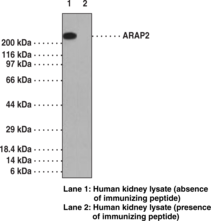ELISA Kits
Showing 151–300 of 3623 results
-
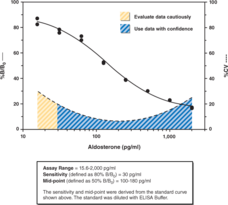
Aldosterone, a steroid hormone secreted by the adrenal cortex, is the principle mineralocorticoid controlling sodium and potassium balance. Serum aldosterone levels in normal upright adult individuals are generally less than 300 pg/ml. Only a fraction of urinary aldosterone is excreted intact, thus urinary excretion of aldosterone in normal adults is typically assessed as a combination of free aldosterone and aldosterone-18-glucuronide and is generally less than 20 µg/24 hr. Cayman’s Aldosterone ELISA Kit is a competitive assay that can be used for quantification of aldosterone in serum, plasma, urine, and other sample matrices. The assay has a range from 15.6-2,000 pg/ml and a sensitivity (80% B/B0) of approximately 30 pg/ml.
Brand:CaymanSKU:501090 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:401094 - 100 ngAvailable on backorder
Cayman’s Alkaline Phosphatase (ALP) Colorimetric Activity Assay Kit provides a convenient method of measuring ALP activity in serum, plasma, tissue samples, and cell lysates with a limit of detection of 0.5 U/L. Measurement of ALP activity is carried out by monitoring the dephosphorylation of the chromogenic substrate p-nitrophenyl phosphate (pNPP). In the first step, ALP dephosphorylates pNPP generating p-nitrophenol. In the second step, the phenolic hydroxyl group is deprotonated under alkaline conditions resulting in p-nitrophenolate, which yields an intense yellow color that can be measured using absorbance at 405 nm. Under circumstances in which ALP activity is rate limiting, the increase in absorbance at 405 nm is directly proportional to ALP activity in the sample.
Brand:CaymanSKU:701710 - 480 wellsAvailable on backorder
ALP Assay Buffer has been tested and formulated to work exclusively with Cayman’s Alkaline Phosphatase Colorimetric Activity Assay Kit (Item No. 701710). Please visit Alkaline Phosphatase Colorimetric Activity Assay Kit (Item No. 701710) for the kit protocol, procedures, and product handling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:400083 - 30 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700261 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700263 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700264 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700265 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700262 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
α-methylacyl-Coenzyme A (α-methylacyl-CoA) racemase (AMACR), is an enzyme involved in the metabolism of branched chain fatty acids and 2-arylpropanoic acids (2-APAs), such as ibuprofen (Item No. 70280).{60129} It is expressed in most human tissues and is localized to peroxisomes and mitochondria.{60129,60130} AMACR converts R-2-methyl fatty acids to S-2-methylacyl-CoA esters via an epimerization reaction prior to their degradation by β-oxidation.{60129} AMACR is overexpressed in localized and metastatic prostate cancer, as well as in a variety of other cancers.{60131} AMACR has been found selectively in patient-derived prostate cancer tumor tissue compared to non-cancer prostate tissue, and has been used as a biomarker of the disease.{60132} Mutations in AMACR resulting in reduced enzyme activity lead to the accumulation of R-2-methyl fatty acids and are associated with neurological and peroxisomal disorders.{60133} Cayman’s AMACR (N-Term) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32274 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
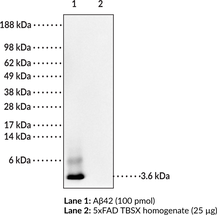
Amyloid plaques composed primarily of the 42 amino acid form of amyloid-β peptide (Aβ42) are a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). However, the roles of the various amyloid β peptide(s), especially Aβ42, related to the neurotoxicity characteristic of AD remains unclear. A major hindrance to evaluating the role of Aβ in AD pathology has been the availability of anti-Aβ antibodies to selectively detect Aβ versus amyloid precursor protein (APP), Aβ40 versus Aβ42, and specific conformations of the peptide, particularly oligomeric forms. MOAB-2 (mouse IgG2b) is a pan-specific antibody specific to Aβ (residues 1-4) that differentiates intracellular Aβ from APP. MOAB-2 does not detect APP in cell culture media/lysates or in brain homogenates from transgenic mice expressing 5 familial AD mutation (5xFAD mice). Intraneuronal Aβ was confirmed by co-localization of MOAB-2 immunoreactivity with C-terminal antibodies specific for Aβ40 and Aβ42, and with cathepsin-D, a lysosomal marker. Additionally, MOAB-2 demonstrates strong intraneuronal and extra-cellular immunoreactivity in 5xFAD and 3xTg mouse brain tissues.{20683}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11610 - 200 µgAvailable on backorder
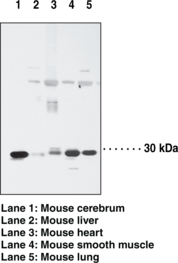
Androgen receptor is a ligand-activated transcription factor and member of the steroid hormone receptor family.{59547,59546} It is composed of an N-terminal regulatory domain (AF-1 site), a DNA-binding domain that contains two zinc fingers, a hinge region containing a nuclear localization signal, and a C-terminal ligand binding domain (AF-2 site). Unligated androgen receptors are localized to the cytoplasm and bound to heat shock protein23 (Hsp23), -56, -70, and -90 in a stable conformation that facilitates androgen binding. Androgen binding induces dissociation of the Hsps and nuclear translocation of the androgen receptor where it binds to androgen response elements (AREs) and induces gene transcription. Mutations in AR, the gene encoding the androgen receptor, induce abnormalities in male development ranging from partial androgen insensitivity to complete male-to-female phenotypic sex reversal.{59546} Androgen receptor knockdown induces bone loss, complete loss of sexual behaviors, and reduced aggressive behaviors in male mice, as well as defective folliculogenesis and reduced fertility in female mice. Expression of C-terminally truncated and constitutively active androgen receptor mutants is associated with reduced progression-free survival, lower prostate-specific androgen (PSA) response rates, and shorter median overall survival in patients with castration-resistant prostate cancer.{59548} Cayman’s Androgen Receptor (N-Term) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes the N-terminus to detect the full-length androgen receptor and its splice variants from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32206 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
The androgen receptor (AR) is an ~100 kDa androgen-dependent transcription factor that is a member of the steroid/nuclear receptor gene superfamily. The AR signaling pathway plays a key role in development and function of male reproductive organs, including the prostate and epididymis. AR also plays a role in nonreproductive organs, such as muscle, hair follicles, and brain. Abnormalities in the AR signaling pathway have been linked to a number of diseases, including prostate cancer, Kennedy’s disease, and male infertility. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt signaling pathway plays an important role in regulating AR activity through phosphorylation of AR at Ser213/210 and Ser791/790. Growth factors or cytokines may induce phosphorylation of AR through the PI3K/Akt pathway. IGF-1 activates the PI3K/AKT pathway in LNCap at high passage number and increases phosphorylation of the AR at Ser213/210 and Ser791/790.{17381} The western blot results also show that inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway by LY294002 prior to incubation with IGF-1 suppressed AR phosphorylation at Ser213/210. Activation of the PI3K/Akt pathway is thought to have a survival role in prostate cancer by protecting cells from apoptosis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13492 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Angiotensin II is a primary reactive vasoconstrictor, the main stimulus for aldosterone release, and one of the causative factors of chronic hypertension. The active angiotensin II octapeptide is released via a tightly controlled series of prohormones and proteases as diagrammed below. Normal human plasma angiotensin II levels are from 10-30 pg/ml when measured at rest in the supine position; they increase on standing, exercise, dehydration, or sodium depletion. The unique, patented ‘Immobilized Antigen’ technology of this angiotensin II immunometric assay allows reliable detection of 1-2 pg/ml, or as little as 10% of the normal human plasma concentration. [Bertin Catalog No. A05880]
Brand:CaymanSKU:589301 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
ANGPTL3 regulates angiogenesis and also directly regulates lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism. ANGPTL3 (human) monoclonal antibody (clone Kairos-37) recognizes the fibrinogen-like domain (FLD) of human ANGPTL3. It detects a band of ~68 kDa and a cleaved band of ~35 kDa by WB. It does not cross-react with other ANGPTL family proteins.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10805 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
ANGPTL3 regulates angiogenesis and also directly regulates lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism. ANGPTL3 (human) monoclonal antibody (clone Kairos-37) recognizes the fibrinogen-like domain (FLD) of human ANGPTL3. It detects a band of ~68 kDa and a cleaved band of ~35 kDa by WB. It does not cross-react with other ANGPTL family proteins.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10805 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
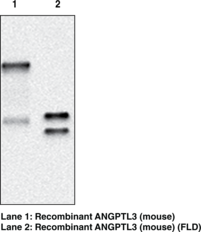
ANGPTL3 regulates angiogenesis and also directly regulates lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism. ANGPTL3 (mouse) monoclonal antibody (clone Kairos3-1541) recognizes mouse ANGPTL3. It detects a band of ~69 kDa by WB.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10806 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
ANGPTL3 regulates angiogenesis and also directly regulates lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism. ANGPTL3 (mouse) monoclonal antibody (clone Kairos3-1541) recognizes mouse ANGPTL3. It detects a band of ~69 kDa by WB.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10806 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
ANGPTL3 regulates angiogenesis and also directly regulates lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism. ANGPTL3 (mouse) monoclonal antibody (clone Kairos3-3741) recognizes mouse ANGPTL3. It detects a band of ~69 kDa by WB and cross-reacts with mouse ANGPTL3 fibrinogen-like domain (FLD).
Brand:CaymanSKU:10807 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
ANGPTL3 regulates angiogenesis and also directly regulates lipid, glucose, and energy metabolism. ANGPTL3 (mouse) monoclonal antibody (clone Kairos3-3741) recognizes mouse ANGPTL3. It detects a band of ~69 kDa by WB and cross-reacts with mouse ANGPTL3 fibrinogen-like domain (FLD).
Brand:CaymanSKU:10807 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Cayman’s Annexin A1 (human) ELISA Kit is a sandwich assay which can be used to measure human annexin A1 in tissue culture media, serum and plasma. The standard curve spans the range of 0.20 – 20 ng/ml. Annexin A1 is a natural anti-inflammatory protein produced by neutrophils and monocytes. The glucocorticoid-induced production and release of annexin A1 is the primary means by which glucocorticoids function as anti-inflammatory agents. Annexin A1 inhibits the synthesis of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids by suppressing the function of secretory phospholipase A2 (sPLA2). This, in turn, limits the recruitment of neutrophils into inflammatory sites and down-regulates the production of pro-inflammatory mediators by those neutrophils that enter inflammatory sites. Annexin A1 also functions in the resolution of inflammation by inducing neutrophil apoptosis, and promoting neutrophil clearance (efferocytosis) by macrophages. The pro-resolving functions of annexin A1 are mediated via binding to FPR2/ALX, a receptor it shares with the specific pro-resolving mediators lipoxin A4 (LXA4) and resolvin D1 (RvD1).
Brand:CaymanSKU:501550 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Annexins are a superfamily of 13 proteins sharing a high degree of homology. They have in common a core C-terminal domain containing calcium and phospholipid binding motifs, allowing most of them to bind to phospholipid membranes in a calcium-dependent manner. The N-terminal domains vary between family members and provide a unique function.{30992}Annexin A1 is an endogenous mediator of inflammation, promoting resolution in a number of ways. Normally expressed in intracellular compartments, it is drawn to the cell membrane and both induced and externalized by glucocorticoid response pathways.{30993,30994} The glucocorticoid-induced production and release of annexin A1 is the primary means by which glucocorticoids function as anti-inflammatory agents. Annexin A1 inhibits the synthesis of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids by suppressing the function of sPLA2. This, in turn, limits the recruitment of neutrophils into inflammatory sites and downregulates the production of pro-inflammatory mediators by those neutrophils that enter inflammatory sites.{30995} Meanwhile, proteolytic fragments generated in response to increased expression are implicated in producing a marker for phagocytosis.{30996} Annexin A1 also functions in the resolution of inflammation by inducing neutrophil apoptosis, and promoting neutrophil clearance (efferocytosis) by macrophages. The pro-resolving functions of annexin A1 are mediated via binding to FPR2/ALX, a receptor it shares with the specific pro-resolving mediators lipoxin A4 (Item No. 90410) and resolvin D1 (Item No. 10012554).{30995} The molecule’s regulatory role has led to investigation of the downstream effects of annexin A1, including cancer, adaptive immunity, and wound repair.{30997,30998,30999} The predicted size of annexin A1 is 38.7 kDa and Cayman’s Annexin A1 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 3F5) detects a size 39 kDa band via western blot.
Brand:CaymanSKU:19707 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Annexins are a superfamily of 13 proteins sharing a high degree of homology. They have in common a core C-terminal domain containing calcium and phospholipid binding motifs, allowing most of them to bind to phospholipid membranes in a calcium-dependent manner. The N-terminal domains vary between family members and provide unique function.{30992} Annexin A1 is an endogenous mediator of inflammation, promoting resolution in a number of ways. Normally expressed in intracellular compartments, it is drawn to the cell membrane and both induced and externalized by glucocorticoid response pathways.{30993,30994} The glucocorticoid-induced production and release of annexin A1 is the primary means by which glucocorticoids function as anti-inflammatory agents. Annexin A1 inhibits the synthesis of pro-inflammatory eicosanoids by suppressing the function of sPLA2. This, in turn, limits the recruitment of neutrophils into inflammatory sites and down-regulates the production of pro-inflammatory mediators by those neutrophils that enter inflammatory sites.{30995} Meanwhile, proteolytic fragments generated in response to increased expression are implicated in producing a marker for phagocytosis.{30996} Annexin A1 also functions in the resolution of inflammation by inducing neutrophil apoptosis, and promoting neutrophil clearance (efferocytosis) by macrophages. The pro-resolving functions of annexin A1 are mediated via binding to FPR2/ALX, a receptor it shares with the specific pro-resolving mediators lipoxin A4 (LXA4; Item No. 90410) and resolvin D1 (RvD1; Item No. 10012554).{30995} The molecule’s regulatory role has led to investigation of the downstream effects of annexin A1, including cancer, adaptive immunity, and wound repair.{30997,30998,30999} The predicted size of annexin A1 is 38.7 kDa and Cayman’s Annexin A1 Polyclonal Antibody detects a size 39 kDa band via Western blot and Immunoprecipitation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:19708 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
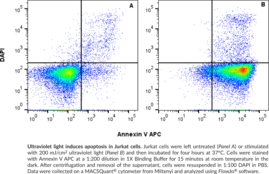
Cayman’s Annexin V APC Assay Kit employs an APC-conjugated annexin V as a probe for phosphatidylserine on the outer membrane of apoptotic cells. DAPI is used as a marker of cell membrane permeability seen in very late apoptotic or necrotic cells. This kit is valuable for researchers looking to assess the degree of apoptosis induced by experimental compounds, and can be useful in pharmacology, immunology, cancer, or physiology research.
Brand:CaymanSKU:601410 - 100 testsAvailable on backorder
One of the hallmarks of the early stages of apoptosis is the redistribution of membrane phospholipids such as phosphatidylserine and phosphatidylethanolamine from the inner to outer leaflet of the membrane bilayer where they are exposed on the cell surface. Externalization of phosphatidylserine residues to the outer plasma membrane leaflet allows their detection via their high affinity for annexin V, a phospholipid binding protein. Cayman’s Annexin V Assay Kit employs a FITC-conjugated Annexin V as a probe for phosphatidylserine on the outer membrane of apoptotic cells. Apoptotic cells bound with fluorochrome-labeled Annexin V can be visualized using fluorescence microscopy or flow cytometry. The reagents provided in the kit are sufficient to run 500 samples when using a 96-well plate format.
Brand:CaymanSKU:600300 - 100 testsAvailable on backorder
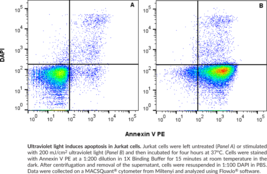
Cayman’s Annexin V PE Assay Kit employs a PE-conjugated annexin V as a probe for phosphatidylserine on the outer membrane of apoptotic cells. DAPI is used as a marker of cell membrane permeability seen in very late apoptotic or necrotic cells. This kit is valuable for researchers looking to assess the degree of apoptosis induced by experimental compounds, and can be useful in pharmacology, immunology, cancer, or physiology research.
Brand:CaymanSKU:601420 - 100 testsAvailable on backorder
5-Hydroxymethylcytosine (5-hmC) is an epigenetic modification formed from the oxidation of 5-methylcytosine by Tet dioxygenases.{17171} 5-hmC is primarily a stable DNA modification, but it can be oxidized by Tet enzymes and its products further modified to generate nonmethylated cytosine, indicating a role as an intermediate in DNA demethylation as well.{49667,29364,49668} It is associated with actively transcribed genes and recognized by a variety of proteins, including proteins involved in DNA repair and DNA metabolic processes.{49667,49668} 5-hmC has been found in all mammalian tissues but levels are higher in the brain relative to other tissues.{49669} The percentage of genomic 5-hmC in mouse cerebellum increases during postnatal development until adulthood, and genes acquiring intragenic 5-hmC are enriched in pathways associated with age-related neurodegenerative disease pathways in adult mice.{20327} In contrast, 5-hmC levels are reduced by up to 8-fold in cancer tissues.{49667,49670} Cayman’s 5-Hydroxymethylcytosine Polyclonal Antibody can be used for dot blot, ELISA, hydroxymethylated DNA immunoprecipitation (hMeDIP), immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20723 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
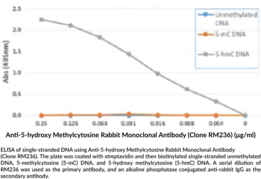
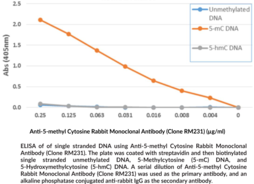
