Chemicals
Showing 31951–32100 of 41137 results
-
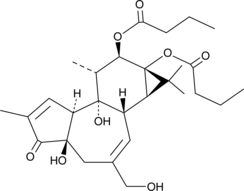
Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate is a phorbol ester and an activator of PKC, including group A (α and γ) and group B (δ, ε, η) PKC isoforms.{45312} It promotes tumor formation to a lesser degree than phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (TPA; Item No. 10008014).{45313} Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate induces papilloma formation in mice with a total dose of 9.7 µmol required to produce papillomas in 50% of survivors after eight weeks.{45314} It also induces inflammation in 50% of mice when administered topically to the ear at a dose of 0.067 µmol/ear.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27785 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate is a phorbol ester and an activator of PKC, including group A (α and γ) and group B (δ, ε, η) PKC isoforms.{45312} It promotes tumor formation to a lesser degree than phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (TPA; Item No. 10008014).{45313} Phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate induces papilloma formation in mice with a total dose of 9.7 µmol required to produce papillomas in 50% of survivors after eight weeks.{45314} It also induces inflammation in 50% of mice when administered topically to the ear at a dose of 0.067 µmol/ear.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27785 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
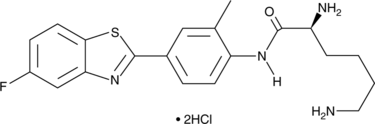
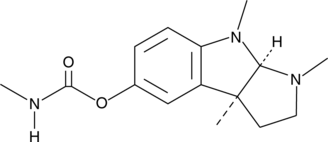
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor that promotes the expression of phase I and II xenobiotic chemical metabolizing enzyme genes, including the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms CYP1A1 and CYP1A2. Phortress is a lysyl amide prodrug of the benzothiazole 5-fluoro 203 (Item No. 17677), a high affinity AhR ligand that elicits antitumor activity by inducing transcription of CYP1A1, which leads to the formation of DNA adducts and cell cycle arrest.{29410,29411} Phortress rapidly reverts to 5-fluoro 203 in carcinoma cell lines, resulting in significant growth inhibition at nanomolar concentrations.{29411} At 20 mg/kg, phortress can suppress the growth of breast and ovarian xenografts in vivo.{29411}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor that promotes the expression of phase I and II xenobiotic chemical metabolizing enzyme genes, including the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms CYP1A1 and CYP1A2. Phortress is a lysyl amide prodrug of the benzothiazole 5-fluoro 203 (Item No. 17677), a high affinity AhR ligand that elicits antitumor activity by inducing transcription of CYP1A1, which leads to the formation of DNA adducts and cell cycle arrest.{29410,29411} Phortress rapidly reverts to 5-fluoro 203 in carcinoma cell lines, resulting in significant growth inhibition at nanomolar concentrations.{29411} At 20 mg/kg, phortress can suppress the growth of breast and ovarian xenografts in vivo.{29411}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-The aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) is a ligand-activated transcription factor that promotes the expression of phase I and II xenobiotic chemical metabolizing enzyme genes, including the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms CYP1A1 and CYP1A2. Phortress is a lysyl amide prodrug of the benzothiazole 5-fluoro 203 (Item No. 17677), a high affinity AhR ligand that elicits antitumor activity by inducing transcription of CYP1A1, which leads to the formation of DNA adducts and cell cycle arrest.{29410,29411} Phortress rapidly reverts to 5-fluoro 203 in carcinoma cell lines, resulting in significant growth inhibition at nanomolar concentrations.{29411} At 20 mg/kg, phortress can suppress the growth of breast and ovarian xenografts in vivo.{29411}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Phosmet is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide.{39994,39995,39996} It reduces apple damage by a large variety of insects, including apple maggots, codling moths, and obliquebanded leafrollers when used as either a border or cover spray at a concentration of 1.9 kg AI/hectare.{39995} Phosmet is effective in controlling S. scabiei in pigs when applied as a 20% pour-on solution.{39996} It is toxic to rats via oral administration (LC50 = 230 mg/kg).{39997} Formulations containing phosmet have been used in the control of insects and mites in agriculture.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25812 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosmet is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide.{39994,39995,39996} It reduces apple damage by a large variety of insects, including apple maggots, codling moths, and obliquebanded leafrollers when used as either a border or cover spray at a concentration of 1.9 kg AI/hectare.{39995} Phosmet is effective in controlling S. scabiei in pigs when applied as a 20% pour-on solution.{39996} It is toxic to rats via oral administration (LC50 = 230 mg/kg).{39997} Formulations containing phosmet have been used in the control of insects and mites in agriculture.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25812 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosmet is an organophosphate insecticide and acaricide.{39994,39995,39996} It reduces apple damage by a large variety of insects, including apple maggots, codling moths, and obliquebanded leafrollers when used as either a border or cover spray at a concentration of 1.9 kg AI/hectare.{39995} Phosmet is effective in controlling S. scabiei in pigs when applied as a 20% pour-on solution.{39996} It is toxic to rats via oral administration (LC50 = 230 mg/kg).{39997} Formulations containing phosmet have been used in the control of insects and mites in agriculture.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25812 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
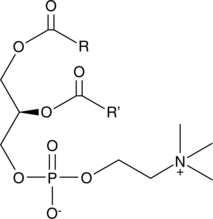
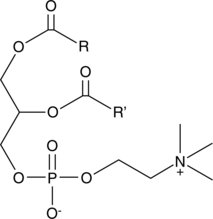
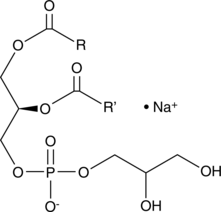
Phosphatidylcholine is the most abundant phospholipid in mammalian, plant, and yeast cells.{38744} It is found mainly in the outer leaflet of cell membranes and can make up approximately half of the total phospholipids.{139} In mammalian tissues, phosphatidylcholine commonly contains a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid at the C-1 and C-2 positions of glycerol, respectively. It is a substrate for various enzymes in cell signaling pathways that is cleaved by phospholipases into diacylglycerol and phosphocholine or phosphatidic acid and choline. Phosphatidylcholines (bovine) is a mixture of isolated bovine phosphatidylcholines with fatty acids of variable chain lengths acylated to the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1070]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24370 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylcholine is the most abundant phospholipid in mammalian, plant, and yeast cells.{38744} It is found mainly in the outer leaflet of cell membranes and can make up approximately half of the total phospholipids.{139} In mammalian tissues, phosphatidylcholine commonly contains a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid at the C-1 and C-2 positions of glycerol, respectively. It is a substrate for various enzymes in cell signaling pathways that is cleaved by phospholipases into diacylglycerol and phosphocholine or phosphatidic acid and choline. Phosphatidylcholines (egg) is a mixture of phosphatidylcholines isolated from chicken egg with fatty acids of variable chain lengths acylated to the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1044]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24343 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
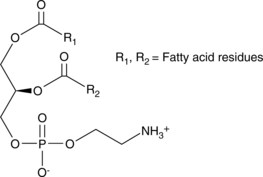
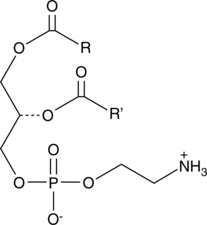
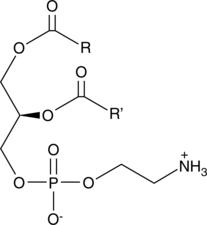
Phosphatidylethanolamine is the most abundant phospholipid in prokaryotes and the second most abundant found in the membrane of mammalian, plant, and yeast cells, comprising approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids.{24442} In the brain, phosphatidylethanolamine comprises almost half of the total phospholipids. It is synthesized mainly through the cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylation pathways, which occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, respectively. It is a precursor in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) and is a source of ethanolamine used in various cellular functions. In E. coli, phosphatidylethanolamine deficiency prevents proper assembly of lactose permease, suggesting a role as a lipid chaperone.{41481} It is a cofactor in the propagation of prions in vitro and can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules even in the absence of RNA.{41480} Phosphatidylethanolamines (bovine) is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from bovine brain with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1069]
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Phosphatidylethanolamine is the most abundant phospholipid in prokaryotes and the second most abundant found in the membrane of mammalian, plant, and yeast cells, comprising approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids.{24442} In the brain, phosphatidylethanolamine comprises almost half of the total phospholipids. It is synthesized mainly through the cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylation pathways, which occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, respectively. It is a precursor in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) and is a source of ethanolamine used in various cellular functions. In E. coli, phosphatidylethanolamine deficiency prevents proper assembly of lactose permease, suggesting a role as a lipid chaperone.{41481} It is a cofactor in the propagation of prions in vitro and can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules even in the absence of RNA.{41480} Phosphatidylethanolamines (bovine) is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from bovine brain with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1069]
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Phosphatidylethanolamine is the most abundant phospholipid in prokaryotes and the second most abundant found in the membrane of mammalian, plant, and yeast cells, comprising approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids.{24442} In the brain, phosphatidylethanolamine comprises almost half of the total phospholipids. It is synthesized mainly through the cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylation pathways, which occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, respectively. It is a precursor in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) and is a source of ethanolamine used in various cellular functions. In E. coli, phosphatidylethanolamine deficiency prevents proper assembly of lactose permease, suggesting a role as a lipid chaperone.{41481} It is a cofactor in the propagation of prions in vitro and can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules even in the absence of RNA.{41480} Phosphatidylethanolamines (bovine) is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from bovine brain with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1069]
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Phosphatidylethanolamine is the most abundant phospholipid in prokaryotes and the second most abundant found in the membrane of mammalian, plant, and yeast cells, comprising approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids.{24442} In the brain, phosphatidylethanolamine comprises almost half of the total phospholipids. It is synthesized mainly through the cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylation pathways, which occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, respectively. It is a precursor in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) and is a source of ethanolamine used in various cellular functions. In E. coli, phosphatidylethanolamine deficiency prevents proper assembly of lactose permease, suggesting a role as a lipid chaperone.{41481} It is a cofactor in the propagation of prions in vitro and can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules even in the absence of RNA.{41480} Phosphatidylethanolamines (bovine) is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from bovine brain with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1069]
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Phosphatidylethanolamine is the most abundant phospholipid in prokaryotes and the second most abundant found in the membrane of mammalian, plant, and yeast cells, comprising approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids.{24442} In the brain, phosphatidylethanolamine comprises almost half of the total phospholipids. It is synthesized mainly through the cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylation pathways, which occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, respectively. It is a precursor in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and arachidonoyl ethanolamide (Item No. 90050) and is a source of ethanolamine used in various cellular functions. In E. coli, phosphatidylethanolamine deficiency prevents proper assembly of lactose permease, suggesting a role as a lipid chaperone.{41481} It is a cofactor in the propagation of prions in vitro and can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules even in the absence of RNA.{41480} Phosphatidylethanolamines (egg) is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from egg with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1045]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24332 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylethanolamine is the most abundant phospholipid in prokaryotes and the second most abundant found in the membrane of mammalian, plant, and yeast cells, comprising approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids.{24442} In the brain, phosphatidylethanolamine comprises almost half of the total phospholipids. It is synthesized mainly through the cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylation pathways, which occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, respectively. It is a precursor in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and arachidonoyl ethanolamide (Item No. 90050) and is a source of ethanolamine used in various cellular functions. In E. coli, phosphatidylethanolamine deficiency prevents proper assembly of lactose permease, suggesting a role as a lipid chaperone.{41481} It is a cofactor in the propagation of prions in vitro and can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules even in the absence of RNA.{41480} Phosphatidylethanolamines (egg) is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from egg with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1045]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24332 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylethanolamine is the most abundant phospholipid in prokaryotes and the second most abundant found in the membrane of mammalian, plant, and yeast cells, comprising approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids.{24442} In the brain, phosphatidylethanolamine comprises almost half of the total phospholipids. It is synthesized mainly through the cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylation pathways, which occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, respectively. It is a precursor in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) and is a source of ethanolamine used in various cellular functions. In E. coli, phosphatidylethanolamine deficiency prevents proper assembly of lactose permease, suggesting a role as a lipid chaperone.{41481} It is a cofactor in the propagation of prions in vitro and can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules even in the absence of RNA.{41480} Phosphatidylethanolamines (soy) is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from soy with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25845 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylethanolamine is the most abundant phospholipid in prokaryotes and the second most abundant found in the membrane of mammalian, plant, and yeast cells, comprising approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids.{24442} In the brain, phosphatidylethanolamine comprises almost half of the total phospholipids. It is synthesized mainly through the cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylation pathways, which occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, respectively. It is a precursor in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) and is a source of ethanolamine used in various cellular functions. In E. coli, phosphatidylethanolamine deficiency prevents proper assembly of lactose permease, suggesting a role as a lipid chaperone.{41481} It is a cofactor in the propagation of prions in vitro and can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules even in the absence of RNA.{41480} Phosphatidylethanolamines (soy) is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from soy with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25845 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylethanolamine is the most abundant phospholipid in prokaryotes and the second most abundant found in the membrane of mammalian, plant, and yeast cells, comprising approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids.{24442} In the brain, phosphatidylethanolamine comprises almost half of the total phospholipids. It is synthesized mainly through the cytidine diphosphate-ethanolamine and phosphatidylserine decarboxylation pathways, which occur in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and mitochondrial membranes, respectively. It is a precursor in the synthesis of phosphatidylcholine and arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA; Item No. 90050) and is a source of ethanolamine used in various cellular functions. In E. coli, phosphatidylethanolamine deficiency prevents proper assembly of lactose permease, suggesting a role as a lipid chaperone.{41481} It is a cofactor in the propagation of prions in vitro and can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules even in the absence of RNA.{41480} Phosphatidylethanolamines (soy) is a mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from soy with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25845 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
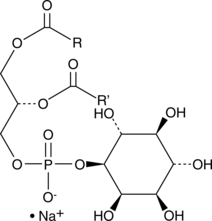
Phosphatidylglycerol is a naturally occurring anionic phospholipid and a constituent of plant, animal, and bacterial cell membranes.{48042,48043} It is less abundant than phosphatidylethanolamine (Item Nos. 16878 | 24332) in prokaryotes and eukaryotes and phosphatidylcholine (Item Nos. 24343 | 24370) in eukaryotes. It is formed via a reaction between CDP-diglyceride with L-α-glycerol 3-phosphate followed by dephosphorylation and is a metabolic precursor of cardiolipin.{48042} Phosphatidylglycerol species containing polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acyl chains inhibit and promote proliferation of murine keratinocytes, respectively.{48044} Phosphatidylglycerol is the second largest lipid component of mammalian lung surfactant, comprising 10% of the lipids, and levels are decreased in the lung surfactant of infants with respiratory distress syndrome.{48043} Phosphatidylglycerols (egg) is a mixture of phosphatidylglycerols isolated from egg with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25846 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylglycerol is a naturally occurring anionic phospholipid and a constituent of plant, animal, and bacterial cell membranes.{48042,48043} It is less abundant than phosphatidylethanolamine (Item Nos. 16878 | 24332) in prokaryotes and eukaryotes and phosphatidylcholine (Item Nos. 24343 | 24370) in eukaryotes. It is formed via a reaction between CDP-diglyceride with L-α-glycerol 3-phosphate followed by dephosphorylation and is a metabolic precursor of cardiolipin.{48042} Phosphatidylglycerol species containing polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acyl chains inhibit and promote proliferation of murine keratinocytes, respectively.{48044} Phosphatidylglycerol is the second largest lipid component of mammalian lung surfactant, comprising 10% of the lipids, and levels are decreased in the lung surfactant of infants with respiratory distress syndrome.{48043} Phosphatidylglycerols (egg) is a mixture of phosphatidylglycerols isolated from egg with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25846 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylglycerol is a naturally occurring anionic phospholipid and a constituent of plant, animal, and bacterial cell membranes.{48042,48043} It is less abundant than phosphatidylethanolamine (Item Nos. 16878 | 24332) in prokaryotes and eukaryotes and phosphatidylcholine (Item Nos. 24343 | 24370) in eukaryotes. It is formed via a reaction between CDP-diglyceride with L-α-glycerol 3-phosphate followed by dephosphorylation and is a metabolic precursor of cardiolipin.{48042} Phosphatidylglycerol species containing polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acyl chains inhibit and promote proliferation of murine keratinocytes, respectively.{48044} Phosphatidylglycerol is the second largest lipid component of mammalian lung surfactant, comprising 10% of the lipids, and levels are decreased in the lung surfactant of infants with respiratory distress syndrome.{48043} Phosphatidylglycerols (egg) is a mixture of phosphatidylglycerols isolated from egg with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25846 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylglycerol is a naturally occurring anionic phospholipid and a constituent of plant, animal, and bacterial cell membranes.{48042,48043} It is less abundant than phosphatidylethanolamine (Item Nos. 16878 | 24332) in prokaryotes and eukaryotes and phosphatidylcholine (Item Nos. 24343 | 24370) in eukaryotes. It is formed via a reaction between CDP-diglyceride with L-α-glycerol 3-phosphate followed by dephosphorylation and is a metabolic precursor of cardiolipin.{48042} Phosphatidylglycerol species containing polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fatty acyl chains inhibit and promote proliferation of murine keratinocytes, respectively.{48044} Phosphatidylglycerol is the second largest lipid component of mammalian lung surfactant, comprising 10% of the lipids, and levels are decreased in the lung surfactant of infants with respiratory distress syndrome.{48043} Phosphatidylglycerols (egg) is a mixture of phosphatidylglycerols isolated from egg with various fatty acyl groups at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25846 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylinositols are glycerophospholipids that contain a glycerol backbone, two non-polar fatty acid tails, and a polar inositol head group.{43000,43001} They are synthesized from cytidine diphosphate diacylglycerol (CPD-DAG) and myoinositol by phosphoinositol synthase and represent approximately 10% of total cellular phospholipids. Phosphatidylinositols can be phosphorylated on their inositol rings to produce phosphoinositides, which have been implicated in calcium regulation, vesicle trafficking, mitogenesis, cell survival, and rearrangement of actin. Phosphatidylinositols (soy) is a mixture of phosphatidylinositols isolated from soy that have variable fatty acyl chain lengths with linoleoyl being the most prevelant. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1336]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24523 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
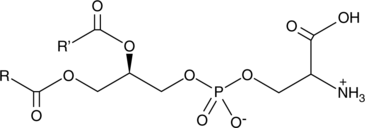
Phosphatidylserine is a naturally occurring phospholipid that comprises 2-10% of total phospholipids in mammals and is enriched in the central nervous system, particularly the retina.{38744} It is anionic and found mainly on the inner leaflet of the cell membrane. It is biosynthesized from phosphatidylcholine (Item Nos. 24343 | 24370) or phosphatidylethanolamine (Item No. 24332) by phosphatidyl synthase 1 (PSS1) or PSS2, respectively, in the endoplasmic reticulum and can be reversibly converted back by the same enzymes. It can also be irreversibly converted to phosphatidylethanolamine by phosphatidylserine decarboxylase in the mitochondria. Phosphatidylserine binds to T cell immunoglobulin mucin type 1 (TIM-1) and TIM-4 receptors as well as brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1), leading to anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic effects.{38745} It is also a cofactor involved in the activation of various signaling pathways through activation of protein kinase C, neutral sphingomyelinase, and c-Raf-1 protein kinase among others.{38744} Phosphatidylserine is externalized during apoptosis by scramblases in the plasma membrane as a signal for phagocytes to engulf the cell.{38746} Phosphatidylserines (bovine) is a mixture of bovine phosphatidylserines containing fatty acids with variable chain lengths at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1047]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24341 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylserine is a naturally occurring phospholipid that comprises 2-10% of total phospholipids in mammals and is enriched in the central nervous system, particularly the retina.{38744} It is anionic and found mainly on the inner leaflet of the cell membrane. It is biosynthesized from phosphatidylcholine (Item Nos. 24343 | 24370) or phosphatidylethanolamine (Item No. 24332) by phosphatidyl synthase 1 (PSS1) or PSS2, respectively, in the endoplasmic reticulum and can be reversibly converted back by the same enzymes. It can also be irreversibly converted to phosphatidylethanolamine by phosphatidylserine decarboxylase in the mitochondria. Phosphatidylserine binds to T cell immunoglobulin mucin type 1 (TIM-1) and TIM-4 receptors as well as brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1), leading to anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic effects.{38745} It is also a cofactor involved in the activation of various signaling pathways through activation of protein kinase C, neutral sphingomyelinase, and c-Raf-1 protein kinase among others.{38744} Phosphatidylserine is externalized during apoptosis by scramblases in the plasma membrane as a signal for phagocytes to engulf the cell.{38746} Phosphatidylserines (bovine) is a mixture of bovine phosphatidylserines containing fatty acids with variable chain lengths at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions. [Matreya, LLC. Catalog No. 1047]
Brand:CaymanSKU:24341 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
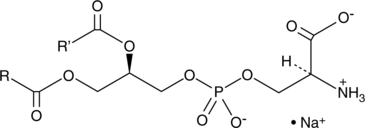
Phosphatidylserine is a naturally occurring phospholipid that comprises 2-10% of total phospholipids in mammals and is enriched in the central nervous system, particularly the retina.{38744} It is anionic and found mainly on the inner leaflet of the cell membrane. It is biosynthesized from phosphatidylcholine (Item Nos. 24343 | 24370) or phosphatidylethanolamine (Item Nos. 16878 | 24332) by phosphatidyl synthase 1 (PSS1) or PSS2, respectively, in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and can be reversibly converted back by the same enzymes. It can also be irreversibly converted to phosphatidylethanolamine by phosphatidylserine decarboxylase in the mitochondria. Phosphatidylserine binds to T cell immunoglobulin mucin type 1 (TIM-1) and TIM-4 receptors as well as brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1), leading to anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic effects.{38745} It is also a cofactor involved in the activation of various signaling pathways through activation of protein kinase C, neutral sphingomyelinase, and c-Raf-1 protein kinase among others.{38744} Phosphatidylserine is externalized during apoptosis by scramblases in the plasma membrane as a signal for phagocytes to engulf the cell.{38746} Phosphatidylserines (soy) is a mixture of soy phosphatidylserines containing fatty acids with variable chain lengths at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25847 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylserine is a naturally occurring phospholipid that comprises 2-10% of total phospholipids in mammals and is enriched in the central nervous system, particularly the retina.{38744} It is anionic and found mainly on the inner leaflet of the cell membrane. It is biosynthesized from phosphatidylcholine (Item Nos. 24343 | 24370) or phosphatidylethanolamine (Item Nos. 16878 | 24332) by phosphatidyl synthase 1 (PSS1) or PSS2, respectively, in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and can be reversibly converted back by the same enzymes. It can also be irreversibly converted to phosphatidylethanolamine by phosphatidylserine decarboxylase in the mitochondria. Phosphatidylserine binds to T cell immunoglobulin mucin type 1 (TIM-1) and TIM-4 receptors as well as brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1), leading to anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic effects.{38745} It is also a cofactor involved in the activation of various signaling pathways through activation of protein kinase C, neutral sphingomyelinase, and c-Raf-1 protein kinase among others.{38744} Phosphatidylserine is externalized during apoptosis by scramblases in the plasma membrane as a signal for phagocytes to engulf the cell.{38746} Phosphatidylserines (soy) is a mixture of soy phosphatidylserines containing fatty acids with variable chain lengths at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25847 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylserine is a naturally occurring phospholipid that comprises 2-10% of total phospholipids in mammals and is enriched in the central nervous system, particularly the retina.{38744} It is anionic and found mainly on the inner leaflet of the cell membrane. It is biosynthesized from phosphatidylcholine (Item Nos. 24343 | 24370) or phosphatidylethanolamine (Item Nos. 16878 | 24332) by phosphatidyl synthase 1 (PSS1) or PSS2, respectively, in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and can be reversibly converted back by the same enzymes. It can also be irreversibly converted to phosphatidylethanolamine by phosphatidylserine decarboxylase in the mitochondria. Phosphatidylserine binds to T cell immunoglobulin mucin type 1 (TIM-1) and TIM-4 receptors as well as brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1), leading to anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic effects.{38745} It is also a cofactor involved in the activation of various signaling pathways through activation of protein kinase C, neutral sphingomyelinase, and c-Raf-1 protein kinase among others.{38744} Phosphatidylserine is externalized during apoptosis by scramblases in the plasma membrane as a signal for phagocytes to engulf the cell.{38746} Phosphatidylserines (soy) is a mixture of soy phosphatidylserines containing fatty acids with variable chain lengths at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25847 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphatidylserine is a naturally occurring phospholipid that comprises 2-10% of total phospholipids in mammals and is enriched in the central nervous system, particularly the retina.{38744} It is anionic and found mainly on the inner leaflet of the cell membrane. It is biosynthesized from phosphatidylcholine (Item Nos. 24343 | 24370) or phosphatidylethanolamine (Item Nos. 16878 | 24332) by phosphatidyl synthase 1 (PSS1) or PSS2, respectively, in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and can be reversibly converted back by the same enzymes. It can also be irreversibly converted to phosphatidylethanolamine by phosphatidylserine decarboxylase in the mitochondria. Phosphatidylserine binds to T cell immunoglobulin mucin type 1 (TIM-1) and TIM-4 receptors as well as brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 1 (BAI1), leading to anti-inflammatory and anti-atherosclerotic effects.{38745} It is also a cofactor involved in the activation of various signaling pathways through activation of protein kinase C, neutral sphingomyelinase, and c-Raf-1 protein kinase among others.{38744} Phosphatidylserine is externalized during apoptosis by scramblases in the plasma membrane as a signal for phagocytes to engulf the cell.{38746} Phosphatidylserines (soy) is a mixture of soy phosphatidylserines containing fatty acids with variable chain lengths at the sn-1 and sn-2 positions.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25847 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
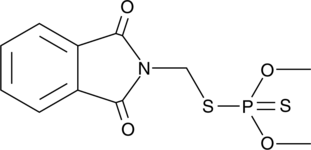
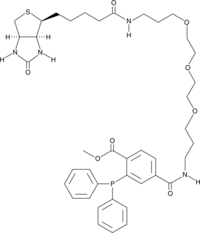
Labeling reactive centers of various types in cells with specific site-directed probes is a common method to explore both function and biochemical modification of proteins. The popular click chemistry method of protein labeling employs use of a reaction between an azido group and an alkyne on complimentary pairs of a specific reactive probe and a labeling agent (i.e. a tag) such as biotin or a fluorophore. The Staudinger ligation is an alternative to the click chemistry reaction in which a phosphine-labeled molecule reacts with an azido group on the opposing molecule of interest. Phosphine biotin is a labeling reagent that selectively reacts with azido groups on modified proteins through the Staudinger ligation reaction. Modified proteins can be detected using common avidin-based biochemical techniques in whole cells or by blotting experiments following SDS-PAGE. For example, phosphine-biotin has been used successfully in conjunction with DAz-1 or DAz-2 to label and detect sulfenic acid sites in proteins.{16660,16658}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Labeling reactive centers of various types in cells with specific site-directed probes is a common method to explore both function and biochemical modification of proteins. The popular click chemistry method of protein labeling employs use of a reaction between an azido group and an alkyne on complimentary pairs of a specific reactive probe and a labeling agent (i.e. a tag) such as biotin or a fluorophore. The Staudinger ligation is an alternative to the click chemistry reaction in which a phosphine-labeled molecule reacts with an azido group on the opposing molecule of interest. Phosphine biotin is a labeling reagent that selectively reacts with azido groups on modified proteins through the Staudinger ligation reaction. Modified proteins can be detected using common avidin-based biochemical techniques in whole cells or by blotting experiments following SDS-PAGE. For example, phosphine-biotin has been used successfully in conjunction with DAz-1 or DAz-2 to label and detect sulfenic acid sites in proteins.{16660,16658}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Labeling reactive centers of various types in cells with specific site-directed probes is a common method to explore both function and biochemical modification of proteins. The popular click chemistry method of protein labeling employs use of a reaction between an azido group and an alkyne on complimentary pairs of a specific reactive probe and a labeling agent (i.e. a tag) such as biotin or a fluorophore. The Staudinger ligation is an alternative to the click chemistry reaction in which a phosphine-labeled molecule reacts with an azido group on the opposing molecule of interest. Phosphine biotin is a labeling reagent that selectively reacts with azido groups on modified proteins through the Staudinger ligation reaction. Modified proteins can be detected using common avidin-based biochemical techniques in whole cells or by blotting experiments following SDS-PAGE. For example, phosphine-biotin has been used successfully in conjunction with DAz-1 or DAz-2 to label and detect sulfenic acid sites in proteins.{16660,16658}
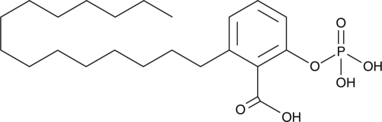
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Phospho-ginkgolic acid is an agonist of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1).{50772} Phospho-ginkgolic acid (10 μM) induces S1P1 receptor internalization and increases ERK phosphorylation in a concentration-dependent manner in CHO cells expressing S1P1.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29638 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Phospho-ginkgolic acid is an agonist of sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor 1 (S1P1).{50772} Phospho-ginkgolic acid (10 μM) induces S1P1 receptor internalization and increases ERK phosphorylation in a concentration-dependent manner in CHO cells expressing S1P1.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29638 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor is an inhibitor of PDE4 with an IC50 value of 0.10 μM for the human recombinant enzyme.{35290}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21191 -Out of stock
Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor is an inhibitor of PDE4 with an IC50 value of 0.10 μM for the human recombinant enzyme.{35290}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21191 -Out of stock
Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor is an inhibitor of PDE4 with an IC50 value of 0.10 μM for the human recombinant enzyme.{35290}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21191 -Out of stock
Phosphodiesterase 4 (PDE4) inhibitor is an inhibitor of PDE4 with an IC50 value of 0.10 μM for the human recombinant enzyme.{35290}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21191 -Out of stock
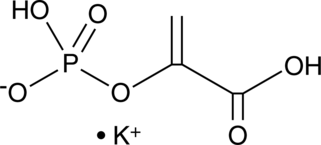
Phosphoenolpyruvic acid plays a role in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. During glycolysis, it is formed by the action of enolase on 2-phosphoglycerate and is metabolized to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase.{21440} One molecule of ATP is formed during its metabolism in this pathway. During gluconeogenesis, it is formed from phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-catalyzed oxaloacetate decarboxylation and GTP hydrolysis.{21440,21442,26065} In plants, it is metabolized to form aromatic amino acids and also serves as a substrate for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase-catalyzed carbon fixation.{21441}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Phosphoenolpyruvic acid plays a role in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. During glycolysis, it is formed by the action of enolase on 2-phosphoglycerate and is metabolized to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase.{21440} One molecule of ATP is formed during its metabolism in this pathway. During gluconeogenesis, it is formed from phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-catalyzed oxaloacetate decarboxylation and GTP hydrolysis.{21440,21442,26065} In plants, it is metabolized to form aromatic amino acids and also serves as a substrate for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase-catalyzed carbon fixation.{21441}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Phosphoenolpyruvic acid plays a role in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. During glycolysis, it is formed by the action of enolase on 2-phosphoglycerate and is metabolized to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase.{21440} One molecule of ATP is formed during its metabolism in this pathway. During gluconeogenesis, it is formed from phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-catalyzed oxaloacetate decarboxylation and GTP hydrolysis.{21440,21442,26065} In plants, it is metabolized to form aromatic amino acids and also serves as a substrate for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase-catalyzed carbon fixation.{21441}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Phosphoenolpyruvic acid plays a role in both glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. During glycolysis, it is formed by the action of enolase on 2-phosphoglycerate and is metabolized to pyruvate by pyruvate kinase.{21440} One molecule of ATP is formed during its metabolism in this pathway. During gluconeogenesis, it is formed from phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase-catalyzed oxaloacetate decarboxylation and GTP hydrolysis.{21440,21442,26065} In plants, it is metabolized to form aromatic amino acids and also serves as a substrate for phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase-catalyzed carbon fixation.{21441}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Enzymatic method the determination of phospholipids- lecithin, lysolecithin, and sphingomyelin in serum.
Brand:FUJIFILM Medical Systems USASKU:997-01801Available on backorder
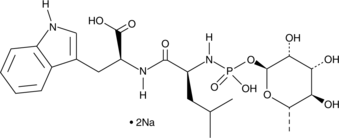
Neprilysin (NEP) and NEP2 are membrane-bound zinc metalloproteases.{24074,24072} Phosphoramidon is a natural and potent inhibitor of NEP and NEP2, with Ki values of 2 nM for both enzymes.{24073,24074} It is also a weak inhibitor of the related zinc metalloprotease endothelin-converting enzyme (Ki = 3.5 µM).{24082} Phosphoramidon has little or no effect on a variety of other proteases, including trypsin, papain, chymotrypsin, pepsin, and angiotensin-converting enzyme.{24073}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Neprilysin (NEP) and NEP2 are membrane-bound zinc metalloproteases.{24074,24072} Phosphoramidon is a natural and potent inhibitor of NEP and NEP2, with Ki values of 2 nM for both enzymes.{24073,24074} It is also a weak inhibitor of the related zinc metalloprotease endothelin-converting enzyme (Ki = 3.5 µM).{24082} Phosphoramidon has little or no effect on a variety of other proteases, including trypsin, papain, chymotrypsin, pepsin, and angiotensin-converting enzyme.{24073}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Neprilysin (NEP) and NEP2 are membrane-bound zinc metalloproteases.{24074,24072} Phosphoramidon is a natural and potent inhibitor of NEP and NEP2, with Ki values of 2 nM for both enzymes.{24073,24074} It is also a weak inhibitor of the related zinc metalloprotease endothelin-converting enzyme (Ki = 3.5 µM).{24082} Phosphoramidon has little or no effect on a variety of other proteases, including trypsin, papain, chymotrypsin, pepsin, and angiotensin-converting enzyme.{24073}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Neprilysin (NEP) and NEP2 are membrane-bound zinc metalloproteases.{24074,24072} Phosphoramidon is a natural and potent inhibitor of NEP and NEP2, with Ki values of 2 nM for both enzymes.{24073,24074} It is also a weak inhibitor of the related zinc metalloprotease endothelin-converting enzyme (Ki = 3.5 µM).{24082} Phosphoramidon has little or no effect on a variety of other proteases, including trypsin, papain, chymotrypsin, pepsin, and angiotensin-converting enzyme.{24073}
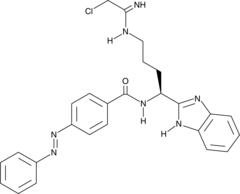
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Photoswitchable PAD inhibitor is a photoactivated protein arginine deiminase (PAD) inhibitor and a derivative of BB-Cl-amidine (Item No. 17079) that contains an azobenzene photoswitch allowing optical control of PAD activity.{35916} Without photoactivation, it is a weak inhibitor of PAD2 (IC50 = >100 µM) and is less potent than BB-Cl-amidine in inhibiting citrulline production in vitro (kinact/KIs = 2,300, 600, 1,000, and 10,510 M-1min-1 for PAD1-4, respectively) and does not inhibit histone H3 citrullination in HEK293T cells overexpressing PAD2 when used at concentrations up to 100 µM. However, it can rapidly be photoactivated with UV-A radiation to the more active cis-isomer, which is an irreversible, competitive inhibitor of histone H3 citrullination with an IC50 value of 9.1 µM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28104 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Photoswitchable PAD inhibitor is a photoactivated protein arginine deiminase (PAD) inhibitor and a derivative of BB-Cl-amidine (Item No. 17079) that contains an azobenzene photoswitch allowing optical control of PAD activity.{35916} Without photoactivation, it is a weak inhibitor of PAD2 (IC50 = >100 µM) and is less potent than BB-Cl-amidine in inhibiting citrulline production in vitro (kinact/KIs = 2,300, 600, 1,000, and 10,510 M-1min-1 for PAD1-4, respectively) and does not inhibit histone H3 citrullination in HEK293T cells overexpressing PAD2 when used at concentrations up to 100 µM. However, it can rapidly be photoactivated with UV-A radiation to the more active cis-isomer, which is an irreversible, competitive inhibitor of histone H3 citrullination with an IC50 value of 9.1 µM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28104 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Photoswitchable PAD inhibitor is a photoactivated protein arginine deiminase (PAD) inhibitor and a derivative of BB-Cl-amidine (Item No. 17079) that contains an azobenzene photoswitch allowing optical control of PAD activity.{35916} Without photoactivation, it is a weak inhibitor of PAD2 (IC50 = >100 µM) and is less potent than BB-Cl-amidine in inhibiting citrulline production in vitro (kinact/KIs = 2,300, 600, 1,000, and 10,510 M-1min-1 for PAD1-4, respectively) and does not inhibit histone H3 citrullination in HEK293T cells overexpressing PAD2 when used at concentrations up to 100 µM. However, it can rapidly be photoactivated with UV-A radiation to the more active cis-isomer, which is an irreversible, competitive inhibitor of histone H3 citrullination with an IC50 value of 9.1 µM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28104 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
PHPS1 is a cell-permeable, phosphotyrosine mimetic that inhibits the Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase (SHP)-2 (IC50 = 2.1 µM; Ki = 0.73 µM).{31309} It is selective for SHP-2, inhibiting ECPTP, PTP1B, SHP-1, and mycobacterium MptpA at relatively higher concentrations (IC50s = 5.4, 19, 30, and 39 µM, respectively).{31309} PHPS1 has been shown to inhibit SHP-2-dependent cellular signaling and tumor cell colony formation.{31309}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
PHPS1 is a cell-permeable, phosphotyrosine mimetic that inhibits the Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase (SHP)-2 (IC50 = 2.1 µM; Ki = 0.73 µM).{31309} It is selective for SHP-2, inhibiting ECPTP, PTP1B, SHP-1, and mycobacterium MptpA at relatively higher concentrations (IC50s = 5.4, 19, 30, and 39 µM, respectively).{31309} PHPS1 has been shown to inhibit SHP-2-dependent cellular signaling and tumor cell colony formation.{31309}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
PHPS1 is a cell-permeable, phosphotyrosine mimetic that inhibits the Src homology region 2 domain-containing phosphatase (SHP)-2 (IC50 = 2.1 µM; Ki = 0.73 µM).{31309} It is selective for SHP-2, inhibiting ECPTP, PTP1B, SHP-1, and mycobacterium MptpA at relatively higher concentrations (IC50s = 5.4, 19, 30, and 39 µM, respectively).{31309} PHPS1 has been shown to inhibit SHP-2-dependent cellular signaling and tumor cell colony formation.{31309}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
PHT-427 is an inhibitor of the serine/threonine kinases Akt and phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDPK1) with Ki values of 2.7 and 5.2 μM, respectively, that selectively binds to the pleckstrin homology binding domain of both kinases.{38927} PHT-427 (10 µM) inhibits PDPK1 and Akt autophosphorylation in BxPC-3 prostate cancer cells. In vivo, PHT-427 (125-250 mg/kg) reduces tumor growth in BxPC-3, Panc-1, MiaPaCa-2, PC3, SK-OV-3, A549, and MCF-7 xenograft mouse models, with up to 80% reduction in growth for those containing PIK3CA mutations. PHT-427 (200 mg/kg) also enhances the antitumor effect of paclitaxel (Item No. 10461) in an MCF-7 breast cancer xenograft mouse model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:24188 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
PHT-427 is an inhibitor of the serine/threonine kinases Akt and phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDPK1) with Ki values of 2.7 and 5.2 μM, respectively, that selectively binds to the pleckstrin homology binding domain of both kinases.{38927} PHT-427 (10 µM) inhibits PDPK1 and Akt autophosphorylation in BxPC-3 prostate cancer cells. In vivo, PHT-427 (125-250 mg/kg) reduces tumor growth in BxPC-3, Panc-1, MiaPaCa-2, PC3, SK-OV-3, A549, and MCF-7 xenograft mouse models, with up to 80% reduction in growth for those containing PIK3CA mutations. PHT-427 (200 mg/kg) also enhances the antitumor effect of paclitaxel (Item No. 10461) in an MCF-7 breast cancer xenograft mouse model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:24188 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
PHT-427 is an inhibitor of the serine/threonine kinases Akt and phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDPK1) with Ki values of 2.7 and 5.2 μM, respectively, that selectively binds to the pleckstrin homology binding domain of both kinases.{38927} PHT-427 (10 µM) inhibits PDPK1 and Akt autophosphorylation in BxPC-3 prostate cancer cells. In vivo, PHT-427 (125-250 mg/kg) reduces tumor growth in BxPC-3, Panc-1, MiaPaCa-2, PC3, SK-OV-3, A549, and MCF-7 xenograft mouse models, with up to 80% reduction in growth for those containing PIK3CA mutations. PHT-427 (200 mg/kg) also enhances the antitumor effect of paclitaxel (Item No. 10461) in an MCF-7 breast cancer xenograft mouse model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:24188 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
PHT-427 is an inhibitor of the serine/threonine kinases Akt and phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase-1 (PDPK1) with Ki values of 2.7 and 5.2 μM, respectively, that selectively binds to the pleckstrin homology binding domain of both kinases.{38927} PHT-427 (10 µM) inhibits PDPK1 and Akt autophosphorylation in BxPC-3 prostate cancer cells. In vivo, PHT-427 (125-250 mg/kg) reduces tumor growth in BxPC-3, Panc-1, MiaPaCa-2, PC3, SK-OV-3, A549, and MCF-7 xenograft mouse models, with up to 80% reduction in growth for those containing PIK3CA mutations. PHT-427 (200 mg/kg) also enhances the antitumor effect of paclitaxel (Item No. 10461) in an MCF-7 breast cancer xenograft mouse model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:24188 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Three Aurora kinases, A-C, are involved in phosphorylation events that are critical for the completion of mitosis.{19817} Aurora A, involved in centrosomal assembly and acentrosomal spindle assembly, is overexpressed in many tumors.{19818} Phthalazinone pyrazole is a potent inhibitor of Aurora A kinase (IC50 = 31 nM).{19005} It does not inhibit Aurora B kinase at doses up to 100 μM.{19005} Phthalazinone pyrazole inhibits the proliferation of HCT116, COLO 205, and MCF-7 cells (IC50 = 7.8, 2.9, and 1.6 μM, respectively).{19005}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10735 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Three Aurora kinases, A-C, are involved in phosphorylation events that are critical for the completion of mitosis.{19817} Aurora A, involved in centrosomal assembly and acentrosomal spindle assembly, is overexpressed in many tumors.{19818} Phthalazinone pyrazole is a potent inhibitor of Aurora A kinase (IC50 = 31 nM).{19005} It does not inhibit Aurora B kinase at doses up to 100 μM.{19005} Phthalazinone pyrazole inhibits the proliferation of HCT116, COLO 205, and MCF-7 cells (IC50 = 7.8, 2.9, and 1.6 μM, respectively).{19005}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10735 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Three Aurora kinases, A-C, are involved in phosphorylation events that are critical for the completion of mitosis.{19817} Aurora A, involved in centrosomal assembly and acentrosomal spindle assembly, is overexpressed in many tumors.{19818} Phthalazinone pyrazole is a potent inhibitor of Aurora A kinase (IC50 = 31 nM).{19005} It does not inhibit Aurora B kinase at doses up to 100 μM.{19005} Phthalazinone pyrazole inhibits the proliferation of HCT116, COLO 205, and MCF-7 cells (IC50 = 7.8, 2.9, and 1.6 μM, respectively).{19005}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10735 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
PHTPP is a pyrazolo[1,5-α]pyrimidine-based ligand that acts as a full antagonist of estrogen ERβ receptors with 36-fold selectivity over ERα.{28105} It exhibits no significant agonism on ERα or ERβ.{28105} This compound has been used to selectively target ERβ in the study of the opposing effects of hormone therapy on tumors expressing either ER subtype. At 100 pM, PHTPP has been found to enhance SKOV3 and OV2008 ovarian cancer cell growth in in vitro assays.{28106}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-PHTPP is a pyrazolo[1,5-α]pyrimidine-based ligand that acts as a full antagonist of estrogen ERβ receptors with 36-fold selectivity over ERα.{28105} It exhibits no significant agonism on ERα or ERβ.{28105} This compound has been used to selectively target ERβ in the study of the opposing effects of hormone therapy on tumors expressing either ER subtype. At 100 pM, PHTPP has been found to enhance SKOV3 and OV2008 ovarian cancer cell growth in in vitro assays.{28106}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-PHTPP is a pyrazolo[1,5-α]pyrimidine-based ligand that acts as a full antagonist of estrogen ERβ receptors with 36-fold selectivity over ERα.{28105} It exhibits no significant agonism on ERα or ERβ.{28105} This compound has been used to selectively target ERβ in the study of the opposing effects of hormone therapy on tumors expressing either ER subtype. At 100 pM, PHTPP has been found to enhance SKOV3 and OV2008 ovarian cancer cell growth in in vitro assays.{28106}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-PHTPP is a pyrazolo[1,5-α]pyrimidine-based ligand that acts as a full antagonist of estrogen ERβ receptors with 36-fold selectivity over ERα.{28105} It exhibits no significant agonism on ERα or ERβ.{28105} This compound has been used to selectively target ERβ in the study of the opposing effects of hormone therapy on tumors expressing either ER subtype. At 100 pM, PHTPP has been found to enhance SKOV3 and OV2008 ovarian cancer cell growth in in vitro assays.{28106}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Phyllanthin is a major bioactive lignan component of P. amarus with antioxidative and hepatoprotective properties. It scavenges DPPH radicals with an IC50 value of 7.4 µM and, at 30 µM, has been shown to alleviate carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation and cytotoxicity in a human hepatoma HepG2 cell line.{29183}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11745 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Phyllanthin is a major bioactive lignan component of P. amarus with antioxidative and hepatoprotective properties. It scavenges DPPH radicals with an IC50 value of 7.4 µM and, at 30 µM, has been shown to alleviate carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation and cytotoxicity in a human hepatoma HepG2 cell line.{29183}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11745 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Phyllanthin is a major bioactive lignan component of P. amarus with antioxidative and hepatoprotective properties. It scavenges DPPH radicals with an IC50 value of 7.4 µM and, at 30 µM, has been shown to alleviate carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation and cytotoxicity in a human hepatoma HepG2 cell line.{29183}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11745 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Phyllanthin is a major bioactive lignan component of P. amarus with antioxidative and hepatoprotective properties. It scavenges DPPH radicals with an IC50 value of 7.4 µM and, at 30 µM, has been shown to alleviate carbon tetrachloride-induced lipid peroxidation and cytotoxicity in a human hepatoma HepG2 cell line.{29183}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11745 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Physcion is a natural anthraquinone. It has been reported to have laxative and anti-inflammatory actions, inhibit kinases and tyrosinase, and have cytotoxicity against cancer cells.{32205} Physcion inhibits 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (IC50 = 38.5 µM), decreasing lipogenesis and RNA biosynthesis in cancer cells, leading to reduced cell proliferation and tumor growth in mice.{32206}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19863 -Available on backorder
Physcion is a natural anthraquinone. It has been reported to have laxative and anti-inflammatory actions, inhibit kinases and tyrosinase, and have cytotoxicity against cancer cells.{32205} Physcion inhibits 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (IC50 = 38.5 µM), decreasing lipogenesis and RNA biosynthesis in cancer cells, leading to reduced cell proliferation and tumor growth in mice.{32206}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19863 -Available on backorder
Physcion is a natural anthraquinone. It has been reported to have laxative and anti-inflammatory actions, inhibit kinases and tyrosinase, and have cytotoxicity against cancer cells.{32205} Physcion inhibits 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (IC50 = 38.5 µM), decreasing lipogenesis and RNA biosynthesis in cancer cells, leading to reduced cell proliferation and tumor growth in mice.{32206}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19863 -Available on backorder
Physcion is a natural anthraquinone. It has been reported to have laxative and anti-inflammatory actions, inhibit kinases and tyrosinase, and have cytotoxicity against cancer cells.{32205} Physcion inhibits 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase (IC50 = 38.5 µM), decreasing lipogenesis and RNA biosynthesis in cancer cells, leading to reduced cell proliferation and tumor growth in mice.{32206}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19863 -Available on backorder
Physostigmine is a natural, reversible cholinesterase (ChE) inhibitor that inhibits both acetyl ChE and butyryl ChE (IC50s = 28 and 16 nM, respectively).{24084,24085} ChE inhibitors, including physostigmine, have potential value in ameliorating dementia associated with neurodegenerative diseases.{18344,23018,24086,24083}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13027 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Physostigmine is a natural, reversible cholinesterase (ChE) inhibitor that inhibits both acetyl ChE and butyryl ChE (IC50s = 28 and 16 nM, respectively).{24084,24085} ChE inhibitors, including physostigmine, have potential value in ameliorating dementia associated with neurodegenerative diseases.{18344,23018,24086,24083}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13027 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Physostigmine is a natural, reversible cholinesterase (ChE) inhibitor that inhibits both acetyl ChE and butyryl ChE (IC50s = 28 and 16 nM, respectively).{24084,24085} ChE inhibitors, including physostigmine, have potential value in ameliorating dementia associated with neurodegenerative diseases.{18344,23018,24086,24083}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13027 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Physostigmine is a natural, reversible cholinesterase (ChE) inhibitor that inhibits both acetyl ChE and butyryl ChE (IC50s = 28 and 16 nM, respectively).{24084,24085} ChE inhibitors, including physostigmine, have potential value in ameliorating dementia associated with neurodegenerative diseases.{18344,23018,24086,24083}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13027 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
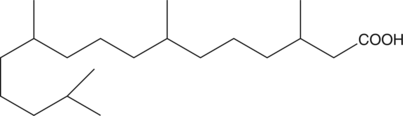
Phytanic acid is a saturated 20-carbon branched-chain fatty acid which can only be derived from dietary sources. In cases of peroxisomal disorders, elevated levels of phytanic acid have been observed, and this is linked to diseases such as infantile phytanic acid storage disease and Refsum’s disease.{1912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90360 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Phytanic acid is a saturated 20-carbon branched-chain fatty acid which can only be derived from dietary sources. In cases of peroxisomal disorders, elevated levels of phytanic acid have been observed, and this is linked to diseases such as infantile phytanic acid storage disease and Refsum’s disease.{1912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90360 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Phytanic acid is a saturated 20-carbon branched-chain fatty acid which can only be derived from dietary sources. In cases of peroxisomal disorders, elevated levels of phytanic acid have been observed, and this is linked to diseases such as infantile phytanic acid storage disease and Refsum’s disease.{1912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90360 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Phytanic acid is a saturated 20-carbon branched-chain fatty acid which can only be derived from dietary sources. In cases of peroxisomal disorders, elevated levels of phytanic acid have been observed, and this is linked to diseases such as infantile phytanic acid storage disease and Refsum’s disease.{1912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90360 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder