Chemicals
Showing 30151–30300 of 41137 results
-
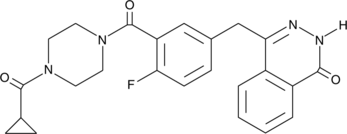
Many of the products generated by alkylating agents on DNA can be efficiently repaired by normal base excision repair (BER).{20677} Some poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs) assist in the repair of single-strand DNA nicks, an important step in BER.{22577} Olaparib is a potent inhibitor of PARP1 and PARP2 (IC50 = 5 and 1 nM, respectively) but is less effective against the PARP tankyrase-1 (IC50 = 1.5 µM).{24275} It can be used in cells and in animals, alone or in combination therapy with alkylating agents, to block BER and increase cancer cell death.{24275,20554,20549,20553}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10621 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
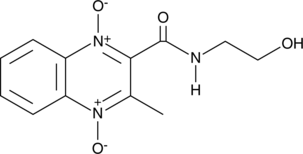
Olaquindox is an antibiotic and a swine growth regulator.{46313} In vivo, olaquindox (100 mg/kg) decreases E. coli-induced diarrhea and the number of intraepithelial lymphocytes in the ileum and increases body weight in geld piglets. Olaquindox induces bleeding, intramuscular edema, vacuolar degeneration, and deformation of renal tubules in C. carpio.{46314} It decreases mean body weight and increases the number of dead fetuses in pregnant rats when administered at a dose of 110 mg/kg and increases the number of external deformities, including bent tail, craniorachischisis, exencephaly, and anophthalmia in rat pups born to exposed pregnant mothers.{46315} Formulations containing olaquindox have been used as growth promoting agents in bovine livestock.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27725 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Olaquindox is an antibiotic and a swine growth regulator.{46313} In vivo, olaquindox (100 mg/kg) decreases E. coli-induced diarrhea and the number of intraepithelial lymphocytes in the ileum and increases body weight in geld piglets. Olaquindox induces bleeding, intramuscular edema, vacuolar degeneration, and deformation of renal tubules in C. carpio.{46314} It decreases mean body weight and increases the number of dead fetuses in pregnant rats when administered at a dose of 110 mg/kg and increases the number of external deformities, including bent tail, craniorachischisis, exencephaly, and anophthalmia in rat pups born to exposed pregnant mothers.{46315} Formulations containing olaquindox have been used as growth promoting agents in bovine livestock.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27725 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Olaquindox is an antibiotic and a swine growth regulator.{46313} In vivo, olaquindox (100 mg/kg) decreases E. coli-induced diarrhea and the number of intraepithelial lymphocytes in the ileum and increases body weight in geld piglets. Olaquindox induces bleeding, intramuscular edema, vacuolar degeneration, and deformation of renal tubules in C. carpio.{46314} It decreases mean body weight and increases the number of dead fetuses in pregnant rats when administered at a dose of 110 mg/kg and increases the number of external deformities, including bent tail, craniorachischisis, exencephaly, and anophthalmia in rat pups born to exposed pregnant mothers.{46315} Formulations containing olaquindox have been used as growth promoting agents in bovine livestock.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27725 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
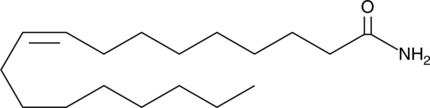
Oleamide is an amide of oleic acid (Item No. 90260) and an agonist of cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptors (Ki = 8.13 µM in a radioligand binding assay).{11820} It is selective for CB1 over CB2 receptors, where it inhibits binding of the CB receptor full agonist CP 55,940 by only 42.5% in HEK-293T cells expressing human CB2 receptors when used at a concentration of 100 µM. Oleamide (10 µM) inhibits cAMP accumulation induced by forskolin (Item No. 11018) in N1E 115 mouse neuroblastoma cells, an effect that is reversed by the CB1 antagonist SR141716A. Oleamide was first identified in the cerebrospinal fluid of sleep-deprived cats, and it has also been detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of rats and humans.{1317} In rats, it induces physiological sleep when administered at doses ranging from 5 to 50 mg and increases food intake when administered into the nucleus accumbens shell, and in group-housed and socially isolated mice, it has anxiolytic-like effects.{1317,42212,42213} Oleamide also induces transactivation of PPARα, PPARβ, and PPARγ and inhibits activity of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) at concentrations in the low micromolar range.{32696}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90375 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleamide is an amide of oleic acid (Item No. 90260) and an agonist of cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptors (Ki = 8.13 µM in a radioligand binding assay).{11820} It is selective for CB1 over CB2 receptors, where it inhibits binding of the CB receptor full agonist CP 55,940 by only 42.5% in HEK-293T cells expressing human CB2 receptors when used at a concentration of 100 µM. Oleamide (10 µM) inhibits cAMP accumulation induced by forskolin (Item No. 11018) in N1E 115 mouse neuroblastoma cells, an effect that is reversed by the CB1 antagonist SR141716A. Oleamide was first identified in the cerebrospinal fluid of sleep-deprived cats, and it has also been detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of rats and humans.{1317} In rats, it induces physiological sleep when administered at doses ranging from 5 to 50 mg and increases food intake when administered into the nucleus accumbens shell, and in group-housed and socially isolated mice, it has anxiolytic-like effects.{1317,42212,42213} Oleamide also induces transactivation of PPARα, PPARβ, and PPARγ and inhibits activity of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) at concentrations in the low micromolar range.{32696}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90375 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleamide is an amide of oleic acid (Item No. 90260) and an agonist of cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptors (Ki = 8.13 µM in a radioligand binding assay).{11820} It is selective for CB1 over CB2 receptors, where it inhibits binding of the CB receptor full agonist CP 55,940 by only 42.5% in HEK-293T cells expressing human CB2 receptors when used at a concentration of 100 µM. Oleamide (10 µM) inhibits cAMP accumulation induced by forskolin (Item No. 11018) in N1E 115 mouse neuroblastoma cells, an effect that is reversed by the CB1 antagonist SR141716A. Oleamide was first identified in the cerebrospinal fluid of sleep-deprived cats, and it has also been detected in the cerebrospinal fluid of rats and humans.{1317} In rats, it induces physiological sleep when administered at doses ranging from 5 to 50 mg and increases food intake when administered into the nucleus accumbens shell, and in group-housed and socially isolated mice, it has anxiolytic-like effects.{1317,42212,42213} Oleamide also induces transactivation of PPARα, PPARβ, and PPARγ and inhibits activity of the sarco/endoplasmic reticulum Ca2+-ATPase (SERCA) at concentrations in the low micromolar range.{32696}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90375 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
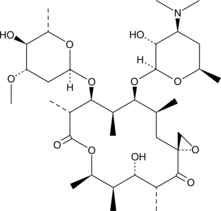
Oleandomycin is a classic macrolide antibiotic produced by strains of Streptomyces that demonstrates antimicrobial activity similar to penicillin and erythromycin.{26969} Structurally, it consists of a macrocyclic lactone ring of 14 carbon atoms with one sugar, oleandrose, and one amino sugar, desoxamine, attached to the lactone ring. The mechanism of its biosynthesis and development of resistance to its antibiotic activity have been studied in order to understand the reactive enzymes in these processes.{26969,26968}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Oleandomycin is a classic macrolide antibiotic produced by strains of Streptomyces that demonstrates antimicrobial activity similar to penicillin and erythromycin.{26969} Structurally, it consists of a macrocyclic lactone ring of 14 carbon atoms with one sugar, oleandrose, and one amino sugar, desoxamine, attached to the lactone ring. The mechanism of its biosynthesis and development of resistance to its antibiotic activity have been studied in order to understand the reactive enzymes in these processes.{26969,26968}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Oleandrin is a glycoside that has been found in N. oleander and has diverse biological activities.{48914,48915,48916,48917} It inhibits NF-κB activation induced by hydrogen peroxide, LPS, okadaic acid (Item No. 10011490), ceramide, or TNF in U937 cells when used at a concentration of 1 µg/ml.{48914} Oleandrin inhibits transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) replication without inducing cytotoxicity in swine testis cells (IC50 = 147 nM).{48915} It reduces pyramidal neuron cell death induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) in cultured rat brain explant slices.{48916} Oleandrin reduces viability and inhibits migration of U87MG, A172, U251, and GBM19 glioma cells.{48917} In vivo, oleandrin (0.3 mg/kg) reduces tumor size and increases survival in U78MG, GL261, and U251 glioma mouse xenograft models.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29871 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleandrin is a glycoside that has been found in N. oleander and has diverse biological activities.{48914,48915,48916,48917} It inhibits NF-κB activation induced by hydrogen peroxide, LPS, okadaic acid (Item No. 10011490), ceramide, or TNF in U937 cells when used at a concentration of 1 µg/ml.{48914} Oleandrin inhibits transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) replication without inducing cytotoxicity in swine testis cells (IC50 = 147 nM).{48915} It reduces pyramidal neuron cell death induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) in cultured rat brain explant slices.{48916} Oleandrin reduces viability and inhibits migration of U87MG, A172, U251, and GBM19 glioma cells.{48917} In vivo, oleandrin (0.3 mg/kg) reduces tumor size and increases survival in U78MG, GL261, and U251 glioma mouse xenograft models.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29871 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleandrin is a glycoside that has been found in N. oleander and has diverse biological activities.{48914,48915,48916,48917} It inhibits NF-κB activation induced by hydrogen peroxide, LPS, okadaic acid (Item No. 10011490), ceramide, or TNF in U937 cells when used at a concentration of 1 µg/ml.{48914} Oleandrin inhibits transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) replication without inducing cytotoxicity in swine testis cells (IC50 = 147 nM).{48915} It reduces pyramidal neuron cell death induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) in cultured rat brain explant slices.{48916} Oleandrin reduces viability and inhibits migration of U87MG, A172, U251, and GBM19 glioma cells.{48917} In vivo, oleandrin (0.3 mg/kg) reduces tumor size and increases survival in U78MG, GL261, and U251 glioma mouse xenograft models.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29871 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleandrin is a glycoside that has been found in N. oleander and has diverse biological activities.{48914,48915,48916,48917} It inhibits NF-κB activation induced by hydrogen peroxide, LPS, okadaic acid (Item No. 10011490), ceramide, or TNF in U937 cells when used at a concentration of 1 µg/ml.{48914} Oleandrin inhibits transmissible gastroenteritis virus (TGEV) replication without inducing cytotoxicity in swine testis cells (IC50 = 147 nM).{48915} It reduces pyramidal neuron cell death induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) in cultured rat brain explant slices.{48916} Oleandrin reduces viability and inhibits migration of U87MG, A172, U251, and GBM19 glioma cells.{48917} In vivo, oleandrin (0.3 mg/kg) reduces tumor size and increases survival in U78MG, GL261, and U251 glioma mouse xenograft models.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29871 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
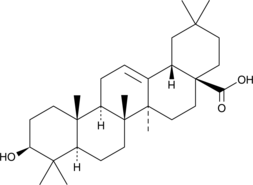
Oleanolic acid is a triterpenoid that is synthesized in many plants by the cyclization of squalene. Traditionally used in Asian medicine, oleanolic acid has long been known to have anti-inflammatory, anti-hyperlipidemic, and hepatoprotective in vivo effects.{20968,20967,20970} It has also been found to have antiviral and anti-tumor actions.{20966,20967} Synthetic triterpenoids based on oleanolic acid have been shown to bind specific proteins by Michael addition.{20969} Important protein targets include Keap1, IKK, JAK1, STAT3, PTEN, and proteins associated with the actin cytoskeleton.{20969}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11726 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Oleanolic acid is a triterpenoid that is synthesized in many plants by the cyclization of squalene. Traditionally used in Asian medicine, oleanolic acid has long been known to have anti-inflammatory, anti-hyperlipidemic, and hepatoprotective in vivo effects.{20968,20967,20970} It has also been found to have antiviral and anti-tumor actions.{20966,20967} Synthetic triterpenoids based on oleanolic acid have been shown to bind specific proteins by Michael addition.{20969} Important protein targets include Keap1, IKK, JAK1, STAT3, PTEN, and proteins associated with the actin cytoskeleton.{20969}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11726 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleanolic acid is a triterpenoid that is synthesized in many plants by the cyclization of squalene. Traditionally used in Asian medicine, oleanolic acid has long been known to have anti-inflammatory, anti-hyperlipidemic, and hepatoprotective in vivo effects.{20968,20967,20970} It has also been found to have antiviral and anti-tumor actions.{20966,20967} Synthetic triterpenoids based on oleanolic acid have been shown to bind specific proteins by Michael addition.{20969} Important protein targets include Keap1, IKK, JAK1, STAT3, PTEN, and proteins associated with the actin cytoskeleton.{20969}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11726 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
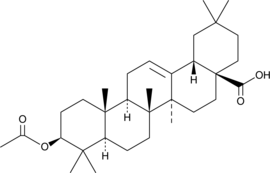
Oleanolic acid acetate is a triterpene that has been found in the root bark of M. macrophylla and has diverse biological activities.{48970,48971,48972,48973} It is active against P. gingivalis (MIC = 39 µg/ml).{48970} Oleanolic acid acetate (5-50 µM) induces apoptosis in and reduces viability of HCT116 colon carcinoma cells.{48971} It induces apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro and inhibits capillary vessel formation in a Matrigel™ plug assay in mice.{48972} Oleanolic acid acetate (2, 10, and 50 mg/kg) reduces the number of skin lesions, epidermal thickness and immune cell infiltration, and serum IgE, IgG2a, and histamine levels in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis.{48973}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29764 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleanolic acid acetate is a triterpene that has been found in the root bark of M. macrophylla and has diverse biological activities.{48970,48971,48972,48973} It is active against P. gingivalis (MIC = 39 µg/ml).{48970} Oleanolic acid acetate (5-50 µM) induces apoptosis in and reduces viability of HCT116 colon carcinoma cells.{48971} It induces apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro and inhibits capillary vessel formation in a Matrigel™ plug assay in mice.{48972} Oleanolic acid acetate (2, 10, and 50 mg/kg) reduces the number of skin lesions, epidermal thickness and immune cell infiltration, and serum IgE, IgG2a, and histamine levels in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis.{48973}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29764 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleanolic acid acetate is a triterpene that has been found in the root bark of M. macrophylla and has diverse biological activities.{48970,48971,48972,48973} It is active against P. gingivalis (MIC = 39 µg/ml).{48970} Oleanolic acid acetate (5-50 µM) induces apoptosis in and reduces viability of HCT116 colon carcinoma cells.{48971} It induces apoptosis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) in vitro and inhibits capillary vessel formation in a Matrigel™ plug assay in mice.{48972} Oleanolic acid acetate (2, 10, and 50 mg/kg) reduces the number of skin lesions, epidermal thickness and immune cell infiltration, and serum IgE, IgG2a, and histamine levels in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis.{48973}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29764 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
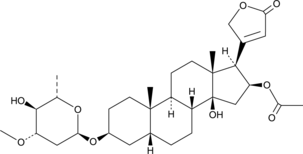
Oleanolic acid acrylate (OAA) is an agonist of the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtype 5-HT1A and a derivative of oleanolic acid (Item No. 11726).{50366} It acts as an agonist at the 5-HT1A receptor in mouse hippocampal homogenates in a [35S]GTPγS binding assay (EC50 = 0.79 µM). It is also a selective inhibitor of MAO-A over MAO-B (IC50s = 48.8 µM and >100 µM, respectively). In mice, OAA (10 mg/kg) reduces immobility in the forced swim test and increases the number of crossings and time spent at the center in the open field test, indicating anti-depressant-like and anxiolytic activities.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27206 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleanolic acid acrylate (OAA) is an agonist of the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtype 5-HT1A and a derivative of oleanolic acid (Item No. 11726).{50366} It acts as an agonist at the 5-HT1A receptor in mouse hippocampal homogenates in a [35S]GTPγS binding assay (EC50 = 0.79 µM). It is also a selective inhibitor of MAO-A over MAO-B (IC50s = 48.8 µM and >100 µM, respectively). In mice, OAA (10 mg/kg) reduces immobility in the forced swim test and increases the number of crossings and time spent at the center in the open field test, indicating anti-depressant-like and anxiolytic activities.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27206 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleanolic acid acrylate (OAA) is an agonist of the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtype 5-HT1A and a derivative of oleanolic acid (Item No. 11726).{50366} It acts as an agonist at the 5-HT1A receptor in mouse hippocampal homogenates in a [35S]GTPγS binding assay (EC50 = 0.79 µM). It is also a selective inhibitor of MAO-A over MAO-B (IC50s = 48.8 µM and >100 µM, respectively). In mice, OAA (10 mg/kg) reduces immobility in the forced swim test and increases the number of crossings and time spent at the center in the open field test, indicating anti-depressant-like and anxiolytic activities.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27206 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
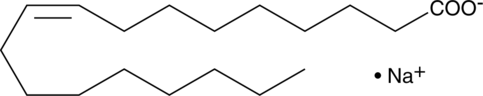
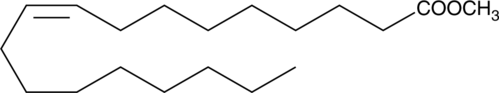
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90260 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90260 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90260 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90260 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:24659 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:24659 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:24659 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:24659 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
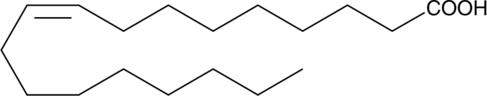
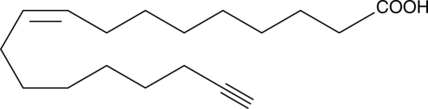
Oleic acid (Item No. 90260) is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. Oleic acid contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml.{3964} fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation is inhibited by 55% and 68%, respectively, using 5 µM oleic acid. This inhibition is comparable to that observed using arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 ) under the same conditions.{2095} Oleic acid, whether applied extracellularly (EC50 = ~60 µM) to human platelets or released from membrane phospholipids, causes an increase in intracellular calcium levels.{4198} Oleic acid alkyne is a form of oleic acid with an ω-terminal alkyne. The terminal alkyne group can be used in click chemistry linking reactions, to tag oleic acid with fluorescent or biotinylated labels for analysis of its metabolism and biological activity.{17991,17992,16188,22694}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002078 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid (Item No. 90260) is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. Oleic acid contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml.{3964} fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation is inhibited by 55% and 68%, respectively, using 5 µM oleic acid. This inhibition is comparable to that observed using arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 ) under the same conditions.{2095} Oleic acid, whether applied extracellularly (EC50 = ~60 µM) to human platelets or released from membrane phospholipids, causes an increase in intracellular calcium levels.{4198} Oleic acid alkyne is a form of oleic acid with an ω-terminal alkyne. The terminal alkyne group can be used in click chemistry linking reactions, to tag oleic acid with fluorescent or biotinylated labels for analysis of its metabolism and biological activity.{17991,17992,16188,22694}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002078 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid (Item No. 90260) is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. Oleic acid contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml.{3964} fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation is inhibited by 55% and 68%, respectively, using 5 µM oleic acid. This inhibition is comparable to that observed using arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 ) under the same conditions.{2095} Oleic acid, whether applied extracellularly (EC50 = ~60 µM) to human platelets or released from membrane phospholipids, causes an increase in intracellular calcium levels.{4198} Oleic acid alkyne is a form of oleic acid with an ω-terminal alkyne. The terminal alkyne group can be used in click chemistry linking reactions, to tag oleic acid with fluorescent or biotinylated labels for analysis of its metabolism and biological activity.{17991,17992,16188,22694}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002078 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid (Item No. 90260) is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. Oleic acid contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml.{3964} fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation is inhibited by 55% and 68%, respectively, using 5 µM oleic acid. This inhibition is comparable to that observed using arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010 ) under the same conditions.{2095} Oleic acid, whether applied extracellularly (EC50 = ~60 µM) to human platelets or released from membrane phospholipids, causes an increase in intracellular calcium levels.{4198} Oleic acid alkyne is a form of oleic acid with an ω-terminal alkyne. The terminal alkyne group can be used in click chemistry linking reactions, to tag oleic acid with fluorescent or biotinylated labels for analysis of its metabolism and biological activity.{17991,17992,16188,22694}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002078 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
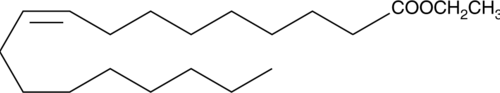
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. It contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid ethyl ester is a neutral, more lipid-soluble form of oleic acid. As the free acid, it inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% at a concentration of 10 µg/ml.{3964} It inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55% and 68%, respectively, at 5 µM.{2095} Oleic acid, whether applied extracellularly (EC50 = ~60 µM) to human platelets or released from membrane phospholipids, causes an increase in intracellular calcium levels.{4198}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008201 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. It contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid ethyl ester is a neutral, more lipid-soluble form of oleic acid. As the free acid, it inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% at a concentration of 10 µg/ml.{3964} It inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55% and 68%, respectively, at 5 µM.{2095} Oleic acid, whether applied extracellularly (EC50 = ~60 µM) to human platelets or released from membrane phospholipids, causes an increase in intracellular calcium levels.{4198}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008201 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid methyl ester is an esterified version of the free acid which is less water soluble but more amenable for the formulation of oleate-containing diets and dietary supplements. Oleic acid (Item No. 90260) is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. Oleic acid contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20604 -Available on backorder
Oleic acid methyl ester is an esterified version of the free acid which is less water soluble but more amenable for the formulation of oleate-containing diets and dietary supplements. Oleic acid (Item No. 90260) is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. Oleic acid contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20604 -Available on backorder
Oleic acid methyl ester is an esterified version of the free acid which is less water soluble but more amenable for the formulation of oleate-containing diets and dietary supplements. Oleic acid (Item No. 90260) is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. Oleic acid contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20604 -Available on backorder
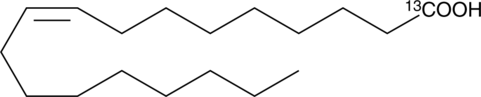
Oleic acid-13C is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) by GC- or LC-MS. Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27869 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid-13C is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) by GC- or LC-MS. Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27869 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid-13C is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) by GC- or LC-MS. Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27869 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid-13C is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleic acid (Item Nos. 90260 | 24659) by GC- or LC-MS. Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and a major component of membrane phospholipids that has been found in human plasma, cell membranes, and adipose tissue.{3964,42296} It contributes approximately 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml. It also inhibits fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation by 55 and 68%, respectively, when used at a concentration of 5 µM, similar to arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607).{2095} Oleic acid (60 µM) induces release of intracellular calcium in human platelets.{4198} In vivo, oleic acid increases TNF-α, IL-8, IL-6, and IL-1β production, neutrophil accumulation, and apoptotic and necrotic cell death in mouse lung and has been used to induce lung injury in a mouse model of acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS).{42296}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27869 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
AcylCoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) is an intracellular cholesteryl ester synthase tied closely to the absorption of dietary cholesterol.{13122} Oleic acid-2,6-diisopropylanilide is an inhibitor of acylCoA:cholesterol acyltransferase with an IC50 of 7 nM.{12463} When co-administered to rabbits or rats fed a high fat, high cholesterol diet, oleic acid-2,6-diisopropylanilide decreased low density lipoproteins and elevated high density lipoprotein levels when administered at 0.05%.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006782 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
AcylCoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) is an intracellular cholesteryl ester synthase tied closely to the absorption of dietary cholesterol.{13122} Oleic acid-2,6-diisopropylanilide is an inhibitor of acylCoA:cholesterol acyltransferase with an IC50 of 7 nM.{12463} When co-administered to rabbits or rats fed a high fat, high cholesterol diet, oleic acid-2,6-diisopropylanilide decreased low density lipoproteins and elevated high density lipoprotein levels when administered at 0.05%.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006782 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
AcylCoA:cholesterol acyltransferase (ACAT) is an intracellular cholesteryl ester synthase tied closely to the absorption of dietary cholesterol.{13122} Oleic acid-2,6-diisopropylanilide is an inhibitor of acylCoA:cholesterol acyltransferase with an IC50 of 7 nM.{12463} When co-administered to rabbits or rats fed a high fat, high cholesterol diet, oleic acid-2,6-diisopropylanilide decreased low density lipoproteins and elevated high density lipoprotein levels when administered at 0.05%.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006782 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
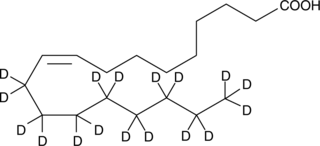
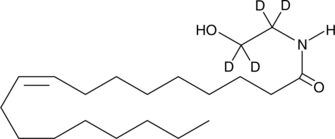
Oleic acid-d17 contains 17 deuterium atoms at the 11, 11, 12, 12, 13, 13, 14, 14, 15, 15, 16, 16, 17, 17, 18, 18, and 18 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleic acid (Item No. 90260) by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. Oleic acid contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml.{3964} fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation is inhibited by 55% and 68%, respectively, using 5 µM oleic acid. This inhibition is comparable to that observed using arachidonic acid under the same conditions.{2095} Oleic acid, whether applied extracellularly (EC50 = ~60 µM) to human platelets or released from membrane phospholipids, causes an increase in intracellular calcium levels.{4198}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000432 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid-d17 contains 17 deuterium atoms at the 11, 11, 12, 12, 13, 13, 14, 14, 15, 15, 16, 16, 17, 17, 18, 18, and 18 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleic acid (Item No. 90260) by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. Oleic acid contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml.{3964} fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation is inhibited by 55% and 68%, respectively, using 5 µM oleic acid. This inhibition is comparable to that observed using arachidonic acid under the same conditions.{2095} Oleic acid, whether applied extracellularly (EC50 = ~60 µM) to human platelets or released from membrane phospholipids, causes an increase in intracellular calcium levels.{4198}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000432 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleic acid-d17 contains 17 deuterium atoms at the 11, 11, 12, 12, 13, 13, 14, 14, 15, 15, 16, 16, 17, 17, 18, 18, and 18 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleic acid (Item No. 90260) by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Oleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid and is one of the major components of membrane phospholipids. Oleic acid contributes about 17% of the total fatty acids esterified to phosphatidylcholine, the major phospholipid class in porcine platelets.{3964} Oleic acid inhibits collagen-stimulated platelet aggregation by approximately 90% when used at a concentration of 10 µg/ml.{3964} fMLF-induced neutrophil aggregation and degranulation is inhibited by 55% and 68%, respectively, using 5 µM oleic acid. This inhibition is comparable to that observed using arachidonic acid under the same conditions.{2095} Oleic acid, whether applied extracellularly (EC50 = ~60 µM) to human platelets or released from membrane phospholipids, causes an increase in intracellular calcium levels.{4198}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000432 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Oleic anhydride is a fatty acid anhydride that inhibits sphingosine-induced phosphorylation of p32 in Jurkat T cells when used at concentrations ranging from 30 to 100 μM.{42362} It has been used in the synthesis of various phospholipids and triglycerides.{42363,42364}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20825 -Out of stock
Oleic anhydride is a fatty acid anhydride that inhibits sphingosine-induced phosphorylation of p32 in Jurkat T cells when used at concentrations ranging from 30 to 100 μM.{42362} It has been used in the synthesis of various phospholipids and triglycerides.{42363,42364}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20825 -Out of stock
Oleic anhydride is a fatty acid anhydride that inhibits sphingosine-induced phosphorylation of p32 in Jurkat T cells when used at concentrations ranging from 30 to 100 μM.{42362} It has been used in the synthesis of various phospholipids and triglycerides.{42363,42364}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20825 -Out of stock
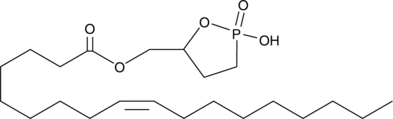
Cyclic phosphatidic acids (cPAs) are naturally occurring analogs of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in which the sn-2 hydroxy group forms a 5-membered ring with the sn-3 phosphate.{17448,17449} Carba-derivatives of cPA (ccPA) are modified at the sn-2 (2-ccPA) or sn-3 (3-ccPA) linkage, preventing the opening of cPA to produce lysophosphatidic acid (LPA).{14910} Oleoyl 3-Carbacyclic Phosphatidic Acid (3-ccPA 18:1) is a cyclic LPA analog that contains the 18:1 fatty acid, oleate, at the sn-1 position of the glycerol backbone.{14910} At 25 μM, it inhibits the transcellular migration of MM1 cells across mesothelial cell monolayers in response to fetal bovine serum (90.1%) or LPA (99.9%) without affecting proliferation.{14910} 3-ccPA 18:1, at 0.1-1.0 μM, significantly inhibits autotaxin,{14911,17450} an enzyme that is important in cancer cell survival, growth, migration, invasion, and metastasis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010299 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Cyclic phosphatidic acids (cPAs) are naturally occurring analogs of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in which the sn-2 hydroxy group forms a 5-membered ring with the sn-3 phosphate.{17448,17449} Carba-derivatives of cPA (ccPA) are modified at the sn-2 (2-ccPA) or sn-3 (3-ccPA) linkage, preventing the opening of cPA to produce lysophosphatidic acid (LPA).{14910} Oleoyl 3-Carbacyclic Phosphatidic Acid (3-ccPA 18:1) is a cyclic LPA analog that contains the 18:1 fatty acid, oleate, at the sn-1 position of the glycerol backbone.{14910} At 25 μM, it inhibits the transcellular migration of MM1 cells across mesothelial cell monolayers in response to fetal bovine serum (90.1%) or LPA (99.9%) without affecting proliferation.{14910} 3-ccPA 18:1, at 0.1-1.0 μM, significantly inhibits autotaxin,{14911,17450} an enzyme that is important in cancer cell survival, growth, migration, invasion, and metastasis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010299 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Cyclic phosphatidic acids (cPAs) are naturally occurring analogs of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in which the sn-2 hydroxy group forms a 5-membered ring with the sn-3 phosphate.{17448,17449} Carba-derivatives of cPA (ccPA) are modified at the sn-2 (2-ccPA) or sn-3 (3-ccPA) linkage, preventing the opening of cPA to produce lysophosphatidic acid (LPA).{14910} Oleoyl 3-Carbacyclic Phosphatidic Acid (3-ccPA 18:1) is a cyclic LPA analog that contains the 18:1 fatty acid, oleate, at the sn-1 position of the glycerol backbone.{14910} At 25 μM, it inhibits the transcellular migration of MM1 cells across mesothelial cell monolayers in response to fetal bovine serum (90.1%) or LPA (99.9%) without affecting proliferation.{14910} 3-ccPA 18:1, at 0.1-1.0 μM, significantly inhibits autotaxin,{14911,17450} an enzyme that is important in cancer cell survival, growth, migration, invasion, and metastasis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010299 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Cyclic phosphatidic acids (cPAs) are naturally occurring analogs of lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) in which the sn-2 hydroxy group forms a 5-membered ring with the sn-3 phosphate.{17448,17449} Carba-derivatives of cPA (ccPA) are modified at the sn-2 (2-ccPA) or sn-3 (3-ccPA) linkage, preventing the opening of cPA to produce lysophosphatidic acid (LPA).{14910} Oleoyl 3-Carbacyclic Phosphatidic Acid (3-ccPA 18:1) is a cyclic LPA analog that contains the 18:1 fatty acid, oleate, at the sn-1 position of the glycerol backbone.{14910} At 25 μM, it inhibits the transcellular migration of MM1 cells across mesothelial cell monolayers in response to fetal bovine serum (90.1%) or LPA (99.9%) without affecting proliferation.{14910} 3-ccPA 18:1, at 0.1-1.0 μM, significantly inhibits autotaxin,{14911,17450} an enzyme that is important in cancer cell survival, growth, migration, invasion, and metastasis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010299 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
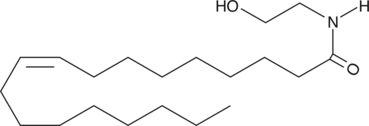
Oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA) is an analog of the endocannabinoid AEA found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90265 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA) is an analog of the endocannabinoid AEA found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90265 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA) is an analog of the endocannabinoid AEA found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90265 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA) is an analog of the endocannabinoid AEA found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90265 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
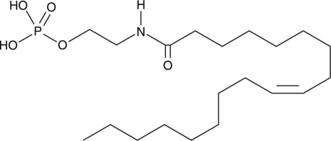
Oleoyl ethanolamide phosphate (OEA-P) is a lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) mimetic, LPA receptor agonist, and phosphate ester of oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA; Item No. 90265).{47608,7616} It selectively increases [35S]GTPγS binding to HEK293T cell membranes expressing LPA1 and LPA2 over LPA3 receptors.{7616} OEA-P induces calcium mobilization and inhibits forskolin-induced cAMP accumulation in MDA-MB-231 cells (EC50s = 1.2 and 101 nM, respectively).{47608}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22886 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide phosphate (OEA-P) is a lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) mimetic, LPA receptor agonist, and phosphate ester of oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA; Item No. 90265).{47608,7616} It selectively increases [35S]GTPγS binding to HEK293T cell membranes expressing LPA1 and LPA2 over LPA3 receptors.{7616} OEA-P induces calcium mobilization and inhibits forskolin-induced cAMP accumulation in MDA-MB-231 cells (EC50s = 1.2 and 101 nM, respectively).{47608}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22886 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide phosphate (OEA-P) is a lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) mimetic, LPA receptor agonist, and phosphate ester of oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA; Item No. 90265).{47608,7616} It selectively increases [35S]GTPγS binding to HEK293T cell membranes expressing LPA1 and LPA2 over LPA3 receptors.{7616} OEA-P induces calcium mobilization and inhibits forskolin-induced cAMP accumulation in MDA-MB-231 cells (EC50s = 1.2 and 101 nM, respectively).{47608}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22886 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide-d2 (OEA-d2) contains two deuterium atoms at the 11 position. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of OEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. OEA is an analogue of the endocannabinoid arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα), exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007823 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide-d2 (OEA-d2) contains two deuterium atoms at the 11 position. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of OEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. OEA is an analogue of the endocannabinoid arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα), exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007823 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide-d2 (OEA-d2) contains two deuterium atoms at the 11 position. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of OEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. OEA is an analogue of the endocannabinoid arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα), exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007823 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide-d2 (OEA-d2) contains two deuterium atoms at the 11 position. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of OEA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. OEA is an analogue of the endocannabinoid arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA) found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα), exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007823 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleoyl ethanolamide by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA) is an analog of the endocannabinoid AEA found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000552 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleoyl ethanolamide by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA) is an analog of the endocannabinoid AEA found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000552 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleoyl ethanolamide by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA) is an analog of the endocannabinoid AEA found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000552 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl ethanolamide-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of oleoyl ethanolamide by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Oleoyl ethanolamide (OEA) is an analog of the endocannabinoid AEA found in brain tissue and in chocolate.{5291} It is one of the long chain fatty acid ethanolamides that accumulates rapidly in infarcted tissue,{2874} but its biosynthesis is reduced in the intestine of rats following food deprivation.{9302} OEA is an endogenous, potent agonist for PPARα, exhibiting an EC50 value of 120 nM in a transactivation assay.{11423} Systemic administration of OEA suppresses food intake and reduces weight gain in rats (10 mg/kg intraperitoneally) and PPARα wild-type mice, but not in PPARα knockout mice.{9302,11423} These data indicate that OEA regulates food intake by a PPARα-mediated mechanism.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000552 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
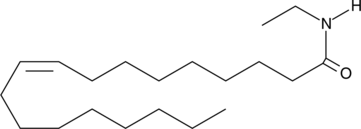
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (anandamide; AEA).{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty amide acyl hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons.{10647} Oleoyl ethyl amide (OEtA) has potent FAAH inhibitory activity (IC50 5.25 nM in rat brain homogenates) but does not inhibit acidic PEAase or bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors. OEtA is therefore a selective FAAH inhibitor with potential analgesic and anxiolytic activity.{11985}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005459 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (anandamide; AEA).{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty amide acyl hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons.{10647} Oleoyl ethyl amide (OEtA) has potent FAAH inhibitory activity (IC50 5.25 nM in rat brain homogenates) but does not inhibit acidic PEAase or bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors. OEtA is therefore a selective FAAH inhibitor with potential analgesic and anxiolytic activity.{11985}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005459 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (anandamide; AEA).{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty amide acyl hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons.{10647} Oleoyl ethyl amide (OEtA) has potent FAAH inhibitory activity (IC50 5.25 nM in rat brain homogenates) but does not inhibit acidic PEAase or bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors. OEtA is therefore a selective FAAH inhibitor with potential analgesic and anxiolytic activity.{11985}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005459 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (anandamide; AEA).{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty amide acyl hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons.{10647} Oleoyl ethyl amide (OEtA) has potent FAAH inhibitory activity (IC50 5.25 nM in rat brain homogenates) but does not inhibit acidic PEAase or bind to CB1 or CB2 receptors. OEtA is therefore a selective FAAH inhibitor with potential analgesic and anxiolytic activity.{11985}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005459 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
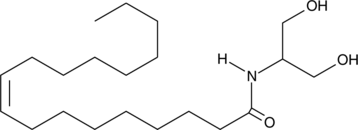
Oleoyl serinol is an analog of ceramide and an agonist of the cannabinoid receptor GPR119 that has an EC50 value of 12 µM for stimulating secretion of GLP-1 in mouse endocrine GLUTag cells.{39726} It has been found in E. coli that express human microbiota N-acyl synthase (hmNAS) genes. It induces cell death of F-11 murine neuroblastoma and apoptosis in U-87 human astrocytoma cells when used at a concentration of 100 µM.{10417} Oleoyl serinol (80 µM) induces formation of a complex including PAR-4 and PKCζ in embryoid body-derived cells, decreases the levels of the pluripotency marker Oct-4 and prostate apoptosis response-4 (PAR-4), which mediates ceramide-induced apoptosis in embryonic stem cells.{39727} It induces apoptosis selectively in rapidly dividing cells over differentiated cells as well as prevents teratoma formation and promotes neural differentiation in a neonatal mouse engraftment model of teratoma formation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Oleoyl serinol is an analog of ceramide and an agonist of the cannabinoid receptor GPR119 that has an EC50 value of 12 µM for stimulating secretion of GLP-1 in mouse endocrine GLUTag cells.{39726} It has been found in E. coli that express human microbiota N-acyl synthase (hmNAS) genes. It induces cell death of F-11 murine neuroblastoma and apoptosis in U-87 human astrocytoma cells when used at a concentration of 100 µM.{10417} Oleoyl serinol (80 µM) induces formation of a complex including PAR-4 and PKCζ in embryoid body-derived cells, decreases the levels of the pluripotency marker Oct-4 and prostate apoptosis response-4 (PAR-4), which mediates ceramide-induced apoptosis in embryonic stem cells.{39727} It induces apoptosis selectively in rapidly dividing cells over differentiated cells as well as prevents teratoma formation and promotes neural differentiation in a neonatal mouse engraftment model of teratoma formation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Oleoyl serinol is an analog of ceramide and an agonist of the cannabinoid receptor GPR119 that has an EC50 value of 12 µM for stimulating secretion of GLP-1 in mouse endocrine GLUTag cells.{39726} It has been found in E. coli that express human microbiota N-acyl synthase (hmNAS) genes. It induces cell death of F-11 murine neuroblastoma and apoptosis in U-87 human astrocytoma cells when used at a concentration of 100 µM.{10417} Oleoyl serinol (80 µM) induces formation of a complex including PAR-4 and PKCζ in embryoid body-derived cells, decreases the levels of the pluripotency marker Oct-4 and prostate apoptosis response-4 (PAR-4), which mediates ceramide-induced apoptosis in embryonic stem cells.{39727} It induces apoptosis selectively in rapidly dividing cells over differentiated cells as well as prevents teratoma formation and promotes neural differentiation in a neonatal mouse engraftment model of teratoma formation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Oleoyl serinol is an analog of ceramide and an agonist of the cannabinoid receptor GPR119 that has an EC50 value of 12 µM for stimulating secretion of GLP-1 in mouse endocrine GLUTag cells.{39726} It has been found in E. coli that express human microbiota N-acyl synthase (hmNAS) genes. It induces cell death of F-11 murine neuroblastoma and apoptosis in U-87 human astrocytoma cells when used at a concentration of 100 µM.{10417} Oleoyl serinol (80 µM) induces formation of a complex including PAR-4 and PKCζ in embryoid body-derived cells, decreases the levels of the pluripotency marker Oct-4 and prostate apoptosis response-4 (PAR-4), which mediates ceramide-induced apoptosis in embryonic stem cells.{39727} It induces apoptosis selectively in rapidly dividing cells over differentiated cells as well as prevents teratoma formation and promotes neural differentiation in a neonatal mouse engraftment model of teratoma formation.
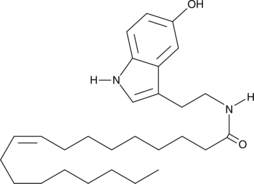
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Oleoyl serotonin is a hybrid molecule patterned after arachidonoyl serotonin (Item No. 70665). Arachidonoyl serotonin is a dual antagonist of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channel, reducing both acute and chronic peripheral pain.{18121,18122} Oleoyl Serotonin inhibits capsaicin-induced TRPV1 channel activation (IC50 = 2.57 μM) without blocking FAAH-mediated hydrolysis of arachidonoyl ethanolamine (IC50 > 50 μM).{18121}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000629 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Oleoyl serotonin is a hybrid molecule patterned after arachidonoyl serotonin (Item No. 70665). Arachidonoyl serotonin is a dual antagonist of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and the transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channel, reducing both acute and chronic peripheral pain.{18121,18122} Oleoyl Serotonin inhibits capsaicin-induced TRPV1 channel activation (IC50 = 2.57 μM) without blocking FAAH-mediated hydrolysis of arachidonoyl ethanolamine (IC50 > 50 μM).{18121}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000629 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
![An agonist of 5-HT1A and a derivative of oleanolic acid; acts as an agonist at the 5-HT1A receptor in mouse hippocampal homogenates in a [35S]GTPγS binding assay (EC50 = 0.79 µM); a selective inhibitor of MAO-A over MAO-B (IC50s = 48.8 µM and >100 µM](https://interpriseusa.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/27206.png)