DNA methylation of cytosine to 5-methyl cytosine (5-mC) is an epigenetic mark that is relatively common in both plants and mammals and plays a role in transcriptional and chromatin regulation. In healthy cells, DNA methylation occurs at CpG sites, but CpG islands are generally not modified. However, tumor cells show an increase in CpG island methylation and a decrease in individual CpG sites.{27017} This ‘hypo-methylation’ can lead to aberrant activation of genes. Anti-5-methyl Cytosine Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM231) is a probe for immunochemical detection of 5-methyl cytosine by methylated DNA immunoprecipitation, IHC, ICC, ELISA, or dot blot.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20722 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
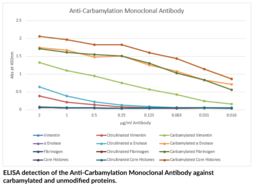
Carbamylation is a non-enzymatic and irreversible post-translational modification whereby cyanate reacts with lysine residues within polypeptide chains to generate ε-carbamyl-lysine (homocitrulline).{34533} Cyanate originates from the decomposition of urea and exists in equilibrium with its reactive form isocyanic acid.{34532} Neutrophil-derived MPO mediates the conversion of thiocyanate to isocyanate at sites of inflammation.{34533,34534} Increased levels of urea associated with chronic kidney disease result in elevated cyanate concentrations and a higher potential for carbamylated proteins.{34535} The presence of carbamylated proteins has been associated with rheumatoid arthritis.{34536} Homocitrulline residues are structurally similar to citrulline, the presence of an additional methylene group on homocitrulline being the only difference. Peptidylarginine deiminase (PAD)-catalyzed formation of citrulline residues on proteins and peptides can indicate many of the same disease states as the presence of homocitrulline residues. The ability to differentiate between citrullinated and carbamylated proteins has been difficult using traditional techniques. Cayman’s Anti-Carbamylation (Homocitrulline) Monoclonal Antibody specifically detects carbamylated proteins and does not detect the unmodified or citrullinated counterparts.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23203 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
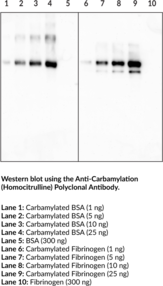
Cayman’s Anti-Carbamylation (Homocitrulline) Polyclonal Antibody specifically detects carbamylated proteins and does not detect the unmodified or citrullinated counterparts. It has been tested for ELISA, Immunoprecipitation, and Western blot applications. Carbamylation is the non-enzymatic and irreversible post-translational modification whereby cyanate reacts with lysine residues within polypeptide chains to generate ε-carbamyl-lysine (homocitrulline).{34533} Cyanate originates from the decomposition of urea and exists in equilibrium with its reactive form isocyanic acid.{34532} Neutrophil derived MPO mediates the conversion of isocyanate from thiocyanate at sites of inflammation.{34533,34534} Increased levels of urea associated with chronic kidney disease result in elevated cyanate concentrations, and a higher potential for carbamylated proteins.{34535} The presence of carbamylated proteins has been associated with rheumatoid arthritis.{34536} Homocitrulline residues are structurally similar to citrulline; the presence of an additional methylene group on homocitrulline being the only difference. Peptidyl arginine deiminase (PAD) mediated citrulline residues on proteins and peptides can indicate many of the same disease states as the presence of homocitrulline residues. The ability to differentiate between citrullinated and carbamylated proteins has been difficult using traditional techniques.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22428 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Anti-cholera toxin B subunit (goat) is a polyclonal anti-choleragenoid from goat that is suitable for use in toxin neutralization and binding assays or for immunohistochemical studies in conjunction with the cholera toxin B subunit. The pentameric B subunit of cholera toxin (Item No. 19654) binds with high efficiency to GM1 monosialoganglioside cell membrane receptors found on mammalian cell surfaces and facilitates entrance of the A subunit into cells.{31319} The cholera toxin B subunit is often used for retrograde track tracing studies in neuroscience research.{31321}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19655 - 100 µLAvailable on backorder
Immunization of mice with citrullinated human fibrinogen, especially mice expressing the human HLA-DR4 transgene, induces an arthritic response driven by the production of antibodies that recognize citrullinated epitopes. The polyclonal antibody response produces antibodies reactive with both citrullinated human fibrinogen and unmodified, noncitrullinated human fibrinogen. Cayman’s Anti-Citrullinated Human Fibrinogen Assay (mouse) is an immunometric (sandwich) assay that can be used to distinguish the antibody response to citrullinated human fibrinogen from the antibody response to unmodified human fibrinogen in mouse serum or plasma. A human fibrinogen affinity sorbent is provided with the kit so that any antibodies capable of reacting with non-citrullinated (unmodified) fibrinogen can be removed prior to analysis of the remaining anti-citrullinated fibrinogen antibodies for an accurate analysis of the anti-citrulline response. This kit uses a citrullinated human fibrinogen-coated plate and a detection antibody recognizing mouse IgG. An anti-citrullinated human fibrinogen monoclonal antibody is included as a standard. The standard curve spans the range of 0.15 to 10 µg/ml, with an an LLOQ of 0.15 µg/ml.
Brand:CaymanSKU:501270 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Citrulline is a noncoding amino acid that is produced by deimination of arginine through the post-translational modification citrullination.{56025} Citrullination is catalyzed by protein arginine deiminases (PADs) that convert positively charged arginine to electrically neutral citrulline, decreasing the isoelectric point of the protein, altering the native protein structure, and influencing protein ionic interactions.{56026} Protein citrullination has roles in many physiological and pathological processes, including autoimmunity, cancer, and neurodegenerative disorders.{56027} Citrullination of arginine 26 on histone H3 by PAD2 (Item No. 10785) displaces histone H3 from chromatin, resulting in chromatin decondensation and estrogen receptor α (ERα) transcriptional activation in a reporter assay.{30729} Citrullinated histones are also a component of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), a network of decondensed DNA and intracellular proteins secreted by neutrophils as a pathogen defense mechanism that is also a source of citrullinated autoantigens.{25917} Increased levels of antibodies to citrullinated protein antigens (ACPAs) are associated with increased disease severity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.{56028} Plasma levels of citrullinated histone H3 are increased in patients with advanced cancer, and citrullinated glial fibrillary acidic protein (citGFAP; Item No. 28622) has been found in postmortem hippocampus from patients with Alzheimer’s disease.{56029,53021} Cayman’s Anti-Citrulline Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 1D9) can be used for ELISA, immunohistochemistry (IHC), and immunoprecipitation (IP) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30773 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
2,4-Dinitrophenol (DNP) is a hapten that induces a strong immune response when attached to proteins or peptides.{48325,48326} DNP can be incorporated at protein carbonyls via covalent linkage of DNP to carbonyl groups using 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH) or through site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids that contain a DNP functional group.{48327,48325} Immunization with DNP-modified proteins or tumor cells induces antibody formation in vivo and has been used in the design of vaccines for clearance of disease-causing cells or viruses and induction of autoimmune diseases such as colitis and thyroiditis in various animal models.{48328,48329} Cayman’s Anti-DNP Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, Western blot, and immunoprecipitation applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25863 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
2,4-Dinitrophenol (DNP) is a hapten that induces a strong immune response when attached to proteins or peptides.{48325,48326} DNP can be incorporated at protein carbonyls via covalent linkage of DNP to carbonyl groups using 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazine (DNPH) or through site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids that contain a DNP functional group.{48325,48327} Immunization with DNP-modified proteins or tumor cells induces antibody formation in vivo and has been used in the design of vaccines for clearance of disease-causing cells or viruses and induction of autoimmune diseases such as colitis and thyroiditis.{48328,48329} Cayman’s Anti-DNP Polyclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, Western blot, and immunoprecipitation applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25864 - 500 µLAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:483152 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:483152 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Anti-EP4 (Prostaglandin E4) receptor (C-term) conjugated to SureLight® APC Antibody: Rabbit anti-EP4 receptor (C-term) IgG Specificity: EP4 receptor C-terminal amino acids 459-488 (GSGRAGPAPKGSSLQVTFPSETLNLSEKCI) Reactivity: Human, murine, rat, and ovine EP4 receptor; non-reactive with EP1, EP2, and EP3 receptors; other species not tested. Dye: SureLight® Allophycocyanin (APC) Excitation max. λ: 650 nm Emission max. λ: 660 nm Uses: Flow cytometry and cell-based assays
Brand:CaymanSKU:16625 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Anti-His-HRP Conjugate has been tested and formulated to work with Cayman’s Kits. Detailed instructions for its use are contained in the respective Cayman Kit booklet.
Brand:CaymanSKU:402054 - 360 µlAvailable on backorder
Anti-His-tag Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM146) is a probe for immunochemical detection of His tags on recombinant proteins by western blot, immunoprecipitation, immunohistochemistry, immunocytochemistry, or flow cytometry. Recombinant proteins are routinely labeled with affinity tags, such as poly-histidine (poly-His), to facilitate both their detection and purification. Poly-His tags are often the tag of choice due to their small size, less potential to interfere in protein folding, weak immunogenicity, and high affinity for Ni2+.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20725 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
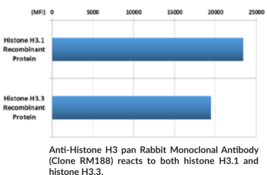
Histone H3 is a nuclear protein and a component of the nucleosome core, a basic unit of chromatin, that is essential for organizing genomic DNA in eukaryotic nuclei.{57056} It is a globular protein that contains an unstructured N-terminal tail that extends outside of the nucleosome core and is subject to various post-translational modifications (PTMs), including methylation, phosphorylation, acetylation, and citrullination.{57056,53978} Histone H3 PTMs function as epigenetic regulators of gene transcription by affecting chromatin structure and providing binding sites for many transcription factors, thus regulating several cellular functions including gene expression, cell cycle, and DNA replication and repair.{57056,56203} Differential methylation of histone H3 at various lysine residues is catalyzed by SET domain-containing methyltransferases and marks sites of transcriptional activation or repression.{57056} Citrullination of histone H3 by protein arginine deiminase 4 (PAD4; Item Nos. 10500 | 25915 | 28910) or PAD2 (Item No. 10785) induces the release of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), a network of decondensed DNA and intracellular proteins secreted by neutrophils as a pathogen defense mechanism.{52711,52712} Histone H3 mutations have been found in patients with diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma, leukemia, or chondroblastoma.{52713,49724} Cayman’s Anti-Histone H3 pan Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM188) can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), multiplex-based assays, and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes all histone H3 proteins independent of post-translational modifications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20724 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Anti-HLA-DR (α and β chains) ELISA Strip Plate has been tested and formulated to work exclusively with Cayman’s HLA-DR (α and β chains) ELISA Kit (Item No. 501810). Please visit HLA-DR (α and β chains) ELISA Kit (Item No. 501810) for the kit protocol, procedures, and product handling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:480130 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Anti-HLA-DR (α and β chains) HRP Conjugate has been tested and formulated to work exclusively with Cayman’s HLA-DR (α and β chains) ELISA Kit (Item No. 501810). Please visit HLA-DR (α and β chains) ELISA Kit (Item No. 501810) for the kit protocol, procedures, and product handling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:480132 - 1.5 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400912 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400962 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400922 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
The Anti-Inflammatory Screening Library consists of 3 plates and contains approximately 235 anti-inflammatory and related compounds in a 96-well Matrix™ tube rack format as 10 mM stock solutions in DMSO. This library includes inhibitors of pro-inflammatory cytokine production, macrophage and T cell activation, cytokine storm receptor signaling, the NLRP3 inflammasome, NF-κB signaling, and kinases involved in canonical and non-canonical inflammatory signaling pathways. It also includes corticosteroids, glucocorticoids, and inhibitors of enzymes involved in inflammatory lipid mediator production and metabolism, such as COX-1 and COX-2, 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO), microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 (mPGES-1), cytosolic phospholipase A2 (cPLA2), and soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH). Additional targets include enzymes and receptors involved in NETosis, coagulation, and platelet aggregation. Please review the product insert for a full list of targets. Stability data is not available for the compounds as supplied in the screening library.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31530 - 50 µlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:483302 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:483302 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:483312 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:483312 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Immunization of mice with chicken egg albumin (ovalbumin/OVA) in a precipitate complex with aluminum hydroxide (alum) is a highly effective means of inducing a potent TH2-mediated immune response. OVA/alum immunized mice produce anti-OVA antibodies predominantly of the IgG1 and IgE isotypes that mediate tissue-specific effector functions in multiple mouse models of chronic inflammation, including allergic asthma, allergic rhinitis, and cutaneous hypersensitivity. When using one of these models, it is often desirable to measure anti-OVA antibody levels in the plasma or serum to determine the effectiveness of the immunization, the activity of a drug, or the effect of a specific gene deletion. The plasma concentration of OVA-specific IgG1, the predominant anti-OVA immunoglobulin isotype found in the serum or plasma of mice immunized with OVA/alum, is typically 1,000-fold greater than that of OVA-specific IgE. Cayman’s Anti-Ovalbumin IgE (mouse) ELISA Kit is an immunometric assay which can be used to measure anti-ovalbumin of the IgE isotype in mouse plasma and serum without prior sample purification. A plate-bound antibody specific for mouse IgE is used to selectively measure ovalbumin-specific IgE, total plasma or serum IgE, which avoids interference from IgG1 binding. A biotin-labeled ovalbumin reagent is then added to quantify the ovalbumin-specific subset of this captured IgE. A monoclonal anti-ovalbumin IgE produced from mice immunized with OVA/alum is used as the standard. The standard curve spans the range of 1.56-100 ng/ml, with an LLOQ of 3.12 ng/ml.
Brand:CaymanSKU:500840 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400844 - 200 ngAvailable on backorder
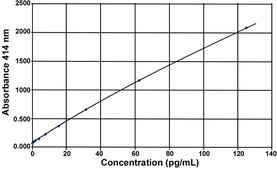
Cayman’s Anti-Ovalbumin IgG1 (mouse) ELISA Kit is an immunometric (i.e., ‘sandwich’) assay which can be used to measure anti-ovalbumin of the IgG1 isotype in mouse plasma and serum without prior sample purification. Affinity-purified anti-ovalbumin IgG1 isolated from the plasma of mice immunized with OVA/alum is used as the standard. The standard curve spans the range of 1.56-200 ng/ml, with an LLOQ of 1.56 ng/ml.
Brand:CaymanSKU:500830 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400834 - 200 ngAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400934 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:489202 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:489202 - 5 eaAvailable on backorder
Histone H2AX, a variant of the nucleosome core histone H2A, undergoes phosphorylation on serine 139 in response to DNA damage, particularly when the damage involves formation of double-strand breaks. Phosphorylated H2AX is also termed γH2AX. Induction of γH2AX in cells exposed to genotoxic agents is considered a sensitive and specific reporter of DNA damage.{32236} This antibody reacts to γH2AX when phosphorylated at Ser139 and does not detect other phosphorylated histones.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20721 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:709002 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004873 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
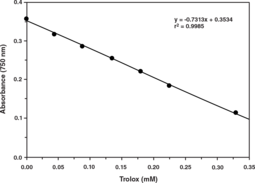
The antioxidant system of living organisms includes enzymes such as superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase; macromolecules such as albumin, ceruloplasmin, and ferritin; and an array of small molecules, including ascorbic acid, α-tocopherol, β-carotene, reduced glutathione, uric acid, and bilirubin. The sum of endogenous and food-derived antioxidants represents the total antioxidant activity of the extracellular fluid. Cooperation of all the different antioxidants provides greater protection against attack by reactive oxygen or nitrogen radicals, than any single compound alone. Thus, the overall antioxidant capacity may give more relevant biological information compared to that obtained by the measurement of individual components, as it considers the cumulative effect of all antioxidants present in plasma and body fluids. The Cayman Chemical Antioxidant Assay Kit measures the total antioxidant capacity of plasma, serum, urine, saliva, or cell lysates. The assay relies on the ability of antioxidants in the sample to inhibit the oxidation of ABTS® (2,2′-azino-di-[3-ethylbenzthiazoline sulphonate]) to ABTS® · + by metmyoglobin.{8832,8913,8915,9407} The capacity of the antioxidants in the sample to prevent ABTS oxidation is compared with that of Trolox, a water-soluble tocopherol analogue, and is quantified as molar Trolox equivalents. Each kit contains assay buffer (10X), chromogen, metmyoglobin, trolox, hydrogen peroxide, a 96 well plate, plate cover, and complete instructions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:709001 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10004876 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
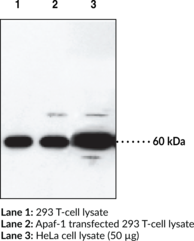
Apoptosis is related to many diseases and is induced by a family of cell death receptors and their ligands. Cell death signals are transduced by death domain containing adapter molecules and members of the caspase family of proteases. The mammalian homologues of the key cell death gene CED-4 in C. elegans has been identified recently from human and mouse and designated Apaf-1 (apoptosis protease-activating factor 1){6894,6873} Apaf-1 binds to cytochrome c (Apaf-2) and caspase-9 (Apaf-3), which leads to caspase-9 activation. Activated caspase-9 in turn cleaves and activates caspase-3, one of the key proteases responsible for the proteolytic cleavage of many key proteins in apoptosis.{6874} Apaf-1 can also associate with caspase-4 and caspase-8.{6878} Apaf-1 is ubiquitously expressed in human tissues.{6894}
Brand:CaymanSKU:160780 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
ApoA1 is a major protein component in high-density lipoproteins (HDLs). It acts as an acceptor for sequential transfers of phospholipids and free cholesterol from peripheral tissues and transports cholesterol to the liver and other tissues for excretion and steroidogenesis.{14038} Serum ApoA1 levels are inversely related to the risk of developing atherosclerosis.{14039} Loss-of-function mutations are causes of diseases such as HDL deficiency type 1 (or Tangier disease) and type 2 (familial hypoalphalipoproteinemia), and systemic non-neuropathic amyloidosis.{14037,14040} Liver and small intestine are two main sources of the protein. ApoA1 is comprised of a single polypeptide chain of 243 amino acid residues with an estimated molecular weight of 28 kDa. Cayman’s ApoA1 Monoclonal Antibody detects the protein from diluted human plasma (≤10 µg total protein) by western blotting. Western blotting of recombinant ApoA1 samples suggest a detection limit of 5 ng.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13042 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
ApoA1 is a major protein component in high-density lipoproteins (HDLs). It acts as an acceptor for sequential transfers of phospholipids and free cholesterol from peripheral tissues as well as transporting cholesterol to the liver and other tissues for excretion and steroidogenesis.{14038} Serum ApoA1 levels are inversely related to the risk of developing atherosclerosis.{14039} Loss-of-function mutations in ApoA1 are causes of diseases such as HDL deficiency type 1 (or Tangier disease) and type 2 (familial hypoalphalipoproteinemia), and systemic non-neuropathic amyloidosis.{14037,14040} Liver and small intestine are two main sources of the protein. Cayman’s ApoA1 Polyclonal Antibody detects the protein by WB analysis at 25 kDa in tissue/cell samples such as liver, intestine, and HepG2 cells.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008463 - 500 μlAvailable on backorder
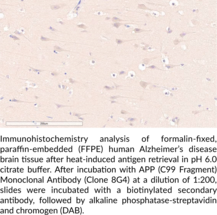
Amyloid precursor protein (APP) is a type I transmembrane protein that has a central role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease, as well as additional roles in brain development, neuronal plasticity, and memory.{59228} APP is cleaved by β-secretase (BACE) in neuronal endosomes during amyloidogenic processing of APP, generating the C-terminal C99 fragment, which is localized to the endoplasmic membrane.{59223,59224} C99 is further cleaved by γ-secretase, liberating the APP intracellular domain (AICD) and generating amyloid-β (Aβ) peptides of various lengths, including Aβ40 (Item No. 21617) and Aβ42 (Item No. 20574), which are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. APP can also be cleaved by α-secretase during non-amyloidogenic processing of APP, which occurs at the neuronal plasma membrane and generates the neuroprotective soluble APP fragment sAPPα, as well as a variety of other fragments, including the C47 fragment.{59228,59226} Transgenic mice expressing mutant forms of APP exhibit extracellular Aβ deposits in the brain, as well as cognitive dysfunction, and are widely used models of Alzheimer’s disease.{59227} Intraneuronal C99 levels are increased in the transgenic APPE693Q mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease, as well as postmortem frontal cortex from patients with sporadic Alzheimer’s disease.{59224,59225} Cayman’s APP (C99 Fragment) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 8G4) can be used for ELISA and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications. The antibody recognizes the C-terminal region corresponding to the C99 fragment to detect intact APP, as well as the C47 APP fragment.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28636 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
ARAP2, also known as centaurin-d-1, is a protein with ARF-GAP, RHO-GAP, ankyrin repeat, RAS-associating, and pleckstrin homology domains. A phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate (PtdIns-(3,4,5)-P3)-dependent GTPase-activating protein, ARAP2, binds to RhoA-GTP, but lacks the predicted catalytic arginine in the RHO-GAP domain and does not have RHO-GAP activity. It modulates actin cytoskeleton remodeling by regulating ARF and RHO family members. Usually ARAP2 is activated by PtdIns-(3,4,5)-P3 binding and can be activated by PtdIns-(3,4)-P2 binding, although with lower efficiency. ARAP2 associates with focal adhesions and functions downstream of RhoA to regulate focal adhesion dynamics. It is usually detected in brain, thymus, lymph node, thyroid, spinal cord, trachea, heart, skeletal muscle, spleen, kidney, liver, placenta, lung, and peripheral blood leukocytes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13495 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Apoptosis is regulated by death domain (DD) and/or caspase recruitment domain (CARD) containing molecules and a caspase family of proteases. CARD domain-containing cell death regulators included RAIDD, Apaf-1, caspase-9, and caspase-2. A novel CARD domain containing protein was recently identified and designated ARC for apoptosis repressor with CARD.{7140} ARC interacts with caspase-2 and -8 and inhibits enzymatic activity of caspase-8. ARC suppresses apoptosis induced by cell death adapters FADD and TRADD and by cell death receptors Fas, TNFR-1 and DR3. The mRNA for ARC is expressed primarily in skeletal muscle and cardiac tissues.{7140}
Brand:CaymanSKU:160737 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
AROS, a nucleolar protein with an unknown function, interacts with extraribosomal protein RPS19, playing a role in the signaling pathways that regulate rRNA transcription. The deduced amino acid sequence of AROS, derived from cDNA, defines an isoelectric point of 11.3. No known functional motifs were found in AROS except a short polylysine tract embedded in a putative nucleolar localization signal. At a basal level the protein is expressed ubiquitously with a significantly high level of expression in some tissues. Human AROS gene is mapped to chromosome 22q13.1.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13496 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:700422 - 25 mlAvailable on backorder
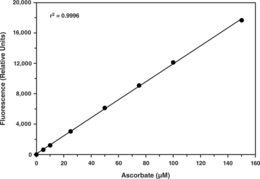
Ascorbate (L-Ascorbic acid or Vitamin C) is a six-carbon lactone that is synthesized from glucose in the liver of most mammalian species, but not by humans. Therefore, humans must obtain ascorbate in their diet in order to survive. In humans, ascorbate acts as an electron donor for eight different enzymes. It also serves as an antioxidant and may be beneficial for reducing the risk of developing chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and cataracts. Cayman’s Ascorbate Assay provides a reproducible, sensitive fluorescence-based tool for quantifying ascorbate from plasma, serum, urine, and fruit juices.
Brand:CaymanSKU:700420 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Domoic acid (DA) and DA derivatives are water-soluble neurotoxins produced by a number of marine algae, in particular those of the genus Pseudo-nitzschia. Blooms of Pseudo-nitzschia may lead to the accumulation of DA in shellfish filter feeders and other marine species. Ingestion of DA-contaminated shellfish causes amnesic shellfish poisoning (ASP) and has been linked to the death of animal and human consumers in severe cases. The European Commission Directive 2002/226/EC has implemented a maximum permitted level (MPL) of 20 mg DA/kg shellfish flesh intended for human consumption, and this level has been adopted by regulatory authorities in most other countries. The ASP ELISA is specific for DA with no cross-reactivity to non-toxic, structural analogues like kainic acid, L-glutamic acid, L-glutamine, formimino-L-glutamic acid, proline or γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA). The assay is primarily intended for use in routine monitoring of DA levels in bivalve molluscs to comply with the regulatory MPL, but is also applicable for DA quantification in other marine matrices.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008673 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Cayman’s Aspartate Aminotransferase Colorimetric Activity Assay Kit provides a convenient method of detecting AST activity in serum, plasma, tissue samples, and cell lysates. Measurement of the AST activity is carried out by monitoring the rate of NADH oxidation in a coupled reaction system employing malate dehydrogenase (MDH). The oxidation of NADH to NAD+ is accompanied by a decrease in absorbance at 340 nm. Under circumstances in which the AST activity rate is limiting, the rate of decrease is directly proportional to the AST activity in the sample. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) is added to prevent interference from endogenous pyruvate normally present in serum.
Brand:CaymanSKU:701640 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Asprosin is a glucogenic protein hormone secreted by white adipose tissue in mammals.{31498} This ~16 kDa protein is a 140 amino acid C-terminal cleavage product produced by furin cleavage of profibrillin. Asprosin increases glucose release via cyclic AMP (cAMP) and protein kinase A (PKA) in hepatocytes via interaction with a cell surface receptor, an effect that can be reversed by suramin, an inhibitor of heterotrimeric G proteins, or Rp-cAMPS (Item No. 16985), an antagonist of cAMP binding to PKA. In vivo, elevated plasma asprosin increases hepatic glucose production but does not affect glucose uptake in peripheral organs in response to insulin. Asprosin is orexigenic, activating AgRP+ neurons in a cAMP-dependent manner which leads to appetite stimulation and increased body weight.{37364} Plasma asprosin is elevated in adult humans and mice with type 2 diabetes mellitus and other genetic conditions that confer insulin resistance.{31498},{37365} Cayman’s Asprosin Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot and immunoprecipitation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23857 - 300 µgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:760114 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
The activating transcription factor 2 (ATF2; also called CRE-BP1) binds to both AP-1 and CRE DNA response elements and is a member of the ATF/CREB family of leucine zipper proteins.{14435} ATF2 has been implicated in the transcriptional regulation of a number of genes including cytokines, cell cycle control, and apoptosis. Various forms of cellular stress, including inflammatory cytokines and UV irradiation, stimulate the transcriptional activity of ATF2.{14433,14436} Stress induced ATF-dependent transcription is dependent on phosphorylation of ATF.{14432,14436} Serine 490 and serine 498 are novel phosphorylation sites on ATF that have recently been identified. ATF2 is particularly abundant in the brain and the ATF2 family of transcription factors is considered an important substrate of signals upstream of the activation of genes associated with neuronal growth and differentiation.{14339} ATF expression has also been linked to depression in humans.{14434}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009410 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
The activating transcription factors (ATFs) belong to the AP-1 family of transcription factors. ATF consists of seven members, ATF1 to 7. ATF7 (originally called ATFa) is ubiquitously expressed in various tissues and plays important roles in G1 and S phases. ATF7 might be important in controlling memory in cells of the innate immune system. [Bertin Catalog No. G01001]
Brand:CaymanSKU:32756 - 100 µlAvailable on backorder
Autophagy-related 4B (ATG4B), also known as autophagin-1, is a cysteine protease and a member of the C54 protease family with dual roles in the progression of autophagy.{42341,42342} It catalyzes the irreversible proteolytic cleavage of human homologs of yeast ATG8 belonging to the microtubule-associated protein 1 A/B-light chain 3 (MAP1LC3/LC3) and the GABA receptor-associated protein (GABARAP) subfamilies, including LC3, GATE16, GABARAP, and ATG8L, to expose a C-terminal glycine residue that is essential to formation of the autophagosome. It also catalyzes the reversible deconjugation of phosphatidylethanolamine from C-terminal glycine lipid-conjugated Atg8 homologs.{42343} ATG4B expression is increased in CD34+ chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) stem and progenitor cells and knockdown of ATG4B expression increases accumulation of LC3-II and p62, indicating impaired autophagy, and reduces the viability and inhibits proliferation of CD34+ CML cells.{42344} Atg4-/- mice exhibit systemic decreases in basal and induced autophagy as well as increased susceptibility to colitis induced by dextran sodium sulfate (DSS) and pulmonary fibrosis induced by bleomycin (Item No. 13877).{42345,42346} Cayman’s ATG4B Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 8A5) can be used for Western blot and ELISA applications. The antibody recognizes ATG4B at approximately 44 kDa from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25963 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
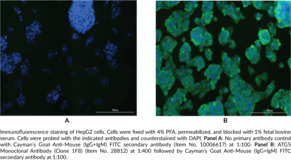
Autophagy-related 5 (ATG5), formerly known as apoptosis-specific protein (ASP), is a protein that is essential to autophagosome elongation.{47096,47097,47098} ATG5 is covalently conjugated to the C-terminal glycine residue of ATG12 (ATG12-ATG5) and forms a non-covalent complex with ATG16 (ATG12-ATG5-ATG16), which functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase-like enzyme to facilitate LC3 transfer from ATG3 to phosphatidylethanolamine in canonical autophagy. ATG12-ATG5 also binds to the ATG12-ATG5-interaction region of the lysosomally localized protein TECPR1, freeing the TECPR1 pleckstrin homology domain to interact with phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate components in the autophagosome membrane, promoting autophagosome-lysosome fusion.{47098} Polymorphisms in ATG5 have been associated with various autoimmune diseases, including lupus nephritis and Behçet’s disease, gastrointestinal and colorectal cancers, as well as sporadic Parkinson’s disease and childhood asthma. Cayman’s ATG5 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 1F8) can be used for ELISA and immunofluorescence applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28812 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
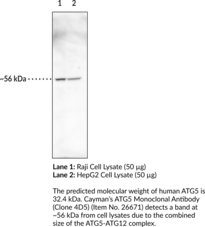
Autophagy-related 5 (ATG5), formerly known as apoptosis-specific protein (ASP), is a protein that is essential to autophagosome elongation.{47096,47097,47098} ATG5 is covalently conjugated to the C-terminal glycine residue of ATG12 (ATG12-ATG5) and forms a non-covalent complex with ATG16 (ATG12-ATG5-ATG16), which functions as an E3 ubiquitin ligase-like enzyme to facilitate LC3 transfer from ATG3 to phosphatidylethanolamine in canonical autophagy. ATG12-ATG5 also binds to the ATG12-ATG5-interaction region of the lysosomally localized protein TECPR1, freeing the TECPR1 pleckstrin homology domain to interact with phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate components in the autophagosome membrane, promoting autophagosome-lysosome fusion.{47098} Polymorphisms in ATG5 have been associated with various autoimmune diseases, including lupus nephritis and Behçet’s disease, gastrointestinal and colorectal cancers, as well as sporadic Parkinson’s disease and childhood asthma. Cayman’s ATG5 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 4D5) can be used for ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and Western blot applications. The antibody recognizes the ATG5-ATG12 complex at approximately 56 kDa from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26671 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder