists as an αα homodimer or αβ heterodimer and is composed of an extracellular IgV-like domain that interacts with MHC class I molecules and a cytoplasmic tail that associates with the tyrosine kinase p56Ick and mediates signal transduction to the TCR. It is expressed on the surface of, and used as a marker for, cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). CD8 is also expressed on natural killer (NK) and dendritic cells and its expression is used to characterize the development stage of thymocytes. CD8 promotes CTL-mediated killing of virally infected cells or cancer cells by binding to antigen-displaying MHC class I molecules and enhancing TCR-mediated intracellular signaling pathways.{53532} Neutralization of circulating CD8+ cells with monoclonal antibodies reduces hepatic virus elimination and decreases splenic CTL activity in a mouse model of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) infection.{53533} Adoptive transfer of antigen-experienced CD8+ T cells, in combination with IL-2, reduces tumor growth and increases survival in a B16/F10 murine melanoma model.{53534} The number of circulating CD8+ T cells is increased in individuals with HIV-1 infection and is associated with stroke, ischemic heart disease, and non-AIDS-related complications.{53535} Cayman’s CD8 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RIV11) can be used for flow cytometry (FC), immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004715 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
CD95 is a type I transmembrane glycoprotein receptor encoded by the FAS gene in humans.{49679} Alternative splicing of FAS generates a soluble form of the protein. CD95 is expressed by activated T and B cells, and thymocytes and has been found in the thymus, liver, heart, and kidney.{49678,49680,49681} CD95 is involved in the induction of apoptosis, as Fas ligand activation of CD95 leads to formation of a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC) comprised of CD95 oligomers, the Fas-associated death domain protein (FADD), procaspase-8, procaspase-10, and c-FLIP.{49682} DISC formation and CD95 internalization is rapid in type I apoptotic cells, where is it associated with plasma membrane lipid rafts, and delayed in type II apoptotic cells, where it is found in both lipid raft- and non-raft regions of the membrane.{49683,11907} CD95 has non-apoptotic activity as well, including activation of the NF-κB signaling pathway and inducing renal tubular epithelial cell migration, among others.{49681} Inhibition or activation of CD95 reduces or promotes cancer cell functions, respectively, in vitro and in vivo in animal models. However, high serum levels of CD95 in patients with various cancers are associated with metastasis, progression, and shorter survival. Mice lacking the gene for CD95 develop spontaneous autoimmunity and have been used as a model of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Mutations in FAS are associated with various cancers and autoimmune lymphoproliferative syndrome (ALPS) type 1a, which is characterized by non-malignant lymphadenopathy and splenomegaly.{49682,49684} Cayman’s CD95 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone IPO-4) can be used for flow cytometry, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC; frozen sections) applications. The antibody recognizes CD95 from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004604 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600613 - 50 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:601104 - 25 µLAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600094 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600302 - 50 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600803 - 200 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600472 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600175 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009906 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600172 - 50 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009322 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009322 - 2 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009322 - 3 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009322 - 4 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009322 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400146 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600054 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600054 - 2 mgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:601105 - 50 µLAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600371 - 50 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600321 - 30 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600092 - 250 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600615 - 2.5 mlAvailable on backorder
Cell-Based Assay EGCG has been formulated and tested to work with Cayman’s Assay Kits. Detailed instructions for its use are contained in the respective Cayman Assay Kit booklet.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011096 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009899 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600802 - 2 mgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600362 - 3 mgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600155 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600332 - 50 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600053 - 100 µLAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600053 - 500 µLAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600052 - 100 µLAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600052 - 500 µLAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600051 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008978 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010215 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600361 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600621 - 50 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600622 - 25 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600441 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600471 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600612 - 25 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600055 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600322 - 50 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600096 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600093 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600095 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600744 - 10 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009869 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600372 - 50 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009866 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:600091 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder