ELISA Kits
Showing 3301–3450 of 3623 results
-
SMADs are a family of intracellular proteins that are essential components in the signaling pathways of the serine/threonine kinase receptors of the transforming growth factor β superfamily.{19294} SMADs can be divided into receptor-regulated SMADs (R-SMADs: SMAD1, SMAD2, SMAD3, SMAD5, SMAD8, and SMAD9), common-mediator SMAD (co-SMAD: SMAD4), and inhibitory SMADs (I-SMADs: SMAD6 and SMAD7). SMAD1, SMAD5, SMAD8, and SMAD9 have high degrees of homology and antibodies are available that recognize sequences common to all of them. SMAD8 and SMAD9 are typically used as alternate names for one another in the literature.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10838 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
SMADs are a family of intracellular proteins that are essential components in the signaling pathways of the serine/threonine kinase receptors of the transforming growth factor β superfamily.{19293} SMADs can be divided into receptor-regulated SMADs (R-SMADs: SMAD1, SMAD2, SMAD3, SMAD5, SMAD8, and SMAD9), common-mediator SMAD (co-SMAD: SMAD4), and inhibitory SMADs (I-SMADs: SMAD6 and SMAD7). SMAD1, SMAD5, SMAD8, and SMAD9 have high degrees of homology and antibodies are available that recognize sequences common to all of them. SMAD8 and SMAD9 are typically used as alternate names for one another in the literature.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10839 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
SMADs are a family of intracellular proteins that are essential components in the signaling pathways of the serine/threonine kinase receptors of the transforming growth factor β superfamily.{19268} SMADs can be divided into receptor-regulated SMADs (R-SMADs: SMAD1, SMAD2, SMAD3, SMAD5, SMAD8, and SMAD9), common-mediator SMAD (co-SMAD: SMAD4), and inhibitory SMADs (I-SMADs: SMAD6 and SMAD7). SMAD1, SMAD5, SMAD8, and SMAD9 have high degrees of homology and antibodies are available that recognize sequences common to all of them. SMAD8 and SMAD9 are typically used as alternate names for one another in the literature.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10845 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700221 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
The survival motor neuron (SMN) protein is a ubiquitously expressed, multifunctional protein with roles in a variety of cellular processes, including small nuclear ribonucleoprotein (snRNP) and spliceosome assembly, translation, cytoskeletal dynamics, and stress granule formation.{56204,56205} It is a 294-amino acid protein encoded by SMN1 in humans and is comprised of an N-terminal basic/lysine-rich domain that interacts with RNA and Gemin-2, a central Tudor domain (Item No. 14136) that functions in a variety of protein-protein interactions, a proline-rich region, and a C-terminal YG box that facilitates SMN oligomerization. Humans also have a second centromeric copy of the gene, called SMN2, that is the result of duplication and inversion and primarily produces a truncated isoform, SMNΔ7, that is less stable, but can also produce small amounts of SMN. Knockout of Smn is embryonic lethal in mice.{56204} In humans, mutations in SMN1 are associated with spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a neuromuscular disorder characterized by degeneration of α motor neurons in the spinal cord and muscle weakness. Cayman’s SMN Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunocytochemistry (ICC) and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes SMN protein at approximately 35 kDa from human, mouse, and rat samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29295 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:32847 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:32861 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:32862 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
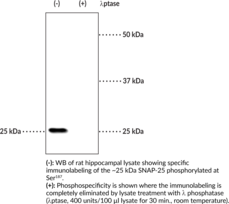
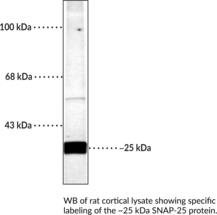
Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 (SNAP-25) is a member of the SNARE complex, which also includes syntaxin and VAMP, that is responsible for fusing synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic plasma membrane to facilitate neurotransmitter release.{55160} Two SNAP-25 isoforms, SNAP-25a and SNAP-25b, are generated through alternative splicing, with SNAP-25b expressed only during the postnatal period and as the predominant isoform in the brain.{55161} SNAP-25 contains two α helices, as well as one large and several smaller intrinsically disordered domains.{55160} SNAP-25 is located primarily on the intracellular side of the presynaptic plasma membrane in neurons and interacts with a variety of proteins to orchestrate vesicle fusion in a calcium-triggered manner and to mediate spine development.{55160} It is also found in the pancreas, enteroendocrine cells, and the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla where it is involved in hormone secretion.{55161} SNAP-25 can be phosphorylated at serine 187 (Ser187) in a neuronal activity-dependent manner by PKC, a modification that increases the rate of synaptic vesicle recruitment and is essential for SNAP-25b inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels (VGCCs) and incorporation of NMDA receptors into the postsynaptic membrane.{55154,55155,55156} Phosphorylation at Ser187 also facilitates neurotransmitter release and inhibits presynaptic short-term plasticity via regulation of synaptic vesicle dynamics.{55157} A point mutation at Ser187 (S187A) induces anxiety-like behavior in mice homozygous for the mutation and induces working memory deficits and an immature phenotype in hippocampal dental granule cells of adult mice heterozygous for the mutation.{55158,55159} Cayman’s SNAP-25 (Phospho-Ser187) Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes SNAP-25 (phospho-Ser187) at approximately 25 kDa from mouse and rat samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29294 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Synaptosomal-associated protein 25 (SNAP-25) is a member of the SNARE complex, which also includes syntaxin and VAMP, that is responsible for fusing synaptic vesicles with the presynaptic plasma membrane to facilitate neurotransmitter release.{55160} Two SNAP-25 isoforms, SNAP-25a and SNAP-25b, are generated through alternative splicing, with SNAP-25b expressed only during the postnatal period and as the predominant isoform in the brain.{55161} SNAP-25 contains two α helices, as well as one large and several smaller intrinsically disordered domains.{55160} It also contains a cluster of closely spaced cysteine residues that are subject to palmitoylation, a modification that regulates the intracellular distribution of SNAP-25, as well as residues subject to phosphorylation, modifications that modulate the rate of vesicle recruitment and its interactions with syntaxin.{55160,55154,55211} SNAP-25 is located primarily on the intracellular side of the presynaptic plasma membrane in neurons and interacts with a variety of proteins to orchestrate vesicle fusion in a calcium-triggered manner and to mediate spine development.{55160} It is also found in the pancreas, enteroendocrine cells, and the chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla where it is involved in hormone secretion.{55161} Decreased expression of SNAP-25 in a heterozygous mouse model leads to moderate hyperactivity, impaired learning and memory, and increased susceptibility to seizures induced by kainate. SNPs in SNAP-25 are associated with attention deficient/hyperactivity disorder, as well as bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, and autism spectrum disorder.{55218} Protein levels of SNAP-25 are decreased in postmortem brain from patients with Down syndrome and Alzheimer’s disease and in postmortem hippocampus from patients with schizophrenia.{52222,55224} Cayman’s SNAP-25 Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes SNAP-25 at 25 kDa from rat samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29293 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Sterol O-acyltransferase 1 (SOAT-1), also known as acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase-1 (ACAT-1), is an enzyme encoded by ACAT1 in humans that catalyzes the intracellular formation of cholesterol esters from cholesterol and long-chain fatty acyl-coenzyme A.{56232} It is ubiquitously expressed and localized to the rough endoplasmic reticulum where it preferentially utilizes oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) or palmitic acid (Item No. 10006627) as fatty acid substrates for the synthesis of cholesterol esters, which are stored intracellularly or packaged into chylomicrons or VLDL and secreted into the blood stream. SOAT-1/ACAT-1 protein levels are increased in macrophages under various pathological conditions, including atherosclerosis.{56233} SOAT-1/ACAT-1 activity is increased by cholesterol in vitro, and ACAT1 expression is increased by stimulation with the pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α or IFN-γ in isolated human and THP-1 monocytes, respectively.{56234,56232} ACAT1 silencing in human H4 neuroglioma cells overexpressing amyloid-β precursor protein (APP) reduces secretion of soluble amyloid-β (Aβ) and Aβ42 (Item No. 20574).{56236} Genome-wide deletion of Acat1 reduces macrophage infiltration and neutral lipid deposition in atherosclerotic aortic lesions and decreases serum total cholesterol levels, but increases brain cholesterol deposition, in ApoE-/- mice fed a Western diet.{56235} Cayman’s SOAT-1/ACAT-1 Polyclonal Antibody can be used for immunoflouresence (IF) immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes the N-terminus to detect full-length SOAT-1/ACAT-1 at approximately 65 kDa from human, mouse, porcine, and rat samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:100028 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Sterol O-acyltransferase 2 (SOAT-2), also known as acyl-coenzyme A:cholesterol acyltransferase-2 (ACAT-2), is an enzyme encoded by ACAT2 in humans that catalyzes the intracellular formation of cholesterol esters from cholesterol and long-chain fatty acyl-coenzyme A.{56232} It is constitutively expressed in the liver and small intestine and localized to the rough endoplasmic reticulum where it preferentially utilizes oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) or palmitic acid (Item No. 10006627) as fatty acid substrates for the synthesis of cholesterol esters, which are stored intracellularly or packaged into chylomicrons or VLDL and secreted into the blood stream. SOAT-2/ACAT-2 protein levels are increased in macrophages under various pathological conditions, including atherosclerosis.{56233} SOAT-2/ACAT-2 activity and protein levels are increased by cholesterol in vitro and in vivo, and ACAT2 expression is increased by the transcription factors hepatocyte nuclear factor 1-α (HNF-1-α) and HNF-4-α in Caco-2 cells and human liver, respectively.{56232} Genome-wide deletion of Acat2 reduces intestinal cholesterol absorption and decreases hepatic, but not plasma, total cholesterol levels in mice fed a high-cholesterol diet.{52780} Liver ACAT2 activity is negatively correlated with plasma HDL-C and ApoA1 in normolipidemic patients.{52781} Cayman’s SOAT-2/ACAT-2 Polyclonal Antibody can be used for immunofluorescence (IF), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes the N-terminal region of SOAT-2/ACAT-2 at approximately 60 kDa from human, mouse, ovine, porcine, and rat samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:100027 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:706001 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:706001 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:706004 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:706003 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:706003 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:706006 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700017 - 10 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700003 - 10 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700003 - 4 mlAvailable on backorder
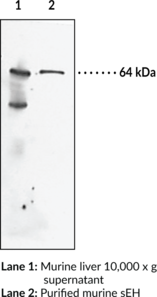
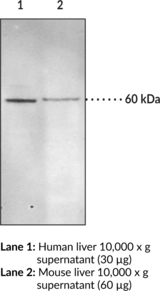
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is a member of the α/β-hydrolase fold enzyme family that catalyzes the hydrolysis of bioactive fatty acid epoxides to inactive vicinal diols.{52737} It is a homodimer in which each subunit is composed of two domains, a C-terminal epoxide hydrolase domain and an N-terminal phosphatase domain.{52738,15765} sEH is localized to the cytoplasm or to peroxisomes in a tissue specific manner and is found in various tissues, including skin, lung, uterus, kidney, brain, and myocardium.{52740,52739} sEH is also expressed in the vasculature and inhibition of sEH attenuates pathogenic vascular remodeling and hypertension via preservation of cardioprotective epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) in rat models of atherosclerosis and hypertension, respectively.{52741} Inhibition of sEH also has a protective role in various diseases including inflammatory bowel disease, osteoarthritis, seizure, stroke, and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as in various chronic pain states.{52737,50771} Cayman’s Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (FL) Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot applications. The antibody recognizes sEH at 64 kDa from human and murine samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13560 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
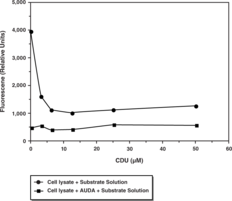
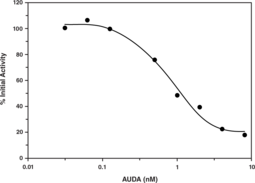
Mammalian soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is a member of the α/β-hydrolase fold family of enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of exogenous and endogenous epoxides to vicinal diols. sEH is a homodimer consisting of two domains.{15765} The C-terminal domain is responsible for the epoxide hydrolase activity while the N-terminal domain has a catalytic center with phosphatase activity. Endogenous substrates for sEH include epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) which exhibit vasodilatory and anti-inflammatory activity.{12607} Inhibition of sEH in animal models was shown to effectively treat hypertension and vascular inflammation as well as related syndromes.{14065} These studies demonstrate the value for targeting sEH for development of small molecule inhibitors as therapeutics. Cayman’s sEH Cell-Based Assay Kit provides a convenient 96-well plate, fluorescence-based method for detecting epoxide hydrolase activity in whole cells. The assay utilizes Epoxy Fluor 7, a sensitive fluorescent substrate for sEH that can be used to monitor the activity of both human and murine enzymes.{14078} Hydrolysis of the substrate epoxide yields a highly fluorescent product, 6-methoxy-2-Naphthaldehyde, that can be monitored at excitation and emission wavelengths of 330 and 465 nm, respectively. 6-Methoxy-2-Naphthaldehyde is included to quantify enzyme activity and a recombinant sEH is included as a positive control. An sEH inhibitor AUDA is also included for checking specificity of the reaction. This assay parallels Cayman’s Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit (Catalog No. 10011671) which uses recombinant protein rather than whole cells for the assay. Together, both assays will help to identify whether or not an inhibitor/activator has a direct or indirect effect on the enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:600090 - 480 wellsAvailable on backorder
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) catalyzes the hydrolysis of exogenous and endogenous epoxides to vicinal diols. Endogenous substrates for sEH include epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) which exhibit vasodialatory and anti-inflammatory activity. Small molecule inhibitors of sEH may therefore hold promise as therapeutics for the treatment of hypertension and vascular inflammation. Cayman’s fluorescence-based sEH Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit provides a convenient method for screening epoxide hydrolase inhibitors. The assay utilizes (3-phenyl-oxiranyl)-acetic acid cyano-(6-methoxy-naphthalen-2-yl)-methyl ester (PHOME) as a substrate. Hydrolysis of PHOME by epoxide hydrolase produces the highly fluorescent 6-methoxy-2-naphthaldehyde which can be analyzed using an excitation wavelength of 330 nm and emission wavelength of 465 nm. Each kit contains buffer, substrate, and sufficient human recombinant sEH for 100 tests.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011671 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
The metabolism of exogenous and endogenous epoxides relies in part upon the activity of soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH).{830} The relevance of sEH to hypertension and inflammation makes it a potentially useful clinical drug target. Specifically, the conversion of epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EpETrEs, EETs) by sEH to the corresponding dihydroxy eicosatrienoic acids (DiHETrEs, DHETs) diminishes their vasodilator activity.{12607} Inhibitors of sEH may therefore have clinical utility for treating hypertension and systemic inflammation.{14065,14072} Cayman’s polyclonal antibody is useful for monitoring the quantity and distribution of sEH.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010146 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
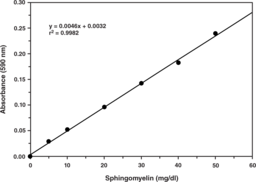
Cayman’s Sphingomyelin (SM) Assay Kit provides a specific, sensitive, and convenient method for quantifying SM in plasma or serum. In this assay, sphingomyelinase is first used to hydrolyze SM to phosphorylcholine and ceramide. Alkaline phosphatase then generates choline from the phosphorylcholine and the newly formed choline is used to generate hydrogen peroxide in a reaction catalyzed by choline oxidase. Finally, with peroxidase as a catalyst, hydrogen peroxide reacts with DAOS and 4-aminoantipyrine to generate a blue color with an optimal absorption at 595 nm.{14806}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009928 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
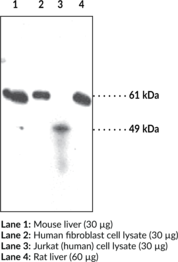
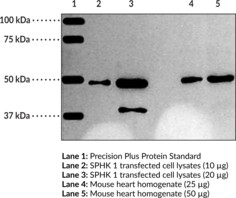
SPHK 1 catalyzes the phosphorylation of sphingosine to sphingosine-1-phosphate. This reaction plays an important role in determining cell proliferation versus cell death.{13916,5545} SPHK 1 is found in a wide variety of tissues and cell types including kidney, liver, spleen, heart, platelets, and human tumors. On a cellular level, it is found in the cytosolic and membrane fractions.{14482} Based on the amino acid sequence, this protein has a molecular weight of approximately 43 kDa. The observed band at 50 kDa may be explained by some reported post translational modifications.{14483}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006822 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
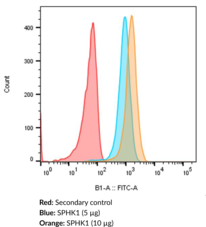
The primary use of this antibody conjugate is for the detection of SPHK1 in intact cells by direct immunolabeling methods such as flow cytometry or immunofluorescence microscopy. SPHK1 is one of the enzymes involved in sphingolipid metabolism. SPHK1 catalyzes the phosphorylation of sphingosine to sphingosine-1-phosphate. This reaction plays an important role in determining cell proliferation versus cell death.{13916,14481} SPHK1 is found in a wide variety of tissues and cell types including kidney, liver, spleen, heart, platelets, and human tumors.{13076} On a cellular level, it is found in the cytosolic and membrane fractions.{14482} Based on the amino acid sequence, this protein has a molecular weight of approximately 43 kDa. Some reported post translational modifications may explain the shift in band migration to 50 kDa.{14483} NOTE: Multiple isoforms of SPHK1 are known and one is 470 amino acids. This likely explains the 50 kDa band observed.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012201 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
sPLA2s are found in the venom of certain snakes (Types IA, IIA, and IIB from vipers, cobras, rattlesnakes, and kraits), in pancreatic juices (Type IB), in rat and murine testes (Type IIC), in placenta, synovial fluids and platelets (Type IIA), and in heart, placenta, lung, mast cells, and P388D1 macrophages (Type V).{3941} Until 1994, the sPLA2 responsible for the release of arachidonic acid in inflammation was believed to be Type IIA. Although recently discovered isoforms of PLA2 clearly contribute to the release of arachidonic acid, sPLA2 (Type IIA) continues to be a protein of interest in the field of inflammation. This ELISA is specific for Type IIA sPLA2, and does not cross react with Type I, Type IV, Type V PLA2, inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-1, or platelet-activating factor. Cayman’s sPLA2 (human Type IIA) ELISA Kit is an immunometric assay that can be used for quantification of sPLA2 in plasma, synovial fluid, and other sample matrices.
Brand:CaymanSKU:501380 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
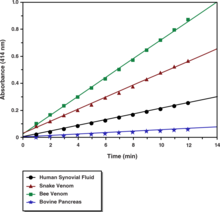
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) catalyzes the hydrolysis of phospholipids at the sn-2 position yielding a free fatty acid and a lysophospholipid.{2489} The release of arachidonic acid from membrane phospholipids by PLA2 is believed to be a key step in the control of eicosanoid production within the cell.{1474} Human synovial sPLA2 is a secreted, 14 kDa protein which is dependent on Ca2+ for optimal activity. Human synovial sPLA2 is 79% homologous to rat platelet and mouse type II sPLA2s.
Brand:CaymanSKU:160500 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) catalyzes the hydrolysis of fatty acids at the sn-2 position of glycerophospholipids. PLA2 (type V) is a secretory PLA2 (sPLA2) of approximately 14 kDa and is one of the isoforms in the growing list of the PLA2 enzyme family.{3506} This enzyme, rather than the sPLA2 (type II), is responsible for arachidonic acid mobilization leading to prostaglandin production in macrophages and mast cells.{3941,4455,4053,8454} Consistent with this role, sPLA2 (type V) is associated with the golgi apparatus, nuclear envelope, and plasma membrane in murine bone marrow-derived mast cells.{7627} sPLA2 (type V) has been cloned from a variety of species including human, mouse, and rat.{7748,5754,7749} The enzyme is expressed in heart, lung, placenta, and spleen, as well as P388D1 macrophages and mast cells.{3941,4455,7749}
Brand:CaymanSKU:160510 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2) (Type V) is a calcium-dependent phospholipase A2 superfamily member that is encoded by PLA2G5 in humans.{56210} It is composed of a highly conserved calcium-binding loop, a heparin-binding domain, and a C-terminal domain that contains a catalytic histidine-aspartic acid dyad and cationic residues that are essential for cell membrane association. Pla2g5 is constitutively expressed in the heart, lung, and spleen and is induced by proinflammatory stimuli in a variety of immune cells and tissues.{12947} Upon activation, sPLA2 (Type V) is released into the extracellular space where it acts in a paracrine or autocrine manner to catalyze the hydrolysis of fatty acids at the sn-2 position of glycerophospholipids, liberating the free fatty acid and lysophospholipid, which serve as substrates for the synthesis of bioactive lipid metabolites.{56210} Pla2g5-/- mice have decreased airway and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) neutrophil infiltration in a model of acute lung injury induced by LPS.{56211} Neonatal mice overexpressing Pla2g5 have increased BALF prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) levels, as well as reduced lung surfactant levels, leading to respiratory failure and death by postnatal day one.{56212} SNPs in PLA2G5 are associated with increased plasma LDL and total cholesterol levels in individuals with type 2 diabetes.{56213} Cayman’s sPLA2 (mouse Type V) Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot applications. The antibody recognizes sPLA2 (Type V) at 16 kDa from human, mouse, and rat samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:160512 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) catalyzes the hydrolysis of phospholipids at the sn-2 position yielding a free fatty acid and a lysophospholipid. The release of arachidonic acid from membrane phospholipids by PLA2 is believed to be a key step in the control of eicosanoid production within the cell.{1474} Mammalian tissues contain many secretory PLA2s (sPLA2s), including types IB, IIA-F, III, V, X, and XII{3506} of which Type V sPLA2 is involved in eicosanoid formation in inflammatory cells, such as macrophages and mast cells.{4455,11782} It has been demonstrated that human type V sPLA2 can bind phosphatidylcholine (PC) membranes and hydrolyze PC substrates much more efficiently than human type IIA sPLA2, which makes it better suited for acting on the outer plasma membrane.{8384} Selective targeting and inhibition of sPLA2s has been problematic as evidenced by the lack of availability of isozyme-specific inhibitors. The Cayman Chemical sPLA2 (Type V) Inhibitor Screening Assay is a convenient colorimetric assay designed for rapid screening of Type V sPLA2 inhibitors in a 96 well format. The sPLA2 (Type V) Inhibitor Screening assay kit includes sufficient human recombinant Type V sPLA2 for a minimum of 100 reactions. Identification of selective sPLA2 inhibitors will offer substantial aid in the elucidation of the specific physiological function of each sPLA2. Each kit contains assay buffer, DTNB, diheptanoyl thio-PC, human sPLA2, a 96 well plate, plate cover, and complete instructions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004883 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:765010 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Phospholipase A2 (PLA2) catalyzes the hydrolysis of phospholipids at the sn-2 position yielding a free fatty acid and a lysophospholipid.{2489} The release of arachidonic acid from membrane phospholipids by PLA2 is believed to be a key step in the control of eicosanoid production within the cell.{1474} The Cayman Chemical secretory PLA2 (sPLA2) Assay kit provides an accurate and convenient method for measurement of sPLA2 activity. This assay uses the 1,2-dithio analog of diheptanoyl phosphatidylcholine which serves as a substrate for most PLA2s (for example, bee and cobra venoms, pancreatic, etc.) with the exception of cytosolic PLA2.{1358,1359} Upon hydrolysis of the thio ester bond at the sn-2 position by PLA2, free thiols are detected using DTNB (5,5-dithio-bis-(2-nitrobenzoic acid)).
Brand:CaymanSKU:765001 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
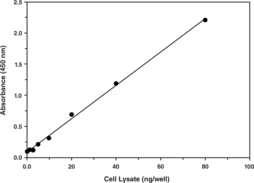
Three known isoforms of SREBP (sterol regulatory element binding protein) transcription factors have been characterized: SREBP-1a, SREBP-1c, and SREBP-2. SREBP-1c acts primarily to activate genes required for fatty acid synthesis, such as acetyl-CoA carboxylase, fatty acid synthase, and long chain fatty acid elongase. In addition, SREBP-1c may also contribute to the regulation of glucose uptake and synthesis through induction of glucokinase. SREBP-1c has important clinical implications in the treatment of many diseases including obesity, diabetes mellitus, insulin resistance, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Cayman’s SREBP-1 Transcription Factor Assay is a non-radioactive, sensitive method for detecting specific transcription factor DNA binding activity. SREBP-1 contained in nuclear extracts and whole cell lysates binds to a dsDNA SREBP response element immobilized to the wells of a 96-well plate. SREBP-1 is detected by addition of a specific primary antibody directed against SREBP-1. A secondary antibody conjugated to HRP is used to provide a sensitive colorimetric readout at 450 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010854 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
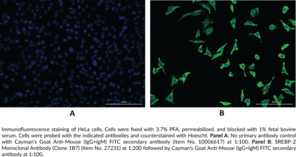
Sterol regulatory element-binding protein-2 (SREBP-2) is a membrane-bound transcription factor encoded by the SREBF2 gene in humans and is involved in the regulation of cholesterol biosynthesis and uptake.{13853,15316,15104} Similar to SREBP-1a and SREBP-1c, SREBP-2 is comprised of an N-terminal acidic domain, a basic-helix-loop-helix leucine zipper (bHLH-Zip) sequence, two transmembrane segments, and a regulatory C-terminal domain.{13853} In the absence of sterols, SREBP-2 undergoes two sequential proteolytic cleavage events resulting in release of the bHLH-Zip-containing N terminus from the endoplasmic reticulum membrane, followed by translocation to the nucleus.{13853,15316} Nuclear SREBP-2 (nSREBP-2) binds to sterol response elements (SREs) in DNA and regulates expression of genes encoding HMG-CoA synthase, HMG-CoA reductase, farnesyl diphosphate synthase, and squalene synthase, among others.{15316} Srebp2 is ubiquitously expressed in mouse tissues and knockout of Srebp2 is embryonic lethal in mice.{12882,15316} Hepatic expression of SREBF2 is seven- and three-fold higher in patients with non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and steatosis, respectively, than that of healthy individuals.{48690} Cayman’s SREBP-2 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 1B7) can be used for immunocytochemistry and immunohistochemistry applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27231 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
SREBPs, including SREBP-1a, SREBP-1c, and SREBP-2, constitute a family of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors that play a critical role in lipid homeostasis by regulating genes involved in cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism.{13853} SREBP-2 regulates cholesterol synthesis by activating the transcription of genes for HMG-CoA reductase and other enzymes of the cholesterol synthetic pathway.{13851} SREBP-2 is ubiquitously detected in various tissues.{12882} Upon cholesterol depletion, the protein is cleaved to its active forms (about 50-68 kDa) and translocated into the nucleus to stimulate transcription of genes involved in the uptake and synthesis of cholesterol.{13148} Cayman’s SREBP-2 polyclonal antibody detects both precursor and active forms of the protein in tissues and cells such as liver, brown fat, testis, HepG2 cells, and human fibroblast. The apparent molecular weight on SDS-PAGE may be higher than the calculated molecular weight (about 126 kDa) due to glycosylation of the protein.{13852}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007663 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Cayman’s SREBP-2 Polyclonal Antibody – Biotinylated detects both precursor and active forms of the protein in tissues and cells such as liver, brown fat, testis, HepG2 cells, and human fibroblast. The apparent molecular weight on SDS-PAGE may be higher than the calculated molecular weight (about 126 kDa) due to glycosylation of the protein.{13852} SREBPs, including SREBP-1a, SREBP-1c, and SREBP-2, constitute a family of basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) transcription factors that play a critical role in lipid homeostasis by regulating genes involved in cholesterol and fatty acid metabolism.{13853} SREBP-2 regulates cholesterol synthesis by activating the transcription of genes for HMG-CoA reductase and other enzymes of the cholesterol synthetic pathway.{13851} SREBP-2 is ubiquitously detected in various tissues.{12882} Upon cholesterol depletion, the protein is cleaved to its active forms (about 50-68 kDa) and translocated into the nucleus to stimulate transcription of genes involved in the uptake and synthesis of cholesterol.{13148}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22728 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Lipid homeostasis in vertebrate cells is regulated by a family of transcription factors called sterol regulatory element-binding proteins (SREBP’s). SREBP’s directly activate the expression of over 30 genes involved in the synthesis and uptake of cholesterol, fatty acids, triglycerides, and phospholipids.{14287} Three different SREBP isoforms designated SREBP-1a, SREBP-1c, and SREBP-2 are encoded by two different genes and belong to the basic helix-loop-helix-leucine zipper (bHLH-ZIP) family of transcription factors.{14286} SREBP-2 performs a critical role in the transcriptional regulation of genes involved in cholesterol synthesis and uptake including HMG-CoA synthase, HMG-CoA reductase, and the LDL receptor. Cayman’s SREBP-2 Transcription Factor Assay is a non-radioactive, sensitive method for detecting specific transcription factor DNA binding activity in nuclear extracts and whole cell lysates. A 96 well enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) replaces the cumbersome radioactive electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA). A specific double stranded DNA (dsDNA) sequence containing the SREBP response element is immobilized to the wells of a 96 well plate. SREBP contained in a nuclear extract, binds specifically to the SREBP response element. SREBP is detected by addition of specific primary antibody directed against SREBP. A secondary antibody conjugated to HRP is added to provide a sensitive colorimetric readout at 450 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007819 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700732 - 12 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700732 - 4 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400432 - 100 dtnAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400432 - 500 dtnAvailable on backorder
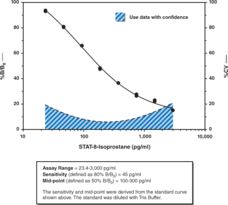
The isoprostanes are a family of eicosanoids of non-enzymatic origin produced by the random oxidation of tissue phospholipids by oxygen radicals. At least one of the isoprostanes, 8-isoprostane (8-iso PGF2α), has biological activity and has implicated as a causative mediator and specific marker of free radical-induced damage in a variety of diseases related to oxidative stress.{1053,1381,9138,9117} Cayman Chemical’s STAT-8-isoprostane ELISA is a competitive assay that permits the rapid measurement of 8-iso PGF2α from biological samples, requiring only 1 hour incubation and development times for each step. This assay format is the similar to that employed in Cayman’s popular 8-isoprostane ELISA (Item No. 516351) with the only change being the use of an alkaline phosphatase tracer in place of an AChE tracer. While Item No. 516351 offers superior sensitivity (IC50 ~35 pg/ml), the new STAT-8-isoprostane Assay offers the convenience of a fast assay while still achieving an IC50 of 180 pg/ml and a detection limit (80% B/B0) of approximately 45 pg/ml.
Brand:CaymanSKU:500431 - 480 solid wellsAvailable on backorder
The isoprostanes are a family of eicosanoids of non-enzymatic origin produced by the random oxidation of tissue phospholipids by oxygen radicals. At least one of the isoprostanes, 8-isoprostane (8-iso PGF2α), has biological activity and has implicated as a causative mediator and specific marker of free radical-induced damage in a variety of diseases related to oxidative stress.{1053,1381,9138,9117} Cayman Chemical’s STAT-8-isoprostane ELISA is a competitive assay that permits the rapid measurement of 8-iso PGF2α from biological samples, requiring only 1 hour incubation and development times for each step. This assay format is the similar to that employed in Cayman’s popular 8-isoprostane ELISA (Item No. 516351) with the only change being the use of an alkaline phosphatase tracer in place of an AChE tracer. While Item No. 516351 offers superior sensitivity (IC50 ~35 pg/ml), the new STAT-8-isoprostane Assay offers the convenience of a fast assay while still achieving an IC50 of 180 pg/ml and a detection limit (80% B/B0) of approximately 45 pg/ml.
Brand:CaymanSKU:500431 - 480 strip wellsAvailable on backorder
The isoprostanes are a family of eicosanoids of non-enzymatic origin produced by the random oxidation of tissue phospholipids by oxygen radicals. At least one of the isoprostanes, 8-isoprostane (8-iso PGF2α), has biological activity and has implicated as a causative mediator and specific marker of free radical-induced damage in a variety of diseases related to oxidative stress.{1053,1381,9138,9117} Cayman Chemical’s STAT-8-isoprostane ELISA is a competitive assay that permits the rapid measurement of 8-iso PGF2α from biological samples, requiring only 1 hour incubation and development times for each step. This assay format is the similar to that employed in Cayman’s popular 8-isoprostane ELISA (Item No. 516351) with the only change being the use of an alkaline phosphatase tracer in place of an AChE tracer. While Item No. 516351 offers superior sensitivity (IC50 ~35 pg/ml), the new STAT-8-isoprostane Assay offers the convenience of a fast assay while still achieving an IC50 of 180 pg/ml and a detection limit (80% B/B0) of approximately 45 pg/ml.
Brand:CaymanSKU:500431 - 96 solid wellsAvailable on backorder
The isoprostanes are a family of eicosanoids of non-enzymatic origin produced by the random oxidation of tissue phospholipids by oxygen radicals. At least one of the isoprostanes, 8-isoprostane (8-iso PGF2α), has biological activity and has implicated as a causative mediator and specific marker of free radical-induced damage in a variety of diseases related to oxidative stress.{1053,1381,9138,9117} Cayman Chemical’s STAT-8-isoprostane ELISA is a competitive assay that permits the rapid measurement of 8-iso PGF2α from biological samples, requiring only 1 hour incubation and development times for each step. This assay format is the similar to that employed in Cayman’s popular 8-isoprostane ELISA (Item No. 516351) with the only change being the use of an alkaline phosphatase tracer in place of an AChE tracer. While Item No. 516351 offers superior sensitivity (IC50 ~35 pg/ml), the new STAT-8-isoprostane Assay offers the convenience of a fast assay while still achieving an IC50 of 180 pg/ml and a detection limit (80% B/B0) of approximately 45 pg/ml.
Brand:CaymanSKU:500431 - 96 strip wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400434 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
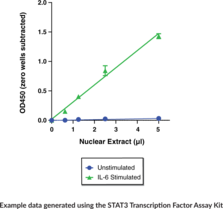
Cayman’s STAT3 Transcription Factor Assay Kit is a non-radioactive, sensitive method for detecting specific STAT3 DNA binding activity in nuclear extracts. As an alternative to the cumbersome electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) or the lower throughput ChIP assay, this ELISA is extremely easy to perform. This kit is an ideal way to measure STAT3 transcriptional activity downstream of cytokine or drug treatment and manipulation of cells in vitro or in vivo. Cayman’s STAT3 Transcription Factor Assay Kit detects human, mouse, rat, and non-human primate STAT3 binding on the DNA target sequence. It does not cross react with other STAT transcription factors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:601950 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012671 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
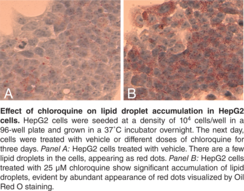
Steatosis, also known as fatty liver, is a pathological process characterized by abnormal accumulation of lipid within cells. While simple steatosis may not be associated with significant impairment of liver function, excessive fat accumulation can lead to cirrhosis and even liver failure. The molecular mechanisms involved in non-alcoholic steatosis are poorly understood and little information is available on the pathway(s) responsible for progressive hepatocellular damage following lipid accumulation. Determining hepatotoxicity is an essential component of the drug discovery process and includes steatosis as one of the key parameters evaluated. Cayman’s Steatosis Colorimetric Assay Kit provides a convenient tool for evaluating steatosis risk of drug candidates. In this assay, Oil Red O is used to stain neutral lipids in hepatocytes. Lipid accumulation is then quantified using a plate reader after the dye is extracted from the lipid droplets. Chloroquine is included in the kit as a positive control.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012643 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
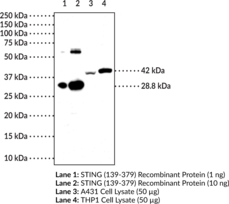
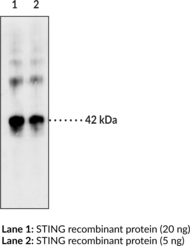
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) is a component of the innate immune response that binds to cyclic dinucleotides (CDNs), which are bacterial second messengers, leading to activation of NF-κB and transcription of immunomodulatory genes, including type I interferon (IFN).{22400,22401,24611,24607} The C-terminal region of STING binds to CDNs, such as cyclic di-GMP (c-di-GMP; Item No. 17144) in the cytoplasm at a ratio of two STING molecules to one c-di-GMP.{24607,39991} Mutations in the C-terminal region modify the activity of STING in a variety of ways.{24607} Certain mutations, such as the mutation found in the Goldenticket mouse strain, I199N, prevent STING from binding to CDNs and from inducing an IFN response. However, other mutations in the C-terminal region allow STING to bind c-di-GMP but not induce IFN, hyperinduce IFN without binding c-di-GMP, or induce IFN only when overexpressed and without binding c-di-GMP. STING inhibition has the potential to be beneficial for the treatment of autoimmune diseases that are associated with uncontrolled activation of the STING pathway, while activation of STING can lead to an adaptive immune response that reduces tumor growth in animal models.{39992,41598,38806,39993} Cayman’s STING (C-Term) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 1B10) can be used for ELISA, IHC, and WB applications. The antibody recognizes the C-terminal region of STING at 42 kDa from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25923 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
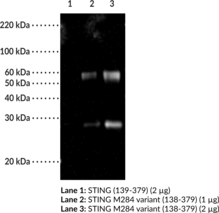
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) is a component of the innate immune response that binds to cyclic dinucleotides, which are bacterial second messengers, leading to activation of NF-κB and transcription of immunomodulatory genes, including type I interferon (IFN).{22400,22401,24611,24607} The R284M mutation in STING is associated with constitutive activation of downstream signaling. It increases the propensity of STING to dimerize and associate with the kinase TBK1 (Item No. 22817), enhancing the ability of STING to activate IRF3 (Item No. 22811) and NF-κB (Item No. 10009818) and induce a type I IFN response.{41454} However, the R284M mutation occurs outside of the dimerization region between positions 153-177, so rather than a direct effect on dimerization, it is predicted to promote or inhibit binding of a cellular factor that stabilizes or impairs STING dimerization. Cayman’s STING M284 variant Monoclonal Antibody preferentially detects overexpressed STING (R284M) versus wild-type STING by Western blot and ELISA.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25922 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Stimulator of interferon genes (STING) is a component of the innate immune response that binds to cyclic dinucleotides, which are bacterial second messengers, leading to activation of NF-κB and transcription of immunomodulatory genes, including type I interferon (IFN).{22400,22401,24611,24607} The R284M mutation in STING is associated with constitutive activation of downstream signaling. It increases the propensity of STING to dimerize and associate with the kinase TBK1 (Item No. 22817), enhancing the ability of STING to activate IRF3 (Item No. 22811) and NF-κB (Item No. 10009818) and induce a type I IFN response.{41454} However, the R284M mutation occurs outside of the dimerization region between positions 153-177, so rather than a direct effect on dimerization, it is predicted to promote or inhibit binding of a cellular factor that stabilizes or impairs STING dimerization. Cayman’s STING M284 variant Polyclonal Antibody preferentially detects overexpressed STING (R284M) versus wild-type STING by Western blot.
Brand:CaymanSKU:24791 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
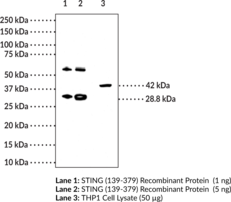
Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) is a component of the innate immune response. STING binds to cyclic dinucleotides, which are bacterial second messengers.{24607} Recognition of cyclic-di-GMP (c-di-GMP), c-di-AMP, or c-GMP-AMP leads to activation of NF-κB and transcription of immunomodulatory genes, including type I interferon (IFN).{22400,22401,24611} Loss of STING regulation contributes to autoimmune disorders through increased IFN activity.{24608} The gene for STING is mutated in the mouse strain Goldenticket, which consequently lacks a type I IFN response to Listeria infection.{24612} Activation of STING by the flavonoid 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA; Item No. 14617) has been shown to kill solid tumors in mice, but the binding site of DMXAA is not conserved in human STING.{24610,24609} Cayman’s STING Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 2C8) can be used for ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and Western blot applications. The antibody recognizes STING at 42 kDa from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:17856 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Stimulator of Interferon Genes (STING) is a component of the innate immune response. STING binds to cyclic dinucleotides, which are bacterial second messengers.{24607} Recognition of cyclic-di-GMP (c-di-GMP), c-di-AMP, or c-GMP-AMP leads to activation of NF-κB and transcription of immunomodulatory genes, including type I interferon (IFN).{22400,22401,24611} Loss of STING regulation contributes to autoimmune disorders through increased IFN activity.{24608} The gene for STING is mutated in the mouse strain Goldenticket, which consequently lacks a type I IFN response to Listeria infection.{24612} Activation of STING by the flavonoid 5,6-dimethylxanthenone-4-acetic acid (DMXAA; Item No. 14617) has been shown to kill solid tumors in mice, but the binding site of DMXAA is not conserved in human STING.{24610,24609}
Brand:CaymanSKU:17857 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Streptavidin conjugated to SureLight® APC – Optimized for protein interaction assays Binding Moiety: Streptavidin Dye: SureLight® Allophycocyanin (APC) Excitation max. λ: 652 nm Emission max. λ: 657.5 nm F:P: 1:1.5 Uses: Optimized for High throughput screening (HTS) and fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) assays targeting protein interactions, flow cytometry
Brand:CaymanSKU:16631 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:483752 - 100 dtnAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:483752 - 500 dtnAvailable on backorder
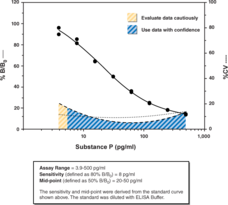
Substance P is a bioactive 11-amino acid peptide (Arg-Pro-Lys-Pro-Gln-Gln-Phe-Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-amide) first isolated in 1931 from brain and intestine. The peptide is involved in many physiological processes including pain modulation, smooth muscle contraction, blood pressure control, kidney function and water homeostasis.{954,1041,10154} Substance P is widely distributed in numerous tissues and body fluids including the central and peripheral nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, visual system and circulatory system.{10154} Cayman’s Substance P ELISA is a competitive assay that provides accurate measurements of Substance P with a working range of 3.9 to 500 pg/ml, typically with an IC50 (50% B/B0) of ~30 pg/ml and IC80 (80% B/B0) of ~8 pg/ml. Inter- and intra-assay CV’s of less than 20% can be achieved at most concentrations of the standard curve. Due to cross-reactivity with Hemokinin-1, we do not recommend this ELISA to measure Substance P in serum and plasma samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:583751 - 480 solid wellsAvailable on backorder
Substance P is a bioactive 11-amino acid peptide (Arg-Pro-Lys-Pro-Gln-Gln-Phe-Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-amide) first isolated in 1931 from brain and intestine. The peptide is involved in many physiological processes including pain modulation, smooth muscle contraction, blood pressure control, kidney function and water homeostasis.{954,1041,10154} Substance P is widely distributed in numerous tissues and body fluids including the central and peripheral nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, visual system and circulatory system.{10154} Cayman’s Substance P ELISA is a competitive assay that provides accurate measurements of Substance P with a working range of 3.9 to 500 pg/ml, typically with an IC50 (50% B/B0) of ~30 pg/ml and IC80 (80% B/B0) of ~8 pg/ml. Inter- and intra-assay CV’s of less than 20% can be achieved at most concentrations of the standard curve. Due to cross-reactivity with Hemokinin-1, we do not recommend this ELISA to measure Substance P in serum and plasma samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:583751 - 480 strip wellsAvailable on backorder
Substance P is a bioactive 11-amino acid peptide (Arg-Pro-Lys-Pro-Gln-Gln-Phe-Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-amide) first isolated in 1931 from brain and intestine. The peptide is involved in many physiological processes including pain modulation, smooth muscle contraction, blood pressure control, kidney function and water homeostasis.{954,1041,10154} Substance P is widely distributed in numerous tissues and body fluids including the central and peripheral nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, visual system and circulatory system.{10154} Cayman’s Substance P ELISA is a competitive assay that provides accurate measurements of Substance P with a working range of 3.9 to 500 pg/ml, typically with an IC50 (50% B/B0) of ~30 pg/ml and IC80 (80% B/B0) of ~8 pg/ml. Inter- and intra-assay CV’s of less than 20% can be achieved at most concentrations of the standard curve. Due to cross-reactivity with Hemokinin-1, we do not recommend this ELISA to measure Substance P in serum and plasma samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:583751 - 96 solid wellsAvailable on backorder
Substance P is a bioactive 11-amino acid peptide (Arg-Pro-Lys-Pro-Gln-Gln-Phe-Phe-Gly-Leu-Met-amide) first isolated in 1931 from brain and intestine. The peptide is involved in many physiological processes including pain modulation, smooth muscle contraction, blood pressure control, kidney function and water homeostasis.{954,1041,10154} Substance P is widely distributed in numerous tissues and body fluids including the central and peripheral nervous system, gastrointestinal tract, respiratory tract, visual system and circulatory system.{10154} Cayman’s Substance P ELISA is a competitive assay that provides accurate measurements of Substance P with a working range of 3.9 to 500 pg/ml, typically with an IC50 (50% B/B0) of ~30 pg/ml and IC80 (80% B/B0) of ~8 pg/ml. Inter- and intra-assay CV’s of less than 20% can be achieved at most concentrations of the standard curve. Due to cross-reactivity with Hemokinin-1, we do not recommend this ELISA to measure Substance P in serum and plasma samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:583751 - 96 strip wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:483754 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700021 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
SUCNR1 is a 334 amino acid-containing membrane receptor, belonging to the G-protein coupled receptor 1 family, characterized by an extracellular N terminus, seven transmembrane regions, and an intracellular C terminus and playing a role in cell communication.{19519,19520} SUCNR1 is a receptor for the citric acid cycle intermediate succinate. It functions in establishing a neovascular network during development and in response to injury. SUCNR1, in response to increased succinate levels, regulates the production of numerous angiogenic factors, including VEGF, and also is involved in the modulation of platelet function. It is known to play an essential role in proliferative ischemic retinopathy and is an attractive target for treating diseases that stem from aberrant neovascularization in the mature retina such as diabetic retinopathy. Expression of SUCNR1 is common in kidney, liver, retina, platelets, and leukocytes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10928 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
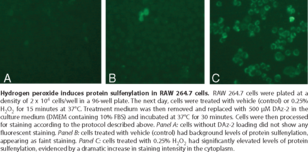
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) react with proteins, resulting in protein modification, such as protein sulfenylation through the reversible oxidation of cysteine residues. Redox-sensitive cysteine residues in proteins can function as sensors of ROS and serve as molecular switches, activating or deactivating proteins, following a change in oxidative state. However, the accumulation of proteins with irreversible cysteine oxidation is a hallmark of stress-induced cellular damage associated with diseases like cancer. Cayman’s Sulfenylated Protein Cell-Based Detection Kit employs the cell-permeable and chemoselective DAz-2 probe to detect sulfenic acid-modified proteins in living cells. It can be used to monitor intracellular sulfenylated protein levels in living cells to discriminate between normal and pathological conditions or to help identify new pathways regulated by sulfenic acid formation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:600320 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
The small ubiquitin like modifier (SUMO) protein is similar in structure and function to ubiquitin. However, SUMO does not typically target proteins for degradation as does ubiquitin.{14288,19512,19511,16072} SUMO is involved with the modification of a very diverse array of targets.{15532} Proteins involved with transcriptional regulation, DNA damage repair, genomic stability, nuclear transport, and histone modification are all subject to modification by SUMO.{19512,15532,19513,15531} SUMO typically functions by covalently binding to a target protein, followed by regulation of protein:protein and protein:DNA interactions.{19512} The SUMO family of proteins is highly conserved from yeast to human. Invertebrates contain a single SUMO gene (Smt3 in yeast and smo-1 in C. elegans), with three members of SUMO being identified in vertebrates to date (SUMO-1, SUMO-2 and SUMO-3).{21733}
Brand:CaymanSKU:12021 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
The Small Ubiquitin Like Modifier (SUMO) protein is similar in structure and function to ubiquitin. However, SUMO does not typically target proteins for degradation as does ubiqutin. {14288,19512,19511,16072} SUMO is involved with the modification of a very diverse array of targets.{15532} Proteins involved with transcriptional regulation, DNA damage repair, genomic stability, nuclear transport, and histone modification are all subject to modification by SUMO.{19512,19513,15531,15532} SUMO typically functions by covalently binding to a target protein, followed by regulation of protein:protein and protein:DNA interactions.{19512} The SUMO family of proteins is highly conserved from yeast to human. Invertebrates contain a single SUMO gene (Smt3 in yeast and smo-1 in C. elegans), with three members of SUMO being identified in vertebrates to date (SUMO-1, SUMO-2 and SUMO-3).{21733}
Brand:CaymanSKU:14697 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:32962 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
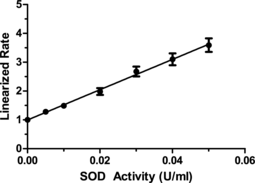
Significant amounts of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in cellular and extracellular environments are crucial for the prevention of diseases linked to oxidative stress. Mutations in SOD account for approximately 20% of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) cases. SOD also appears to be important in the prevention of other neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s Diseases.{10355,3934} The reaction catalyzed by SOD is extremely fast, having a turnover of 2 x 106 M−1sec−1 and the presence of sufficient amounts of the enzyme in cells and tissues typically keeps the concentration of superoxide very low.{10331} Quantification of SOD activity is therefore essential in order to fully characterize the antioxidant capabilities of a biological system. The Cayman Chemical SOD Assay kit is a fast and reliable assay for the measurement of SOD activity from plasma, serum, tissue homogenates, and cell lysates. SOD activity is assessed by measuring the dismutation of superoxide radicals generated by xanthine oxidase and hypoxanthine in a convenient 96 well format. The standard curve generated using this enzyme provides a means to accurately quantify the activity of all three types of SOD (Cu/Zn, Mn, and FeSOD). Each kit contains sufficient reagents to assay 41 samples in duplicate and includes assay buffer, sample buffer, radical detector, SOD (standard), xanthine oxidase, a 96 well plate, and complete instructions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:706002 - 480 wellsAvailable on backorder
Significant amounts of superoxide dismutase (SOD) in cellular and extracellular environments are crucial for the prevention of diseases linked to oxidative stress. Mutations in SOD account for approximately 20% of familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) cases. SOD also appears to be important in the prevention of other neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s Diseases.{10355,3934} The reaction catalyzed by SOD is extremely fast, having a turnover of 2 x 106 M−1sec−1 and the presence of sufficient amounts of the enzyme in cells and tissues typically keeps the concentration of superoxide very low.{10331} Quantification of SOD activity is therefore essential in order to fully characterize the antioxidant capabilities of a biological system. The Cayman Chemical SOD Assay kit is a fast and reliable assay for the measurement of SOD activity from plasma, serum, tissue homogenates, and cell lysates. SOD activity is assessed by measuring the dismutation of superoxide radicals generated by xanthine oxidase and hypoxanthine in a convenient 96 well format. The standard curve generated using this enzyme provides a means to accurately quantify the activity of all three types of SOD (Cu/Zn, Mn, and FeSOD). Each kit contains sufficient reagents to assay 41 samples in duplicate and includes assay buffer, sample buffer, radical detector, SOD (standard), xanthine oxidase, a 96 well plate, and complete instructions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:706002 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Synapsin I plays a key role in synaptic plasticity in brain. This effect is due in large part to the ability of the synapsins to regulate the availability of synaptic vesicles for release. In addition to its role in plasticity, the expression of synapsin I is a precise indicator of synapse formation. Thus, synapsin I immunocytochemistry provides a valuable tool for the study of synaptogenesis. The role of synapsin in synaptic plasticity and in synaptogensis is regulated by phosphorylation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10606 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Synapsin I plays a key role in synaptic plasticity in brain. This effect is due in large part to the ability of the synapsins to regulate the availability of synaptic vesicles for release. In addition to its role in plasticity, the expression of synapsin I is a precise indicator of synapse formation. Thus, synapsin I immunocytochemistry provides a valuable tool for the study of synaptogenesis. The role of synapsin in synaptic plasticity and in synaptogensis is regulated by phosphorylation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10605 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:33008 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:33010 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:33037 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:33056 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Tau is a member of the microtubule-associated protein (MAP) family that facilitates microtubule formation in axons.{55125,55126} It is primarily expressed in neurons and localized to axons, but trace amounts have been observed in glial cells and several peripheral tissues including kidney, lung, and testis. Tau is composed of an N-terminal projection domain that interacts with neurofilaments, cytoplasmic organelles, and neuronal cell membranes and a C-terminal microtubule binding domain that facilitates microtubule polymerization and stabilization. It is encoded by MAPT in humans, a 16-exon gene that produces 6 isoforms via alternative mRNA splicing. Mutations in MAPT lead to changes in expression of tau isoforms and the formation of insoluble protein aggregates that cause familial frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17).{55127} Tau is subject to post-translational modifications, including phosphorylation, and hyperphosphorylation of tau is associated with the formation of neurofibrillary tangles and neuronal cell death in postmortem brains from patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Cayman’s Tau Polyclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC), immunocytochemistry (ICC), and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes three isoforms of tau at approximately 48, 65, and 75 kDa from human, bovine, mouse, porcine, and rat samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29296 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Lipid peroxidation is a well-established mechanism of cellular injury in both plants and animals and is used as an indicator of oxidative stress in cells and tissues. Lipid peroxides, derived from PUFAs, are unstable and decompose to form a complex series of compounds, which include reactive carbonyl compounds, such as malondialdehyde (MDA). MDA can be quantified through a controlled reaction with thiobarbituric acid, generating ‘Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances’ (TBARS). Cayman’s TBARS Assay Kit provides a simple, reproducible, and standardized tool for assaying lipid peroxidation in plasma, serum, urine, tissue homogenates, and cell lysates. The MDA-TBA adduct formed by the reaction of MDA and TBA under high temperature (90-100°C) and acidic conditions can be measured either colorimetrically at 530-540 nm or with much higher sensitivity fluorometrically at an excitation wavelength of 530 nm and an emission wavelength of 550 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:700870 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder