Chemicals
Showing 601–750 of 41137 results
-
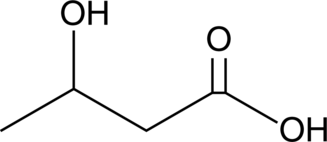
(±)-β-Hydroxybutyrate (βOHB) is an endogenous and specific inhibitor of class I histone deacetylases (HDACs), increasing acetylation of histones in a dose-dependent manner.{22106} It does not increase acetylation of α-tubulin, indicating that it does not inhibit the class IIb HDAC6.{22106} Fasting or caloric restriction, two conditions associated with increased βOHB abundance, increases global histone acetylation in mouse tissues.{22106}
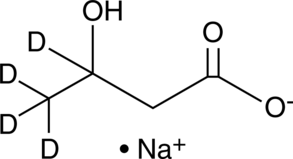
Brand:CaymanSKU:-(±)-β-Hydroxybutyrate-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of (±)-β-hydroxybutyrate by GC- or LC-MS. β-Hydroxybutyrate is a ketone body which is over-produced in ketoacidosis, as can occur with diabetes or alcohol abuse.{22284,22285}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-(±)-β-Hydroxybutyrate-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of (±)-β-hydroxybutyrate by GC- or LC-MS. β-Hydroxybutyrate is a ketone body which is over-produced in ketoacidosis, as can occur with diabetes or alcohol abuse.{22284,22285}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-(±)-β-Hydroxybutyrate-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of (±)-β-hydroxybutyrate by GC- or LC-MS. β-Hydroxybutyrate is a ketone body which is over-produced in ketoacidosis, as can occur with diabetes or alcohol abuse.{22284,22285}
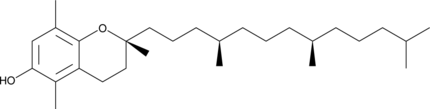
Brand:CaymanSKU:-(±)-β-Tocopherol is a lipid-soluble form of vitamin E with antioxidant activity.{8199} It scavenges 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; Item No. 14805) radicals with an EC50 value of 68.2 μM.{45103} (±)-β-Tocopherol (100 μM) inhibits LPS-induced COX-2 gene expression in mouse RAW 264.7 macrophage cells.{45104} Unlike (±)-α-tocopherol (Item No. 25985), (±)-β-tocopherol does not inhibit smooth muscle cell proliferation, decrease PKC activity, increase phosphoprotein phosphatase 2A (PP2A) activity, or modify expression of the α-tropomyosin gene.{8199} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1071]
Brand:CaymanSKU:26758 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
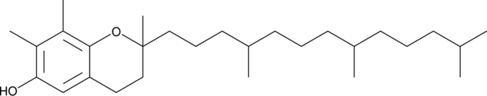
(±)-γ-Tocopherol is a form of vitamin E with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.{15114,15117,8680} It traps and detoxifies reactive nitrogen oxide species, including nitrogen dioxide, in cell-free assays.{15114,15117} It also reduces the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) induced by LPS in RAW 264.7 macrophages and by IL-1β in A549 cells (IC50s = 7.5 and 4 μM, respectively).{8680} (±)-γ-Tocopherol (10 μM) inhibits LPS-induced nitrite release and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in RAW 264.7 cells and reduces COX-2 activity in A549 cells pretreated with IL-1β. Serum levels of (±)-γ-tocopherol are decreased in patients with cardiovascular disease.{15114} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1073]
Brand:CaymanSKU:27193 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
(±)-γ-Tocopherol is a form of vitamin E with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.{15114,15117,8680} It traps and detoxifies reactive nitrogen oxide species, including nitrogen dioxide, in cell-free assays.{15114,15117} It also reduces the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) induced by LPS in RAW 264.7 macrophages and by IL-1β in A549 cells (IC50s = 7.5 and 4 μM, respectively).{8680} (±)-γ-Tocopherol (10 μM) inhibits LPS-induced nitrite release and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in RAW 264.7 cells and reduces COX-2 activity in A549 cells pretreated with IL-1β. Serum levels of (±)-γ-tocopherol are decreased in patients with cardiovascular disease.{15114} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1073]
Brand:CaymanSKU:27193 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
(±)-γ-Tocopherol is a form of vitamin E with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.{15114,15117,8680} It traps and detoxifies reactive nitrogen oxide species, including nitrogen dioxide, in cell-free assays.{15114,15117} It also reduces the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) induced by LPS in RAW 264.7 macrophages and by IL-1β in A549 cells (IC50s = 7.5 and 4 μM, respectively).{8680} (±)-γ-Tocopherol (10 μM) inhibits LPS-induced nitrite release and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in RAW 264.7 cells and reduces COX-2 activity in A549 cells pretreated with IL-1β. Serum levels of (±)-γ-tocopherol are decreased in patients with cardiovascular disease.{15114} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1073]
Brand:CaymanSKU:27193 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
(±)-γ-Tocopherol is a form of vitamin E with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.{15114,15117,8680} It traps and detoxifies reactive nitrogen oxide species, including nitrogen dioxide, in cell-free assays.{15114,15117} It also reduces the synthesis of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) induced by LPS in RAW 264.7 macrophages and by IL-1β in A549 cells (IC50s = 7.5 and 4 μM, respectively).{8680} (±)-γ-Tocopherol (10 μM) inhibits LPS-induced nitrite release and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) expression in RAW 264.7 cells and reduces COX-2 activity in A549 cells pretreated with IL-1β. Serum levels of (±)-γ-tocopherol are decreased in patients with cardiovascular disease.{15114} [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1073]
Brand:CaymanSKU:27193 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
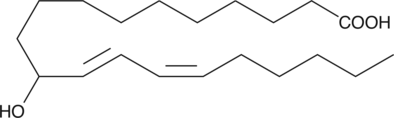
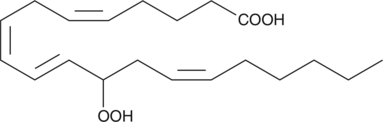
(±)10-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} (±)10-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33400 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)10-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} (±)10-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33400 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)10-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} (±)10-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33400 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)10-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} (±)10-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33400 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
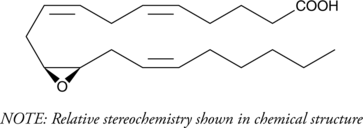
(±)10(11)-DiHDPA is produced from cytochrome P450 epoxygenase action on docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310). It has been shown to inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis in mice and may have additional anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects.{26641,29859}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
(±)10(11)-DiHDPA is produced from cytochrome P450 epoxygenase action on docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310). It has been shown to inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis in mice and may have additional anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects.{26641,29859}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
(±)10(11)-DiHDPA is produced from cytochrome P450 epoxygenase action on docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310). It has been shown to inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis in mice and may have additional anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects.{26641,29859}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
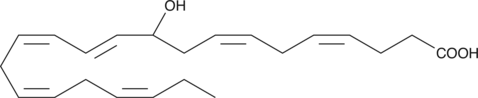
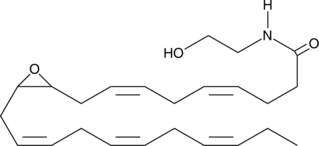
(±)10(11)-EDP ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide and cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonist (EC50s = 0.43 and 22.5 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively).{42488} It is produced though direct epoxygenation of docosahexaenoyl ethanolamide (DHEA; Item No. 10007534) by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases.{42488,40186} 10,11-EDP epoxide (12.5 and 25 μM) reduces the viability of 143B metastatic osteosarcoma cells.{42488} It induces apoptosis and inhibits cell migration in a wound-healing assay in 143B, MG63, and HOS osteosarcoma cells. (±)10(11)-EDP ethanolamide also reduces tube formation by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in a Matrigel™ assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25878 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)10(11)-EDP ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide and cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonist (EC50s = 0.43 and 22.5 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively).{42488} It is produced though direct epoxygenation of docosahexaenoyl ethanolamide (DHEA; Item No. 10007534) by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases.{42488,40186} 10,11-EDP epoxide (12.5 and 25 μM) reduces the viability of 143B metastatic osteosarcoma cells.{42488} It induces apoptosis and inhibits cell migration in a wound-healing assay in 143B, MG63, and HOS osteosarcoma cells. (±)10(11)-EDP ethanolamide also reduces tube formation by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in a Matrigel™ assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25878 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)10(11)-EDP ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide and cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonist (EC50s = 0.43 and 22.5 nM for CB1 and CB2 receptors, respectively).{42488} It is produced though direct epoxygenation of docosahexaenoyl ethanolamide (DHEA; Item No. 10007534) by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases.{42488,40186} 10,11-EDP epoxide (12.5 and 25 μM) reduces the viability of 143B metastatic osteosarcoma cells.{42488} It induces apoptosis and inhibits cell migration in a wound-healing assay in 143B, MG63, and HOS osteosarcoma cells. (±)10(11)-EDP ethanolamide also reduces tube formation by human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in a Matrigel™ assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25878 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
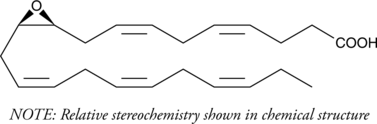
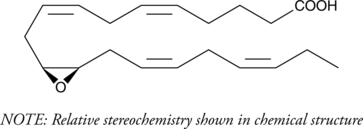
Cytochrome P450 metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids produces numerous bioactive epoxide regioisomers. (±)10(11)-EpDPA is a docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310) epoxygenase metabolite, derived via epoxidation of the 10,11-double bond of DHA. It has been detected in rat brain and spinal cord, as well as human serum, and acts as a substrate for soluble epoxide hydrolase with a Km value of 5.1 µM.{29509,29508} (±)10(11)-EpDPA and other epoxy metabolites of DHA are reported to demonstrate antihyperalgesic activity in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models and to potently inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth in in vitro assays.{29509,26641}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10471 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Cytochrome P450 metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids produces numerous bioactive epoxide regioisomers. (±)10(11)-EpDPA is a docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310) epoxygenase metabolite, derived via epoxidation of the 10,11-double bond of DHA. It has been detected in rat brain and spinal cord, as well as human serum, and acts as a substrate for soluble epoxide hydrolase with a Km value of 5.1 µM.{29509,29508} (±)10(11)-EpDPA and other epoxy metabolites of DHA are reported to demonstrate antihyperalgesic activity in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models and to potently inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth in in vitro assays.{29509,26641}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10471 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
Cytochrome P450 metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids produces numerous bioactive epoxide regioisomers. (±)10(11)-EpDPA is a docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310) epoxygenase metabolite, derived via epoxidation of the 10,11-double bond of DHA. It has been detected in rat brain and spinal cord, as well as human serum, and acts as a substrate for soluble epoxide hydrolase with a Km value of 5.1 µM.{29509,29508} (±)10(11)-EpDPA and other epoxy metabolites of DHA are reported to demonstrate antihyperalgesic activity in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models and to potently inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth in in vitro assays.{29509,26641}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10471 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Cytochrome P450 metabolism of polyunsaturated fatty acids produces numerous bioactive epoxide regioisomers. (±)10(11)-EpDPA is a docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310) epoxygenase metabolite, derived via epoxidation of the 10,11-double bond of DHA. It has been detected in rat brain and spinal cord, as well as human serum, and acts as a substrate for soluble epoxide hydrolase with a Km value of 5.1 µM.{29509,29508} (±)10(11)-EpDPA and other epoxy metabolites of DHA are reported to demonstrate antihyperalgesic activity in inflammatory and neuropathic pain models and to potently inhibit angiogenesis and tumor growth in in vitro assays.{29509,26641}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10471 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
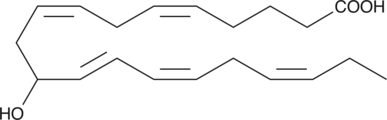
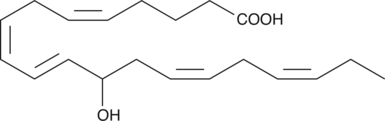
(±)11-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} DHA is metabolized to 11(S)-HDHA by human platelets and canine retina.{7483,7486,7484,7492} In addition to 11(S)-HDHA, 14(S)-HDHA is also produced by platelets.{7483,7484,7492} 11(S)-HDHA was shown to be an inhibitor of U-46619-induced human platelet aggregation and rabbit and rat aortic smooth muscle contraction with IC50 values of about 50, 4.7, and 7.5 µM, respectively.{7484,7481} (±)11-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33450 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} DHA is metabolized to 11(S)-HDHA by human platelets and canine retina.{7483,7486,7484,7492} In addition to 11(S)-HDHA, 14(S)-HDHA is also produced by platelets.{7483,7484,7492} 11(S)-HDHA was shown to be an inhibitor of U-46619-induced human platelet aggregation and rabbit and rat aortic smooth muscle contraction with IC50 values of about 50, 4.7, and 7.5 µM, respectively.{7484,7481} (±)11-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33450 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} DHA is metabolized to 11(S)-HDHA by human platelets and canine retina.{7483,7486,7484,7492} In addition to 11(S)-HDHA, 14(S)-HDHA is also produced by platelets.{7483,7484,7492} 11(S)-HDHA was shown to be an inhibitor of U-46619-induced human platelet aggregation and rabbit and rat aortic smooth muscle contraction with IC50 values of about 50, 4.7, and 7.5 µM, respectively.{7484,7481} (±)11-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33450 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} DHA is metabolized to 11(S)-HDHA by human platelets and canine retina.{7483,7486,7484,7492} In addition to 11(S)-HDHA, 14(S)-HDHA is also produced by platelets.{7483,7484,7492} 11(S)-HDHA was shown to be an inhibitor of U-46619-induced human platelet aggregation and rabbit and rat aortic smooth muscle contraction with IC50 values of about 50, 4.7, and 7.5 µM, respectively.{7484,7481} (±)11-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33450 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HEDE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of 11,14-eicosadienoic acid. There are no reports in the literature of biological activity associated with (±)11-HEDE.
Brand:CaymanSKU:37500 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HEDE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of 11,14-eicosadienoic acid. There are no reports in the literature of biological activity associated with (±)11-HEDE.
Brand:CaymanSKU:37500 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HEDE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of 11,14-eicosadienoic acid. There are no reports in the literature of biological activity associated with (±)11-HEDE.
Brand:CaymanSKU:37500 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HEDE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of 11,14-eicosadienoic acid. There are no reports in the literature of biological activity associated with (±)11-HEDE.
Brand:CaymanSKU:37500 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of eicosapentaenoic acid. It contains equal amounts of 11(S)-HEPE and 11(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)11-HEPE has not been clearly documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32500 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of eicosapentaenoic acid. It contains equal amounts of 11(S)-HEPE and 11(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)11-HEPE has not been clearly documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32500 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of eicosapentaenoic acid. It contains equal amounts of 11(S)-HEPE and 11(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)11-HEPE has not been clearly documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32500 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of eicosapentaenoic acid. It contains equal amounts of 11(S)-HEPE and 11(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)11-HEPE has not been clearly documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:32500 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HETE is an oxylipin formed non-enzymatically from arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{54364,54411} Levels of (±)11-HETE are increased in an in vitro model of lipid peroxidation induced by ferrous ammonium sulfate (FAS) in rat brain homogenates.{2097} Levels are also increased in rat liver in an in vivo model of lipid peroxidation induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). It has been found in skin extracts from individuals with psoriasis and in atherosclerotic plaques.{54412,54413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34500 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HETE is an oxylipin formed non-enzymatically from arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{54364,54411} Levels of (±)11-HETE are increased in an in vitro model of lipid peroxidation induced by ferrous ammonium sulfate (FAS) in rat brain homogenates.{2097} Levels are also increased in rat liver in an in vivo model of lipid peroxidation induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). It has been found in skin extracts from individuals with psoriasis and in atherosclerotic plaques.{54412,54413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34500 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HETE is an oxylipin formed non-enzymatically from arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{54364,54411} Levels of (±)11-HETE are increased in an in vitro model of lipid peroxidation induced by ferrous ammonium sulfate (FAS) in rat brain homogenates.{2097} Levels are also increased in rat liver in an in vivo model of lipid peroxidation induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). It has been found in skin extracts from individuals with psoriasis and in atherosclerotic plaques.{54412,54413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34500 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11-HETE is an oxylipin formed non-enzymatically from arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{54364,54411} Levels of (±)11-HETE are increased in an in vitro model of lipid peroxidation induced by ferrous ammonium sulfate (FAS) in rat brain homogenates.{2097} Levels are also increased in rat liver in an in vivo model of lipid peroxidation induced by carbon tetrachloride (CCl4). It has been found in skin extracts from individuals with psoriasis and in atherosclerotic plaques.{54412,54413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34500 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11(12)-DiHETE is a dihydroxy metabolite of EPA produced by cytochrome P450-mediated epoxide formation and subsequent hydrolysis by epoxide hydrolase. Plasma levels of (±)11(12)-DiHETE are increased over baseline after an oral dose of 1008 mg EPA.{33181}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10466 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11(12)-DiHETE is a dihydroxy metabolite of EPA produced by cytochrome P450-mediated epoxide formation and subsequent hydrolysis by epoxide hydrolase. Plasma levels of (±)11(12)-DiHETE are increased over baseline after an oral dose of 1008 mg EPA.{33181}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10466 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11(12)-DiHETE is a dihydroxy metabolite of EPA produced by cytochrome P450-mediated epoxide formation and subsequent hydrolysis by epoxide hydrolase. Plasma levels of (±)11(12)-DiHETE are increased over baseline after an oral dose of 1008 mg EPA.{33181}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10466 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11(12)-EET is a fully racemic version of the R/S enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) by cytochrome P450 enzymes.{463,729,39722} A higher proportion of 11(R),12(S)-EET is produced by the CYP450 isoforms CYP2C23 and CYP2C24 while CYP2B2 produces a higher proportion of 11(S),12(R)-EET.{39722} 11(12)-EET has been shown, along with 8(9)-EET (Item No. 50351), to play a role in the recovery of depleted calcium pools in cultured smooth muscle cells.{5318} It also inhibits basolateral 18-pS potassium channels in the renal cortical collecting duct when used at a concentration of 100 nM.{39723} 11(12)-EET (50 µg/kg per day) increases adhesion of isolated peripheral blood leukocytes in a chamber coated with P-selectin and ICAM-1 but does not affect choroidal neovascularization size following laser photocoagulation.{39724} It also has anti-inflammatory, angiogenic, and cardioprotective properties.{39725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:50511 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11(12)-EET is a fully racemic version of the R/S enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) by cytochrome P450 enzymes.{463,729,39722} A higher proportion of 11(R),12(S)-EET is produced by the CYP450 isoforms CYP2C23 and CYP2C24 while CYP2B2 produces a higher proportion of 11(S),12(R)-EET.{39722} 11(12)-EET has been shown, along with 8(9)-EET (Item No. 50351), to play a role in the recovery of depleted calcium pools in cultured smooth muscle cells.{5318} It also inhibits basolateral 18-pS potassium channels in the renal cortical collecting duct when used at a concentration of 100 nM.{39723} 11(12)-EET (50 µg/kg per day) increases adhesion of isolated peripheral blood leukocytes in a chamber coated with P-selectin and ICAM-1 but does not affect choroidal neovascularization size following laser photocoagulation.{39724} It also has anti-inflammatory, angiogenic, and cardioprotective properties.{39725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:50511 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11(12)-EET is a fully racemic version of the R/S enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) by cytochrome P450 enzymes.{463,729,39722} A higher proportion of 11(R),12(S)-EET is produced by the CYP450 isoforms CYP2C23 and CYP2C24 while CYP2B2 produces a higher proportion of 11(S),12(R)-EET.{39722} 11(12)-EET has been shown, along with 8(9)-EET (Item No. 50351), to play a role in the recovery of depleted calcium pools in cultured smooth muscle cells.{5318} It also inhibits basolateral 18-pS potassium channels in the renal cortical collecting duct when used at a concentration of 100 nM.{39723} 11(12)-EET (50 µg/kg per day) increases adhesion of isolated peripheral blood leukocytes in a chamber coated with P-selectin and ICAM-1 but does not affect choroidal neovascularization size following laser photocoagulation.{39724} It also has anti-inflammatory, angiogenic, and cardioprotective properties.{39725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:50511 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)11(12)-EET is a fully racemic version of the R/S enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) by cytochrome P450 enzymes.{463,729,39722} A higher proportion of 11(R),12(S)-EET is produced by the CYP450 isoforms CYP2C23 and CYP2C24 while CYP2B2 produces a higher proportion of 11(S),12(R)-EET.{39722} 11(12)-EET has been shown, along with 8(9)-EET (Item No. 50351), to play a role in the recovery of depleted calcium pools in cultured smooth muscle cells.{5318} It also inhibits basolateral 18-pS potassium channels in the renal cortical collecting duct when used at a concentration of 100 nM.{39723} 11(12)-EET (50 µg/kg per day) increases adhesion of isolated peripheral blood leukocytes in a chamber coated with P-selectin and ICAM-1 but does not affect choroidal neovascularization size following laser photocoagulation.{39724} It also has anti-inflammatory, angiogenic, and cardioprotective properties.{39725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:50511 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item No. 90110) is converted to epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EpETE) by several cytochrome P450 isoforms.{18671} The major product of this epoxygenase pathway, (±)17(18)-EpETE (Item No. 50861), relaxes vascular and airway smooth muscle by binding large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels by directly interacting with BKα channel subunits.{9825,18669,18670} (±)11(12)-EpETE is an epoxygenase pathway product produced from EPA by CYP450 both in vitro and in vivo.{18671,18672} The biological actions and physiological effects of this epoxide remain to be determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10462 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item No. 90110) is converted to epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EpETE) by several cytochrome P450 isoforms.{18671} The major product of this epoxygenase pathway, (±)17(18)-EpETE (Item No. 50861), relaxes vascular and airway smooth muscle by binding large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels by directly interacting with BKα channel subunits.{9825,18669,18670} (±)11(12)-EpETE is an epoxygenase pathway product produced from EPA by CYP450 both in vitro and in vivo.{18671,18672} The biological actions and physiological effects of this epoxide remain to be determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10462 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item No. 90110) is converted to epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EpETE) by several cytochrome P450 isoforms.{18671} The major product of this epoxygenase pathway, (±)17(18)-EpETE (Item No. 50861), relaxes vascular and airway smooth muscle by binding large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels by directly interacting with BKα channel subunits.{9825,18669,18670} (±)11(12)-EpETE is an epoxygenase pathway product produced from EPA by CYP450 both in vitro and in vivo.{18671,18672} The biological actions and physiological effects of this epoxide remain to be determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10462 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item No. 90110) is converted to epoxyeicosatetraenoic acids (EpETE) by several cytochrome P450 isoforms.{18671} The major product of this epoxygenase pathway, (±)17(18)-EpETE (Item No. 50861), relaxes vascular and airway smooth muscle by binding large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BKCa) channels by directly interacting with BKα channel subunits.{9825,18669,18670} (±)11(12)-EpETE is an epoxygenase pathway product produced from EPA by CYP450 both in vitro and in vivo.{18671,18672} The biological actions and physiological effects of this epoxide remain to be determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10462 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
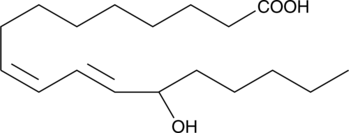
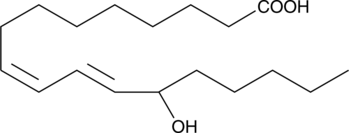
(±)12-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 12(S)-HEPE and 12(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)12-HEPE is likely mediated by one of the individual isomers, most commonly the 12(S) isomer in mammalian systems. 12-HEPE inhibits platelet aggregation with the same potency as 12-HETE, exhibiting IC50 values of 24 and 25 µM, respectively.{11169} These compounds are also equipotent as inhibitors of U46619-induced contraction of rat aorta (IC50s = 8.6-8.8 µM).{7481}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32540 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 12(S)-HEPE and 12(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)12-HEPE is likely mediated by one of the individual isomers, most commonly the 12(S) isomer in mammalian systems. 12-HEPE inhibits platelet aggregation with the same potency as 12-HETE, exhibiting IC50 values of 24 and 25 µM, respectively.{11169} These compounds are also equipotent as inhibitors of U46619-induced contraction of rat aorta (IC50s = 8.6-8.8 µM).{7481}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32540 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 12(S)-HEPE and 12(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)12-HEPE is likely mediated by one of the individual isomers, most commonly the 12(S) isomer in mammalian systems. 12-HEPE inhibits platelet aggregation with the same potency as 12-HETE, exhibiting IC50 values of 24 and 25 µM, respectively.{11169} These compounds are also equipotent as inhibitors of U46619-induced contraction of rat aorta (IC50s = 8.6-8.8 µM).{7481}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32540 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 12(S)-HEPE and 12(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)12-HEPE is likely mediated by one of the individual isomers, most commonly the 12(S) isomer in mammalian systems. 12-HEPE inhibits platelet aggregation with the same potency as 12-HETE, exhibiting IC50 values of 24 and 25 µM, respectively.{11169} These compounds are also equipotent as inhibitors of U46619-induced contraction of rat aorta (IC50s = 8.6-8.8 µM).{7481}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32540 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. The biological activity of (±)12-HETE is similar to that of its constituent enantiomers (Item Nos. 34560 and 34570). It aggregates neutrophils with an EC50 value of 40 nM.{2091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34550 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. The biological activity of (±)12-HETE is similar to that of its constituent enantiomers (Item Nos. 34560 and 34570). It aggregates neutrophils with an EC50 value of 40 nM.{2091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34550 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. The biological activity of (±)12-HETE is similar to that of its constituent enantiomers (Item Nos. 34560 and 34570). It aggregates neutrophils with an EC50 value of 40 nM.{2091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34550 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. The biological activity of (±)12-HETE is similar to that of its constituent enantiomers (Item Nos. 34560 and 34570). It aggregates neutrophils with an EC50 value of 40 nM.{2091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34550 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
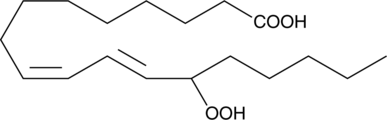
(±)12-HpETE is one of the six monohydroperoxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) and consists of an equal mixture of the R and S isomers. Reduction of the hydroperoxide yields the more stable hydroxyl fatty acid (±)12-HETE (Item No. 34550). The biological activity of (±)12-HpETE has not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10138 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12-HpETE is one of the six monohydroperoxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) and consists of an equal mixture of the R and S isomers. Reduction of the hydroperoxide yields the more stable hydroxyl fatty acid (±)12-HETE (Item No. 34550). The biological activity of (±)12-HpETE has not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10138 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12-HpETE is one of the six monohydroperoxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) and consists of an equal mixture of the R and S isomers. Reduction of the hydroperoxide yields the more stable hydroxyl fatty acid (±)12-HETE (Item No. 34550). The biological activity of (±)12-HpETE has not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10138 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
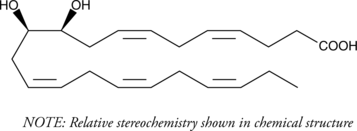
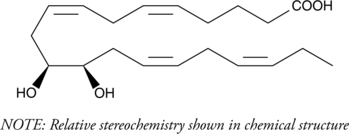
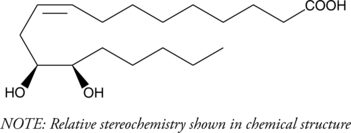
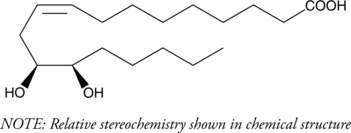
(±)12(13)-DiHOME is the diol form of (±)12(13)-EpOME (Item No. 52450), a cytochrome P450-derived epoxide of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) also known as isoleukotoxin.{8529} It is formed from 12(13)-EpOME by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in neutrophils.{17057} 12(13)-DiHOME is toxic to Sf21 cells expressing sEH and to lacZ-expressing control cells, unlike isoleukotoxin, which is only toxic to cells containing sEH.{8529,17057} Levels of 12(13)-DiHOME are increased in rat spinal cord following burn injury, and it enhances cold tolerance, increases fatty acid uptake into brown adipocytes, and decreases serum triglyceride levels in mice.{35412,34553} Levels are also elevated in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) in humans following exposure to biodiesel exhaust and in exhaled breath condensate in patients with allergic asthma following allergen exposure.{42556,42557} Plasma levels of 12(13)-DiHOME are increased immediately following moderate-intensity exercise in mice and humans, an effect that can be prevented by brown adipose tissue removal in the mouse.{35413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009832 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12(13)-DiHOME is the diol form of (±)12(13)-EpOME (Item No. 52450), a cytochrome P450-derived epoxide of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) also known as isoleukotoxin.{8529} It is formed from 12(13)-EpOME by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in neutrophils.{17057} 12(13)-DiHOME is toxic to Sf21 cells expressing sEH and to lacZ-expressing control cells, unlike isoleukotoxin, which is only toxic to cells containing sEH.{8529,17057} Levels of 12(13)-DiHOME are increased in rat spinal cord following burn injury, and it enhances cold tolerance, increases fatty acid uptake into brown adipocytes, and decreases serum triglyceride levels in mice.{35412,34553} Levels are also elevated in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) in humans following exposure to biodiesel exhaust and in exhaled breath condensate in patients with allergic asthma following allergen exposure.{42556,42557} Plasma levels of 12(13)-DiHOME are increased immediately following moderate-intensity exercise in mice and humans, an effect that can be prevented by brown adipose tissue removal in the mouse.{35413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009832 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12(13)-DiHOME is the diol form of (±)12(13)-EpOME (Item No. 52450), a cytochrome P450-derived epoxide of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) also known as isoleukotoxin.{8529} It is formed from 12(13)-EpOME by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in neutrophils.{17057} 12(13)-DiHOME is toxic to Sf21 cells expressing sEH and to lacZ-expressing control cells, unlike isoleukotoxin, which is only toxic to cells containing sEH.{8529,17057} Levels of 12(13)-DiHOME are increased in rat spinal cord following burn injury, and it enhances cold tolerance, increases fatty acid uptake into brown adipocytes, and decreases serum triglyceride levels in mice.{35412,34553} Levels are also elevated in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) in humans following exposure to biodiesel exhaust and in exhaled breath condensate in patients with allergic asthma following allergen exposure.{42556,42557} Plasma levels of 12(13)-DiHOME are increased immediately following moderate-intensity exercise in mice and humans, an effect that can be prevented by brown adipose tissue removal in the mouse.{35413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009832 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12(13)-DiHOME is the diol form of (±)12(13)-EpOME (Item No. 52450), a cytochrome P450-derived epoxide of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) also known as isoleukotoxin.{8529} It is formed from 12(13)-EpOME by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in neutrophils.{17057} 12(13)-DiHOME is toxic to Sf21 cells expressing sEH and to lacZ-expressing control cells, unlike isoleukotoxin, which is only toxic to cells containing sEH.{8529,17057} Levels of 12(13)-DiHOME are increased in rat spinal cord following burn injury, and it enhances cold tolerance, increases fatty acid uptake into brown adipocytes, and decreases serum triglyceride levels in mice.{35412,34553} Levels are also elevated in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) in humans following exposure to biodiesel exhaust and in exhaled breath condensate in patients with allergic asthma following allergen exposure.{42556,42557} Plasma levels of 12(13)-DiHOME are increased immediately following moderate-intensity exercise in mice and humans, an effect that can be prevented by brown adipose tissue removal in the mouse.{35413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009832 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)12(13)-DiHOME is the diol form of (±)12(13)-EpOME (Item No. 52450), a cytochrome P450-derived epoxide of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) also known as isoleukotoxin.{8529} It is formed from 12(13)-EpOME by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) in neutrophils.{17057} 12(13)-DiHOME is toxic to Sf21 cells expressing sEH and to lacZ-expressing control cells, unlike isoleukotoxin, which is only toxic to cells containing sEH.{8529,17057} Levels of 12(13)-DiHOME are increased in rat spinal cord following burn injury, and it enhances cold tolerance, increases fatty acid uptake into brown adipocytes, and decreases serum triglyceride levels in mice.{35412,34553} Levels are also elevated in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) in humans following exposure to biodiesel exhaust and in exhaled breath condensate in patients with allergic asthma following allergen exposure.{42556,42557} Plasma levels of 12(13)-DiHOME are increased immediately following moderate-intensity exercise in mice and humans, an effect that can be prevented by brown adipose tissue removal in the mouse.{35413} (±)12(13)-DiHOME MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of (±)12(13)-DiHOME (Item No. 10009832) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This (±)12(13)-DiHOME MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31027 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
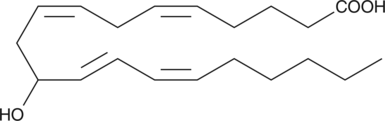
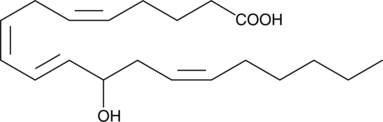
(±)13-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} Fresh water hydra was shown to metabolize DHA to 13(R)-HDHA, presumably via the 11R-lipoxygenase activity.{2263} (±)13-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33500 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} Fresh water hydra was shown to metabolize DHA to 13(R)-HDHA, presumably via the 11R-lipoxygenase activity.{2263} (±)13-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33500 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} Fresh water hydra was shown to metabolize DHA to 13(R)-HDHA, presumably via the 11R-lipoxygenase activity.{2263} (±)13-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33500 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} Fresh water hydra was shown to metabolize DHA to 13(R)-HDHA, presumably via the 11R-lipoxygenase activity.{2263} (±)13-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33500 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HODE is one of the two racemic monohydroxy fatty acids resulting from the non-enzymatic oxidation of linoleic acid. It is the principle hydroxylated fatty acid in human psoriatic skin scales, with a mean concentration of 17 ng/mg.{178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38600 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HODE is one of the two racemic monohydroxy fatty acids resulting from the non-enzymatic oxidation of linoleic acid. It is the principle hydroxylated fatty acid in human psoriatic skin scales, with a mean concentration of 17 ng/mg.{178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38600 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HODE is one of the two racemic monohydroxy fatty acids resulting from the non-enzymatic oxidation of linoleic acid. It is the principle hydroxylated fatty acid in human psoriatic skin scales, with a mean concentration of 17 ng/mg.{178}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38600 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
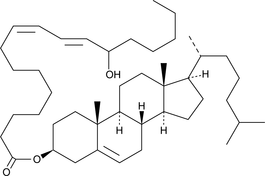
(±)13-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions{2227} and shown to be produced by Cu2+-catalyzed oxidation of LDL.{2228} Later studies determined that 15-LO from rabbit reticulocytes and human monocytes were able to metabolize cholesteryl linoleate, a major component of LDL, to 13-HODE cholesteryl ester.{1126,2412}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38601 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions{2227} and shown to be produced by Cu2+-catalyzed oxidation of LDL.{2228} Later studies determined that 15-LO from rabbit reticulocytes and human monocytes were able to metabolize cholesteryl linoleate, a major component of LDL, to 13-HODE cholesteryl ester.{1126,2412}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38601 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HODE cholesteryl ester was originally extracted from atherosclerotic lesions{2227} and shown to be produced by Cu2+-catalyzed oxidation of LDL.{2228} Later studies determined that 15-LO from rabbit reticulocytes and human monocytes were able to metabolize cholesteryl linoleate, a major component of LDL, to 13-HODE cholesteryl ester.{1126,2412}
Brand:CaymanSKU:38601 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HODE is one of the two racemic monohydroxy fatty acids resulting from the non-enzymatic oxidation of linoleic acid. It is the principle hydroxylated fatty acid in human psoriatic skin scales, with a mean concentration of 17 ng/mg.{178} (±)13-HODE MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of (±)13-HODE (Item No. 38600) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This (±)13-HODE MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26006 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HpODE is a racemic mixture of hydroperoxides derived non-enzymatically from linoleic acid through the action of reactive oxygen species. Lipid hydroperoxides, including 13-HpODE, have limited direct biological actions, such as the activation of lipoxygenases.{2686} Normally, (±)13-HpODE is rapidly reduced to (±)13-HODE, a compound which exhibits many biological activities.{4193} Importantly, 13-HpODE can also be metabolized to unsaturated aldehydes that can, in turn, covalently bind to DNA, amino acids, and proteins.{19115,19116,11490}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10704 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HpODE is a racemic mixture of hydroperoxides derived non-enzymatically from linoleic acid through the action of reactive oxygen species. Lipid hydroperoxides, including 13-HpODE, have limited direct biological actions, such as the activation of lipoxygenases.{2686} Normally, (±)13-HpODE is rapidly reduced to (±)13-HODE, a compound which exhibits many biological activities.{4193} Importantly, 13-HpODE can also be metabolized to unsaturated aldehydes that can, in turn, covalently bind to DNA, amino acids, and proteins.{19115,19116,11490}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10704 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HpODE is a racemic mixture of hydroperoxides derived non-enzymatically from linoleic acid through the action of reactive oxygen species. Lipid hydroperoxides, including 13-HpODE, have limited direct biological actions, such as the activation of lipoxygenases.{2686} Normally, (±)13-HpODE is rapidly reduced to (±)13-HODE, a compound which exhibits many biological activities.{4193} Importantly, 13-HpODE can also be metabolized to unsaturated aldehydes that can, in turn, covalently bind to DNA, amino acids, and proteins.{19115,19116,11490}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10704 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)13-HpODE is a racemic mixture of hydroperoxides derived non-enzymatically from linoleic acid through the action of reactive oxygen species. Lipid hydroperoxides, including 13-HpODE, have limited direct biological actions, such as the activation of lipoxygenases.{2686} Normally, (±)13-HpODE is rapidly reduced to (±)13-HODE, a compound which exhibits many biological activities.{4193} Importantly, 13-HpODE can also be metabolized to unsaturated aldehydes that can, in turn, covalently bind to DNA, amino acids, and proteins.{19115,19116,11490}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10704 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder