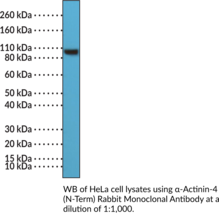ELISA Kits
Showing 3601–3623 of 3623 results
-
Brand:CaymanSKU:100020 - 500 µl
Available on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:100018 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:100018 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:100017 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:100017 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:171142 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:171142 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
α-Actinin-4 (ACTN4) is a filamentous actin-crosslinking protein and member of the α-actinin protein family with roles in the regulation of cytoskeletal integrity and cell movement, as well as gene transcription.{59664,59662} It is composed of an N-terminal actin-binding region with two calponin-homology repeats, a rod domain containing four spectrin-like repeats that is essential for anti-parallel dimerization, and a C-terminal calmodulin-like domain.{59664} ACTN4 is ubiquitously expressed in non-muscle cells and primarily localized to the cytoplasm where it participates in cytoskeletal organization.{59662} However, ACTN4 can be translocated to the nucleus and induce transcription via interaction with nuclear receptors, including estrogen receptor α, retinoic acid receptors (RARs), and the vitamin D receptor, and acts as a transcriptional co-activator of NF-κB. Mutation of ACTN4 induces podocyte injury caused by cytoskeletal dysregulation and proteotoxicity and has been seen in patients with hereditary focal segmental glomerulosclerosis.{59663} ACTN4 is overexpressed and associated with tumor metastasis in various cancers.{59662} Cayman’s α-Actinin-4 (N-Term) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32239 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
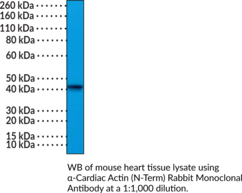
α-Cardiac actin is one of the main actin isoforms found in adult cardiac muscle and the predominant actin in the embryonic heart.{60039,60040} It is a globular protein that forms microfilaments at the Z-disc of sarcomeres and interacts with myosin to perform myofilament, and thus cardiac muscle, contractions.{60041} Knockout of Actc1, the gene encoding α-cardiac actin, is embryonic lethal in approximately half of mice and generally lethal within two weeks of birth for the other 50%.{60039} Mutations in ACTC1 are associated with atrial septal defects, familial hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy.{60040,60042} Cayman’s α-Cardiac Actin (N-Term) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32211 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
α-Enolase, also known as enolase 1, is a glycolytic enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 2-phosphoglycerate to phosphoenolpyruvate.{42086} It is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues, including liver, spleen, kidney, and brain. In cells, α-enolase is primarily localized to the cytoplasm, however, an alternatively translated form localizes to the nucleus and lacks glycolytic enzyme activity.{42086,42087} α-Enolase also functions as a cell surface receptor for plasminogen on pathogens and activated immune cells, as an oxidative stress protein in endothelial cells, and as a chromatin binding partner to facilitate transcription.{42087,42088,42089} The ENO1 promoter contains a hypoxia-response element, allowing α-enolase to facilitate aerobic glycolysis and contribute to the Warburg effect in tumor cells.{42087} α-Enolase is overexpressed in multiple tumors, including glioma, neuroblastoma, pancreatic, prostate, and hepatocellular carcinomas. Its role as a plasminogen receptor facilitates extracellular matrix degradation and cancer invasion.{42089} α-Enolase is an autoantigen in asthma, Hashimoto’s encephalopathy, and rheumatoid arthritis, and has been found in the serum of pediatric patients with juvenile idiopathic arthritis.{42090,42091,42092,36062} Cayman’s α-Enolase Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot and ELISA applications. The antibody recognizes α-enolase at ~47 kDa from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20491 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
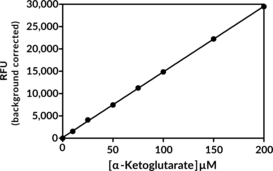
Cayman’s α-Ketoglutarate (α-KG) Fluorometric Detection Assay provides a fluorescence-based method for quantifying α-KG in biological samples such as serum, plasma, urine, and tissue. It can also be utilized to determine intracellular and extracellular α-KG concentrations in cell culture samples. In this assay, alanine transaminase (ALT) deaminates α-KG to form pyruvate.{33073,33074} Pyruvate is then oxidized by pyruvate oxidase to yield acetyl phosphate, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and carbon dioxide.{33075} As H2O2 is produced, the cycling mechanism of horseradish peroxidase results in the concurrent reduction of H2O2 to H2O and oxidation of 10-acetyl-3,7-dihydroxyphenoxazine (ADHP) to produce the highly fluorescent compound resorufin.{33076} Resorufin fluorescence is analyzed with an excitation wavelength between 530-540 nm and an emission wavelength between 585-595 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:701350 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
α-Synuclein is a 140-amino acid intracellular protein encoded by the SNCA gene in humans.{46939} It is primarily localized to the synaptic terminal of neurons in both the central and peripheral nervous systems where it has a role in regulation of synaptic vesicle docking and neurotransmitter release.{46938} α-Synuclein is an intrinsically disordered, multi-domain protein.{46939,46937} It exists as monomer in the cytoplasm, however, mutations, posttranslational modifications, and changes in cellular environmental conditions can induce oligomerization and aggregate formation that lead to various pathologies, including Parkinson’s disease, Lewy body disease, multiple system atrophy (MSA), and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Phosphorylation of α-synuclein at serine 129 (Ser129) is increased in response to mitochondrial stress and is reduced by lysosome inhibition in SH-SY5Y cells.{46941} It enhances α-synuclein-induced neurotoxicity in Drosophila and rat models of Parkinson’s disease.{46942,46941} Levels of phosphorylated Ser129 (phospho-Ser129) are increased in Lewy bodies in postmortem brains from patients with Parkinson’s disease and Lewy body disease compared with control individuals.{46942,46940,46941} Cayman’s α-Synuclein (Phospho-Ser129) Polyclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes α-synuclein (phospho-Ser129) at approximately 15 kDa from human, mouse, and rat samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29252 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
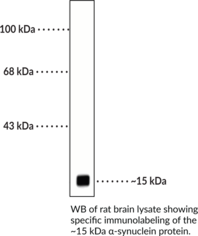
α-Synuclein is a 140-amino acid intracellular protein encoded by the SNCA gene in humans.{46939} It is primarily localized to the synaptic terminal of neurons in both the central and peripheral nervous systems where it has a role in regulation of synaptic vesicle docking and neurotransmitter release.{46938} α-Synuclein is an intrinsically disordered, multi-domain protein composed of a negatively charged C-terminal domain that provides structural flexibility, a central hydrophobic region with a high propensity to aggregate, and a positively charged N-terminal domain containing a repeated consensus sequence KTKEGV.{46939,46937} It exists as monomer in the cytoplasm, however, mutations, posttranslational modifications, and changes in cellular environmental conditions can induce oligomerization and aggregate formation. Aggregated α-synuclein is found in Lewy bodies that occur in Parkinson’s disease and diffuse Lewy body disease, as well as in glial cells in postmortem brains from patients with multiple system atrophy (MSA) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Cayman’s α-Synuclein Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunocytochemistry (ICC) and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes α-synuclein at approximately 15 kDa from human, mouse, and rat samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29251 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
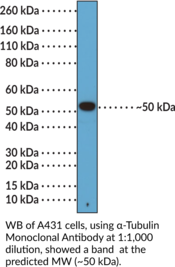
α-Tubulin is a cytoskeletal protein and constituent of microtubules, a cytoskeletal assembly that has roles in a variety of cellular processes, including cell motility, division, differentiation, and intracellular transport.{57121} α-Tubulin is highly conserved in eukaryotes and expressed in a cell- and isotype-specific manner.{57122} There are eight human α-tubulin isotypes that consist of an N-terminal domain, which binds GTP and is required for microtubule self-assembly, and a variable C-terminal tail, which contains interaction sites for microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) and is subject to a variety of post-translational modifications that regulate microtubule function and stability.{57123,57124,57121,57125} Cayman’s α-Tubulin Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunocytochemistry (ICC) and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes α-tubulin at approximately 50 kDa.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32126 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
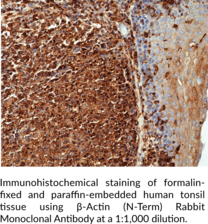
β-Actin is a cytoskeletal protein with roles in cell division, migration, and homeostasis that is encoded by ACTB in humans.{52776,52777} It is ubiquitously expressed, localized to the cytosol, and conserved from birds to mammals. β-Actin is enriched at the leading edge of migrating cells and Actb-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) exhibit decreased migration velocity, increased apoptosis, and decreased proliferation.{52776} Actb knockout is early embryonic lethal in mice, indicating that β-actin is essential for embryonic development. ACTBR183W and ACTBE346K gain-of-function mutations have been found in patients with deafness, developmental mutations, and juvenile-onset dystonia and neutrophil dysfunction, respectively.{52778} Cayman’s β-Actin (N-Term) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP), immunocytochemistry (ICC), immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunoprecipitation (IP), and Western blot (WB) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32127 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
β-Catenin is a central component of the cadherin cell adhesion complex and plays an essential role in neural development in the Wingless/Wnt signaling pathway.{14334,14336} The role of β-catenin in these processes is thought to be regulated by the sequential phosphorylation of Ser29, Ser33, Ser37, and Thr41 by glycogen synthase kinase 3β (GSK3β).{14335} This hyperphosphorylation promotes the ubiquitylation and targeted destruction of β-catenin. Mutations in components of this phosphorylation-regulated process that prevent β-catenin hyperphosphorylation by GSK3β are strongly associated with cancers.{14335,14336,14337}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009180 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
β-Catenin is a multifunctional protein known to be part of the Wnt pathway, playing essential roles in development and carcinogenesis.{11352,11347,11344} β-Catenin can act as a regulator of the cell cycle and apoptosis in a variety of different cell systems.{11349,11350} The entire primary amino acid sequence is identical among human, rat, and mouse, indicating critical functions of this protein{11351,11348,11345}. Cayman’s β-catenin polyclonal antibody can be used for Western blot and immunohistochemical (formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded tissue) analysis of β-catenin on samples of human, murine, rat, porcine and bovine origin. The antibody recognizes β-Catenin at 91 kDa from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:100029 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
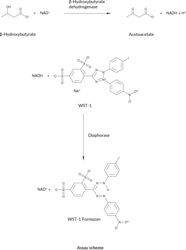
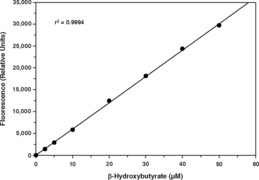
β-Hydroxybutyrate (β-HB; 3-hydroxybutyric acid) is a “ketone body” which is produced in the liver, mainly from the oxidation of fatty acids, and is exported to peripheral tissues for use as an energy source. The term ‘ketone body’ refers to three molecules, acetoacetate, β-HB, and acetone. β-HB and acetoacetate transport energy from the liver to the other tissues and acetone is generated by spontaneous decarboxylation of acetoacetate.{17093} The presence of ketosis may be normal or pathologic. Normally ketosis can indicate that lipid metabolism has been activated and the pathway of lipid degradation is intact. Normal ketosis is prevalent in many circumstances such as during fasting, after prolonged exercise or after a high fat diet. Pathological causes of ketosis include multiple organ failure, diabetes, childhood hypoglycemia, corticosteroid or growth hormone deficiency, intoxication with alcohol or salicylates and several inborn errors of metabolism.{17094} In acutely ill patients, these ketone bodies can accumulate in the body to cause ketoacidosis, which leads to the potentially life threatening condition known as metabolic acidosis.{17125} The presence and degree of ketosis can be determined by measuring blood levels of β-HB. Ordinarily, β-HB accounts for approximately 75% of the ketone bodies in serum.{17126,17127,17095} Measurement of β-HB provides a reliable index of the level of ketoacidosis, including the detection of subclinical ketosis.{17096,17097,17128} In diabetics, β-HB measurements (and blood glucose) can be used for the assessment of the severity of diabetic coma and is essential for the exclusion of hyperosmolar non-ketotic diabetic coma. The measurement of β-HB is also used to monitor insulin requirements, based on existing hyperketonemia.{17098} β-HB has more recently been evaluated for use in neurodegenerative diseases and inhibition of adipocyte lipolysis.{17099,17100,17101,17102,17103} Cayman’s β-HB (Ketone Body) Assay Kit provides a simple, reproducible, and sensitive tool for measuring β-HB levels in plasma, serum, urine, cell lysates, or tissue homogenates. The method for β-HB determination is based upon the oxidation of D-3-Hydroxybutyrate to acetoacetate by the enzyme 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase.{17104} Concomitant with this oxidation, the cofactor NAD+ is reduced to NADH. In the presence of diaphorase, NADH reacts with the colorimetric detector WST-1 to produce a formazan dye with an absorbance maximum at 445-455 nm. The absorbance of the dye is directly proportional to the β-HB concentration.
Brand:CaymanSKU:700190 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
β-Hydroxybutyrate (β-HB; 3-hydroxybutyric acid) is produced in the liver, mainly from the oxidation of fatty acids, and exported to peripheral tissues for use as an energy source. Measurement of β-HB can provide a reliable index of the level of normal ketosis as well as detect pathological ketoacidosis, including the assessment of the severity of diabetic coma and monitor insulin requirements in diabetic patients. Cayman’s β-HB (Ketone Body) Fluorometric Assay Kit provides a simple, reproducible, and sensitive tool for assaying β-HB from plasma, serum, urine, tissue homogenates, and cell culture samples. The method for β-HB determination is based upon the oxidation of D-3-Hydroxybutyrate to acetoacetate by the enzyme 3-hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase. Concomitant with this oxidation, the cofactor NAD+ is reduced to NADH. NADH reacts with the fluorometric developer to yield a highly fluorescent product which can be analyzed with an excitation wavelength of 530-540 nm and an emission wavelength of 585-595 nm. The fluorescence is directly proportional to the β-HB concentration.
Brand:CaymanSKU:700740 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700191 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
β2-Microglobulin is a 99-amino acid protein and the light chain component of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I molecules.{45065} It is non-covalently associated with the MHC class I α chain and comprises a protein-building subunit of the MHC class I molecule to facilitate complex transport to the cell surface and antigen presentation to cytotoxic T cells. β2-Microglobulin is found in cells, as well as in extracellular fluids, including urine and serum, and MHC class I-associated β2-microglobulin exhibits dissociation and equilibrium exchange with circulating soluble β2-microglobulin. Serum levels of β2-microglobulin are increased in patients with renal failure, systemic amyloidosis, various autoimmune diseases, including multiple sclerosis, chronic infections, and a variety of cancers.{45065,45066,45067,45064} It mediates signaling pathways that promote cellular growth, angiogenesis, epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), and bone metastasis and is used as a predictive biomarker of survival in multiple myeloma and colorectal cancers.{45065} Cayman’s β2-Microglobulin Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot and ELISA applications. This antibody recognizes β2-Microglobulin at ~13.7 kDa from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26130 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
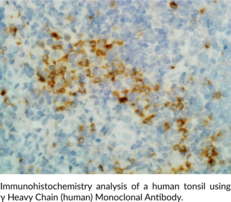
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{53881,53882} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in rabbit serum. IgG consists of two identical heavy chains, also known as γ heavy chains, of approximately 50 kDa each and two identical light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{53881} The heavy chains are linked together by a single disulfide bond to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains through additional disulfide bonds to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively. IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{53881,55170,53883} γ-Heavy chains are truncated and unable to associate with IgG light chains in patients with the rare disease γ heavy chain disease.{53884} Cayman’s γ Heavy Chain (human) Monoclonal antibody can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications. The antibody recognizes γ heavy chain from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32107 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
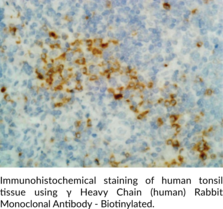
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{53881,53882} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in rabbit serum. IgG consists of two identical heavy chains, also known as γ heavy chains, of approximately 50 kDa each and two identical light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{53881} The heavy chains are linked together by a single disulfide bond to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains through additional disulfide bonds to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively. IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{53881,55170,53883} γ Heavy chains are truncated and unable to associate with IgG light chains in patients with the rare disease γ heavy chain disease.{53884} Cayman’s γ Heavy Chain (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody – Biotinylated can be used for ELISA and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fc region of the γ heavy chain from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32364 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder