Description
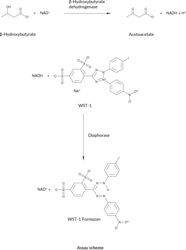
β-HB is a “ketone body” which is produced in the liver, mainly from the oxidation of fatty acids, and is exported to peripheral tissues for use as an energy source. Normally ketosis can indicate that lipid metabolism has been activated and the pathway of lipid degradation is intact. Pathological causes of ketosis include multiple organ failure, diabetes, childhood hypoglycemia, corticosteroid or growth hormone deficiency, intoxication with alcohol or salicylates and several inborn errors of metabolism. Cayman’s β-HB (Ketone Body) Assay provides a simple, reproducible, and sensitive tool for measuring β-HB levels in plasma, serum, or urine in a 96-well plate format with a colorimetric readout at 445-455 nm.
Formulation:
Formal name:
Synonyms: 3-Hydroxybutyric Acid|β-HB
Host:
Imunogen:
Applications:
Clone:
Purity:
Origin:
Product Type|Assay Kits|Colorimetric Assays||Product Type|Assay Kits|Detection Kits||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Inborn Errors of Metabolism||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Diabetes||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders