Chemicals
Showing 30751–30900 of 41137 results
-
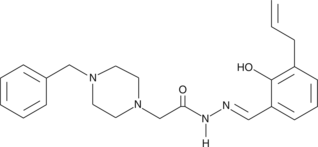
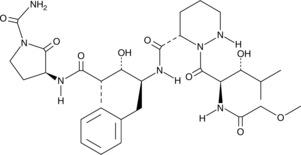
Apoptosis can be induced when procaspase-3 is activated and converted to caspase-3. Procaspase-activating compound 1 (PAC-1) is a procaspase-3 activator and a potential drug treatment in cancer cell lines with elevated levels of procaspase-3.{14401} PAC-1’s effectiveness was found to be directly proportional to the procaspase-3 concentration present in cells. In cancer cells, PAC-1 had an IC50 value of 3 nM for induction of cell death, whereas in cells from adjacent normal tissue IC50 values of 3.2-8.5 µM were observed.{14401}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009317 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
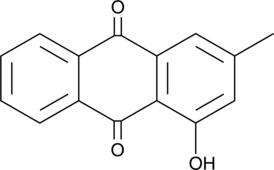
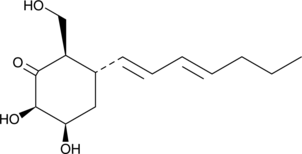
Pachybasin is an anthraquinone fungal metabolite.{48175,48176,48177} It inhibits the growth of E. coli, S. aureus, B. subtilis, and M. luteus bacteria (MICs = 64, 32, 64, and 64 μg/ml, respectively) and C. albicans, S. cerevisiae, A. niger, A. flavus, and F. oxysporum fungi (MICs = 64, 64, 64, 64, and 16 μg/ml, respectively).{48175} It also induces germ tube malformation in B. graminis fungi.{48176} Pachybasin induces developmental retardation and notochord distortions and increases mortality in zebrafish embryos when used at concentrations ranging from 1 to 100 μM.{48177}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27268 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
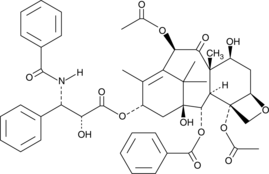
Paclitaxel, a potent disruptor of microtubules derived from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, is widely used as a chemotherapeutic compound. Tested against a panel of cervical (HeLa), lung (A549), breast (MCF-7), colon (HT-29), ovarian (OVG-1), and pancreatic (PC-Sh) carcinomas, paclitaxel demonstrates IC50 values ranging from 2.5-7.5 nM.{18505} Paclitaxel disrupts multipolar spindle formation, inducing cell cycle arrest in various human cell cancer lines (IC50s = 6.7-18.5 nM) at both prophase and G1.{18494} It initiates apoptosis of cancer cells through multiple mechanisms involving p53-dependent and -independent pathways, Bcl-2 family members, cyclin-dependent kinases, and c-Jun N-terminal kinases/stress-activated protein kinases.{18495}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10461 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
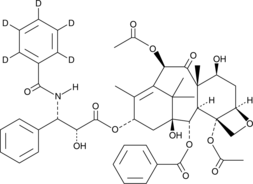
Paclitaxel, a potent disruptor of microtubules derived from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, is widely used as a chemotherapeutic compound. Tested against a panel of cervical (HeLa), lung (A549), breast (MCF-7), colon (HT-29), ovarian (OVG-1), and pancreatic (PC-Sh) carcinomas, paclitaxel demonstrates IC50 values ranging from 2.5-7.5 nM.{18505} Paclitaxel disrupts multipolar spindle formation, inducing cell cycle arrest in various human cell cancer lines (IC50s = 6.7-18.5 nM) at both prophase and G1.{18494} It initiates apoptosis of cancer cells through multiple mechanisms involving p53-dependent and -independent pathways, Bcl-2 family members, cyclin-dependent kinases, and c-Jun N-terminal kinases/stress-activated protein kinases.{18495}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10461 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Paclitaxel, a potent disruptor of microtubules derived from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, is widely used as a chemotherapeutic compound. Tested against a panel of cervical (HeLa), lung (A549), breast (MCF-7), colon (HT-29), ovarian (OVG-1), and pancreatic (PC-Sh) carcinomas, paclitaxel demonstrates IC50 values ranging from 2.5-7.5 nM.{18505} Paclitaxel disrupts multipolar spindle formation, inducing cell cycle arrest in various human cell cancer lines (IC50s = 6.7-18.5 nM) at both prophase and G1.{18494} It initiates apoptosis of cancer cells through multiple mechanisms involving p53-dependent and -independent pathways, Bcl-2 family members, cyclin-dependent kinases, and c-Jun N-terminal kinases/stress-activated protein kinases.{18495}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10461 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Paclitaxel, a potent disruptor of microtubules derived from the bark of the Pacific yew tree, is widely used as a chemotherapeutic compound. Tested against a panel of cervical (HeLa), lung (A549), breast (MCF-7), colon (HT-29), ovarian (OVG-1), and pancreatic (PC-Sh) carcinomas, paclitaxel demonstrates IC50 values ranging from 2.5-7.5 nM.{18505} Paclitaxel disrupts multipolar spindle formation, inducing cell cycle arrest in various human cell cancer lines (IC50s = 6.7-18.5 nM) at both prophase and G1.{18494} It initiates apoptosis of cancer cells through multiple mechanisms involving p53-dependent and -independent pathways, Bcl-2 family members, cyclin-dependent kinases, and c-Jun N-terminal kinases/stress-activated protein kinases.{18495}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10461 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
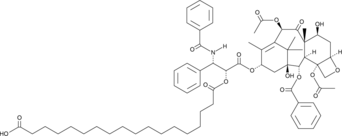
Paclitaxel octadecanedioate is a prodrug form of paclitaxel (Item No. 10461) that is comprised of paclitaxel conjugated to 1,18-octadecanedioic acid.{50209} Unlike paclitaxel, it does not promote tubulin polymerization in vitro when used at a concentration of 10 μM. A 5:1 mixture of paclitaxel octadecanedioate:human serum albumin (HSA) is cytotoxic to HT-1080, PANC-1, and HT-29 cells (IC50s = 12, 2.48, and 8.62 nM, respectively). This mixture reduces tumor growth and increases survival in an HT-1080 mouse xenograft model in a dose-dependent manner.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28635 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Paclitaxel octadecanedioate is a prodrug form of paclitaxel (Item No. 10461) that is comprised of paclitaxel conjugated to 1,18-octadecanedioic acid.{50209} Unlike paclitaxel, it does not promote tubulin polymerization in vitro when used at a concentration of 10 μM. A 5:1 mixture of paclitaxel octadecanedioate:human serum albumin (HSA) is cytotoxic to HT-1080, PANC-1, and HT-29 cells (IC50s = 12, 2.48, and 8.62 nM, respectively). This mixture reduces tumor growth and increases survival in an HT-1080 mouse xenograft model in a dose-dependent manner.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28635 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Paclitaxel octadecanedioate is a prodrug form of paclitaxel (Item No. 10461) that is comprised of paclitaxel conjugated to 1,18-octadecanedioic acid.{50209} Unlike paclitaxel, it does not promote tubulin polymerization in vitro when used at a concentration of 10 μM. A 5:1 mixture of paclitaxel octadecanedioate:human serum albumin (HSA) is cytotoxic to HT-1080, PANC-1, and HT-29 cells (IC50s = 12, 2.48, and 8.62 nM, respectively). This mixture reduces tumor growth and increases survival in an HT-1080 mouse xenograft model in a dose-dependent manner.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28635 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Paclitaxel octadecanedioate is a prodrug form of paclitaxel (Item No. 10461) that is comprised of paclitaxel conjugated to 1,18-octadecanedioic acid.{50209} Unlike paclitaxel, it does not promote tubulin polymerization in vitro when used at a concentration of 10 μM. A 5:1 mixture of paclitaxel octadecanedioate:human serum albumin (HSA) is cytotoxic to HT-1080, PANC-1, and HT-29 cells (IC50s = 12, 2.48, and 8.62 nM, respectively). This mixture reduces tumor growth and increases survival in an HT-1080 mouse xenograft model in a dose-dependent manner.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28635 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Paclitaxel-d5 contains five deuterium atoms. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of paclitaxel (Item No. 10461) using GC- or LC-MS. Paclitaxel is cytotoxic against a variety of cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 2.5-7.5 nM.{18505} It disrupts multipolar spindle formation, inducing cell cycle arrest in various human cell cancer lines (IC50s = 6.7-18.5 nM) at both prophase and G1.{18494} It also initiates apoptosis of cancer cells through multiple mechanisms involving p53-dependent and -independent pathways, Bcl-2 family members, cyclin-dependent kinases, and c-Jun N-terminal kinases/stress-activated protein kinases.{18495}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22092 -Out of stock
Paclobutrazol (PBZ) is a triazole-containing plant growth retardant that is known to inhibit the biosynthesis of gibberellins.{30671,21397} It also has antifungal activities.{30669} PBZ, which is transported acropetally in plants, can also suppress the synthesis of abscisic acid and induce chilling tolerance in plants.{30671,30667,30668} PBZ is typically used to support research on the role of gibberellins in plant biology.{30670,30666}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) and Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) are tyrosine kinases that mediate cytokine signaling and are frequently mutated in cancers, particularly acute myeloid leukemia.{27422,27424} Pacritinib is an inhibitor of both FLT3 and JAK2 (IC50s = 22 and 23 nM, respectively).{27422} It also blocks the activities of the FLT3 D835Y mutant, FLT3 with internal tandem duplications (ITDs), and JAK2 with a V617F substitution (IC50s = 6, 20-180, and 220 nM, respectively).{27422} Pacritinib also inhibits JAK1, JAK3, and TYK2 (IC50s = 1280, 520, and 50 nM, respectively).{27422} Pacritinib is orally bioavailable, inhibiting FLT3 and JAK2 signaling, tumor growth, and metastasis in xenografts in mice.{27422} It is synergistic with the histone deacetylase inhibitor pracinostat (also known as SB 939, Item No. 10443), decreasing cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis in cells carrying either the JAK2 V617F mutation or FLT3 with ITDs, both in vitro and in vivo.{27423} Pacritinib has potential in resolving hematological malignancies.{27424}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) and Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) are tyrosine kinases that mediate cytokine signaling and are frequently mutated in cancers, particularly acute myeloid leukemia.{27422,27424} Pacritinib is an inhibitor of both FLT3 and JAK2 (IC50s = 22 and 23 nM, respectively).{27422} It also blocks the activities of the FLT3 D835Y mutant, FLT3 with internal tandem duplications (ITDs), and JAK2 with a V617F substitution (IC50s = 6, 20-180, and 220 nM, respectively).{27422} Pacritinib also inhibits JAK1, JAK3, and TYK2 (IC50s = 1280, 520, and 50 nM, respectively).{27422} Pacritinib is orally bioavailable, inhibiting FLT3 and JAK2 signaling, tumor growth, and metastasis in xenografts in mice.{27422} It is synergistic with the histone deacetylase inhibitor pracinostat (also known as SB 939, Item No. 10443), decreasing cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis in cells carrying either the JAK2 V617F mutation or FLT3 with ITDs, both in vitro and in vivo.{27423} Pacritinib has potential in resolving hematological malignancies.{27424}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
FMS-like tyrosine kinase 3 (FLT3) and Janus kinase 2 (JAK2) are tyrosine kinases that mediate cytokine signaling and are frequently mutated in cancers, particularly acute myeloid leukemia.{27422,27424} Pacritinib is an inhibitor of both FLT3 and JAK2 (IC50s = 22 and 23 nM, respectively).{27422} It also blocks the activities of the FLT3 D835Y mutant, FLT3 with internal tandem duplications (ITDs), and JAK2 with a V617F substitution (IC50s = 6, 20-180, and 220 nM, respectively).{27422} Pacritinib also inhibits JAK1, JAK3, and TYK2 (IC50s = 1280, 520, and 50 nM, respectively).{27422} Pacritinib is orally bioavailable, inhibiting FLT3 and JAK2 signaling, tumor growth, and metastasis in xenografts in mice.{27422} It is synergistic with the histone deacetylase inhibitor pracinostat (also known as SB 939, Item No. 10443), decreasing cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis in cells carrying either the JAK2 V617F mutation or FLT3 with ITDs, both in vitro and in vivo.{27423} Pacritinib has potential in resolving hematological malignancies.{27424}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
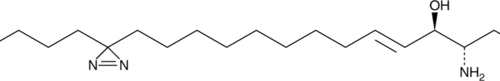
pacSphingosine (d18:1) is a photoreactive probe for the study of sphingosine metabolism.{45245} It contains a terminal clickable alkyne moiety and a photoactivatable diazirine group that allow its interaction with sphingosine binding proteins and photo-activated cross-linking of its interacting partners, respectively. pacSphingosine (d18:1) has been used to monitor the metabolism of sphingosine and visualize protein-lipid interaction complexes in S1PL-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs).
Brand:CaymanSKU:25364 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
pacSphingosine (d18:1) is a photoreactive probe for the study of sphingosine metabolism.{45245} It contains a terminal clickable alkyne moiety and a photoactivatable diazirine group that allow its interaction with sphingosine binding proteins and photo-activated cross-linking of its interacting partners, respectively. pacSphingosine (d18:1) has been used to monitor the metabolism of sphingosine and visualize protein-lipid interaction complexes in S1PL-/- mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs).
Brand:CaymanSKU:25364 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Padanamide A is a bacterial metabolite originally isolated from a marine Streptomyces species.{42129} It is active against five strains of P. falciparum (EC50s = 160-340 nM), is not cytotoxic to HEK293 or HepG2 human cell lines, but is cytotoxic to Jurkat T lymphocytes with an IC50 value of approximately 60 µg/ml.{42130,42131}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25085 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Padanamide A is a bacterial metabolite originally isolated from a marine Streptomyces species.{42129} It is active against five strains of P. falciparum (EC50s = 160-340 nM), is not cytotoxic to HEK293 or HepG2 human cell lines, but is cytotoxic to Jurkat T lymphocytes with an IC50 value of approximately 60 µg/ml.{42130,42131}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25085 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Paeoniflorin is a monoterpene glycoside first isolated from the roots of peony. It has diverse cellular actions, including modulating NMDA and TRPV1 receptors.{31755,31756} Paeoniflorin is reported to inhibit testosterone synthesis and stimulate aromatase activity.{31757} It also reduces inflammatory signaling by inhibiting p38 MAP kinase and blocks pancreatic cancer cell apoptosis by suppressing MMP-9 and ERK signaling.{31758,31759,31760} Presumably through some of these actions, paeoniflorin has analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions in mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:19861 -Available on backorder
Paeoniflorin is a monoterpene glycoside first isolated from the roots of peony. It has diverse cellular actions, including modulating NMDA and TRPV1 receptors.{31755,31756} Paeoniflorin is reported to inhibit testosterone synthesis and stimulate aromatase activity.{31757} It also reduces inflammatory signaling by inhibiting p38 MAP kinase and blocks pancreatic cancer cell apoptosis by suppressing MMP-9 and ERK signaling.{31758,31759,31760} Presumably through some of these actions, paeoniflorin has analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions in mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:19861 -Available on backorder
Paeoniflorin is a monoterpene glycoside first isolated from the roots of peony. It has diverse cellular actions, including modulating NMDA and TRPV1 receptors.{31755,31756} Paeoniflorin is reported to inhibit testosterone synthesis and stimulate aromatase activity.{31757} It also reduces inflammatory signaling by inhibiting p38 MAP kinase and blocks pancreatic cancer cell apoptosis by suppressing MMP-9 and ERK signaling.{31758,31759,31760} Presumably through some of these actions, paeoniflorin has analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions in mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:19861 -Available on backorder
Paeoniflorin is a monoterpene glycoside first isolated from the roots of peony. It has diverse cellular actions, including modulating NMDA and TRPV1 receptors.{31755,31756} Paeoniflorin is reported to inhibit testosterone synthesis and stimulate aromatase activity.{31757} It also reduces inflammatory signaling by inhibiting p38 MAP kinase and blocks pancreatic cancer cell apoptosis by suppressing MMP-9 and ERK signaling.{31758,31759,31760} Presumably through some of these actions, paeoniflorin has analgesic and anti-inflammatory actions in mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:19861 -Available on backorder
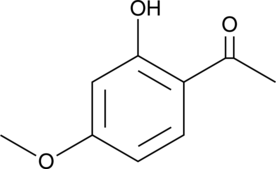
Paeonol is a phenol that has been found in Paeonia and has diverse biological activities.{31764,58139,31762,31761} It inhibits LPS- and IFN-γ-induced migration and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in BV-2 microglia when used at concentrations of 10 and 30 µM.{31764} Paeonol inhibits histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells induced by compound 48/80 (Item No. 22173) and reduces mortality in a mouse model of compound 48/80-induced anaphylactic shock when administered at a dose of 0.5 mg per animal.{58139} It reduces hepatic necrosis and serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in a mouse model of hepatotoxicity induced by acetaminophen (Item No. 10024) when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg.{31762} Paeonol (30, 50, and 100 mg/kg) inhibits carrageenan-induced thermal hyperalgesia and production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) in rats.{31761}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19862 -Available on backorder
Paeonol is a phenol that has been found in Paeonia and has diverse biological activities.{31764,58139,31762,31761} It inhibits LPS- and IFN-γ-induced migration and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in BV-2 microglia when used at concentrations of 10 and 30 µM.{31764} Paeonol inhibits histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells induced by compound 48/80 (Item No. 22173) and reduces mortality in a mouse model of compound 48/80-induced anaphylactic shock when administered at a dose of 0.5 mg per animal.{58139} It reduces hepatic necrosis and serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in a mouse model of hepatotoxicity induced by acetaminophen (Item No. 10024) when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg.{31762} Paeonol (30, 50, and 100 mg/kg) inhibits carrageenan-induced thermal hyperalgesia and production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) in rats.{31761}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19862 -Available on backorder
Paeonol is a phenol that has been found in Paeonia and has diverse biological activities.{31764,58139,31762,31761} It inhibits LPS- and IFN-γ-induced migration and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in BV-2 microglia when used at concentrations of 10 and 30 µM.{31764} Paeonol inhibits histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells induced by compound 48/80 (Item No. 22173) and reduces mortality in a mouse model of compound 48/80-induced anaphylactic shock when administered at a dose of 0.5 mg per animal.{58139} It reduces hepatic necrosis and serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in a mouse model of hepatotoxicity induced by acetaminophen (Item No. 10024) when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg.{31762} Paeonol (30, 50, and 100 mg/kg) inhibits carrageenan-induced thermal hyperalgesia and production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) in rats.{31761}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19862 -Available on backorder
Paeonol is a phenol that has been found in Paeonia and has diverse biological activities.{31764,58139,31762,31761} It inhibits LPS- and IFN-γ-induced migration and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in BV-2 microglia when used at concentrations of 10 and 30 µM.{31764} Paeonol inhibits histamine release from rat peritoneal mast cells induced by compound 48/80 (Item No. 22173) and reduces mortality in a mouse model of compound 48/80-induced anaphylactic shock when administered at a dose of 0.5 mg per animal.{58139} It reduces hepatic necrosis and serum levels of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) in a mouse model of hepatotoxicity induced by acetaminophen (Item No. 10024) when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg.{31762} Paeonol (30, 50, and 100 mg/kg) inhibits carrageenan-induced thermal hyperalgesia and production of nitric oxide (NO) and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010) in rats.{31761}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19862 -Available on backorder
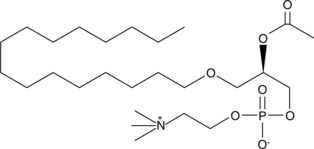
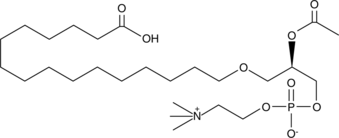
PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration,{1437} and the production of reactive oxygen species, and IL-6 in human macrophages.{367,2296} It is a more potent mediator of platelet aggregation than PAF C-18.{3786} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60900 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration,{1437} and the production of reactive oxygen species, and IL-6 in human macrophages.{367,2296} It is a more potent mediator of platelet aggregation than PAF C-18.{3786} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60900 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration,{1437} and the production of reactive oxygen species, and IL-6 in human macrophages.{367,2296} It is a more potent mediator of platelet aggregation than PAF C-18.{3786} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60900 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration,{1437} and the production of reactive oxygen species, and IL-6 in human macrophages.{367,2296} It is a more potent mediator of platelet aggregation than PAF C-18.{3786} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60900 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration and the production of reactive oxygen species and IL-6.{1437,367,2296} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis, inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{5841,303} PAF C-16 Carboxylic acid is modified with a carboxylic acid group terminating the C-16 alkyl chain. This provides a convenient site for chemical crosslinking.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration and the production of reactive oxygen species and IL-6.{1437,367,2296} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis, inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{5841,303} PAF C-16 Carboxylic acid is modified with a carboxylic acid group terminating the C-16 alkyl chain. This provides a convenient site for chemical crosslinking.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration and the production of reactive oxygen species and IL-6.{1437,367,2296} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis, inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{5841,303} PAF C-16 Carboxylic acid is modified with a carboxylic acid group terminating the C-16 alkyl chain. This provides a convenient site for chemical crosslinking.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration and the production of reactive oxygen species and IL-6.{1437,367,2296} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis, inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{5841,303} PAF C-16 Carboxylic acid is modified with a carboxylic acid group terminating the C-16 alkyl chain. This provides a convenient site for chemical crosslinking.
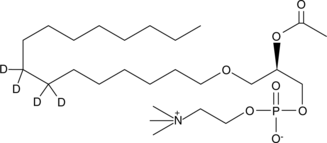
Brand:CaymanSKU:-PAF C-16-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the 7, 7′, 8, and 8′ positions of the hexadecyl moiety. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of PAF C-16 by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration,{1437} the production of reactive oxygen species,{367} and IL-6{2296} in human macrophages. It is a more potent mediator of platelet aggregation than PAF C-18{3786}. Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:360900 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
PAF C-16-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the 7, 7′, 8, and 8′ positions of the hexadecyl moiety. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of PAF C-16 by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration,{1437} the production of reactive oxygen species,{367} and IL-6{2296} in human macrophages. It is a more potent mediator of platelet aggregation than PAF C-18{3786}. Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:360900 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
PAF C-16-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the 7, 7′, 8, and 8′ positions of the hexadecyl moiety. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of PAF C-16 by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. PAF C-16 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is a potent mediator of neutrophil migration,{1437} the production of reactive oxygen species,{367} and IL-6{2296} in human macrophages. It is a more potent mediator of platelet aggregation than PAF C-18{3786}. Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:360900 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
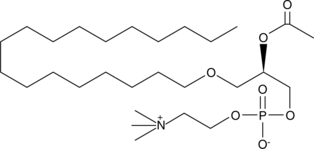
PAF C-18 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is less potent than PAF C-16 in the induction of platelet aggregation, but equipotent in activation of guinea pig macrophages.{3786} PAF C-18 induces the release of PGE2 and TXB2 from albumin-elicited guinea pig macrophages, and enhances the spreading of plated macrophages.{640} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60910 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
PAF C-18 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is less potent than PAF C-16 in the induction of platelet aggregation, but equipotent in activation of guinea pig macrophages.{3786} PAF C-18 induces the release of PGE2 and TXB2 from albumin-elicited guinea pig macrophages, and enhances the spreading of plated macrophages.{640} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60910 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
PAF C-18 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is less potent than PAF C-16 in the induction of platelet aggregation, but equipotent in activation of guinea pig macrophages.{3786} PAF C-18 induces the release of PGE2 and TXB2 from albumin-elicited guinea pig macrophages, and enhances the spreading of plated macrophages.{640} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60910 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
PAF C-18 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced upon stimulation through two distinct pathways known as the “remodeling” and ‘de novo’ pathways.{939} It is less potent than PAF C-16 in the induction of platelet aggregation, but equipotent in activation of guinea pig macrophages.{3786} PAF C-18 induces the release of PGE2 and TXB2 from albumin-elicited guinea pig macrophages, and enhances the spreading of plated macrophages.{640} Pathological processes involving PAF include necrotizing enterocolitis,{5841} inflammation, asthma, and allergy.{303}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60910 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
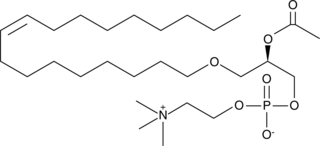
PAF C-18:1 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced by cells upon stimulation and plays a role in the establishment and maintenance of the inflammatory response. It is less potent than PAF C-16 (Item No. 60900) and PAF C-18 (Item No. 60910) in the induction of neutrophil chemotaxis, but is equipotent to PAF C-16 and PAF C-18 in promoting eosinophil migration.{1437,30475} PAF C-18:1 activates the PAF receptor and has been used in antibody binding experiments to determine the importance of an acyl linkage at the sn-2 position for recognition at this receptor.{1629}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
PAF C-18:1 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced by cells upon stimulation and plays a role in the establishment and maintenance of the inflammatory response. It is less potent than PAF C-16 (Item No. 60900) and PAF C-18 (Item No. 60910) in the induction of neutrophil chemotaxis, but is equipotent to PAF C-16 and PAF C-18 in promoting eosinophil migration.{1437,30475} PAF C-18:1 activates the PAF receptor and has been used in antibody binding experiments to determine the importance of an acyl linkage at the sn-2 position for recognition at this receptor.{1629}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
PAF C-18:1 is a naturally occurring phospholipid produced by cells upon stimulation and plays a role in the establishment and maintenance of the inflammatory response. It is less potent than PAF C-16 (Item No. 60900) and PAF C-18 (Item No. 60910) in the induction of neutrophil chemotaxis, but is equipotent to PAF C-16 and PAF C-18 in promoting eosinophil migration.{1437,30475} PAF C-18:1 activates the PAF receptor and has been used in antibody binding experiments to determine the importance of an acyl linkage at the sn-2 position for recognition at this receptor.{1629}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
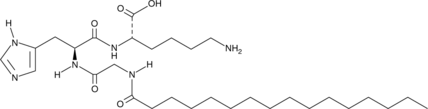
Pal-GHK is a form of the extracellular matrix-derived peptide GHK (Item No. 27168) containing palmitic acid (Item No. 10006627), which allows it to penetrate the stratum corneum to the epidermal and dermal skin layers.{42842} Pal-GHK (0.5 µM) increases collagen synthesis in human skin fibroblasts in vitro. It reduces collagen degradation ex vivo in patient-derived human skin samples irradiated with UVA light when used at a concentration of 6 ppm. It has been used with the zwitterionic surfactant C12 dodecyldimethylamine oxide (C12DMAO) to study self-assembly of the mixture into aggregates, ribbons, and nanobelts.{42843,42844} Pal-GHK has also been used as an internal standard for the quantification of pal-KTTKS in anti-wrinkle creams by LC-MS/MS.{42845}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27059 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Pal-GHK is a form of the extracellular matrix-derived peptide GHK (Item No. 27168) containing palmitic acid (Item No. 10006627), which allows it to penetrate the stratum corneum to the epidermal and dermal skin layers.{42842} Pal-GHK (0.5 µM) increases collagen synthesis in human skin fibroblasts in vitro. It reduces collagen degradation ex vivo in patient-derived human skin samples irradiated with UVA light when used at a concentration of 6 ppm. It has been used with the zwitterionic surfactant C12 dodecyldimethylamine oxide (C12DMAO) to study self-assembly of the mixture into aggregates, ribbons, and nanobelts.{42843,42844} Pal-GHK has also been used as an internal standard for the quantification of pal-KTTKS in anti-wrinkle creams by LC-MS/MS.{42845}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27059 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Pal-GHK is a form of the extracellular matrix-derived peptide GHK (Item No. 27168) containing palmitic acid (Item No. 10006627), which allows it to penetrate the stratum corneum to the epidermal and dermal skin layers.{42842} Pal-GHK (0.5 µM) increases collagen synthesis in human skin fibroblasts in vitro. It reduces collagen degradation ex vivo in patient-derived human skin samples irradiated with UVA light when used at a concentration of 6 ppm. It has been used with the zwitterionic surfactant C12 dodecyldimethylamine oxide (C12DMAO) to study self-assembly of the mixture into aggregates, ribbons, and nanobelts.{42843,42844} Pal-GHK has also been used as an internal standard for the quantification of pal-KTTKS in anti-wrinkle creams by LC-MS/MS.{42845}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27059 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Pal-GHK is a form of the extracellular matrix-derived peptide GHK (Item No. 27168) containing palmitic acid (Item No. 10006627), which allows it to penetrate the stratum corneum to the epidermal and dermal skin layers.{42842} Pal-GHK (0.5 µM) increases collagen synthesis in human skin fibroblasts in vitro. It reduces collagen degradation ex vivo in patient-derived human skin samples irradiated with UVA light when used at a concentration of 6 ppm. It has been used with the zwitterionic surfactant C12 dodecyldimethylamine oxide (C12DMAO) to study self-assembly of the mixture into aggregates, ribbons, and nanobelts.{42843,42844} Pal-GHK has also been used as an internal standard for the quantification of pal-KTTKS in anti-wrinkle creams by LC-MS/MS.{42845}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27059 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
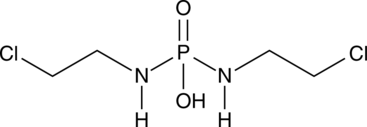
Palifosfamide is an active metabolite of the DNA alkylating agent ifosfamide (Item No. 17562).{52428} Palifosfamide is formed through hydroxylation of ifosfamide by various hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms.{52429} It is cytotoxic to L1210 and CCRF-CEM cancer cells when used at a concentration of 100 µM.{52430} Palifosfamide (100 mg/kg per day) reduces tumor growth in murine Lewis lung carcinoma and L1210 leukemia models, as well as a rat Yoshida ascitic sarcoma model.{52428}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29887 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Palifosfamide is an active metabolite of the DNA alkylating agent ifosfamide (Item No. 17562).{52428} Palifosfamide is formed through hydroxylation of ifosfamide by various hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms.{52429} It is cytotoxic to L1210 and CCRF-CEM cancer cells when used at a concentration of 100 µM.{52430} Palifosfamide (100 mg/kg per day) reduces tumor growth in murine Lewis lung carcinoma and L1210 leukemia models, as well as a rat Yoshida ascitic sarcoma model.{52428}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29887 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Palifosfamide is an active metabolite of the DNA alkylating agent ifosfamide (Item No. 17562).{52428} Palifosfamide is formed through hydroxylation of ifosfamide by various hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms.{52429} It is cytotoxic to L1210 and CCRF-CEM cancer cells when used at a concentration of 100 µM.{52430} Palifosfamide (100 mg/kg per day) reduces tumor growth in murine Lewis lung carcinoma and L1210 leukemia models, as well as a rat Yoshida ascitic sarcoma model.{52428}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29887 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Palifosfamide is an active metabolite of the DNA alkylating agent ifosfamide (Item No. 17562).{52428} Palifosfamide is formed through hydroxylation of ifosfamide by various hepatic cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoforms.{52429} It is cytotoxic to L1210 and CCRF-CEM cancer cells when used at a concentration of 100 µM.{52430} Palifosfamide (100 mg/kg per day) reduces tumor growth in murine Lewis lung carcinoma and L1210 leukemia models, as well as a rat Yoshida ascitic sarcoma model.{52428}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29887 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
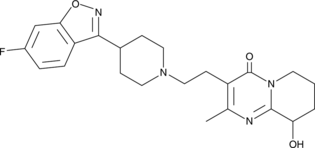
Paliperidone is an atypical antipsychotic.{42913} It is an inverse agonist of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors (IC50s = 1 and 0.9 nM, respectively), as well as an antagonist at these receptors (Kis = 0.4 and 0.1 nM, respectively).{25512} Paliperidone also binds to α1- and α2-adrenergic receptors, histamine H1 receptors, and the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtypes 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT2C (Kds = 10.1, 80, 3.4, 480, 19, 1.21, and 48 nM, respectively).{25511} It improves spatial working memory in a T-maze alternation task in a maternal immune activation mouse model of schizophrenia when administered at a dose of 0.05 mg/kg per day.{42913} Paliperidone is also an active metabolite of the atypical antipsychotic risperidone (Item No. 13629).{25511} Formulations containing paliperidone have been used in the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Paliperidone is an atypical antipsychotic.{42913} It is an inverse agonist of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors (IC50s = 1 and 0.9 nM, respectively), as well as an antagonist at these receptors (Kis = 0.4 and 0.1 nM, respectively).{25512} Paliperidone also binds to α1- and α2-adrenergic receptors, histamine H1 receptors, and the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtypes 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT2C (Kds = 10.1, 80, 3.4, 480, 19, 1.21, and 48 nM, respectively).{25511} It improves spatial working memory in a T-maze alternation task in a maternal immune activation mouse model of schizophrenia when administered at a dose of 0.05 mg/kg per day.{42913} Paliperidone is also an active metabolite of the atypical antipsychotic risperidone (Item No. 13629).{25511} Formulations containing paliperidone have been used in the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Paliperidone is an atypical antipsychotic.{42913} It is an inverse agonist of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors (IC50s = 1 and 0.9 nM, respectively), as well as an antagonist at these receptors (Kis = 0.4 and 0.1 nM, respectively).{25512} Paliperidone also binds to α1- and α2-adrenergic receptors, histamine H1 receptors, and the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtypes 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT2C (Kds = 10.1, 80, 3.4, 480, 19, 1.21, and 48 nM, respectively).{25511} It improves spatial working memory in a T-maze alternation task in a maternal immune activation mouse model of schizophrenia when administered at a dose of 0.05 mg/kg per day.{42913} Paliperidone is also an active metabolite of the atypical antipsychotic risperidone (Item No. 13629).{25511} Formulations containing paliperidone have been used in the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Paliperidone is an atypical antipsychotic.{42913} It is an inverse agonist of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors (IC50s = 1 and 0.9 nM, respectively), as well as an antagonist at these receptors (Kis = 0.4 and 0.1 nM, respectively).{25512} Paliperidone also binds to α1- and α2-adrenergic receptors, histamine H1 receptors, and the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtypes 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT2C (Kds = 10.1, 80, 3.4, 480, 19, 1.21, and 48 nM, respectively).{25511} It improves spatial working memory in a T-maze alternation task in a maternal immune activation mouse model of schizophrenia when administered at a dose of 0.05 mg/kg per day.{42913} Paliperidone is also an active metabolite of the atypical antipsychotic risperidone (Item No. 13629).{25511} Formulations containing paliperidone have been used in the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
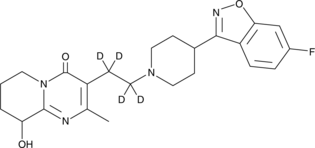
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Paliperidone-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of paliperidone (Item No. 15556) by GC- or LC-MS. Paliperidone is an atypical antipsychotic.{42913} It is an inverse agonist of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors (IC50s = 1 and 0.9 nM, respectively), as well as an antagonist at these receptors (Kis = 0.4 and 0.1 nM, respectively).{25512} Paliperidone also binds to α1- and α2-adrenergic receptors, histamine H1 receptors, and the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtypes 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT2C (Kds = 10.1, 80, 3.4, 480, 19, 1.21, and 48 nM, respectively).{25511} It improves spatial working memory in a T-maze alternation task in a maternal immune activation mouse model of schizophrenia when administered at a dose of 0.05 mg/kg per day.{42913} Paliperidone is also an active metabolite of the atypical antipsychotic risperidone (Item No. 13629).{25511} Formulations containing paliperidone have been used in the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28484 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Paliperidone-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of paliperidone (Item No. 15556) by GC- or LC-MS. Paliperidone is an atypical antipsychotic.{42913} It is an inverse agonist of dopamine D2 and D3 receptors (IC50s = 1 and 0.9 nM, respectively), as well as an antagonist at these receptors (Kis = 0.4 and 0.1 nM, respectively).{25512} Paliperidone also binds to α1- and α2-adrenergic receptors, histamine H1 receptors, and the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtypes 5-HT1A, 5-HT1D, 5-HT2A, and 5-HT2C (Kds = 10.1, 80, 3.4, 480, 19, 1.21, and 48 nM, respectively).{25511} It improves spatial working memory in a T-maze alternation task in a maternal immune activation mouse model of schizophrenia when administered at a dose of 0.05 mg/kg per day.{42913} Paliperidone is also an active metabolite of the atypical antipsychotic risperidone (Item No. 13629).{25511} Formulations containing paliperidone have been used in the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28484 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
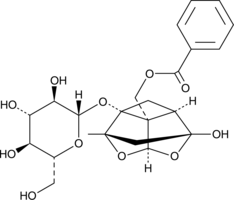
Palitantin is a fungal metabolite originally isolated from P. palitans.{39756} It inhibits HIV-1 integrase with IC50 values of 350 and 268 µM for 3’-processing and strand transfer activity, respectively.{39757} Palitantin has been used as a standard for dereplication of natural products.{41781}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25208 - 2.5 mgAvailable on backorder
Palitantin is a fungal metabolite originally isolated from P. palitans.{39756} It inhibits HIV-1 integrase with IC50 values of 350 and 268 µM for 3’-processing and strand transfer activity, respectively.{39757} Palitantin has been used as a standard for dereplication of natural products.{41781}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25208 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Palmatine is an alkaloid that has been found in C. rhizoma and has diverse biological activities.{47685,52524,52525,52526,52527} It inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE; IC50s = 0.51 and 6.84 µM, respectively).{47685} Palmatine (20, 40, and 80 µM) reduces Zika virus infection of Vero cells in a concentration-dependent manner.{52524} In vivo, palmatine (50 and 100 mg/kg) reduces colonic myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and IL-10, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels, as well as protects mucosal integrity in a mouse model of colitis induced by dextran sulfate (DSS; Item No. 23250).{52525} It reduces stomach ulcer area in a rat model of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers.{52526} Palmatine (10 and 20 mg/kg) reduces the number of small intestine and colon tumors in the ApcMin+/- mouse model of multiple intestinal neoplasia.{52527}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30318 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Palmatine is an alkaloid that has been found in C. rhizoma and has diverse biological activities.{47685,52524,52525,52526,52527} It inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE; IC50s = 0.51 and 6.84 µM, respectively).{47685} Palmatine (20, 40, and 80 µM) reduces Zika virus infection of Vero cells in a concentration-dependent manner.{52524} In vivo, palmatine (50 and 100 mg/kg) reduces colonic myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and IL-10, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels, as well as protects mucosal integrity in a mouse model of colitis induced by dextran sulfate (DSS; Item No. 23250).{52525} It reduces stomach ulcer area in a rat model of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers.{52526} Palmatine (10 and 20 mg/kg) reduces the number of small intestine and colon tumors in the ApcMin+/- mouse model of multiple intestinal neoplasia.{52527}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30318 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
Palmatine is an alkaloid that has been found in C. rhizoma and has diverse biological activities.{47685,52524,52525,52526,52527} It inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and butyrylcholinesterase (BChE; IC50s = 0.51 and 6.84 µM, respectively).{47685} Palmatine (20, 40, and 80 µM) reduces Zika virus infection of Vero cells in a concentration-dependent manner.{52524} In vivo, palmatine (50 and 100 mg/kg) reduces colonic myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and IL-10, IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α levels, as well as protects mucosal integrity in a mouse model of colitis induced by dextran sulfate (DSS; Item No. 23250).{52525} It reduces stomach ulcer area in a rat model of acetic acid-induced gastric ulcers.{52526} Palmatine (10 and 20 mg/kg) reduces the number of small intestine and colon tumors in the ApcMin+/- mouse model of multiple intestinal neoplasia.{52527}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30318 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
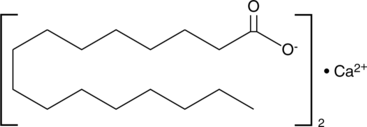
Saturated fatty acids are synthesized by both plants and animals from acetyl coenzyme A as a form of long-term energy storage. Saturated fatty acids are synthesized by both plants and animals from acetyl coenzyme A as a form of long-term energy storage. Palmitic acid is a common 16-carbon saturated fat that represents 10-20% of the normal dietary fat intake. Palmitic acid also makes up approximately 25% of the total plasma fatty acids in plasma lipoproteins.{1935} Saturated free fatty acids induce the expression of cyclooxygenase 2,{10646} and after protein acylation, are used to confer lipid anchoring to a variety of signaling molecules.{3997,4849,6115,11095} Palmitate is the salt (in this case calcium) of palmitic acid. It is this anion that is observed at physiological pH. Calcium palmitate is one of the major components of gallstones.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010279 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Saturated fatty acids are synthesized by both plants and animals from acetyl coenzyme A as a form of long-term energy storage. Saturated fatty acids are synthesized by both plants and animals from acetyl coenzyme A as a form of long-term energy storage. Palmitic acid is a common 16-carbon saturated fat that represents 10-20% of the normal dietary fat intake. Palmitic acid also makes up approximately 25% of the total plasma fatty acids in plasma lipoproteins.{1935} Saturated free fatty acids induce the expression of cyclooxygenase 2,{10646} and after protein acylation, are used to confer lipid anchoring to a variety of signaling molecules.{3997,4849,6115,11095} Palmitate is the salt (in this case calcium) of palmitic acid. It is this anion that is observed at physiological pH. Calcium palmitate is one of the major components of gallstones.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010279 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Saturated fatty acids are synthesized by both plants and animals from acetyl coenzyme A as a form of long-term energy storage. Saturated fatty acids are synthesized by both plants and animals from acetyl coenzyme A as a form of long-term energy storage. Palmitic acid is a common 16-carbon saturated fat that represents 10-20% of the normal dietary fat intake. Palmitic acid also makes up approximately 25% of the total plasma fatty acids in plasma lipoproteins.{1935} Saturated free fatty acids induce the expression of cyclooxygenase 2,{10646} and after protein acylation, are used to confer lipid anchoring to a variety of signaling molecules.{3997,4849,6115,11095} Palmitate is the salt (in this case calcium) of palmitic acid. It is this anion that is observed at physiological pH. Calcium palmitate is one of the major components of gallstones.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010279 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
Saturated fatty acids are synthesized by both plants and animals from acetyl coenzyme A as a form of long-term energy storage. Saturated fatty acids are synthesized by both plants and animals from acetyl coenzyme A as a form of long-term energy storage. Palmitic acid is a common 16-carbon saturated fat that represents 10-20% of the normal dietary fat intake. Palmitic acid also makes up approximately 25% of the total plasma fatty acids in plasma lipoproteins.{1935} Saturated free fatty acids induce the expression of cyclooxygenase 2,{10646} and after protein acylation, are used to confer lipid anchoring to a variety of signaling molecules.{3997,4849,6115,11095} Palmitate is the salt (in this case calcium) of palmitic acid. It is this anion that is observed at physiological pH. Calcium palmitate is one of the major components of gallstones.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010279 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
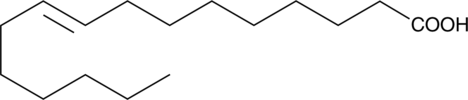
Palmitelaidic acid is a trans isomer of palmitoleic acid (Item Nos. 10009871 | 21911) and dietary fatty acid that has been found in dairy fat products and various partially hydrogenated oils.{54366,54368} It decreases nitric oxide (NO) production and levels of soluble E-selectin in isolated human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) when used at a concentration of 20 µM.{54366} Palmitelaidic acid (49 µM) inhibits Sendai virus-induced hemolysis of isolated human erythrocytes.{54367} Increased serum levels of palmitelaidic acid are associated with higher levels of LDL, but lower levels of triglycerides, fasting insulin, blood pressure, and incidence of diabetes.{54368}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001798 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Palmitelaidic acid is a trans isomer of palmitoleic acid (Item Nos. 10009871 | 21911) and dietary fatty acid that has been found in dairy fat products and various partially hydrogenated oils.{54366,54368} It decreases nitric oxide (NO) production and levels of soluble E-selectin in isolated human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) when used at a concentration of 20 µM.{54366} Palmitelaidic acid (49 µM) inhibits Sendai virus-induced hemolysis of isolated human erythrocytes.{54367} Increased serum levels of palmitelaidic acid are associated with higher levels of LDL, but lower levels of triglycerides, fasting insulin, blood pressure, and incidence of diabetes.{54368}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001798 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Palmitelaidic acid is a trans isomer of palmitoleic acid (Item Nos. 10009871 | 21911) and dietary fatty acid that has been found in dairy fat products and various partially hydrogenated oils.{54366,54368} It decreases nitric oxide (NO) production and levels of soluble E-selectin in isolated human aortic endothelial cells (HAECs) when used at a concentration of 20 µM.{54366} Palmitelaidic acid (49 µM) inhibits Sendai virus-induced hemolysis of isolated human erythrocytes.{54367} Increased serum levels of palmitelaidic acid are associated with higher levels of LDL, but lower levels of triglycerides, fasting insulin, blood pressure, and incidence of diabetes.{54368}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001798 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
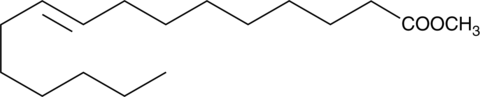
Palmitoleic acid (Item No. 10009871) is a common constituent of the triglycerides of human adipose tissue. Palmitoleic acid-based diets raise low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and diminish high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, even when dietary intake of cholesterol is maintained at a low level.{16300} Palmitelaidic acid (Item No. 9001798) is the trans isomer of the 16:1 fatty acid palmitoleic acid. While its effects on cholesterol levels are poorly studied, palmitelaidic acid can have very different effects from those of palmitoleic acid on lipid metabolism and mobilization.{22779,22780} Palmitelaidic acid methyl ester is an ester version of the free acid which may be more amenable for the formulation of fatty acid-containing diets and dietary supplements.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001797 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Palmitoleic acid (Item No. 10009871) is a common constituent of the triglycerides of human adipose tissue. Palmitoleic acid-based diets raise low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and diminish high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, even when dietary intake of cholesterol is maintained at a low level.{16300} Palmitelaidic acid (Item No. 9001798) is the trans isomer of the 16:1 fatty acid palmitoleic acid. While its effects on cholesterol levels are poorly studied, palmitelaidic acid can have very different effects from those of palmitoleic acid on lipid metabolism and mobilization.{22779,22780} Palmitelaidic acid methyl ester is an ester version of the free acid which may be more amenable for the formulation of fatty acid-containing diets and dietary supplements.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001797 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Palmitoleic acid (Item No. 10009871) is a common constituent of the triglycerides of human adipose tissue. Palmitoleic acid-based diets raise low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and diminish high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, even when dietary intake of cholesterol is maintained at a low level.{16300} Palmitelaidic acid (Item No. 9001798) is the trans isomer of the 16:1 fatty acid palmitoleic acid. While its effects on cholesterol levels are poorly studied, palmitelaidic acid can have very different effects from those of palmitoleic acid on lipid metabolism and mobilization.{22779,22780} Palmitelaidic acid methyl ester is an ester version of the free acid which may be more amenable for the formulation of fatty acid-containing diets and dietary supplements.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001797 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Palmitoleic acid (Item No. 10009871) is a common constituent of the triglycerides of human adipose tissue. Palmitoleic acid-based diets raise low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and diminish high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, even when dietary intake of cholesterol is maintained at a low level.{16300} Palmitelaidic acid (Item No. 9001798) is the trans isomer of the 16:1 fatty acid palmitoleic acid. While its effects on cholesterol levels are poorly studied, palmitelaidic acid can have very different effects from those of palmitoleic acid on lipid metabolism and mobilization.{22779,22780} Palmitelaidic acid methyl ester is an ester version of the free acid which may be more amenable for the formulation of fatty acid-containing diets and dietary supplements.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001797 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
Palmitic acid is a common 16-carbon saturated fat that represents 10-20% of human dietary fat intake and comprises approximately 25 and 65% of human total plasma lipids and saturated fatty acids, respectively.{45765,1935} Acylation of palmitic acid to proteins facilitates anchoring of membrane-bound proteins to the lipid bilayer and trafficking of intracellular proteins, promotes protein-vesicle interactions, and regulates various G protein-coupled receptor functions.{45765} Palmitic acid (200 µM) increases NF-ĸB p65 levels, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activity, and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in AsPC-1 pancreatic cancer cells, as well as increases migration of AsPC-1 cells.{45766} It increases COX-2 levels in RAW 264.7 cells and increases LPS-induced IL-1β levels and caspase-1 activity in isolated mouse peritoneal macrophages.{10646,45767} Dietary administration of palmitic acid (2.2% w/w for 12 weeks) increases mouse hippocampal β-secretase 1 (BACE1) activity and amyloid β (1-42) (Aβ42; Item No. 20574) levels.{45768} It also induces systolic contractile dysfunction in isolated mouse hearts.{45769} Red blood cell palmitic acid levels are increased in patients with metabolic syndrome compared to patients without metabolic syndrome and are also increased in the plasma of patients with type 2 diabetes compared to individuals without diabetes.{45771,45772}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006627 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
Palmitic acid is a common 16-carbon saturated fat that represents 10-20% of human dietary fat intake and comprises approximately 25 and 65% of human total plasma lipids and saturated fatty acids, respectively.{45765,1935} Acylation of palmitic acid to proteins facilitates anchoring of membrane-bound proteins to the lipid bilayer and trafficking of intracellular proteins, promotes protein-vesicle interactions, and regulates various G protein-coupled receptor functions.{45765} Palmitic acid (200 µM) increases NF-ĸB p65 levels, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activity, and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in AsPC-1 pancreatic cancer cells, as well as increases migration of AsPC-1 cells.{45766} It increases COX-2 levels in RAW 264.7 cells and increases LPS-induced IL-1β levels and caspase-1 activity in isolated mouse peritoneal macrophages.{10646,45767} Dietary administration of palmitic acid (2.2% w/w for 12 weeks) increases mouse hippocampal β-secretase 1 (BACE1) activity and amyloid β (1-42) (Aβ42; Item No. 20574) levels.{45768} It also induces systolic contractile dysfunction in isolated mouse hearts.{45769} Red blood cell palmitic acid levels are increased in patients with metabolic syndrome compared to patients without metabolic syndrome and are also increased in the plasma of patients with type 2 diabetes compared to individuals without diabetes.{45771,45772}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006627 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
Palmitic acid is a common 16-carbon saturated fat that represents 10-20% of human dietary fat intake and comprises approximately 25 and 65% of human total plasma lipids and saturated fatty acids, respectively.{45765,1935} Acylation of palmitic acid to proteins facilitates anchoring of membrane-bound proteins to the lipid bilayer and trafficking of intracellular proteins, promotes protein-vesicle interactions, and regulates various G protein-coupled receptor functions.{45765} Palmitic acid (200 µM) increases NF-ĸB p65 levels, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activity, and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in AsPC-1 pancreatic cancer cells, as well as increases migration of AsPC-1 cells.{45766} It increases COX-2 levels in RAW 264.7 cells and increases LPS-induced IL-1β levels and caspase-1 activity in isolated mouse peritoneal macrophages.{10646,45767} Dietary administration of palmitic acid (2.2% w/w for 12 weeks) increases mouse hippocampal β-secretase 1 (BACE1) activity and amyloid β (1-42) (Aβ42; Item No. 20574) levels.{45768} It also induces systolic contractile dysfunction in isolated mouse hearts.{45769} Red blood cell palmitic acid levels are increased in patients with metabolic syndrome compared to patients without metabolic syndrome and are also increased in the plasma of patients with type 2 diabetes compared to individuals without diabetes.{45771,45772}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006627 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
Palmitic acid is a common 16-carbon saturated fat that represents 10-20% of human dietary fat intake and comprises approximately 25 and 65% of human total plasma lipids and saturated fatty acids, respectively.{45765,1935} Acylation of palmitic acid to proteins facilitates anchoring of membrane-bound proteins to the lipid bilayer and trafficking of intracellular proteins, promotes protein-vesicle interactions, and regulates various G protein-coupled receptor functions.{45765} Palmitic acid (200 µM) increases NF-ĸB p65 levels, matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) activity, and production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in AsPC-1 pancreatic cancer cells, as well as increases migration of AsPC-1 cells.{45766} It increases COX-2 levels in RAW 264.7 cells and increases LPS-induced IL-1β levels and caspase-1 activity in isolated mouse peritoneal macrophages.{10646,45767} Dietary administration of palmitic acid (2.2% w/w for 12 weeks) increases mouse hippocampal β-secretase 1 (BACE1) activity and amyloid β (1-42) (Aβ42; Item No. 20574) levels.{45768} It also induces systolic contractile dysfunction in isolated mouse hearts.{45769} Red blood cell palmitic acid levels are increased in patients with metabolic syndrome compared to patients without metabolic syndrome and are also increased in the plasma of patients with type 2 diabetes compared to individuals without diabetes.{45771,45772}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006627 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
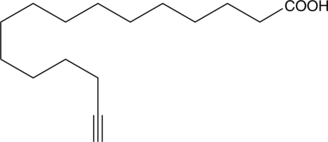
Protein S-palmitoylation is the post-translational acylation of proteins and serves to regulate localization, stability, and interaction with associates and substrates.{20656} Palmitic acid alkyne is a form of palmitic acid (Item No. 10006627) with an ω-terminal alkyne. The terminal alkyne group can be used in linking reactions, known as click chemistry; this chemistry is characterized by high dependability and specificity of the azide-alkyne bioconjugation reactions.{17991,17992} The use of palmitic acid alkyne and related lipids in isolating palmitoylated proteins has been described.{17771,20657,22694}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Protein S-palmitoylation is the post-translational acylation of proteins and serves to regulate localization, stability, and interaction with associates and substrates.{20656} Palmitic acid alkyne is a form of palmitic acid (Item No. 10006627) with an ω-terminal alkyne. The terminal alkyne group can be used in linking reactions, known as click chemistry; this chemistry is characterized by high dependability and specificity of the azide-alkyne bioconjugation reactions.{17991,17992} The use of palmitic acid alkyne and related lipids in isolating palmitoylated proteins has been described.{17771,20657,22694}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-