ELISA Kits
Showing 1801–1950 of 3623 results
-
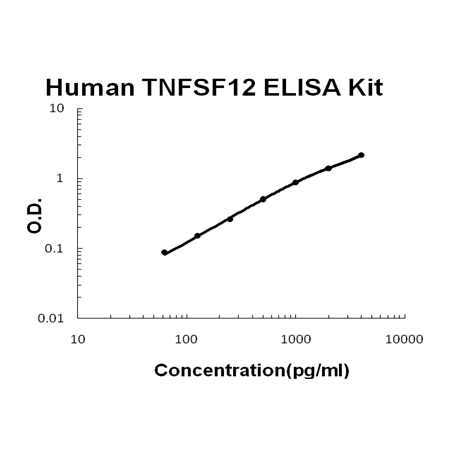
For quantitative detection of human TNFSF12 in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0920Available on backorder
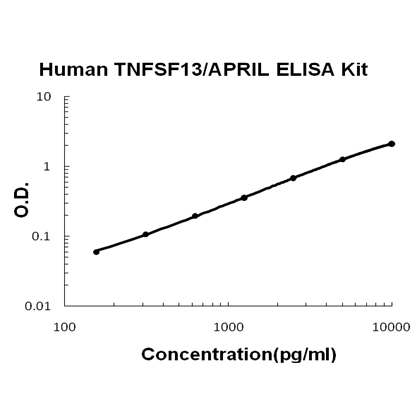
For quantitative detection of human TNFSF13 in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0921Available on backorder
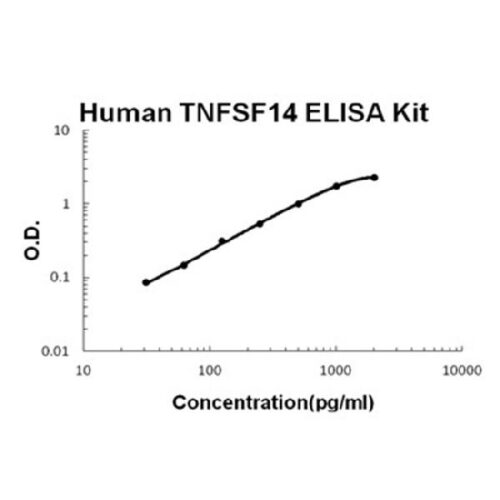
For quantitative detection of human TNFSF14 in cell culture supernates, serum, plasma(heparin, EDTA) and saliva.
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0990Available on backorder
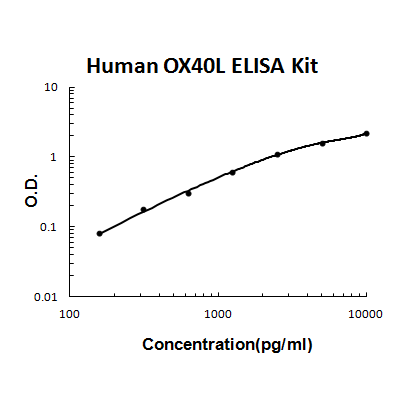
For quantitative detection of human TNFSF4 in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0857Available on backorder
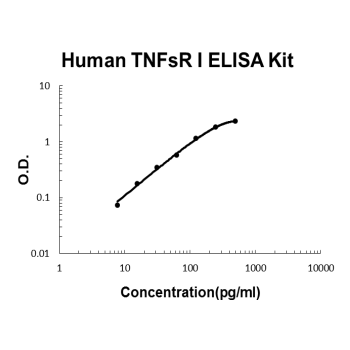
For quantitative detection of human TNFsRⅠin cell culture supernates, serum, plasma( heparin, EDTA, citrate) and urine.
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0528Available on backorder
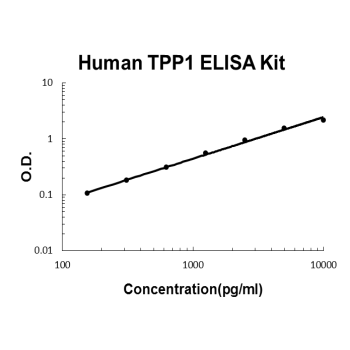
For quantitative detection of human TPP1 in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK2042Available on backorder
For quantitative detection of human TRAIL in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum, plasma(heparin, EDTA) and saliva.
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0532Available on backorder
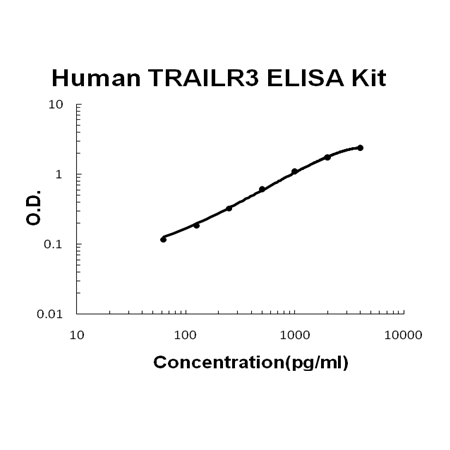
For Quantitative Detection of human TRAILR3 in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0533Available on backorder
For quantitative detection of human TTR in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1684Available on backorder
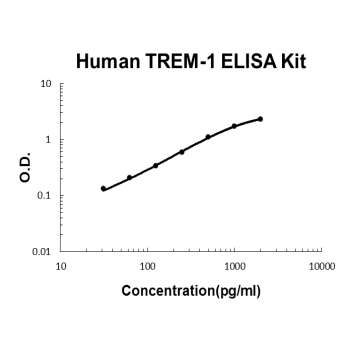
For quantitative detection of Human TREM-1 in cell culture supernates, lysates, tissue, serum and plasma(heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0844Available on backorder
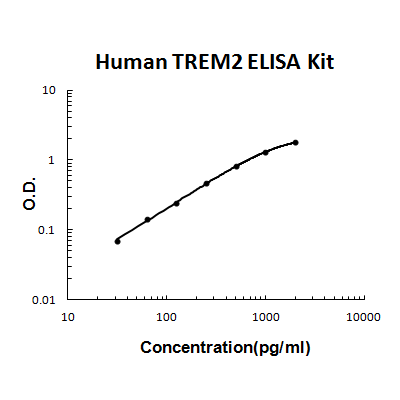
For quantitative detection of human TREM2 in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1678Available on backorder
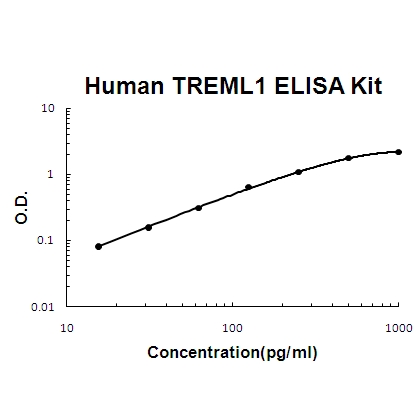
For quantitative detection of human TREML1 in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1521Available on backorder
For quantitative detection of human TREML2 in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1985Available on backorder
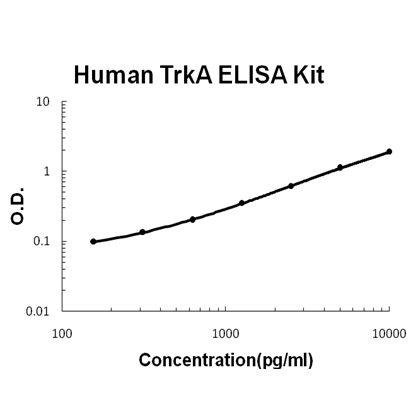
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0846Available on backorder
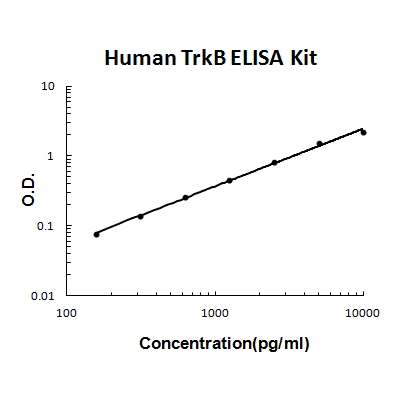
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0848Available on backorder
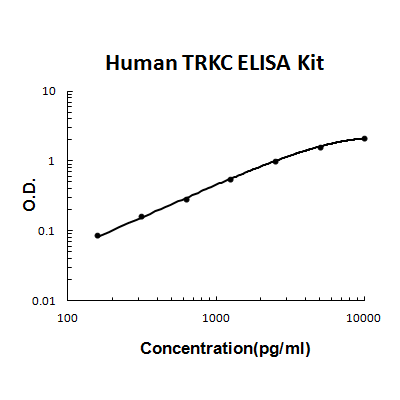
For quantitative detection of human TRKC in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1676Available on backorder
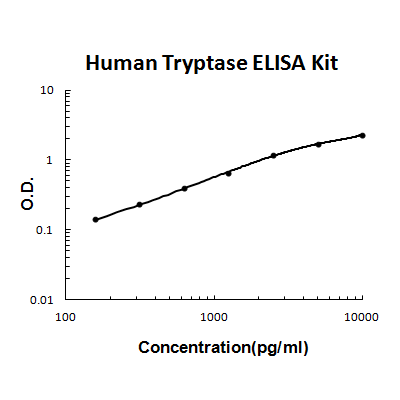
For quantitative detection of human Tryptase in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0898Available on backorder
For quantitative detection of human TSKU in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1859Available on backorder
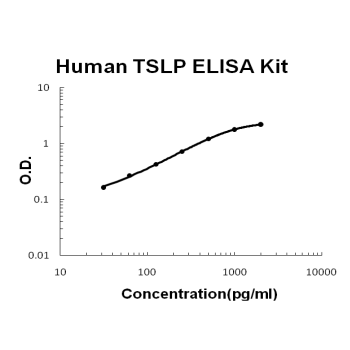
For quantitative detection of human TSLP in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0958Available on backorder
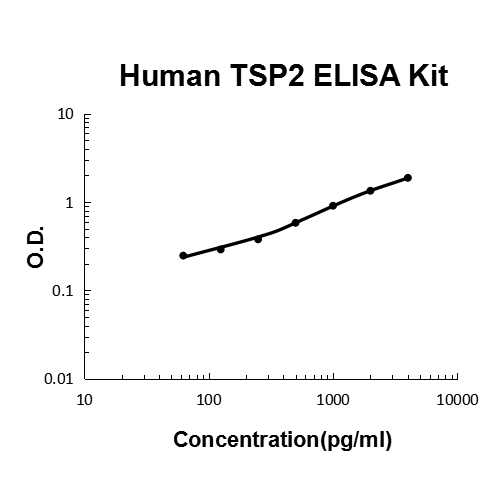
For quantitative detection of human TSP2 in cell culture supernates, serum, plasma(heparin, EDTA) and human milk.
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0642Available on backorder
For quantitative detection of human ULBP1 in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1685Available on backorder
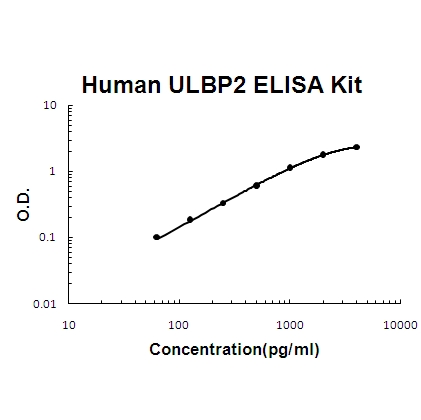
For quantitative detection of human ULBP2 in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1593Available on backorder
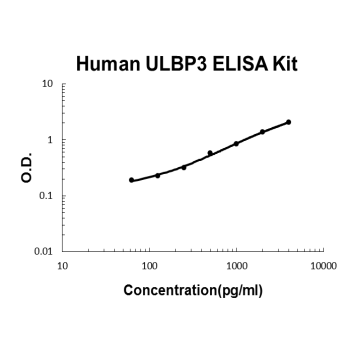
For quantitative detection of human ULBP3 in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1686Available on backorder
For quantitative detection of human uPA in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0535Available on backorder
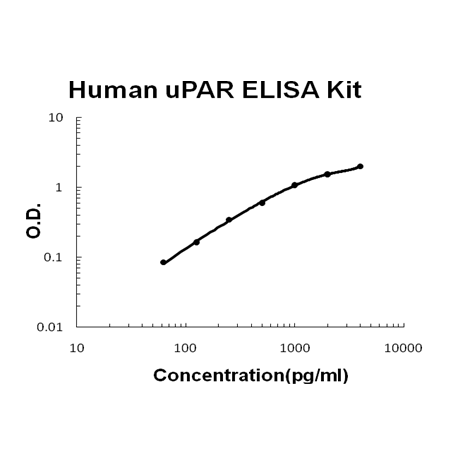
For quantitative detection of human uPAR in cell culture supernates, serum, plasma(heparin, EDTA) and urine.
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0536Available on backorder
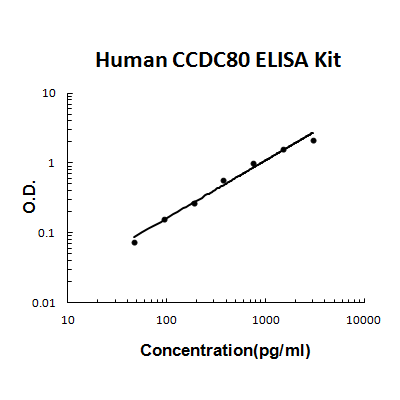
For quantitative detection of human URB/CCDC80 in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1962Available on backorder
For quantitative detection of human Uromodulin in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1690Available on backorder
For Quantitative Detection of human VAP-1 in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1646Available on backorder
For quantitative detection of human VCAM-1 in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0537Available on backorder
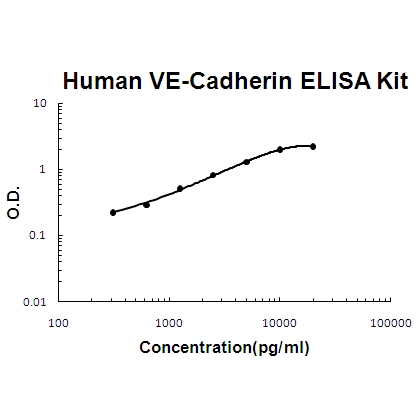
For quantitative detection of human VE-Cadherin in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1317Available on backorder
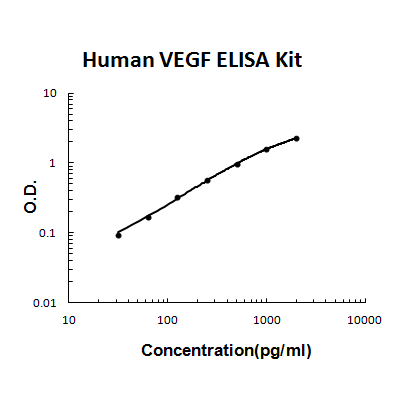
For quantitative detection of human VEGF in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma(heparin, EDTA, citrate).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0539Available on backorder
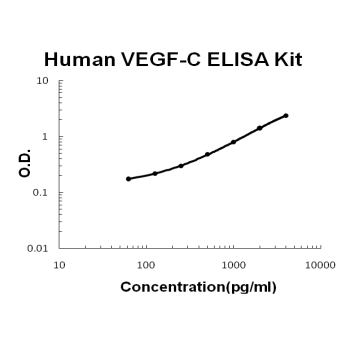
For quantitative detection of human VEGF-C in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0588Available on backorder
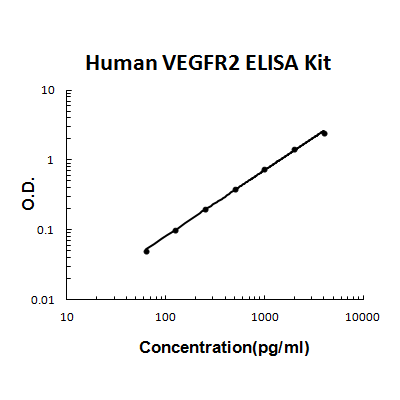
For quantitative detection of human VEGFR2 in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0544Available on backorder
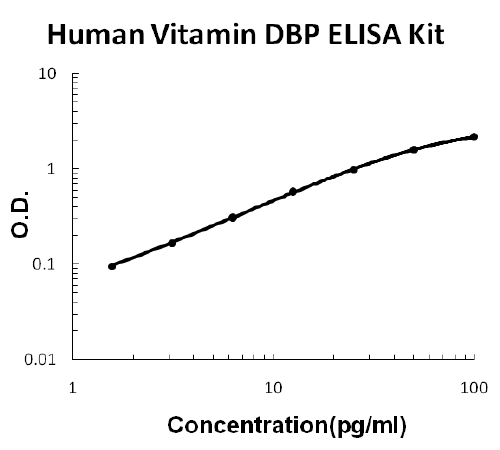
For Quantitative Detection of human Vitamin DBP in cell culture supernates, serum, plasma (heparin, EDTA), saliva, urine and human milk.
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1641Available on backorder
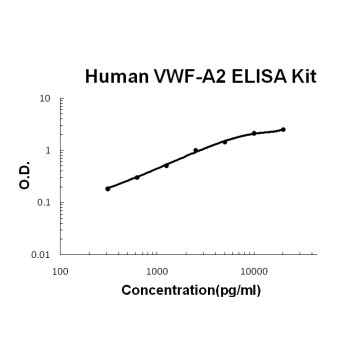
For quantitative detection of human VWF-A2 in cell culture supernates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1743Available on backorder
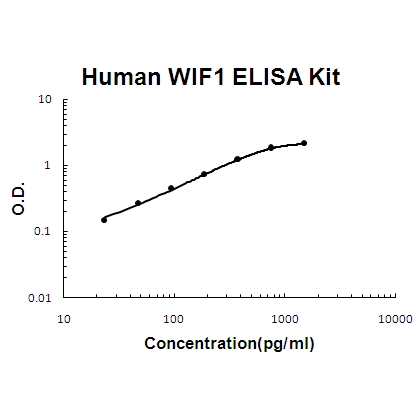
For quantitative detection of human WIF1 in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1524Available on backorder
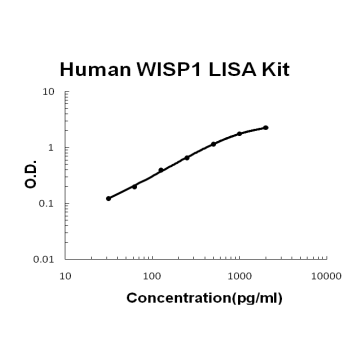
For quantitative detection of human WISP1 in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK1204Available on backorder
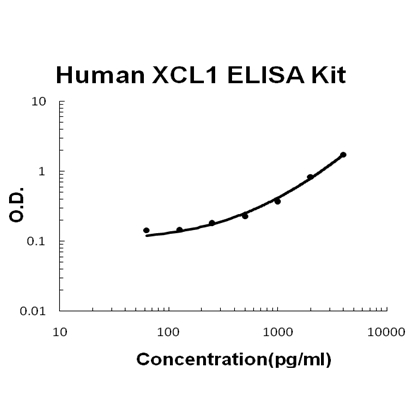
For quantitative detection of human XCL1 in cell culture supernates, cell lysates, serum and plasma (heparin, EDTA).
Brand:Boster BioSKU:EK0802Available on backorder
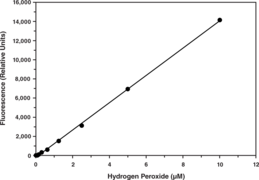
Reactive oxygen species, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide are generated by phagocytes and participate in damaging invading miccroorganisms or other biologic targets.{29448} Cayman’s H2O2 Cell-Based Assay Kit provides a simple fluorometric method for the sensitive quantitation of extracellular H2O2 produced by cultured cells. H2O2 is detected using ADHP (10-acetyl-3,7-dihydroxyphenoxazine), a highly sensitive and stable probe for H2O2.{5816} In the presence of horseradish peroxidase, ADHP reacts with H2O2 with a 1:1 stoichiometry to produce highly fluorescent resorufin.{13685} Resorufin fluorescence can be read using an excitation wavelength between 530-560 nm and an emission wavelength of 590 nm. Catalase, an H2O2 scavenger, is included in the kit for checking specificity of the assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:600050 - 480 wellsAvailable on backorder
Reactive oxygen species, such as hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and superoxide are generated by phagocytes and participate in damaging invading miccroorganisms or other biologic targets.{29448} Cayman’s H2O2 Cell-Based Assay Kit provides a simple fluorometric method for the sensitive quantitation of extracellular H2O2 produced by cultured cells. H2O2 is detected using ADHP (10-acetyl-3,7-dihydroxyphenoxazine), a highly sensitive and stable probe for H2O2.{5816} In the presence of horseradish peroxidase, ADHP reacts with H2O2 with a 1:1 stoichiometry to produce highly fluorescent resorufin.{13685} Resorufin fluorescence can be read using an excitation wavelength between 530-560 nm and an emission wavelength of 590 nm. Catalase, an H2O2 scavenger, is included in the kit for checking specificity of the assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:600050 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
I2PP2A/SET is a multitasking protein, involved in apoptosis, transcription, nucleosome assembly, and histone binding. The SET gene produces two isoforms from transcript variants. Isoform 1 and 2 interact directly with each other and with ANP32A within the tripartite inhibitor of acetyltransferases (INHAT) complex, inhibiting EP300/CREBBP and PCAF-mediated acetylation of histones. The two isoforms differ in their amino termini but are identical through the regions used as antigens for preparing this antibody.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13782 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
The IFN-α is one of the member of the type I interferons (IFNs) family and it is mainly involved in innate immunity. IFN-α 1 is secreted by immune (lymphocytes, NK cells, B cells, T cells, and macrophages) and non-immune cells (fibroblasts, endothelial cells, osteoblasts, and others) in answer to a viral infection. The main function of the IFN-α 1 is to alert the organism in case of viral infection by detection of abnormal double stranded DNA, but also to inhibit virus multiplication by action on the translation in infected cells. An abnormal production of IFN-α 1 induces immune dysfunction such as autoimmune diseases (systemic lupus erythematosus, rheumatoid arthritis) or mediates tissue inflammation. [Bertin Catalog No. A05412]
Brand:CaymanSKU:23618 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Also known as type II interferons, IFN-γ is a glycoprotein of 146 amino acids. IFN-γ is a cytokine critical for the innate and adaptive immunity. It is produced predominantly by natural killer (NK) and natural killer T (NKT) cells as part of the innate immune response and by T helper cells and cytotoxic T lymphocyte (CTL) as part of the adaptive immunity. IFN-γ has antiviral, immunoregulatory, and anti-tumor properties. IFN-γ: Promotes the NK cell activity Increases the antigen presentation by action on the lysosome activity of macrophages Promotes Th1 differentiation, and suppresses Th2 differentiation which would cause a humoral (antibody) response Modulates the production of IgG2a and IgG3 from activated plasma B cells Increases expression of class I MHC molecules as well as class II MHC on antigen-presenting cells Promotes adhesion and binding required for leukocyte migration IFN-γ interacts with other cytokines, either in a synergistic (e.g., TNF) or antagonistic (e.g., IL-4) fashion. [Bertin Catalog No. A05413]
Brand:CaymanSKU:23619 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
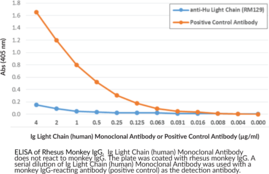
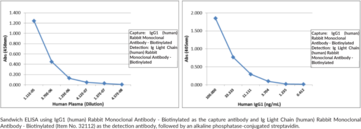
Immunoglobulins are members of the glycoprotein superfamily that play a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} They are produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells as antibodies.{55225} Immunoglobulins are composed of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} Mammalian immunoglobulins contain either Igκ or Igλ light chains, each of which are composed of a constant and variable domain.{28687} The ratio of Igκ to Igλ light-chain containing antibodies varies between species, with ratios of 20:1, 2:1, and 1:20 in mice, humans, and cattle, respectively. Igκ and Igλ free light chains (FLCs) are produced during immunoglobulin synthesis, and accumulation of these FLCs is associated with various disorders, including light-chain deposition disease, multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic nephropathy, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).{55225,55232,53885} Cayman’s Ig Light Chain (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody be used for ELISA, flow cytometry (FC), immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications. The antibody recognizes both the Igĸ and Igλ light chains from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32111 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulins are members of the glycoprotein superfamily that play a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} They are produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells as antibodies.{55225} Immunoglobulins are composed of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} Mammalian immunoglobulins contain either Igκ or Igλ light chains, each of which are composed of a constant and variable domain.{28687} The ratio of Igκ to Igλ light-chain containing antibodies varies between species, with ratios of 20:1, 2:1, and 1:20 in mice, humans, and cattle, respectively. Igκ and Igλ free light chains (FLCs) are produced during immunoglobulin synthesis, and accumulation of these FLCs is associated with various disorders, including light-chain deposition disease, multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic nephropathy, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).{55225,55232,53885} Cayman’s Ig Light Chain (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody – Biotinylated be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications. The antibody recognizes both the Igĸ and Igλ light chains from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32112 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
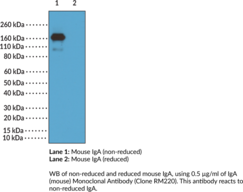
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins with roles in host defense against intestinal pathogens and both quantitative and qualitative control of host commensal microbiota composition.{53918,53919} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant antibody on mucosal surfaces that comprises at least 70% of all Ig produced in mice. Mouse IgA consists of two heavy chains of approximately 53.5 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{53917} Unlike human IgA, mouse IgA exists as a single isotype and is primarily found as a dimer that lacks the disulfide bonds between the light and heavy chains present in other Ig classes.{53917,53920} Production of IgA is induced in the gut only in animals containing intestinal microbes, and the number of IgA-producing plasma cells is reduced in germ-free mice.{53918} IgA-deficient mice exhibit increased lethality compared with wild-type mice in a model of influenza infection, as well as reduced bacterial clearance in a model of G. muris infection. However, IgA deficiency does not affect clearance of vaginal infection with herpes simplex virus 2 (HSV-2), indicating redundancy in pathogen protection with compensation by antibodies of other isotypes or innate immune mechanisms at mucosal surfaces. Cayman’s IgA (mouse) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM220) can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB; non-reducing conditions) applications. The antibody recognizes IgA at approximately 160 kDa from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20715 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
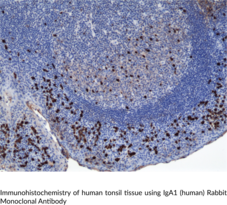
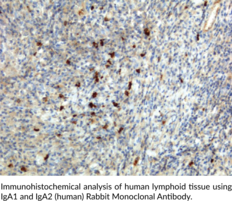
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins with roles in host defense against intestinal pathogens and both quantitative and qualitative control of host commensal microbiota composition.{53918,53919} Human IgA consists of two identical light chains of approximately 25 kDa each, as well as two heavy chains of approximately 60 kDa each that contain C-terminal extensions, known as tailpieces, which allow for IgA oligomerization.{53927,53925} There are two IgA subclasses, IgA1 and IgA2, which are encoded by IGHA1/α1 and IGHA2/α2, respectively, and have differences primarily in the hinge and heavy chain constant regions.{53925} IgA is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant antibody on mucosal surfaces that comprises at least 70% of all Ig produced in mice.{53918,53919} Monomeric IgA1 is predominant in the serum, but dimeric secretory IgA (SIgA) is the predominant form in mucosal surfaces and secretions with the ratio of subclasses varying based on the IgA-secreting cell types present.{53925,53921} Dimeric and polymeric IgA bind to Igα Fc receptor I (FcαRI) and the IgM- and IgA-binding high affinity Igα and Igµ Fc receptor (Fcα/µ-R), which are both involved in mediating immune responses.{53921,53922} Production of IgA is induced in the gut only in animals containing intestinal microbes, and the number of IgA-producing plasma cells is reduced in germ-free mice.{53918} The extended hinge region of IgA1 contains O-linked glycan side chains, which have altered galactosylation and form circulating immune complexes in patients with IgA neuropathy (IgAN), an autoimmune inflammatory disease characterized by IgA1-containing deposits in the glomerular mesangium, tea-colored urine, proteinuria, and, potentially, renal failure.{56183,56184} IgA levels are increased in certain gastrointestinal tract and liver diseases, with IgA1 levels increased to a higher degree than IgA2 levels in patients with chronic hepatitis.{56183} Cayman’s IgA1 (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32115 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins with roles in host defense against intestinal pathogens and both quantitative and qualitative control of host commensal microbiota composition.{53918,53919} Human IgA consists of two identical light chains of approximately 25 kDa each, as well as two heavy chains of approximately 60 kDa each that contain C-terminal extensions, known as tailpieces, which allow for IgA oligomerization.{53927,53925} There are two IgA subclasses, IgA1 and IgA2, which are encoded by IGHA1/α1 and IGHA2/α2, respectively, and have differences primarily in the hinge and heavy chain constant regions.{53925} IgA is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant antibody on mucosal surfaces that comprises at least 70% of all Ig produced in mice.{53918,53919} Monomeric IgA1 is predominant in the serum, but dimeric secretory IgA (SIgA) is the predominant form in mucosal surfaces and secretions with the ratio of subclasses varying based on the IgA-secreting cell types present.{53925,53921} Dimeric and polymeric IgA bind to Igα Fc receptor I (FcαRI) and the IgM- and IgA-binding high affinity Igα and Igµ Fc receptor (Fcα/µ-R), which are both involved in mediating immune responses.{53921,53922} Production of IgA is induced in the gut only in animals containing intestinal microbes, and the number of IgA-producing plasma cells is reduced in germ-free mice.{53918} Serum levels of IgA are decreased in patients with IgA deficiency, who are typically asymptomatic but may have allergy or autoimmune disorders or experience recurrent infections.{53923} IgA deposits in vessels and, in certain cases, the glomerulus in children with IgA vasculitis (IgAV), a disorder characterized by vascular inflammation, purpura, joint pain, gastrointestinal disturbances, and, in severe cases, glomerulonephritis.{53924} Cayman’s IgA1 and IgA2 (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32114 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
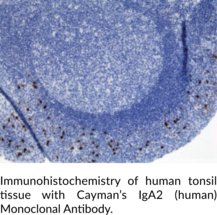
Immunoglobulin A (IgA) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins with roles in host defense against intestinal pathogens and both quantitative and qualitative control of host commensal microbiota composition.{53918,53919} Human IgA consists of two identical light chains of approximately 25 kDa each, as well as two heavy chains of approximately 60 kDa each that contain C-terminal extensions, known as tailpieces, which allow for IgA oligomerization.{53927,53925} There are two IgA subclasses, IgA1 and IgA2, which are encoded by IGHA1/α1 and IGHA2/α2, respectively, and have differences primarily in the hinge and heavy chain constant regions.{53925} IgA is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant antibody on mucosal surfaces that comprises at least 70% of all Ig produced in mice.{53918,53919} Monomeric IgA1 is predominant in the serum, but dimeric secretory IgA (SIgA) is the predominant form in mucosal surfaces and secretions with the ratio of subclasses varying based on the IgA-secreting cell types present.{53925,53921} Dimeric and polymeric IgA bind to Igα Fc receptor I (FcαRI) and the IgM- and IgA-binding high affinity Igα and Igµ Fc receptor (Fcα/µ-R), which are both involved in mediating immune responses.{53921,53922} Production of IgA is induced in the gut only in animals containing intestinal microbes, and the number of IgA-producing plasma cells is reduced in germ-free mice.{53918} IgA levels are increased in certain gastrointestinal tract and liver diseases, with IgA2 levels increased to a higher degree than IgA1 levels in patients with Crohn’s disease and alcoholic liver disease.{56183} Cayman’s IgA2 (human) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32116 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
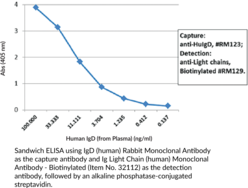
Immunoglobulin D (IgD) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that functions as a B cell antigen receptor (BCR) and has roles in adaptive immunity.{52717} Human IgD is composed of two Igδ heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two Igĸ or Igλ light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{52718,28520} It is expressed on the surface of antigen-naïve mature B cells, which are found in germinal centers and peripheral blood, as well as certain subsets of circulating memory B cells.{52717,52719} IgD levels increase during B cell maturation and are regulated by alternative splicing of an mRNA transcript that is common to the µ and δ heavy chains of IgM and IgD, respectively.{52717,52720} Upon antigen activation, IgD can undergo class switch recombination to the immunoglobulin isotypes IgA, IgE, or IgG, each of which has a distinct effector function.{52721} IgD can also be produced from IgM by class switch recombination, leading to the generation of IgD-secreting plasma cells that have roles in mucosal immunity.{52722} IgD binds to basophil and mast cell lines, as well as the respiratory pathogens M. catarrhalis and H. influenzae, in vitro.{52723} Serum IgD levels are increased in patients with a variety of conditions, including leprosy, tuberculosis, malaria, or Hodgkin’s lymphoma and is a hallmark of hyperimmunoglobulinemia D syndrome (HIDS), an autoinflammatory condition characterized by febrile episodes.{52724} Cayman’s IgD (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32117 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
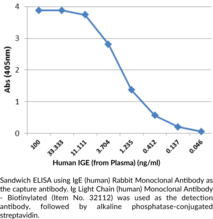
Immunoglobulin E (IgE) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in type I hypersensitivity reactions and the immune response to parasites.{28520,54323,54324} It is synthesized by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the least abundant circulating antibody in human serum.{28520,54323} IgE consists of two light chains and two heavy chains, or ε chains, that contain one variable region and four Ig-like constant domains Cε1-Cε4, but lacks the flexible hinge region seen in IgD, IgG, and IgA.{54324,54325} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgE binds to type I Fcε receptors (FcεRIs) on the surface of mast cells, basophils, and antigen-presenting dendritic cells.{54323} Multivalent antigen binding to IgE on the surface of mast cells induces IgE crosslinking and mast cell degranulation to initiate type I hypersensitivity reactions, including, but not limited to, systemic anaphylaxis, wheal and flare responses, allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma, and food allergies. Serum levels of IgE are elevated in response to parasitic infection and IgE directly binds parasites to target the parasite for eosinophil degranulation-induced destruction. Cayman’s IgE (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32118 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Insulin-like growth factor binding protein 5 (IGFBP5) is a secreted protein that binds IGF-1 and restricts it from accessing its cell-surface receptor (IGF-1R). This aids in regulation of cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis.{14904} IGFBP5 also displays IGF-1 independent transactivational activity in the nucleus.{14903} Some tissues and cell types with higher levels of this protein include kidney, heart, placenta, and skeletal cells.{14902} Expression has also been reported in a variety of cancers, including mammary gland and neuroblastoma.{14904,14899} Cayman’s IGFBP5 Polyclonal Antibody is directed against a synthetic peptide sequence that partially overlaps the IGFBP5 region identified as a nuclear localization signal.{14903} IGFBP5 (272 amino acids) has a calculated molecular weight of 30.6 kDa. Cayman’s IGFBP5 Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot applications and recognizes IGFBP5 at 33 kDa from mouse and rat samples. Reported glycosylation and phosphorylation sites may explain the band migration to 33 kDa.{14904,14901}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008207 - 500 µlAvailable on backorder
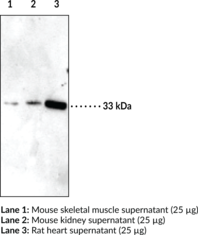
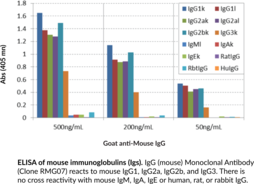
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in mice: IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and, in a strain-specific manner, IgG2a or IgG2c.{55172,53858} Formulations containing humanized, chimeric, or murine IgG monoclonal antibodies have been used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases, such as ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and asthma, as well as cancer.{55173} Cayman’s IgG (mouse) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RMG07) can be used for ELISA, flow cytometry (FC), and immunoprecipitation (IP) applications. The antibody recognizes IgG from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22469 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
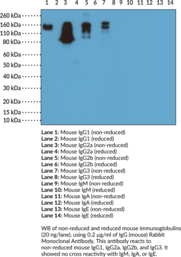
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in mice: IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and, in a strain-specific manner, IgG2a or IgG2c.{55172,53858} Formulations containing humanized, chimeric, or murine IgG monoclonal antibodies have been used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases, such as ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and asthma, as well as cancer.{55173} Cayman’s IgG (mouse) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB; non-reducing conditions) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fc region of IgG from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32002 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
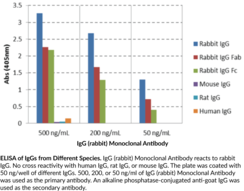
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{53881,53882} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in rabbit serum. IgG consists of two identical heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two identical light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{53881} The heavy chains are linked together by a single disulfide bond to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains through additional disulfide bonds to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively. IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{53881,55170,53883} Rabbits express three light chains, IgGκ (K1), IgGκ (K2), and IgGγ, with IgGκ (K1)-containing IgGs comprising approximately 90% of the total IgG population. Unlike human and mouse IgG, rabbit IgG has a single subclass and a short upper and middle hinge length of only 11 residues that facilitates the hinge extension necessary for binding of the Fc receptor (FcR) and activating complement component 1q (C1q) to facilitate complement activation.{53882,53880} Cayman’s IgG (rabbit) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32105 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
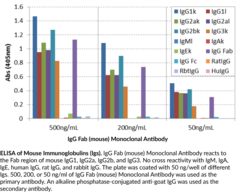
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in mice: IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and, in a strain-specific manner, IgG2a or IgG2c.{55172,53858} Formulations containing humanized, chimeric, or murine IgG monoclonal antibodies have been used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases, such as ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and asthma, as well as cancer.{55173} Cayman’s IgG Fab (mouse) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, flow cytometry (FC), and immunoprecipitation (IP) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fab region of IgG from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21780 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{53880,53881,53882} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in rabbit serum. IgG consists of two identical heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two identical light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{53880,53881} The heavy chains are linked together by a single disulfide bond to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains through additional disulfide bonds to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively. IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{53880,53881,55170,53883} Rabbits express three light chains, IgGκ (K1), IgGκ (K2), and IgGγ, with IgGκ (K1)-containing IgGs comprising approximately 90% of the total IgG population. Unlike human and mouse IgG, rabbit IgG has a single subclass and a short upper and middle hinge length of only 11 residues that facilitates the hinge extension necessary for binding of the Fc receptor (FcR) and activating complement component 1q (C1q) to facilitate complement activation.{53880,53882} Cayman’s IgG Fab (rabbit) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fab region of non-reduced IgG at approximately 150 kDa from rabbit samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32099 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
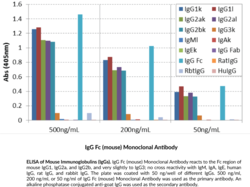
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in mice: IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and, in a strain-specific manner, IgG2a or IgG2c.{55172,53858} Formulations containing humanized, chimeric, or murine IgG monoclonal antibodies have been used in the treatment of inflammatory diseases, such as ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and asthma, as well as cancer.{55173} Cayman’s IgG Fc (mouse) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA. The antibody recognizes the Fc region of IgG from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32106 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{53881,53882} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in rabbit serum. IgG consists of two identical heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two identical light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{53881} The heavy chains are linked together by a single disulfide bond to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains through additional disulfide bonds to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively. IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170,53881,53883} Rabbits express three light chains, IgGκ (K1), IgGκ (K2), and IgGγ, with IgGκ (K1)-containing IgGs comprising approximately 90% of the total IgG population. Unlike human and mouse IgG, rabbit IgG has a single subclass and a short upper and middle hinge length of only 11 residues that facilitates the hinge extension necessary for binding of the Fc receptor (FcR) and activating complement component 1q (C1q) to facilitate complement activation.{53882,53880} Cayman’s IgG Fc (rabbit) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB; non-reducing conditions) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fc region of IgG at approximately 150 kDa from rabbit samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32104 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400914 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
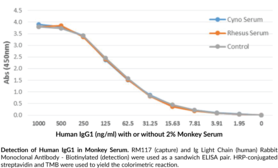
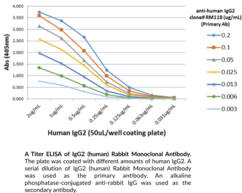
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in humans, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4, each of which has a distinct effector function. IgG1 binds to Fc receptors to induce Fc receptor-mediated effector functions, as well as Cq1 to induce complement activation in response to soluble and membrane protein antigens. Maternal IgG1s are shared with the fetus via placental transfer and children with group B streptococcal-induced sepsis are born to mothers with decreased serum levels of IgG1 compared with mothers of uninfected children.{53928} Cayman’s IgG1 (human) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32119 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in humans, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4, each of which has a distinct effector function. IgG1 binds to Fc receptors to induce Fc receptor-mediated effector functions, as well as Cq1 to induce complement activation in response to soluble and membrane protein antigens. Maternal IgG1s are shared with the fetus via placental transfer and children with group B streptococcal-induced sepsis are born to mothers with decreased serum levels of IgG1 compared with mothers of uninfected children.{53928} Cayman’s IgG1 (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody – Biotinylated can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications. The antibody recognizes the heavy chain of human IgG1.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32373 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
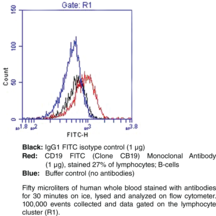
The IgG1 isotype control FITC is fluorescein conjugated non-specific mouse IgG1 produced from hybridoma clone MOPC-21. This conjugate should be used as a control antibody in direct fluorescence immunostaining experiments which utilize a mouse IgG1-fluorescein conjugate as the primary antibody.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10343 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400964 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in humans, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4, each of which has a distinct effector function. IgG2 is primarily responsible for anticarbohydrate responses against bacterial polysaccharides but, unlike IgG1, IgG2 does not bind Fc receptors or induce Fc receptor-mediated effector functions.{53928} Maternal IgG2s are shared with the fetus via placental transfer and mothers of children born with group B streptococcal-induced sepsis have decreased serum levels of IgG2 compared with mothers of children born uninfected. Serum levels of IgG2 are also decreased in patients with recurrent infections with capsulated bacteria, sinopulmonary infections, and otitis media. IgG2 (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA. The antibody recognizes the heavy chain of IgG2 from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32121 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in mice: IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and, in a strain-specific manner, IgG2a or IgG2c.{55172,53858} In vivo, class switching to the IgG2a isotype can happen via IFN-γ-dependent and -independent mechanisms, with the former resulting from the cognate interaction of B cells with T helper 1 (Th1) cells.{52651} IgG2a is the predominant isotype produced in response to infection with DNA or RNA viruses in mice.{52652} Cayman’s IgG2a (mouse) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB; non-reducing conditions) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fc region of IgG2a from mouse samples at approximately 150 kDa.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32005 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in mice: IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and, in a strain-specific manner, IgG2a or IgG2c.{55172,53858} In vivo, class switching to the IgG2a isotype can happen via IFN-γ-dependent and -independent mechanisms, with the former resulting from the cognate interaction of B cells with T helper 1 (Th1) cells.{52651} IgG2a is the predominant isotype produced in response to infection with DNA or RNA viruses in mice.{52652} Cayman’s IgG2a (mouse) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody – Biotinylated can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB; non-reducing conditions) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fc region of IgG2a at approximately 150 kDa from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32352 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in mice: IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and, in a strain-specific manner, IgG2a or IgG2c.{55172,53858} In vivo, class switching to the IgG2a isotype can happen via IFN-γ-dependent and -independent mechanisms, with the former resulting from the cognate interaction of B cells with T helper 1 (Th1) cells.{52651} IgG2a is the predominant isotype produced in response to infection with DNA or RNA viruses in mice.{52652} Mammalian immunoglobulins contain either Igκ or Igλ light chains, each of which are composed of a constant and variable domain.{28687} Cayman’s IgG2aκ (mouse) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM107) can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB; non-reducing conditions) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fab region of IgG2aκ from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32004 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in mice: IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and, in a strain-specific manner, IgG2a or IgG2c.{55172,53858} Class switching to the IgG2b isotype occurs via TGF-β stimulation during the early immune response.{57049} IgG2b binds to activating Fcγ receptors (FcγRs) and is involved in complement fixation.{55172} Cayman’s IgG2b (mouse) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM108) can be used for ELISA, flow cytometry (FC), immunoprecipitation (IP), and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fc region of non-reduced and reduced IgG2b at approximately 150 and 50 kDa, respectively, from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32089 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in mice: IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and, in a strain-specific manner, IgG2a or IgG2c.{55172,53858} IgG2c is encoded by Ighg2c and is expressed in certain inbred mouse strains, such as C57BL/6, C57BL/10, SJL, and NOD mice.{53858} Class switching to the IgG2c isotype occurs via IFN-γ stimulation during the early immune response.{56168} IgG2c binds to the high affinity Igγ Fc receptor I (FcγRI) on dendritic cells and the low affinity FcγRIII and FcγRIV, which are expressed on a variety of immune cells, and is involved in complement activation.{56169,56170} Cayman’s IgG2c (mouse) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB; non-reducing conditions) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fc region of IgG2c from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32102 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
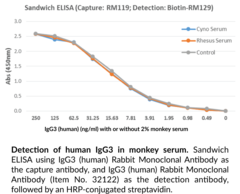
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in humans, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4, each of which has a distinct effector function. IgG3 production is driven by bacterial- or viral-associated antigens, including HIV-1 and Staphylococcus antigens, and occurs early in the immune response following IgM class-switching.{55170,52653} IgG3 binds to and neutralizes pathogens, as well as activates complement and opsonizes bacteria, leading to complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and ADCC, respectively. Serum IgG3 levels are increased in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).{52654} Cayman’s IgG3 (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32122 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
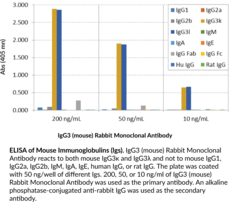
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG exists as four isotypes in mice: IgG1, IgG2b, IgG3, and, in a strain-specific manner, IgG2a or IgG2c.{55172,53858} IgG3 production is driven by bacterial- or viral-associated antigens, including HIV-1 and Staphylococcus antigens, and occurs early in the immune response following IgM class-switching.{55170,52653} IgG3 binds to and neutralizes pathogens, as well as activates complement and opsonizes bacteria, leading to complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and antibody-dependent cell cytotoxicity (ADCC), respectively. Serum IgG3 levels are increased in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis, Sjögren’s syndrome, systemic sclerosis, or systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).{52654} Cayman’s IgG3 (mouse) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes the Fab region of IgG3 from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32098 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400924 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
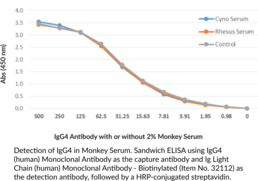
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in humans, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4, each of which has a distinct effector function. IgG4 is the least predominant IgG isotype in human serum and contains a serine at position 228 in its hinge region that facilitates Fab arm exchange, resulting in two antigen-binding sites and a functionally monovalent antibody.{53943} Increased serum levels of IgG4 positively correlate with desensitization and allergen tolerance in beekeepers, laboratory workers chronically exposed to rodent allergens, and individuals undergoing allergy immunotherapy for severe allergies to cats, dust mites, birch pollen, and wasps. Cayman’s IgG4 (human) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes whole IgG4 at approximately 150 kDa under non-reducing conditions and the IgG4 heavy chain at approximately 50 kDa under reducing conditions from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32123 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
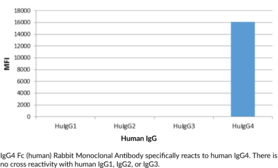
Immunoglobulin G (IgG) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} It is produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells and is the most abundant circulating antibody in human and mouse serum.{28520,55170,55174} IgG consists of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} IgG is produced following IgM class-switching in response to infection and is involved in numerous humoral host defense responses, including antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC), toxin neutralization, and pathogen opsonization.{55170} IgG exists as four isotypes in humans, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, and IgG4, each of which has a distinct effector function. IgG4 is the least predominant IgG isotype in human serum and contains a serine at position 228 in its hinge region that facilitates Fab arm exchange, resulting in two antigen-binding sites and a functionally monovalent antibody.{53943} Increased serum levels of IgG4 positively correlate with desensitization and allergen tolerance in beekeepers, laboratory workers chronically exposed to rodent allergens, and individuals undergoing allergy immunotherapy for severe allergies to cats, dust mites, birch pollen, and wasps. Cayman’s IgG4 Fc (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32124 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
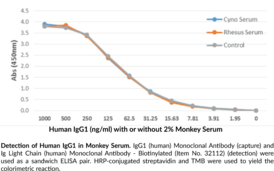
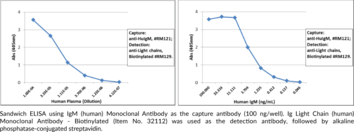
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response and in mucosal immunology.{28520,53830} IgM consists of two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each, as well as two heavy chains of approximately 70 kDa each that contain C-terminal extensions, known as tailpieces, which allow for IgM oligomerization.{53830,53831} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} Five IgM proteins oligomerize via disulfide bonds in the presence of a 15-kDa joining chain, a process that is required for transcytosis of IgM from plasma cells to mucosal epithelial cells via the polyimmunoglobulin receptor (pIgR).{53830} Monomeric and oligomeric IgM are both ligands for the IgM and IgA-binding high affinity Igα and the Igμ Fc receptor (Fcα/μ-R) on dendritic cells, which mediates cellular uptake of IgM-conjugated antigens, and the IgM-binding Fcμ-R on B and T cells, which is important for B cell maturation among other functions.{53830,53832,53833,53834} IgM is produced primarily in the plasma by naïve B cells and expressed in its monomeric low-affinity form on the cell surface.{28520} Activated B cells secrete pentameric high-affinity IgM, which opsonizes antigens to target them for removal by phagocytes and to activate complement via the classical pathway.{28520,53835} IgM antibodies are produced early in infection and have been used to determine exposure to a specific pathogen.{28520} IgM levels are elevated in hyper-IgM syndromes, which are characterized by dysfunctions in Ig class switching recombination.{53836} Cayman’s IgM (human) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32113 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
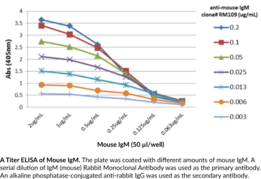
Immunoglobulin M (IgM) is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response and in mucosal immunology.{28520,53830} IgM consists of two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each, as well as two heavy chains of approximately 70 kDa each that contain C-terminal extensions, known as tailpieces, which allow for IgM oligomerization.{53830,53831} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} Five IgM proteins oligomerize via disulfide bonds in the presence of a 15-kDa joining chain, a process that is required for transcytosis of IgM from plasma cells to mucosal epithelial cells via the polyimmunoglobulin receptor (pIgR).{53830} Monomeric and oligomeric IgM are both ligands for the IgM and IgA-binding high affinity Igα and the Igμ Fc receptor (Fcα/μ-R) on dendritic cells, which mediates cellular uptake of IgM-conjugated antigens, and the IgM-binding Fcμ-R on B and T cells, which is important for B cell maturation among other functions.{53830,53832,53833,53834} IgM is produced primarily in the plasma by naïve B cells and expressed in its monomeric low-affinity form on the cell surface.{28520} Activated B cells secrete pentameric high-affinity IgM, which opsonizes antigens to target them for removal by phagocytes and to activate complement via the classical pathway.{28520,53835} IgM antibodies are produced early in infection and have been used to determine exposure to a specific pathogen.{28520} IgM levels are elevated in hyper-IgM syndromes, which are characterized by dysfunctions in Ig class switching recombination.{53836} Cayman’s IgM (mouse) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM109) can be used for ELISA, flow cytometry (FC), and immunoprecipitation (IP) applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32101 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
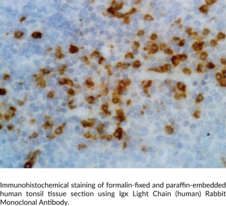
Igκ light chain is one type of light chain found in immunoglobulins, which are part of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} Immunoglobulins are produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells as antibodies.{55225} They are composed of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} Mammalian immunoglobulins contain either Igκ or Igλ light chains, each of which are composed of a constant and variable domain.{28687} The ratio of Igκ to Igλ light chain-containing antibodies varies between species, with ratios of 20:1, 2:1, and 1:20 in mice, humans, and cattle, respectively. Igκ and Igλ free light chains (FLCs) are produced during immunoglobulin synthesis, and accumulation of these FLCs, primarily Igκ, is associated with various disorders, including light-chain deposition disease, multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic nephropathy, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).{55225,55232,53885} Cayman’s Igκ Light Chain (human) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, flow cytometry (FC), immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications. The antibody recognizes the κ light chain from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32108 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Igκ light chain is one type of light chain found in immunoglobulins, which are part of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} Immunoglobulins are produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells as antibodies.{55225} They are composed of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} Mammalian immunoglobulins contain either Igκ or Igλ light chains, each of which are composed of a constant and variable domain.{28687} The ratio of Igκ to Igλ light chain-containing antibodies varies between species, with ratios of 20:1, 2:1, and 1:20 in mice, humans, and cattle, respectively. Igκ and Igλ free light chains (FLCs) are produced during immunoglobulin synthesis, and accumulation of these FLCs, primarily Igκ, is associated with various disorders, including light-chain deposition disease, multiple myeloma, rheumatoid arthritis, diabetic nephropathy, and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE).{55225,55232,53885} Cayman’s Igκ Light Chain (mouse) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes non-reduced and reduced Igκ light chain from mouse samples at approximately 159 and 25 kDa, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32001 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
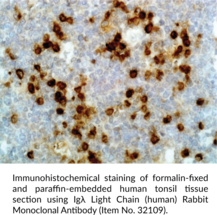
Igλ light chain is one type of light chain found in immunoglobulins, which are part of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} Immunoglobulins are produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells as antibodies.{55225} They are composed of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} Mammalian immunoglobulins contain either Igκ or Igλ light chains, each of which are composed of a constant and variable domain.{55225,28687} The ratio of Igκ to Igλ light chain-containing antibodies varies between species, with ratios of 20:1, 2:1, and 1:20 in mice, humans, and cattle, respectively. In systemic amyloidosis, a clonal population of plasma cells produces light chains that form amyloid fibrils, and the type of free light chains (FLCs) produced is predominantly Igλ with an Igκ to Igλ ratio of 1:3 or, in amyloidosis patients with nephrotic-range proteinuria, 1:5.{52650} Cayman’s Igλ Light Chain (human) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA, flow cytometry (FC), immunocytochemistry (ICC), and immunohistochemistry (IHC) applications. The antibody recognizes the λ light chain from human samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32109 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Igλ light chain is one type of light chain found in immunoglobulins, which are part of the immunoglobulin superfamily of glycoproteins that plays a central role in the adaptive immune response.{28520} Immunoglobulins are produced by B cells and later secreted by plasma cells as antibodies.{55225} They are composed of two heavy chains of approximately 50 kDa each and two light chains of approximately 25 kDa each.{28520} The heavy chains are linked together by disulfide bonds to form an Fc region and also combine with the light chains to form the Fab region, which mediate receptor and antigen binding, respectively.{55171} Mammalian immunoglobulins contain either Igκ or Igλ light chains each of which are composed of a constant and variable domain.{55225,28687} The ratio of Igκ to Igλ light chain containing antibodies varies between species, with ratios of 20:1, 2:1, and 1:20 in mice, humans, and cattle, respectively. In systemic amyloidosis, a clonal population of plasma cells produces light chains that form amyloid fibrils, and the type of free light chains (FLCs) produced is predominantly Igλ with an Igκ to Igλ ratio of 1:3 or, in amyloidosis patients with nephrotic-range proteinuria, 1:5.{52650} Cayman’s Igλ Light Chain (mouse) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody can be used for ELISA and Western blot (WB; non-reducing conditions) applications. The antibody recognizes the Igλ light chain from mouse samples.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32000 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Nuclear Factor-κB (NF-κB) is sequestered in the cytoplasm by the IκB family of inhibitory proteins that mask the nuclear localization signal of NF-κB, thereby preventing translocation of NF-κB to the nucleus.{18540} External stimuli such as tumor necrosis factor or other cytokines result in phosphorylation and degradation of IκB, releasing NF-κB dimers. NF-κB dimers subsequently translocate to the nucleus and activate target genes. Synthesis of IκBα is autoregulated.{18541} IκB proteins are phosphorylated by IκB kinase complex consisting of at least three proteins, IKK1/α, IKK2/β, and IKK3/γ.{18542,18543,18544,18658,18545} IKKγ preferentially interacts with IKKβ and is required for activation of IKK complex. IKKγ is also known as NF-κB essential modulator (NEMO).{18545} The human T cell leukemia virus type I Tax oncoprotein that activates NF-κB binds neither to IKKα nor IKKβ, but complexes directly with IKKγ.{18659} This suggests that IKKγ may be a key molecule acting as an adapter for oncoprotein specific signaling to IKKα and IKKβ.{18659}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13931 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Also known as cytokine synthesis inhibitory factor (CSIF), interleukin-10 (IL-10) is a polypeptide of 157 amino acids glycosylated. The mature IL-10 is an homodimer linked by two intrachain disulfide bridges (each sub-unit is 157 aa). IL-10 is produced by innate and non-innate cells, it is a cytokine of the innate and adaptive immunity. The mammalian cells known to secrete IL-10 are NK cells, cytotoxic T cells, memory Th1 and Th2 cells, macrophages monocytes, B cells, dendritic cells, hepatic stellates, keratinocytes, and fetal erythroblasts. IL-10 is a cytokine with multiple pleiotropic effects in immunoregulation and inflammation. IL-10 is characterized like anti-inflammatory cytokine: It represses the expression of inflammatory cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), IL-6 and IL-1β, in macrophage. IL-10 is an immunoregulation cytokine and negative regulate Th1 responses by downmodulating antigen presenting capacity of APC. Due to its central function, a dysregulation of the production of the lL-10 is implicated in asthma or autoimmune diseases. IL-10 is currently studied in immuno-oncology. [Bertin Catalog No. A05414]
Brand:CaymanSKU:23620 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a protein of 212 amino acids. It’s a pleiotropic cytokine which has an impact on the regulation of immune and nonimmune events. It is produced by the monocytes and macrophages in response to other inflammatory cytokines like IL-11 and the tumor necrosis factor-β (TNF-β). IL-6 acts on immune and nonimmune cells: It helps to differentiate T cells from B cells but it is also vital for the development of blood cells (white cells, red cells or platelets). Due to these target cells, IL-6 is an activator of immune system and inflammation. It also controls the metabolism by action on adipocytes, the bone metabolism and the pain. A dysregulation in IL-6 production induces many disorders such as autoimmune diseases, inflammation, diabetes or cancer. [Bertin Catalog No. A05410]
Brand:CaymanSKU:23615 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011325 - 10 mlAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:400054 - 10 mlAvailable on backorder
Immunoassay Buffer C Concentrate (10X) has been formulated and tested to work with Cayman’s Assay Kits. Detailed instructions for its use are contained in the respective Cayman Assay Kit booklet.
Brand:CaymanSKU:401703 - 10 mlAvailable on backorder
Immunoassay Buffer D Concentrate (5X) has been tested and formulated to work exclusively with Cayman’s Benzodiazepine ELISA Kit (Item No. 501800). Please visit Benzodiazepine ELISA Kit (Item No. 501800) for the kit protocol, procedures, and product handling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:400108 - 10 mlAvailable on backorder
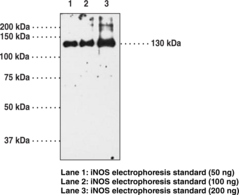
Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) catalyzes the biosynthesis of nitric oxide from L-arginine. Constitutively expressed NOS is found in brain (nNOS) and endothelial cells (eNOS). iNOS is a soluble enzyme found in a variety of tissues including macrophages, hepatocytes, vascular smooth muscle cells, and chondrocytes.{1243,4141} iNOS expression is increased by a variety of factors including LPS, IFN-γ, Il-1β, and TNF-α, whereas expression is deceased by dexamethasone.{1904,1970,2111,3440,4851} The enzyme has been cloned from several species including mouse, rat, and human with homology of at least 80% between these species.{4141} The calculated molecular weight of the protein from the deduced amino acid sequence is 130,000 – 131,000.{1243}
Brand:CaymanSKU:160862 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
This immunoassay is based on a sandwich technique. Wells of supplied plate are coated with a monoclonal antibody specific to insulin. Insulin is introduced in the wells where it is bound by the monoclonal antibody coated on the plate. Insulin is then detected by an insulin-specific monoclonal antibody tagged with acetylcholinesterase (AChE). The two antibodies thus form a sandwich by binding on different epitopes of insulin. The concentration of insulin is determined by measuring the enzymatic activity of immobilized tracer using Ellman’s reagent. AchE tracer acts on Ellman’s reagent to form a yellow compound that strongly absorbs at 405 nm or at 414 nm . Insulin in a polypeptide composed of 51 amino acids divided into two chains (A and B) linked by disulfide bonds. Both chains are organized as alpha helix. Insulin is produced by the beta cells of the pancreatic islets in form of a precursor (prepro-insulin) and is modified to obtain the pro-insulin (peptide signal elimination) and finally insulin (peptide C elimination). The main function of the insulin is the regulation of the glucose concentration in the organism. The dysregulation of the production of insulin induced many disorders including diabetes. [Bertin Bioreagent Product Number [A05322]]
Brand:CaymanSKU:26619 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Insulin is a polypeptide hormone with molecular weight of 6,000 Daltons, composed of two peptides chains, A and B, jointed by two cross-linked disulphide bonds and synthesised by the beta cells of the islets of Langherans of the pancreas. Insulin influences most of the metabolic functions of the body. Its best known action is to lower the blood glucose concentration by increasing the rate at which glucose is converted to glycogen in the liver and muscles and to fat in adipose tissue, by stimulating the rate of glucose metabolism and by depressing gluconeogenesis. Focus on hemolysis: Hemolysis interferes with the assay by degrading insulin. To prevent hemolysis consequences, an inhibitor cocktail (Item No. 18429) and a procedure are available. [Bertin Catalog No. A05105.480 wells]
Brand:CaymanSKU:589501 - 480 wellsAvailable on backorder
Insulin is a polypeptide hormone with molecular weight of 6,000 Daltons, composed of two peptides chains, A and B, jointed by two cross-linked disulphide bonds and synthesised by the beta cells of the islets of Langherans of the pancreas. Insulin influences most of the metabolic functions of the body. Its best known action is to lower the blood glucose concentration by increasing the rate at which glucose is converted to glycogen in the liver and muscles and to fat in adipose tissue, by stimulating the rate of glucose metabolism and by depressing gluconeogenesis. Focus on hemolysis: Hemolysis interferes with the assay by degrading insulin. To prevent hemolysis consequences, an inhibitor cocktail (Item No. 18429) and a procedure are available. [Bertin Catalog No. A05105.480 wells]
Brand:CaymanSKU:589501 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) is a name for a family of proteins which include IL-α, IL-1β, ILra (interleukin receptor antagonist), and IL-18. IL-1α is synthesized as a 33 kDa (271 amino acid) pro-cytokine that is enzymatically cleaved by calpain into the active 159 amino acid, 17 kDa peptide.{10662,10661,10667} IL-1α is produced by many cells types including macrophages, monocytes, astrocytes, keratinocytes, adipocytes, T-cells, and eosinophils.{866} Although IL-1α and IL-1β exhibit only 26% amino acid identity,{10662} they bind to the same cell-surface receptors, IL-1 RI and IL-1 RII, present on a variety of cell types involved in immune or inflammatory responses.{10660,10775,10668} Normal production of IL-1 is critical for mediating host responses to infection and injury.{7221,11054} Disease states in which IL-1 actively participates include inflammatory diseases such as arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, and shock, as well as atherosclerosis, allergy, and some types of cancer.{7221,11054} Cayman’s IL-1α (human) ELISA Kit is an immunometric (i.e., sandwich) ELISA that permits IL-1α measurements within the range of 3.9-250 pg/ml, typically with a limit of detection of 3.9 pg/ml.
Brand:CaymanSKU:583301 - 480 wellsAvailable on backorder