Chemicals
Showing 7501–7650 of 41137 results
-
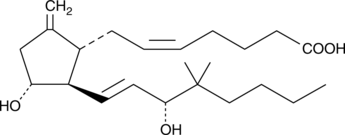
9-deoxy-9-methylene-16,16-dimethyl Prostaglandin E2 (Meteneprost) is a potent analog of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) with an extended half-life in vivo. In combination with various other prostaglandin derivatives, it results in the termination of first trimester pregnancy in monkeys. A single intramuscular injection containing 0.5 mg of meteneprost and 7.5 mg of 17-phenyl trinor PGF1α is very effective in terminating early pregnancy.{4692} This prostaglandin mixture is ineffective on monkeys in their third trimester of pregnancy.{4692} Meteneprost, when compared to PGE2 and PGF1α, in monkey and rat, does not result in unwanted side effects such as fever or gastrointestinal problems.{4692,464}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-9-deoxy-9-methylene-16,16-dimethyl Prostaglandin E2 (Meteneprost) is a potent analog of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) with an extended half-life in vivo. In combination with various other prostaglandin derivatives, it results in the termination of first trimester pregnancy in monkeys. A single intramuscular injection containing 0.5 mg of meteneprost and 7.5 mg of 17-phenyl trinor PGF1α is very effective in terminating early pregnancy.{4692} This prostaglandin mixture is ineffective on monkeys in their third trimester of pregnancy.{4692} Meteneprost, when compared to PGE2 and PGF1α, in monkey and rat, does not result in unwanted side effects such as fever or gastrointestinal problems.{4692,464}
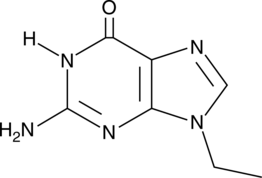
Brand:CaymanSKU:-9-Ethylguanine is a model nucleobase that is used to study DNA interactions with organometallic complexes, especially those designed to target tumors.{30452,30451,30450,30453}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
9-Ethylguanine is a model nucleobase that is used to study DNA interactions with organometallic complexes, especially those designed to target tumors.{30452,30451,30450,30453}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
9-Ethylguanine is a model nucleobase that is used to study DNA interactions with organometallic complexes, especially those designed to target tumors.{30452,30451,30450,30453}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
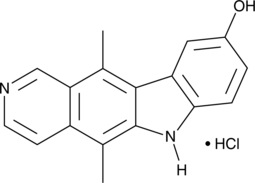
9-Hydroxyellipticine is a derivative of ellipticine (Item No. 18742) with diverse biological activities.{45370,45371,45372} It inhibits aroclor-induced activation of aniline hydroxylase, aminopyrine N-demethylase, and 7-ethoxycourmarin O-deethylase in rat liver microsomes (Kis = 3.5, 0.6, and 0.74 μM, respectively).{45370} 9-Hydroxyellipticine inhibits the growth of L1210 murine leukemia cells (IC50 = 3 nM) in vitro and increases survival in an L1210 mouse leukemia model.{45371,45372} It inhibits carrageenan-induced edema and UV-induced erythema in guinea pigs.{45373}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
9-Hydroxyellipticine is a derivative of ellipticine (Item No. 18742) with diverse biological activities.{45370,45371,45372} It inhibits aroclor-induced activation of aniline hydroxylase, aminopyrine N-demethylase, and 7-ethoxycourmarin O-deethylase in rat liver microsomes (Kis = 3.5, 0.6, and 0.74 μM, respectively).{45370} 9-Hydroxyellipticine inhibits the growth of L1210 murine leukemia cells (IC50 = 3 nM) in vitro and increases survival in an L1210 mouse leukemia model.{45371,45372} It inhibits carrageenan-induced edema and UV-induced erythema in guinea pigs.{45373}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
9-Hydroxyellipticine is a derivative of ellipticine (Item No. 18742) with diverse biological activities.{45370,45371,45372} It inhibits aroclor-induced activation of aniline hydroxylase, aminopyrine N-demethylase, and 7-ethoxycourmarin O-deethylase in rat liver microsomes (Kis = 3.5, 0.6, and 0.74 μM, respectively).{45370} 9-Hydroxyellipticine inhibits the growth of L1210 murine leukemia cells (IC50 = 3 nM) in vitro and increases survival in an L1210 mouse leukemia model.{45371,45372} It inhibits carrageenan-induced edema and UV-induced erythema in guinea pigs.{45373}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
9-Hydroxyellipticine is a derivative of ellipticine (Item No. 18742) with diverse biological activities.{45370,45371,45372} It inhibits aroclor-induced activation of aniline hydroxylase, aminopyrine N-demethylase, and 7-ethoxycourmarin O-deethylase in rat liver microsomes (Kis = 3.5, 0.6, and 0.74 μM, respectively).{45370} 9-Hydroxyellipticine inhibits the growth of L1210 murine leukemia cells (IC50 = 3 nM) in vitro and increases survival in an L1210 mouse leukemia model.{45371,45372} It inhibits carrageenan-induced edema and UV-induced erythema in guinea pigs.{45373}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
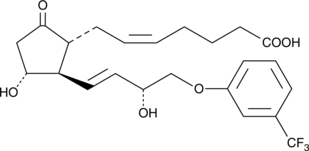
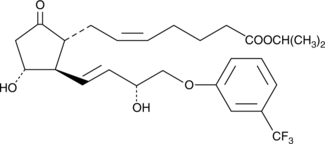
9-keto Fluprostenol is an analog of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) with structural modifications intended to give it a prolonged half-life and greater potency. Fluprostenol is a well-studied, potent analog of PGF2α and acts primarily through the FP receptor.{1182} Oxidation at C-9 of fluprostenol yields 9-keto fluprostenol. It is anticipated that this analog will have strong affinity for EP receptors and act as a PGE2 agonist. However, no studies on the pharmacology of this compound have been published to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
9-keto Fluprostenol is an analog of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) with structural modifications intended to give it a prolonged half-life and greater potency. Fluprostenol is a well-studied, potent analog of PGF2α and acts primarily through the FP receptor.{1182} Oxidation at C-9 of fluprostenol yields 9-keto fluprostenol. It is anticipated that this analog will have strong affinity for EP receptors and act as a PGE2 agonist. However, no studies on the pharmacology of this compound have been published to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
9-keto Fluprostenol is an analog of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) with structural modifications intended to give it a prolonged half-life and greater potency. Fluprostenol is a well-studied, potent analog of PGF2α and acts primarily through the FP receptor.{1182} Oxidation at C-9 of fluprostenol yields 9-keto fluprostenol. It is anticipated that this analog will have strong affinity for EP receptors and act as a PGE2 agonist. However, no studies on the pharmacology of this compound have been published to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Fluprostenol is a well-studied, potent analog of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) and acts primarily through the FP receptor.{1182} Oxidation at C-9 of fluprostenol yields 9-keto fluprostenol. Prostaglandin esters are known to be hydrolyzed in the eye to the corresponding free acids.{8148} However, the use of prostaglandin esters as prodrugs outside the eye is relatively unexplored. 9-keto Fluprostenol is an analog of PGE2 with structural modifications intended to give it a prolonged half-life and greater potency. 9-keto Fluprostenol isopropyl ester has the potential to act as an EP agonist in prodrug form. However, no studies on the pharmacology of this compound have been published to date. In addition 9-keto fluprostenol isopropyl ester is a potential metabolite of Travoprost, which is the Alcon trade name for fluprostenol isopropyl ester. In monkey cornea, this transformation was observed as a product of NADP+-dependent 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase when the closely related analog Latanoprost was used as a substrate.{9831} Certain F-series prostaglandins have been shown to be converted to the corresponding E-series compounds in rabbit liver{6609} and human platelet{11048} preparations.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Fluprostenol is a well-studied, potent analog of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) and acts primarily through the FP receptor.{1182} Oxidation at C-9 of fluprostenol yields 9-keto fluprostenol. Prostaglandin esters are known to be hydrolyzed in the eye to the corresponding free acids.{8148} However, the use of prostaglandin esters as prodrugs outside the eye is relatively unexplored. 9-keto Fluprostenol is an analog of PGE2 with structural modifications intended to give it a prolonged half-life and greater potency. 9-keto Fluprostenol isopropyl ester has the potential to act as an EP agonist in prodrug form. However, no studies on the pharmacology of this compound have been published to date. In addition 9-keto fluprostenol isopropyl ester is a potential metabolite of Travoprost, which is the Alcon trade name for fluprostenol isopropyl ester. In monkey cornea, this transformation was observed as a product of NADP+-dependent 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase when the closely related analog Latanoprost was used as a substrate.{9831} Certain F-series prostaglandins have been shown to be converted to the corresponding E-series compounds in rabbit liver{6609} and human platelet{11048} preparations.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Fluprostenol is a well-studied, potent analog of prostaglandin F2α (PGF2α) and acts primarily through the FP receptor.{1182} Oxidation at C-9 of fluprostenol yields 9-keto fluprostenol. Prostaglandin esters are known to be hydrolyzed in the eye to the corresponding free acids.{8148} However, the use of prostaglandin esters as prodrugs outside the eye is relatively unexplored. 9-keto Fluprostenol is an analog of PGE2 with structural modifications intended to give it a prolonged half-life and greater potency. 9-keto Fluprostenol isopropyl ester has the potential to act as an EP agonist in prodrug form. However, no studies on the pharmacology of this compound have been published to date. In addition 9-keto fluprostenol isopropyl ester is a potential metabolite of Travoprost, which is the Alcon trade name for fluprostenol isopropyl ester. In monkey cornea, this transformation was observed as a product of NADP+-dependent 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase when the closely related analog Latanoprost was used as a substrate.{9831} Certain F-series prostaglandins have been shown to be converted to the corresponding E-series compounds in rabbit liver{6609} and human platelet{11048} preparations.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
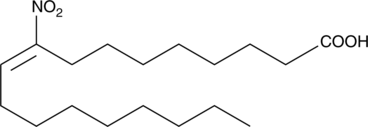
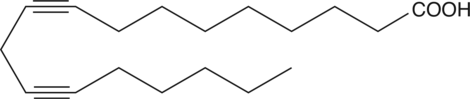
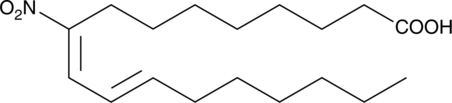
Nitrated unsaturated fatty acids, such as 10- and 12-nitrolinoleate (LNO2; Item No. 10037), cholesteryl nitrolinoleate, and nitrohydroxylinoleate, represent a new class of endogenous lipid-derived signalling molecules. LNO2 isomers serve as potent endogenous ligands for PPARγ and can also decompose or be metabolized to release nitric oxide.{11912,13284,13287,13288} 9-Nitrooleate is one of two regioisomers of nitrooleate, the other being 10-nitrooleate (Item No. 10008043) (OA-NO2; used for the mixture of isomers), which are formed by nitration of oleic acid in approximately equal proportions in vivo.{14255} Peroxynitrite, acidified nitrite, and myeloperoxidase in the presence of H2O2 and nitrite, all mediate the nitration of oleic acid. OA-NO2 is found in human plasma as the free acid and esterified in phospholipids at concentrations of 619 ± 52 nM and 302 ± 369 nM, respectively. OA-NO2 activates PPARγ approximately 7-fold at a concentration of 1 µM and effectively promotes differentiation 3T3-L1 preadipocytes to adipocytes at 3 µM.{14255}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008042 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Nitrated unsaturated fatty acids, such as 10- and 12-nitrolinoleate (LNO2; Item No. 10037), cholesteryl nitrolinoleate, and nitrohydroxylinoleate, represent a new class of endogenous lipid-derived signalling molecules. LNO2 isomers serve as potent endogenous ligands for PPARγ and can also decompose or be metabolized to release nitric oxide.{11912,13284,13287,13288} 9-Nitrooleate is one of two regioisomers of nitrooleate, the other being 10-nitrooleate (Item No. 10008043) (OA-NO2; used for the mixture of isomers), which are formed by nitration of oleic acid in approximately equal proportions in vivo.{14255} Peroxynitrite, acidified nitrite, and myeloperoxidase in the presence of H2O2 and nitrite, all mediate the nitration of oleic acid. OA-NO2 is found in human plasma as the free acid and esterified in phospholipids at concentrations of 619 ± 52 nM and 302 ± 369 nM, respectively. OA-NO2 activates PPARγ approximately 7-fold at a concentration of 1 µM and effectively promotes differentiation 3T3-L1 preadipocytes to adipocytes at 3 µM.{14255}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008042 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Nitrated unsaturated fatty acids, such as 10- and 12-nitrolinoleate (LNO2; Item No. 10037), cholesteryl nitrolinoleate, and nitrohydroxylinoleate, represent a new class of endogenous lipid-derived signalling molecules. LNO2 isomers serve as potent endogenous ligands for PPARγ and can also decompose or be metabolized to release nitric oxide.{11912,13284,13287,13288} 9-Nitrooleate is one of two regioisomers of nitrooleate, the other being 10-nitrooleate (Item No. 10008043) (OA-NO2; used for the mixture of isomers), which are formed by nitration of oleic acid in approximately equal proportions in vivo.{14255} Peroxynitrite, acidified nitrite, and myeloperoxidase in the presence of H2O2 and nitrite, all mediate the nitration of oleic acid. OA-NO2 is found in human plasma as the free acid and esterified in phospholipids at concentrations of 619 ± 52 nM and 302 ± 369 nM, respectively. OA-NO2 activates PPARγ approximately 7-fold at a concentration of 1 µM and effectively promotes differentiation 3T3-L1 preadipocytes to adipocytes at 3 µM.{14255}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008042 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Nitrated unsaturated fatty acids, such as 10- and 12-nitrolinoleate (LNO2; Item No. 10037), cholesteryl nitrolinoleate, and nitrohydroxylinoleate, represent a new class of endogenous lipid-derived signalling molecules. LNO2 isomers serve as potent endogenous ligands for PPARγ and can also decompose or be metabolized to release nitric oxide.{11912,13284,13287,13288} 9-Nitrooleate is one of two regioisomers of nitrooleate, the other being 10-nitrooleate (Item No. 10008043) (OA-NO2; used for the mixture of isomers), which are formed by nitration of oleic acid in approximately equal proportions in vivo.{14255} Peroxynitrite, acidified nitrite, and myeloperoxidase in the presence of H2O2 and nitrite, all mediate the nitration of oleic acid. OA-NO2 is found in human plasma as the free acid and esterified in phospholipids at concentrations of 619 ± 52 nM and 302 ± 369 nM, respectively. OA-NO2 activates PPARγ approximately 7-fold at a concentration of 1 µM and effectively promotes differentiation 3T3-L1 preadipocytes to adipocytes at 3 µM.{14255}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008042 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-OAHSA is a form of FAHFA in which oleic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. Among the FAHFA family members, OAHSAs are the most abundantly expressed in the serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-OAHSA is a form of FAHFA in which oleic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. Among the FAHFA family members, OAHSAs are the most abundantly expressed in the serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-OAHSA is a form of FAHFA in which oleic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. Among the FAHFA family members, OAHSAs are the most abundantly expressed in the serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
9-oxo-10(E),12(E)-Octadecadienoic acid (9-oxoODA) is a natural agonist, abundant in tomatoes, that activates PPARα at 10-20 µM.{18815} It is produced from conjugated linoleic acid, which is also known to be a PPARα agonist.{18815,15462} 9-oxoODA increases the expression of genes regulated by PPARα in primary mouse hepatocytes, altering lipid metabolism.{18815}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10685 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
9-oxo-10(E),12(E)-Octadecadienoic acid (9-oxoODA) is a natural agonist, abundant in tomatoes, that activates PPARα at 10-20 µM.{18815} It is produced from conjugated linoleic acid, which is also known to be a PPARα agonist.{18815,15462} 9-oxoODA increases the expression of genes regulated by PPARα in primary mouse hepatocytes, altering lipid metabolism.{18815}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10685 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
9-oxo-10(E),12(E)-Octadecadienoic acid (9-oxoODA) is a natural agonist, abundant in tomatoes, that activates PPARα at 10-20 µM.{18815} It is produced from conjugated linoleic acid, which is also known to be a PPARα agonist.{18815,15462} 9-oxoODA increases the expression of genes regulated by PPARα in primary mouse hepatocytes, altering lipid metabolism.{18815}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10685 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
9-Oxononanoic acid is an oxidized fatty acid formed via the autoxidation of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909).{45988,45989} It increases phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity and production of thromboxane B2 (TXB2; Item No. 19030) in isolated human plasma.{45988} 9-Oxononanoic acid decreases hepatic de novo fatty acid synthesis and increases hepatic carnitine palmitoyltransferase activity, a marker of β-oxidation, in rats.{45989}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29882 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
9-Oxononanoic acid is an oxidized fatty acid formed via the autoxidation of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909).{45988,45989} It increases phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity and production of thromboxane B2 (TXB2; Item No. 19030) in isolated human plasma.{45988} 9-Oxononanoic acid decreases hepatic de novo fatty acid synthesis and increases hepatic carnitine palmitoyltransferase activity, a marker of β-oxidation, in rats.{45989}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29882 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
9-Oxononanoic acid is an oxidized fatty acid formed via the autoxidation of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909).{45988,45989} It increases phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity and production of thromboxane B2 (TXB2; Item No. 19030) in isolated human plasma.{45988} 9-Oxononanoic acid decreases hepatic de novo fatty acid synthesis and increases hepatic carnitine palmitoyltransferase activity, a marker of β-oxidation, in rats.{45989}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29882 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
9-Oxononanoic acid is an oxidized fatty acid formed via the autoxidation of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909).{45988,45989} It increases phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activity and production of thromboxane B2 (TXB2; Item No. 19030) in isolated human plasma.{45988} 9-Oxononanoic acid decreases hepatic de novo fatty acid synthesis and increases hepatic carnitine palmitoyltransferase activity, a marker of β-oxidation, in rats.{45989}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29882 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
9-OxoODE results from oxidation of the allylic hydroxyl of either 9(S)- or 9(R)-HODE. Rabbit reticulocyte plasma and mitochondrial membranes contain both 9- and 13-oxoODEs, representing about 2% of the total linoleate residues in the membranes. Most of these oxidized linoleate residues are esterified to membrane lipids.{2262,2326,2261}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38420 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9-OxoODE results from oxidation of the allylic hydroxyl of either 9(S)- or 9(R)-HODE. Rabbit reticulocyte plasma and mitochondrial membranes contain both 9- and 13-oxoODEs, representing about 2% of the total linoleate residues in the membranes. Most of these oxidized linoleate residues are esterified to membrane lipids.{2262,2326,2261}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38420 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
9-OxoODE results from oxidation of the allylic hydroxyl of either 9(S)- or 9(R)-HODE. Rabbit reticulocyte plasma and mitochondrial membranes contain both 9- and 13-oxoODEs, representing about 2% of the total linoleate residues in the membranes. Most of these oxidized linoleate residues are esterified to membrane lipids.{2262,2326,2261}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38420 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
9-OxoOTrE is produced by the oxidation of 9-HpOTrE.{14394} 9-OxoOTrE exhibits antimicrobial activity against plant pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria and fungi.{14395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009215 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9-OxoOTrE is produced by the oxidation of 9-HpOTrE.{14394} 9-OxoOTrE exhibits antimicrobial activity against plant pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria and fungi.{14395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009215 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
9-OxoOTrE is produced by the oxidation of 9-HpOTrE.{14394} 9-OxoOTrE exhibits antimicrobial activity against plant pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria and fungi.{14395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009215 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
9-OxoOTrE is produced by the oxidation of 9-HpOTrE.{14394} 9-OxoOTrE exhibits antimicrobial activity against plant pathogenic microorganisms including bacteria and fungi.{14395}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009215 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHPA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy palmitic acid. Among the FAHFA family members, PAHSAs are the most abundant in the adipose tissue of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-PAHPA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHPA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy palmitic acid. Among the FAHFA family members, PAHSAs are the most abundant in the adipose tissue of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-PAHPA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHPA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy palmitic acid. Among the FAHFA family members, PAHSAs are the most abundant in the adipose tissue of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-PAHPA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHSA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. PAHSAs are the most abundant forms of FAHFA in serum as well as white and brown adipose tissues of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress Glut4 specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} 9-PAHSA is the predominant isomer of PAHSA in wild type and AG4OX mice.{27644} It is found in humans and is reduced in the serum and adipose tissues of insulin-resistant humans.{27644} 9-PAHSA improves glucose tolerance, stimulates insulin secretion, and has anti-inflammatory effects in mice.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHSA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. PAHSAs are the most abundant forms of FAHFA in serum as well as white and brown adipose tissues of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress Glut4 specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} 9-PAHSA is the predominant isomer of PAHSA in wild type and AG4OX mice.{27644} It is found in humans and is reduced in the serum and adipose tissues of insulin-resistant humans.{27644} 9-PAHSA improves glucose tolerance, stimulates insulin secretion, and has anti-inflammatory effects in mice.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to a hydroxylated C-16 or C-18 lipid. 9-PAHSA is a FAHFA in which palmitic acid is esterified to 9-hydroxy stearic acid. PAHSAs are the most abundant forms of FAHFA in serum as well as white and brown adipose tissues of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress Glut4 specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} 9-PAHSA is the predominant isomer of PAHSA in wild type and AG4OX mice.{27644} It is found in humans and is reduced in the serum and adipose tissues of insulin-resistant humans.{27644} 9-PAHSA improves glucose tolerance, stimulates insulin secretion, and has anti-inflammatory effects in mice.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity in mice.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-POHSA is a FAHFA consisting of palmitoleic acid esterified at the 9-position of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of POHSA are significantly elevated in serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-POHSA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity in mice.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-POHSA is a FAHFA consisting of palmitoleic acid esterified at the 9-position of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of POHSA are significantly elevated in serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-POHSA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity in mice.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-POHSA is a FAHFA consisting of palmitoleic acid esterified at the 9-position of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of POHSA are significantly elevated in serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644} As other FAHFAs improve glucose tolerance, stimulate insulin secretion, and have anti-inflammatory effects, 9-POHSA may be a bioactive lipid with roles in metabolic syndrome and inflammation.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
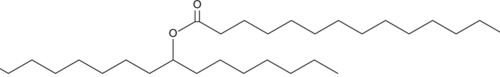
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-SAHSA is a FAHFA in which stearic acid is esterified at the 9th carbon of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of SAHSA are moderately elevated in the serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-SAHSA is a FAHFA in which stearic acid is esterified at the 9th carbon of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of SAHSA are moderately elevated in the serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Branched fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids (FAHFAs) are newly identified endogenous lipids regulated by fasting and high-fat feeding and associated with insulin sensitivity.{27644} Structurally, these esters are comprised of a C-16 or C-18 fatty acid (e.g., palmitoleic, palmitic, oleic, or stearic acid) linked to either a C-16 or C-18 hydroxy substituent. 9-SAHSA is a FAHFA in which stearic acid is esterified at the 9th carbon of hydroxy stearic acid. The levels of SAHSA are moderately elevated in the serum of glucose tolerant AG4OX mice, which overexpress the Glut4 glucose transporter specifically in adipose tissue.{27644}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
9,10-Anthracenediyl-bis(methylene)dimalonic acid (ABMDMA) is a reagent used to detect singlet oxygen generation. This water-soluble derivative of anthracene can be photobleached by singlet oxygen to its corresponding endoperoxide. This reaction can be monitored spectrophotometrically by recording the decrease in optical density at 400 nm (ABMDMA ex/em max. = 380/407 nm in 0.1 M phosphate pH 7.0).{31532}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19580 -Available on backorder
9,10-Anthracenediyl-bis(methylene)dimalonic acid (ABMDMA) is a reagent used to detect singlet oxygen generation. This water-soluble derivative of anthracene can be photobleached by singlet oxygen to its corresponding endoperoxide. This reaction can be monitored spectrophotometrically by recording the decrease in optical density at 400 nm (ABMDMA ex/em max. = 380/407 nm in 0.1 M phosphate pH 7.0).{31532}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19580 -Available on backorder
9,10-Anthracenediyl-bis(methylene)dimalonic acid (ABMDMA) is a reagent used to detect singlet oxygen generation. This water-soluble derivative of anthracene can be photobleached by singlet oxygen to its corresponding endoperoxide. This reaction can be monitored spectrophotometrically by recording the decrease in optical density at 400 nm (ABMDMA ex/em max. = 380/407 nm in 0.1 M phosphate pH 7.0).{31532}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19580 -Available on backorder
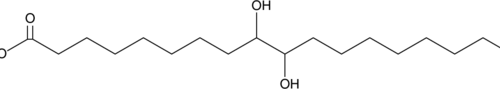
9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid is an oxidation product of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) that can be formed from oleic acid in HepG2 cells.{52024} It activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in CV-1 cells when used at concentrations ranging from 50 to 100 µM.{52025} 9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid (4% in the diet) decreases blood glucose levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and decreases body weight in high-fat diet-fed KKAy diabetic mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28612 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid is an oxidation product of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) that can be formed from oleic acid in HepG2 cells.{52024} It activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in CV-1 cells when used at concentrations ranging from 50 to 100 µM.{52025} 9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid (4% in the diet) decreases blood glucose levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and decreases body weight in high-fat diet-fed KKAy diabetic mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28612 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid is an oxidation product of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) that can be formed from oleic acid in HepG2 cells.{52024} It activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in CV-1 cells when used at concentrations ranging from 50 to 100 µM.{52025} 9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid (4% in the diet) decreases blood glucose levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and decreases body weight in high-fat diet-fed KKAy diabetic mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28612 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid is an oxidation product of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) that can be formed from oleic acid in HepG2 cells.{52024} It activates peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in CV-1 cells when used at concentrations ranging from 50 to 100 µM.{52025} 9,10-Dihydroxystearic acid (4% in the diet) decreases blood glucose levels, increases insulin sensitivity, and decreases body weight in high-fat diet-fed KKAy diabetic mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28612 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Ro 3-1314 is an inhibitor of both COX and lipoxygenase.{1260,1261} Ro 3-1314 inhibits ram seminal vesicle COX with a Ki of 0.6 µM.{1260} It is a more effective inhibitor of COX-1 than of 15-LO, inhibiting 95% and 68%, respectively, of these enzymatic activities when used at a concentration of 48 µM.{1261}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90400 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Ro 3-1314 is an inhibitor of both COX and lipoxygenase.{1260,1261} Ro 3-1314 inhibits ram seminal vesicle COX with a Ki of 0.6 µM.{1260} It is a more effective inhibitor of COX-1 than of 15-LO, inhibiting 95% and 68%, respectively, of these enzymatic activities when used at a concentration of 48 µM.{1261}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90400 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Ro 3-1314 is an inhibitor of both COX and lipoxygenase.{1260,1261} Ro 3-1314 inhibits ram seminal vesicle COX with a Ki of 0.6 µM.{1260} It is a more effective inhibitor of COX-1 than of 15-LO, inhibiting 95% and 68%, respectively, of these enzymatic activities when used at a concentration of 48 µM.{1261}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90400 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
(9E)-Erythromycin A oxime is a metabolite of the semisynthetic antibiotic roxithromycin (Item No. 19465).{43949}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27966 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
(9E)-Erythromycin A oxime is a metabolite of the semisynthetic antibiotic roxithromycin (Item No. 19465).{43949}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27966 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
(9E)-Erythromycin A oxime is a metabolite of the semisynthetic antibiotic roxithromycin (Item No. 19465).{43949}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27966 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
(9E)-Erythromycin A oxime is a metabolite of the semisynthetic antibiotic roxithromycin (Item No. 19465).{43949}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27966 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
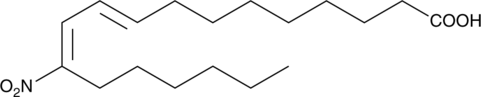
9(E),11(E)-12-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9(Z),11(E)-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30834 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-12-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9(Z),11(E)-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30834 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-12-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9(Z),11(E)-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30834 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-12-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9(Z),11(E)-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9(E),11(E)-12-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30834 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-9-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9E,11E-9-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9Z,11E-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9E,11E-9-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30160 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-9-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9E,11E-9-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9Z,11E-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9E,11E-9-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30160 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-9-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9E,11E-9-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9Z,11E-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9E,11E-9-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30160 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E)-9-nitro Conjugated linoleic acid (9E,11E-9-nitro CLA) is a nitrated fatty acid. It is formed from 9Z,11E-CLA (Item No. 90140) upon exposure to acidified nitrite, peroxynitrite, gaseous nitrogen dioxide, or a combination of myeloperoxidase, hydrogen peroxide, and nitrite.{50928} It is also formed in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages, an effect that can be reduced by the nitric oxide synthase (NOS) inhibitor L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{55206} 9E,11E-9-nitro CLA has been found in human plasma.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30160 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
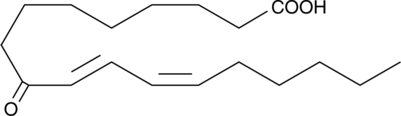
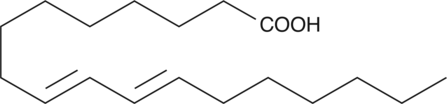
9(E),11(E)-Conjugated linoleic acid (9(E),11(E)-CLA) refers to a family of 8 geometric isomers of linoleic acid in which the two double bonds are contiguous. 9(E),11(E)-CLA is the 9,11 all-trans isomer of linoleic acid. CLA was originally identified in ground beef, but it is also present in a variety of dairy products. CLA is effective at reducing mammary tumors in rats at levels as low as 0.1% by weight of their diet.{1568} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1181]
Brand:CaymanSKU:90370 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
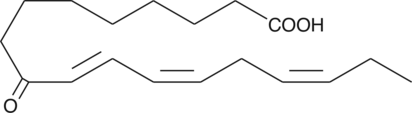
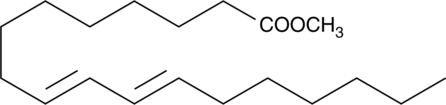
9(E),11(E)-Conjugated linoleic acid methyl ester has been found in thermally stressed cooking oils and may be used as a marker of adulteration of olive oils with lower quality oils.{38903} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1257]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24580 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
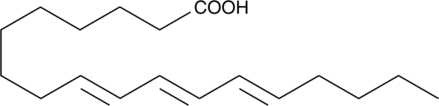
9(E),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic acid (β-ESA) is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid that is found in plant seed oils and in mixtures of conjugated linolenic acids synthesized by the alkaline isomerization of linolenic acid.{37085} It reduces growth of Caco-2 colon cancer cells in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner. In vitro, β-ESA induces DNA fragmentation and upregulation of pro-apoptotic Bax mRNA. β-ESA decreases protein expression of the apoptosis suppression factor Bcl-2 and induces apoptosis in T24 bladder cancer cells via production of reactive oxygen species.{37086} It also inhibits bacterial fatty acid dioxygenase with a Ki value of 49 nM in vitro.{37087}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22976 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic acid (β-ESA) is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid that is found in plant seed oils and in mixtures of conjugated linolenic acids synthesized by the alkaline isomerization of linolenic acid.{37085} It reduces growth of Caco-2 colon cancer cells in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner. In vitro, β-ESA induces DNA fragmentation and upregulation of pro-apoptotic Bax mRNA. β-ESA decreases protein expression of the apoptosis suppression factor Bcl-2 and induces apoptosis in T24 bladder cancer cells via production of reactive oxygen species.{37086} It also inhibits bacterial fatty acid dioxygenase with a Ki value of 49 nM in vitro.{37087}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22976 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
9(E),11(E),13(E)-Octadecatrienoic acid (β-ESA) is a conjugated polyunsaturated fatty acid that is found in plant seed oils and in mixtures of conjugated linolenic acids synthesized by the alkaline isomerization of linolenic acid.{37085} It reduces growth of Caco-2 colon cancer cells in a dose-dependent and time-dependent manner. In vitro, β-ESA induces DNA fragmentation and upregulation of pro-apoptotic Bax mRNA. β-ESA decreases protein expression of the apoptosis suppression factor Bcl-2 and induces apoptosis in T24 bladder cancer cells via production of reactive oxygen species.{37086} It also inhibits bacterial fatty acid dioxygenase with a Ki value of 49 nM in vitro.{37087}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22976 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
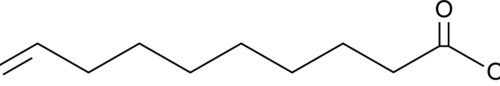
9(E),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid is an ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid and an isomer of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) that contains a trans double bond at the C9 position. It has been found as a minor component of bovine milk fat and in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils.{53913} 9(E),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid levels increase in rabbit meat following supplementation with heated sunflower oil, α-tocopheryl acetate, and zinc.{53914}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005146 - 2 mgAvailable on backorder
9(E),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid is an ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid and an isomer of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) that contains a trans double bond at the C9 position. It has been found as a minor component of bovine milk fat and in partially hydrogenated vegetable oils.{53913} 9(E),12(Z)-Octadecadienoic acid levels increase in rabbit meat following supplementation with heated sunflower oil, α-tocopheryl acetate, and zinc.{53914}
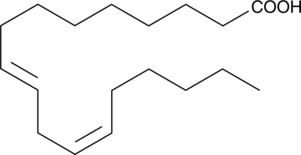
Brand:CaymanSKU:-9(R)-HETE is an enantiomer which makes up 50% of (±)9-HETE (Item No. 34400). At a concentration of 300 nM, 9(R)-HETE activates RXRγ-dependent transcription 1.5 fold relative to a control.{2565} Stereochemical assignment of the (R) enantiomer is based on comparison of chiral HPLC retention times to published results. {30214}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34405 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
9(R)-HETE is an enantiomer which makes up 50% of (±)9-HETE (Item No. 34400). At a concentration of 300 nM, 9(R)-HETE activates RXRγ-dependent transcription 1.5 fold relative to a control.{2565} Stereochemical assignment of the (R) enantiomer is based on comparison of chiral HPLC retention times to published results. {30214}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34405 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
9(R)-HETE is an enantiomer which makes up 50% of (±)9-HETE (Item No. 34400). At a concentration of 300 nM, 9(R)-HETE activates RXRγ-dependent transcription 1.5 fold relative to a control.{2565} Stereochemical assignment of the (R) enantiomer is based on comparison of chiral HPLC retention times to published results. {30214}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34405 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
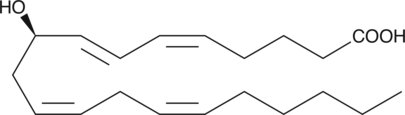
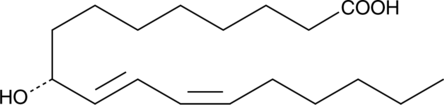
9(R)-HODE is one of several monohydroxylated products of linoleic acid. All known mammalian lipoxygenases appear to catalyze the oxygenation of arachidonic and linoleic acid to give products having strictly the (S) configuration at the site of oxygen insertion. However, both human umbilical vein endothelial cells and bovine aorta endothelial cells have been shown to produce 9(R)-HODE when incubated with linoleic acid.{2369,1528} The physiological function of 9(R)-HODE and the enzyme that catalyzes its formation have not been determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:38405 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder