Chemicals
Showing 9751–9900 of 41137 results
-
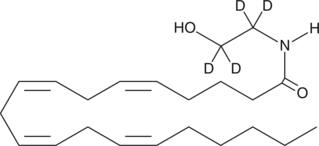
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d4 (AEA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors and mimics the pharmacologic effects of Δ9-THC.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011178 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d4 (AEA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors and mimics the pharmacologic effects of Δ9-THC.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011178 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d4 (AEA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors and mimics the pharmacologic effects of Δ9-THC.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011178 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d4 (AEA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors and mimics the pharmacologic effects of Δ9-THC.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011178 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
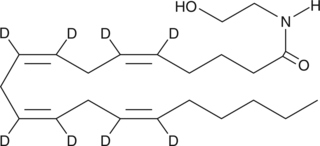
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d8 (AEA-8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390050 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d8 (AEA-8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390050 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d8 (AEA-8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390050 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide-d8 (AEA-8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of AEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. AEA is the ethanolamine amide of arachidonic acid, first isolated from porcine brain.{1134} It is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors.{2713} AEA inhibits the specific binding of [3H]-HU-243 to synaptosomal membranes with a Ki value of 52 nM, compared to 46 nM for Δ9-THC.{1134}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390050 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
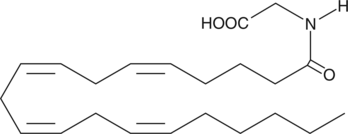
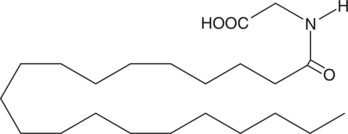
Arachidonoyl glycine (N-arachidonyl glycine; NAGly) has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; anandamide),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl CoA. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signaling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90051 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine (N-arachidonyl glycine; NAGly) has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; anandamide),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl CoA. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signaling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90051 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine (N-arachidonyl glycine; NAGly) has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; anandamide),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl CoA. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signaling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90051 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine (N-arachidonyl glycine; NAGly) has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; anandamide),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl CoA. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signaling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90051 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
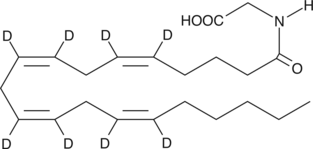
Arachidonoyl glycine-d8 (NAGly-d8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of NAGly by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. NAGly has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl coenzyme A. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signalling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007531 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine-d8 (NAGly-d8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of NAGly by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. NAGly has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl coenzyme A. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signalling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007531 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine-d8 (NAGly-d8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of NAGly by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. NAGly has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl coenzyme A. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signalling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007531 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl glycine-d8 (NAGly-d8) contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of NAGly by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. NAGly has been isolated from cell cultures treated with arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA),{9578} from extracts of mammalian brain,{9579,9589} and has also been synthesized as an analog of AEA for structure/activity testing.{9580} NAGly may be produced endogenously via oxidation of AEA, or by transacylation of arachidonoyl coenzyme A. NAGly is reported to have analgesic activities in whole animal experiments.{9578,9579,9589} Since it seems to be a very poor ligand for the CB1 receptor,{9580} these effects are probably mediated via other signalling pathways.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007531 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
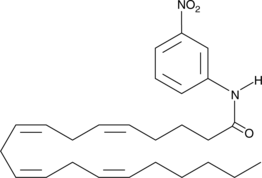
Arachidonoyl m-Nitroaniline (AmNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (arachidonyl ethanolamide; AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate (see also Decanoyl m-Nitroaniline; Item No. 90349). Exposure of AmNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye m-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90059 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl m-Nitroaniline (AmNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (arachidonyl ethanolamide; AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate (see also Decanoyl m-Nitroaniline; Item No. 90349). Exposure of AmNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye m-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90059 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl m-Nitroaniline (AmNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (arachidonyl ethanolamide; AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate (see also Decanoyl m-Nitroaniline; Item No. 90349). Exposure of AmNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye m-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90059 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl m-Nitroaniline (AmNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (arachidonyl ethanolamide; AEA). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate (see also Decanoyl m-Nitroaniline; Item No. 90349). Exposure of AmNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye m-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 410 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96 well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90059 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
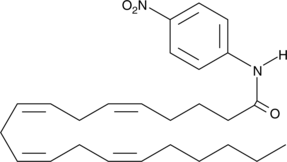
Arachidonoyl p-nitroaniline (ApNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (AEA; Item No. 90050). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate. (See also Decanoyl p-Nitroaniline – Catalog No. 90349). Exposure of ApNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye p-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 382 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96-well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10168 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl p-nitroaniline (ApNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (AEA; Item No. 90050). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate. (See also Decanoyl p-Nitroaniline – Catalog No. 90349). Exposure of ApNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye p-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 382 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96-well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10168 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl p-nitroaniline (ApNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (AEA; Item No. 90050). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate. (See also Decanoyl p-Nitroaniline – Catalog No. 90349). Exposure of ApNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye p-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 382 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96-well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10168 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl p-nitroaniline (ApNA) is one of several nitroaniline fatty acid amides which can be used to measure fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) activity.{8928} FAAH is a relatively unselective enzyme in that it accepts a variety of amide head groups other than the ethanolamine of its nominal endogenous substrate anandamide (AEA; Item No. 90050). It also will hydrolyze fatty acid amides with fewer carbons and fewer double bonds than arachidonate. (See also Decanoyl p-Nitroaniline – Catalog No. 90349). Exposure of ApNA to FAAH activity results in the release of the yellow colorimetric dye p-nitroaniline (ε = 13,500 at 382 nm). This offers the potential for fast and convenient measurements of FAAH activity using a 96-well plate spectrophotometer.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10168 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
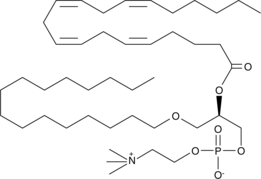
Arachidonoyl PAF C-16 is the product of acylation of lyso-PAF C-16 by a CoA-independent transacylase.{245,2101} It is the most common precursor for formation of PAF C-16 by the remodeling pathway.{939}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60904 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl PAF C-16 is the product of acylation of lyso-PAF C-16 by a CoA-independent transacylase.{245,2101} It is the most common precursor for formation of PAF C-16 by the remodeling pathway.{939}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60904 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl PAF C-16 is the product of acylation of lyso-PAF C-16 by a CoA-independent transacylase.{245,2101} It is the most common precursor for formation of PAF C-16 by the remodeling pathway.{939}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60904 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl PAF C-16 is the product of acylation of lyso-PAF C-16 by a CoA-independent transacylase.{245,2101} It is the most common precursor for formation of PAF C-16 by the remodeling pathway.{939}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60904 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
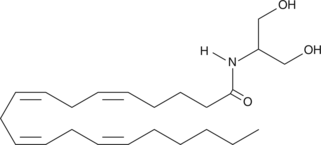
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) has been isolated from porcine brain, and has been characterized as the natural endocannabinoid ligand for the CB1 receptor.{4614,5306} Replacement of the sn-2 oxygen in the glycerol moiety of 2-AG with a nitrogen atom gives arachidonoyl serinol.{3301} Arachidonoyl serinol is much more stable than 2-AG. However, it is at least a log less potent as a CB1 receptor agonist than 2-AG.{5306}
Brand:CaymanSKU:62170 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) has been isolated from porcine brain, and has been characterized as the natural endocannabinoid ligand for the CB1 receptor.{4614,5306} Replacement of the sn-2 oxygen in the glycerol moiety of 2-AG with a nitrogen atom gives arachidonoyl serinol.{3301} Arachidonoyl serinol is much more stable than 2-AG. However, it is at least a log less potent as a CB1 receptor agonist than 2-AG.{5306}
Brand:CaymanSKU:62170 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) has been isolated from porcine brain, and has been characterized as the natural endocannabinoid ligand for the CB1 receptor.{4614,5306} Replacement of the sn-2 oxygen in the glycerol moiety of 2-AG with a nitrogen atom gives arachidonoyl serinol.{3301} Arachidonoyl serinol is much more stable than 2-AG. However, it is at least a log less potent as a CB1 receptor agonist than 2-AG.{5306}
Brand:CaymanSKU:62170 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) has been isolated from porcine brain, and has been characterized as the natural endocannabinoid ligand for the CB1 receptor.{4614,5306} Replacement of the sn-2 oxygen in the glycerol moiety of 2-AG with a nitrogen atom gives arachidonoyl serinol.{3301} Arachidonoyl serinol is much more stable than 2-AG. However, it is at least a log less potent as a CB1 receptor agonist than 2-AG.{5306}
Brand:CaymanSKU:62170 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl serotonin is an inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), the enzyme responsible for inactivation of anandamide and other endogenous cannabinoids. It inhibits the FAAH activity isolated from mouse neuroblastoma cells with an IC50 value of 12 µM. Both the Km and the Vmax of the enzyme are affected, indicating the Arachidonoyl serotonin is a very tight binding, competitive inhibitor of FAAH. Arachidonoyl serotonin does not inhibit cPLA2 and is essentially devoid of cannabimimetic activity.{6644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70665 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl serotonin is an inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), the enzyme responsible for inactivation of anandamide and other endogenous cannabinoids. It inhibits the FAAH activity isolated from mouse neuroblastoma cells with an IC50 value of 12 µM. Both the Km and the Vmax of the enzyme are affected, indicating the Arachidonoyl serotonin is a very tight binding, competitive inhibitor of FAAH. Arachidonoyl serotonin does not inhibit cPLA2 and is essentially devoid of cannabimimetic activity.{6644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70665 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl serotonin is an inhibitor of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), the enzyme responsible for inactivation of anandamide and other endogenous cannabinoids. It inhibits the FAAH activity isolated from mouse neuroblastoma cells with an IC50 value of 12 µM. Both the Km and the Vmax of the enzyme are affected, indicating the Arachidonoyl serotonin is a very tight binding, competitive inhibitor of FAAH. Arachidonoyl serotonin does not inhibit cPLA2 and is essentially devoid of cannabimimetic activity.{6644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70665 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
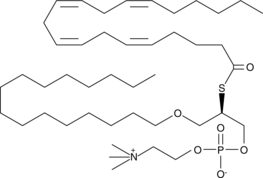
Arachidonoyl Thio-PC is a substrate for many phospholipase A2s (PLA2s) including sPLA2, cPLA2, and iPLA2. Cleavage of the sn-2 fatty acid by PLA2 results in generation of a free thiol which reacts with chromogenic reagents such as DTNB (Ellman’s reagent) and DTP to allow quantitation of PLA2 activity.{1356} Isozyme-specific cPLA2 activity can be measured by excluding or inhibiting sPLA2 and iPLA2 activities in the assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:62240 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl Thio-PC is a substrate for many phospholipase A2s (PLA2s) including sPLA2, cPLA2, and iPLA2. Cleavage of the sn-2 fatty acid by PLA2 results in generation of a free thiol which reacts with chromogenic reagents such as DTNB (Ellman’s reagent) and DTP to allow quantitation of PLA2 activity.{1356} Isozyme-specific cPLA2 activity can be measured by excluding or inhibiting sPLA2 and iPLA2 activities in the assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:62240 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl Thio-PC is a substrate for many phospholipase A2s (PLA2s) including sPLA2, cPLA2, and iPLA2. Cleavage of the sn-2 fatty acid by PLA2 results in generation of a free thiol which reacts with chromogenic reagents such as DTNB (Ellman’s reagent) and DTP to allow quantitation of PLA2 activity.{1356} Isozyme-specific cPLA2 activity can be measured by excluding or inhibiting sPLA2 and iPLA2 activities in the assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:62240 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous agonist of the central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor.{7182,7183} It is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system and is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in rat brain.{7183,6819} Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) hydrolyzes 2-AG to arachidonic acid and glycerol, thereby terminating its biological actions.{11364} Arachidonoyl-1-thio-glycerol is a thioester substrate analog of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol that can be utilized for the measurement of MAGL activity.{13593} Hydrolysis of the thioester bond by MAGL generates a free thiol that reacts rapidly with the chromogenic reagent DTNB (Ellman’s reagent) resulting a yellow product with an absorbance maximum at 412 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007904 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous agonist of the central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor.{7182,7183} It is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system and is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in rat brain.{7183,6819} Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) hydrolyzes 2-AG to arachidonic acid and glycerol, thereby terminating its biological actions.{11364} Arachidonoyl-1-thio-glycerol is a thioester substrate analog of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol that can be utilized for the measurement of MAGL activity.{13593} Hydrolysis of the thioester bond by MAGL generates a free thiol that reacts rapidly with the chromogenic reagent DTNB (Ellman’s reagent) resulting a yellow product with an absorbance maximum at 412 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007904 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous agonist of the central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor.{7182,7183} It is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system and is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in rat brain.{7183,6819} Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) hydrolyzes 2-AG to arachidonic acid and glycerol, thereby terminating its biological actions.{11364} Arachidonoyl-1-thio-glycerol is a thioester substrate analog of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol that can be utilized for the measurement of MAGL activity.{13593} Hydrolysis of the thioester bond by MAGL generates a free thiol that reacts rapidly with the chromogenic reagent DTNB (Ellman’s reagent) resulting a yellow product with an absorbance maximum at 412 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007904 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous agonist of the central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor.{7182,7183} It is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system and is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in rat brain.{7183,6819} Monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) hydrolyzes 2-AG to arachidonic acid and glycerol, thereby terminating its biological actions.{11364} Arachidonoyl-1-thio-glycerol is a thioester substrate analog of 2-arachidonoyl glycerol that can be utilized for the measurement of MAGL activity.{13593} Hydrolysis of the thioester bond by MAGL generates a free thiol that reacts rapidly with the chromogenic reagent DTNB (Ellman’s reagent) resulting a yellow product with an absorbance maximum at 412 nm.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007904 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
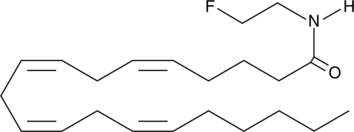
Arachidonoyl-2′-fluoroethylamide (2-fluoro AEA) is an analog of anandamide in which the alcohol of the ethanolamide group has been removed and replaced with a fluorine atom. This substitution adds considerably increased binding affinity for the CB1 receptor (Kis = 26.7 and 908 nM for CB1 and CB2, respectively). It also contributes additional selectivity, in that binding to CB2 is decreased relative to AEA.{7422} However, the in vivo activity of 2-fluoro AEA is enhanced much less than the binding affinity, because the analog remains a good substrate for FAAH and is rapidly hydrolyzed by this enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90054 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl-2′-fluoroethylamide (2-fluoro AEA) is an analog of anandamide in which the alcohol of the ethanolamide group has been removed and replaced with a fluorine atom. This substitution adds considerably increased binding affinity for the CB1 receptor (Kis = 26.7 and 908 nM for CB1 and CB2, respectively). It also contributes additional selectivity, in that binding to CB2 is decreased relative to AEA.{7422} However, the in vivo activity of 2-fluoro AEA is enhanced much less than the binding affinity, because the analog remains a good substrate for FAAH and is rapidly hydrolyzed by this enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90054 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl-2′-fluoroethylamide (2-fluoro AEA) is an analog of anandamide in which the alcohol of the ethanolamide group has been removed and replaced with a fluorine atom. This substitution adds considerably increased binding affinity for the CB1 receptor (Kis = 26.7 and 908 nM for CB1 and CB2, respectively). It also contributes additional selectivity, in that binding to CB2 is decreased relative to AEA.{7422} However, the in vivo activity of 2-fluoro AEA is enhanced much less than the binding affinity, because the analog remains a good substrate for FAAH and is rapidly hydrolyzed by this enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90054 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl-2′-fluoroethylamide (2-fluoro AEA) is an analog of anandamide in which the alcohol of the ethanolamide group has been removed and replaced with a fluorine atom. This substitution adds considerably increased binding affinity for the CB1 receptor (Kis = 26.7 and 908 nM for CB1 and CB2, respectively). It also contributes additional selectivity, in that binding to CB2 is decreased relative to AEA.{7422} However, the in vivo activity of 2-fluoro AEA is enhanced much less than the binding affinity, because the analog remains a good substrate for FAAH and is rapidly hydrolyzed by this enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90054 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
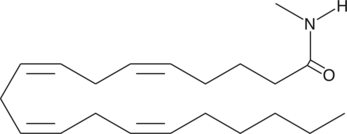
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase. Arachidonoyl-N-methyl amide is an analog of anandamide that binds to the human central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor with a Ki of 60 nM.{9580} It inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication 100% at a concentration of 50 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007294 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase. Arachidonoyl-N-methyl amide is an analog of anandamide that binds to the human central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor with a Ki of 60 nM.{9580} It inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication 100% at a concentration of 50 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007294 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase. Arachidonoyl-N-methyl amide is an analog of anandamide that binds to the human central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor with a Ki of 60 nM.{9580} It inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication 100% at a concentration of 50 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007294 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase. Arachidonoyl-N-methyl amide is an analog of anandamide that binds to the human central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor with a Ki of 60 nM.{9580} It inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication 100% at a concentration of 50 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007294 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
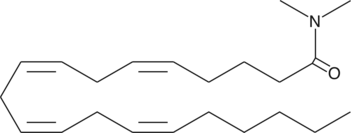
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase. Arachidonoyl-N,N-dimethyl amide is an analog of anandamide that exhibits weak or no binding to the human central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor (Ki >1 µM).{9580} It inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication 100% at a concentration of 50 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007293 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase. Arachidonoyl-N,N-dimethyl amide is an analog of anandamide that exhibits weak or no binding to the human central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor (Ki >1 µM).{9580} It inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication 100% at a concentration of 50 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007293 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase. Arachidonoyl-N,N-dimethyl amide is an analog of anandamide that exhibits weak or no binding to the human central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor (Ki >1 µM).{9580} It inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication 100% at a concentration of 50 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007293 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Anandamide (AEA) is an endogenous cannabinoid that binds to both central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors. The biological actions of AEA are terminated by cellular uptake and hydrolysis of the amide bond by the enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase. Arachidonoyl-N,N-dimethyl amide is an analog of anandamide that exhibits weak or no binding to the human central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor (Ki >1 µM).{9580} It inhibits rat glial gap junction cell-cell communication 100% at a concentration of 50 µM.{8122}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007293 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
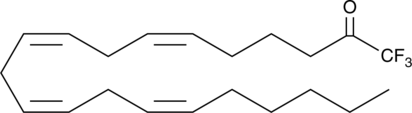
ATK is an analog of arachidonic acid in which the carboxyl group is replaced by a trifluoromethyl ketone group.{929} It inhibits the activity of the 85 kDa cPLA2 and the 80 kDa macrophage iPLA2 without altering the activity of the 14 kDa sPLA2s.{929,1291,2992} ATK is useful for differentiating the effects of cPLA2 and iPLA2 from sPLA2.{1530,1531}
Brand:CaymanSKU:62120 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
ATK is an analog of arachidonic acid in which the carboxyl group is replaced by a trifluoromethyl ketone group.{929} It inhibits the activity of the 85 kDa cPLA2 and the 80 kDa macrophage iPLA2 without altering the activity of the 14 kDa sPLA2s.{929,1291,2992} ATK is useful for differentiating the effects of cPLA2 and iPLA2 from sPLA2.{1530,1531}
Brand:CaymanSKU:62120 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
ATK is an analog of arachidonic acid in which the carboxyl group is replaced by a trifluoromethyl ketone group.{929} It inhibits the activity of the 85 kDa cPLA2 and the 80 kDa macrophage iPLA2 without altering the activity of the 14 kDa sPLA2s.{929,1291,2992} ATK is useful for differentiating the effects of cPLA2 and iPLA2 from sPLA2.{1530,1531}
Brand:CaymanSKU:62120 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
ATK is an analog of arachidonic acid in which the carboxyl group is replaced by a trifluoromethyl ketone group.{929} It inhibits the activity of the 85 kDa cPLA2 and the 80 kDa macrophage iPLA2 without altering the activity of the 14 kDa sPLA2s.{929,1291,2992} ATK is useful for differentiating the effects of cPLA2 and iPLA2 from sPLA2.{1530,1531}
Brand:CaymanSKU:62120 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
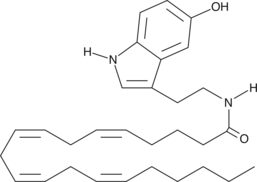
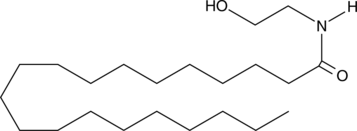
The endocannabinoids present a rich system of central cannabinoid (CB1), peripheral cannabinoid (CB2), and non-CB receptor-mediated pharmacology that has stimulated research in many fields including memory, weight loss and appetite, neurodegeneration, tumor surveillance, analgesia, and inflammation.{7991,7912} Arachidoyl ethanolamide is one of the saturated fatty acyl ethanolamides devoid of classical (CB1/CB2) activity. Arachidoyl ethanolamide does not bind to the murine CB1 receptor{9580} and does not compete with anandamide as a substrate for the endocannabinoid hydrolytic enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase.{9532} Non-CB receptor-mediated pharmacology of the saturated ethanolamides is still being elucidated.{10785}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005765 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
The endocannabinoids present a rich system of central cannabinoid (CB1), peripheral cannabinoid (CB2), and non-CB receptor-mediated pharmacology that has stimulated research in many fields including memory, weight loss and appetite, neurodegeneration, tumor surveillance, analgesia, and inflammation.{7991,7912} Arachidoyl ethanolamide is one of the saturated fatty acyl ethanolamides devoid of classical (CB1/CB2) activity. Arachidoyl ethanolamide does not bind to the murine CB1 receptor{9580} and does not compete with anandamide as a substrate for the endocannabinoid hydrolytic enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase.{9532} Non-CB receptor-mediated pharmacology of the saturated ethanolamides is still being elucidated.{10785}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005765 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
The endocannabinoids present a rich system of central cannabinoid (CB1), peripheral cannabinoid (CB2), and non-CB receptor-mediated pharmacology that has stimulated research in many fields including memory, weight loss and appetite, neurodegeneration, tumor surveillance, analgesia, and inflammation.{7991,7912} Arachidoyl ethanolamide is one of the saturated fatty acyl ethanolamides devoid of classical (CB1/CB2) activity. Arachidoyl ethanolamide does not bind to the murine CB1 receptor{9580} and does not compete with anandamide as a substrate for the endocannabinoid hydrolytic enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase.{9532} Non-CB receptor-mediated pharmacology of the saturated ethanolamides is still being elucidated.{10785}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005765 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
The endocannabinoids present a rich system of central cannabinoid (CB1), peripheral cannabinoid (CB2), and non-CB receptor-mediated pharmacology that has stimulated research in many fields including memory, weight loss and appetite, neurodegeneration, tumor surveillance, analgesia, and inflammation.{7991,7912} Arachidoyl ethanolamide is one of the saturated fatty acyl ethanolamides devoid of classical (CB1/CB2) activity. Arachidoyl ethanolamide does not bind to the murine CB1 receptor{9580} and does not compete with anandamide as a substrate for the endocannabinoid hydrolytic enzyme fatty acid amide hydrolase.{9532} Non-CB receptor-mediated pharmacology of the saturated ethanolamides is still being elucidated.{10785}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005765 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000325 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000325 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000325 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000325 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Xestospongins and araguspongins are marine natural products first isolated from Pacific basin sponges, and noted to have vasodilatory properties.{9844} Inositol phosphates (IP) are important signal transduction messengers acting via IP3 receptors to promote the mobilization of Ca2+ from intracellular stores.{8344} Araguspongin B antagonizes the calcium-releasing action of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate at the receptor level in cerebral microsomes, with an IC50 of 0.6 µM.{9845} It is nearly as potent as xestospongin C as an antagonist of the IP3 receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006797 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Xestospongins and araguspongins are marine natural products first isolated from Pacific basin sponges, and noted to have vasodilatory properties.{9844} Inositol phosphates (IP) are important signal transduction messengers acting via IP3 receptors to promote the mobilization of Ca2+ from intracellular stores.{8344} Araguspongin B antagonizes the calcium-releasing action of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate at the receptor level in cerebral microsomes, with an IC50 of 0.6 µM.{9845} It is nearly as potent as xestospongin C as an antagonist of the IP3 receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006797 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
Araloside A is a triterpenoid saponin that has been found in A. taibaiensis and has anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective effects.{46919,46918} It increases apoptosis of and decreases production of IL-1β and IL-6 in human MH7A rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes when used at concentrations ranging from 4 to 16 µM.{46919} Araloside A (50 and 100 mg/kg) reduces gastric acid secretion and lesion size in rat models of hydrochloric acid and ethanol-, aspirin-, water immersion stress-, or pyloric ligation-induced ulcer formation.{46918}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30219 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Araloside A is a triterpenoid saponin that has been found in A. taibaiensis and has anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective effects.{46919,46918} It increases apoptosis of and decreases production of IL-1β and IL-6 in human MH7A rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes when used at concentrations ranging from 4 to 16 µM.{46919} Araloside A (50 and 100 mg/kg) reduces gastric acid secretion and lesion size in rat models of hydrochloric acid and ethanol-, aspirin-, water immersion stress-, or pyloric ligation-induced ulcer formation.{46918}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30219 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Araloside A is a triterpenoid saponin that has been found in A. taibaiensis and has anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective effects.{46919,46918} It increases apoptosis of and decreases production of IL-1β and IL-6 in human MH7A rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes when used at concentrations ranging from 4 to 16 µM.{46919} Araloside A (50 and 100 mg/kg) reduces gastric acid secretion and lesion size in rat models of hydrochloric acid and ethanol-, aspirin-, water immersion stress-, or pyloric ligation-induced ulcer formation.{46918}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30219 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Araloside A is a triterpenoid saponin that has been found in A. taibaiensis and has anti-inflammatory and gastroprotective effects.{46919,46918} It increases apoptosis of and decreases production of IL-1β and IL-6 in human MH7A rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes when used at concentrations ranging from 4 to 16 µM.{46919} Araloside A (50 and 100 mg/kg) reduces gastric acid secretion and lesion size in rat models of hydrochloric acid and ethanol-, aspirin-, water immersion stress-, or pyloric ligation-induced ulcer formation.{46918}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30219 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
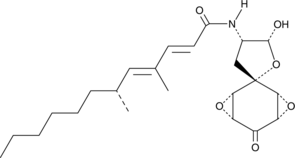
Aramchol, also known as arachidyl amido cholanoic acid, is a conjugate of arachidic acid (Item No. 9000339) and cholic acid (Item No. 20250).{38185} It reduces ex vivo cholesterol crystallization in native human bile and dissolves pre-formed cholesterol crystals in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo, aramchol completely prevents the formation of cholesterol crystals and gallstones in mice fed a lithogenic, high-fat diet. It also prevents lithogenic, high-fat diet-induced fatty liver in mice, rats, and hamsters.{38186} Formulations containing aramchol have been investigated clinically for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).{38187}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22478 -Out of stock
Aramchol, also known as arachidyl amido cholanoic acid, is a conjugate of arachidic acid (Item No. 9000339) and cholic acid (Item No. 20250).{38185} It reduces ex vivo cholesterol crystallization in native human bile and dissolves pre-formed cholesterol crystals in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo, aramchol completely prevents the formation of cholesterol crystals and gallstones in mice fed a lithogenic, high-fat diet. It also prevents lithogenic, high-fat diet-induced fatty liver in mice, rats, and hamsters.{38186} Formulations containing aramchol have been investigated clinically for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).{38187}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22478 -Out of stock
Aramchol, also known as arachidyl amido cholanoic acid, is a conjugate of arachidic acid (Item No. 9000339) and cholic acid (Item No. 20250).{38185} It reduces ex vivo cholesterol crystallization in native human bile and dissolves pre-formed cholesterol crystals in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo, aramchol completely prevents the formation of cholesterol crystals and gallstones in mice fed a lithogenic, high-fat diet. It also prevents lithogenic, high-fat diet-induced fatty liver in mice, rats, and hamsters.{38186} Formulations containing aramchol have been investigated clinically for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).{38187}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22478 -Out of stock
Aramchol, also known as arachidyl amido cholanoic acid, is a conjugate of arachidic acid (Item No. 9000339) and cholic acid (Item No. 20250).{38185} It reduces ex vivo cholesterol crystallization in native human bile and dissolves pre-formed cholesterol crystals in a dose-dependent manner. In vivo, aramchol completely prevents the formation of cholesterol crystals and gallstones in mice fed a lithogenic, high-fat diet. It also prevents lithogenic, high-fat diet-induced fatty liver in mice, rats, and hamsters.{38186} Formulations containing aramchol have been investigated clinically for the treatment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).{38187}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22478 -Out of stock
Aranciamycin is a fungal metabolite that has been found in Streptomyces and has diverse biological activities.{52436,52437} It inhibits C. histolyticum collagenase but not elastase or trypsin in cell-free assays (IC50s = 0.37, >10, and >10 µM, respectively).{52436} Aranciamycin is active against M. bovis and B. subtilis (MICs = 30 and 15 µM, respectively).{52437} It is cytotoxic to HepG2 cells (IC50 = 18 µM).
Brand:CaymanSKU:29575 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Aranorosin is a fungal metabolite originally isolated from P. roseus.{48197} It has antimicrobial activity against B. subtilis, A. niger, and C. albicans when used at a concentration of 1 mg/ml. Aranorosin also reduces viability in apoptosis-resistant HeLa/Bcl-2 cells.{48198}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27478 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Aranorosin is a fungal metabolite originally isolated from P. roseus.{48197} It has antimicrobial activity against B. subtilis, A. niger, and C. albicans when used at a concentration of 1 mg/ml. Aranorosin also reduces viability in apoptosis-resistant HeLa/Bcl-2 cells.{48198}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27478 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Aranorosin is a fungal metabolite originally isolated from P. roseus.{48197} It has antimicrobial activity against B. subtilis, A. niger, and C. albicans when used at a concentration of 1 mg/ml. Aranorosin also reduces viability in apoptosis-resistant HeLa/Bcl-2 cells.{48198}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27478 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
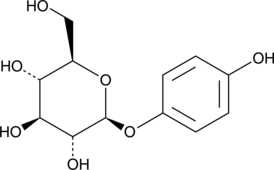
Arbutin is a glycosylated hydroquinone that has been found in Arctostaphylos plants and has diverse biological activities, including tyrosinase inhibitory, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties.{42646,42647} It inhibits human tyrosinase activity in crude tyrosinase solution isolated from human melanocytes (IC50s = 5.7 and 18.9 mM using L-tyrosine and L-DOPA as substrates, respectively) as well as in intact melanocytes (IC50 = 0.5 mM).{42648} Arbutin (50 μM) inhibits hemolysis induced by the free radical generator AAPH (Item No. 82235) in sheep erythrocytes and inhibits AAPH-induced decreases in cell viability in cultured human skin fibroblasts when used at concentrations greater than 125 μM.{42647} In an LPS-induced rat model of acute lung injury, arbutin (50 mg/kg) prevents increases in IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels in lung tissue and serum.{42649} Formulations containing arbutin have been used in the treatment of hyperpigmentation disorders.{42646,42648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26407 - 10 gAvailable on backorder