Chemicals
Showing 28201–28350 of 41137 results
-
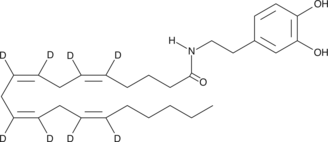
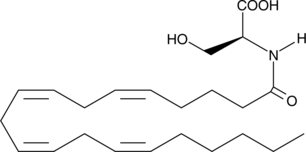
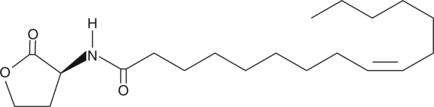
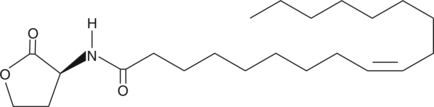
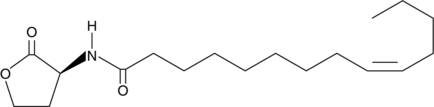
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine-d8 contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of N-arachidonoyl dopamine by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including NADA, have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} NADA is the amide of the neurotransmitter dopamine and arachidonic acid. NADA is a CB1-selective cannabinoid agonist, inducing the typical tetrad of hypothermia, analgesia, catalepsy, and hypomotility in rats which exceeds that of anandamide (AEA).{9213} NADA is a full agonist at the vanilloid receptor 1, but is inactive on the dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors. NADA is also a potent inhibitor (IC50 = 0.25 µM) of the proliferation of MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Recent reports of NADA’s endothelium-dependent vasodilation indicate that some of its cannabinergic activities antagonized by SR141716A may be non-CB1/CB2 dependent.{11224}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007431 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine-d8 contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of N-arachidonoyl dopamine by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including NADA, have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} NADA is the amide of the neurotransmitter dopamine and arachidonic acid. NADA is a CB1-selective cannabinoid agonist, inducing the typical tetrad of hypothermia, analgesia, catalepsy, and hypomotility in rats which exceeds that of anandamide (AEA).{9213} NADA is a full agonist at the vanilloid receptor 1, but is inactive on the dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors. NADA is also a potent inhibitor (IC50 = 0.25 µM) of the proliferation of MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Recent reports of NADA’s endothelium-dependent vasodilation indicate that some of its cannabinergic activities antagonized by SR141716A may be non-CB1/CB2 dependent.{11224}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007431 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine-d8 contains eight deuterium atoms at the 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, and 15 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of N-arachidonoyl dopamine by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including NADA, have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} NADA is the amide of the neurotransmitter dopamine and arachidonic acid. NADA is a CB1-selective cannabinoid agonist, inducing the typical tetrad of hypothermia, analgesia, catalepsy, and hypomotility in rats which exceeds that of anandamide (AEA).{9213} NADA is a full agonist at the vanilloid receptor 1, but is inactive on the dopaminergic D1 and D2 receptors. NADA is also a potent inhibitor (IC50 = 0.25 µM) of the proliferation of MCF-7 breast carcinoma cells. Recent reports of NADA’s endothelium-dependent vasodilation indicate that some of its cannabinergic activities antagonized by SR141716A may be non-CB1/CB2 dependent.{11224}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007431 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
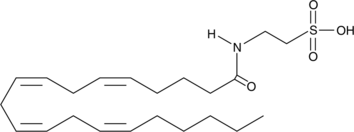
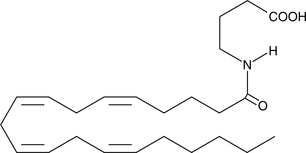
N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an arachidonoyl amino acid.{16245} It is oxygenated by 12(S)- and 15(S)-lipoxygenase and is converted to 12-HETE-taurine (12-HETE-T) in murine resident peritoneal macrophages.{46067} N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an activator of the transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) channels TRPV1 and TRPV4 (EC50s = 28 and 21 µM, respectively).{16245} It increases calcium flux in HIT-T15 pancreatic β-cells and INS-1 rat islet cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM and increases insulin secretion from 832/13 INS-1 pancreatic β-cells.{46068} The levels of N-arachidonoyl taurine are changed in mouse brain following administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).{46069}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005537 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an arachidonoyl amino acid.{16245} It is oxygenated by 12(S)- and 15(S)-lipoxygenase and is converted to 12-HETE-taurine (12-HETE-T) in murine resident peritoneal macrophages.{46067} N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an activator of the transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) channels TRPV1 and TRPV4 (EC50s = 28 and 21 µM, respectively).{16245} It increases calcium flux in HIT-T15 pancreatic β-cells and INS-1 rat islet cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM and increases insulin secretion from 832/13 INS-1 pancreatic β-cells.{46068} The levels of N-arachidonoyl taurine are changed in mouse brain following administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).{46069}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005537 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an arachidonoyl amino acid.{16245} It is oxygenated by 12(S)- and 15(S)-lipoxygenase and is converted to 12-HETE-taurine (12-HETE-T) in murine resident peritoneal macrophages.{46067} N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an activator of the transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) channels TRPV1 and TRPV4 (EC50s = 28 and 21 µM, respectively).{16245} It increases calcium flux in HIT-T15 pancreatic β-cells and INS-1 rat islet cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM and increases insulin secretion from 832/13 INS-1 pancreatic β-cells.{46068} The levels of N-arachidonoyl taurine are changed in mouse brain following administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).{46069}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005537 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an arachidonoyl amino acid.{16245} It is oxygenated by 12(S)- and 15(S)-lipoxygenase and is converted to 12-HETE-taurine (12-HETE-T) in murine resident peritoneal macrophages.{46067} N-Arachidonoyl taurine is an activator of the transient receptor potential vanilloid (TRPV) channels TRPV1 and TRPV4 (EC50s = 28 and 21 µM, respectively).{16245} It increases calcium flux in HIT-T15 pancreatic β-cells and INS-1 rat islet cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM and increases insulin secretion from 832/13 INS-1 pancreatic β-cells.{46068} The levels of N-arachidonoyl taurine are changed in mouse brain following administration of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC).{46069}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005537 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
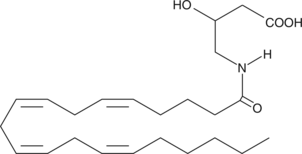
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-3-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAG-3H-ABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly; Item No. 90051) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAG-3H-ABA was also found in rat brain by LC-MS techniques, but has not been fully characterized to date. Most arachidonoyl amino acids are poor ligands for the CB1 receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10158 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-3-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAG-3H-ABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly; Item No. 90051) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAG-3H-ABA was also found in rat brain by LC-MS techniques, but has not been fully characterized to date. Most arachidonoyl amino acids are poor ligands for the CB1 receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10158 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-3-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAG-3H-ABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly; Item No. 90051) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAG-3H-ABA was also found in rat brain by LC-MS techniques, but has not been fully characterized to date. Most arachidonoyl amino acids are poor ligands for the CB1 receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10158 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-3-hydroxy-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAG-3H-ABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly; Item No. 90051) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAG-3H-ABA was also found in rat brain by LC-MS techniques, but has not been fully characterized to date. Most arachidonoyl amino acids are poor ligands for the CB1 receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10158 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
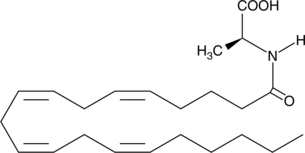
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-L-alanine (NALA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NALA may have activity at cannabinoid receptor and/or VR1, but has not been fully characterized to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90065 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-L-alanine (NALA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NALA may have activity at cannabinoid receptor and/or VR1, but has not been fully characterized to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90065 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-L-alanine (NALA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NALA may have activity at cannabinoid receptor and/or VR1, but has not been fully characterized to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90065 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-arachidonoyl-L-alanine (NALA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.{9589} The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NALA may have activity at cannabinoid receptor and/or VR1, but has not been fully characterized to date.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90065 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl amides of both amino acids and neurotransmitters such as dopamine have been previously reported in the literature.{9213} N-Arachidonoyl-L-serine (ARA-S) is one such recently isolated endocannabinoid with an unusual activity profile. ARA-S does not bind to central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors or vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1). Like cannabidiol, ARA-S (5 mg/kg) antagonizes the hypotensive effects of a 10 mg/kg IV bolus of abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) in an anesthetized rat blood pressure model.{11984} However, similar to Abn-CBD, ARA-S relaxes isolated rat mesenteric arteries and abdominal aorta as well as increases phosphorylation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in HUVEC.{14066} The precise mechanisms of action by ARA-S and Abn-DBD in various vascular preparations appears to be different and requires further investigation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005455 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl amides of both amino acids and neurotransmitters such as dopamine have been previously reported in the literature.{9213} N-Arachidonoyl-L-serine (ARA-S) is one such recently isolated endocannabinoid with an unusual activity profile. ARA-S does not bind to central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors or vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1). Like cannabidiol, ARA-S (5 mg/kg) antagonizes the hypotensive effects of a 10 mg/kg IV bolus of abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) in an anesthetized rat blood pressure model.{11984} However, similar to Abn-CBD, ARA-S relaxes isolated rat mesenteric arteries and abdominal aorta as well as increases phosphorylation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in HUVEC.{14066} The precise mechanisms of action by ARA-S and Abn-DBD in various vascular preparations appears to be different and requires further investigation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005455 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl amides of both amino acids and neurotransmitters such as dopamine have been previously reported in the literature.{9213} N-Arachidonoyl-L-serine (ARA-S) is one such recently isolated endocannabinoid with an unusual activity profile. ARA-S does not bind to central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors or vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1). Like cannabidiol, ARA-S (5 mg/kg) antagonizes the hypotensive effects of a 10 mg/kg IV bolus of abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) in an anesthetized rat blood pressure model.{11984} However, similar to Abn-CBD, ARA-S relaxes isolated rat mesenteric arteries and abdominal aorta as well as increases phosphorylation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in HUVEC.{14066} The precise mechanisms of action by ARA-S and Abn-DBD in various vascular preparations appears to be different and requires further investigation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005455 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Arachidonoyl amides of both amino acids and neurotransmitters such as dopamine have been previously reported in the literature.{9213} N-Arachidonoyl-L-serine (ARA-S) is one such recently isolated endocannabinoid with an unusual activity profile. ARA-S does not bind to central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors or vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1). Like cannabidiol, ARA-S (5 mg/kg) antagonizes the hypotensive effects of a 10 mg/kg IV bolus of abnormal cannabidiol (Abn-CBD) in an anesthetized rat blood pressure model.{11984} However, similar to Abn-CBD, ARA-S relaxes isolated rat mesenteric arteries and abdominal aorta as well as increases phosphorylation of Akt and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) in HUVEC.{14066} The precise mechanisms of action by ARA-S and Abn-DBD in various vascular preparations appears to be different and requires further investigation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005455 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-Arachidonoyl-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAGABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAGABA was also found to suppress normal responses to pain, but has not been fully characterized to date.{9589}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90067 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-Arachidonoyl-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAGABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAGABA was also found to suppress normal responses to pain, but has not been fully characterized to date.{9589}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90067 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Several different arachidonoyl amino acids, including N-Arachidonoyl-γ-aminobutyric acid (NAGABA), have been isolated and characterized from bovine brain.The glycine congener (NAGly) was further characterized and found to suppress formalin-induced pain in rats. NAGABA was also found to suppress normal responses to pain, but has not been fully characterized to date.{9589}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90067 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
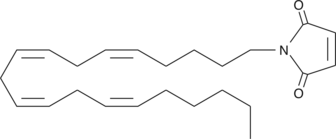
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous agonist of the central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.{7183,7182,9610} 2-AG is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system and is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in rat brain.{7183,6819} Monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) hydrolyzes 2-AG to arachidonic acid and glycerol, thereby terminating its biological actions.{11364} N-Arachidonyl maleimide (NAM) is a potent, irreversible inhibitor of monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) or MGL-like activity in rat cerebellar membranes, exhibiting an IC50 value of 140 nM.{13255} Inhibition of MGL by the sulfhydryl-reactive maleimide group of NAM suggests a critical cysteine residue is present in the substrate-binding site of the enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007517 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous agonist of the central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.{7183,7182,9610} 2-AG is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system and is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in rat brain.{7183,6819} Monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) hydrolyzes 2-AG to arachidonic acid and glycerol, thereby terminating its biological actions.{11364} N-Arachidonyl maleimide (NAM) is a potent, irreversible inhibitor of monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) or MGL-like activity in rat cerebellar membranes, exhibiting an IC50 value of 140 nM.{13255} Inhibition of MGL by the sulfhydryl-reactive maleimide group of NAM suggests a critical cysteine residue is present in the substrate-binding site of the enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007517 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous agonist of the central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors.{7183,7182,9610} 2-AG is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system and is the most abundant molecular species of monoacylglycerol found in rat brain.{7183,6819} Monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) hydrolyzes 2-AG to arachidonic acid and glycerol, thereby terminating its biological actions.{11364} N-Arachidonyl maleimide (NAM) is a potent, irreversible inhibitor of monoacylglycerol lipase (MGL) or MGL-like activity in rat cerebellar membranes, exhibiting an IC50 value of 140 nM.{13255} Inhibition of MGL by the sulfhydryl-reactive maleimide group of NAM suggests a critical cysteine residue is present in the substrate-binding site of the enzyme.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007517 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
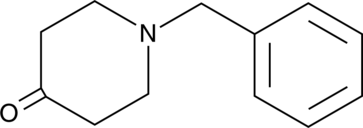
N-Benzyl-4-piperidone (Item No. 21962) is an analytical reference standard that is structurally categorized as a piperidine. It is a starting material that is used in the synthesis of fentanyl (Item Nos. ISO60197 | 14719) and related compounds. The physiological and toxicological properties of this compound are not known. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21962 -Out of stock
N-Benzyl-4-piperidone (Item No. 21962) is an analytical reference standard that is structurally categorized as a piperidine. It is a starting material that is used in the synthesis of fentanyl (Item Nos. ISO60197 | 14719) and related compounds. The physiological and toxicological properties of this compound are not known. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21962 -Out of stock
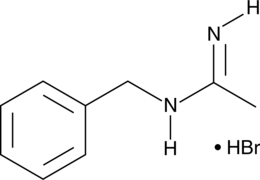
Of the different types of nitric oxide synthases (NOS), the inducible (iNOS) form contributes to inflammation and immune response while the constitutively-expressed endothelial (eNOS) enzyme plays important roles in regulating vascular tone. N-Benzylacetamidine is a potent inhibitor of iNOS (IC50 = 0.20 μM), with over 1,000-fold selectivity compared to eNOS (IC50 = 350 µM).{17417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Of the different types of nitric oxide synthases (NOS), the inducible (iNOS) form contributes to inflammation and immune response while the constitutively-expressed endothelial (eNOS) enzyme plays important roles in regulating vascular tone. N-Benzylacetamidine is a potent inhibitor of iNOS (IC50 = 0.20 μM), with over 1,000-fold selectivity compared to eNOS (IC50 = 350 µM).{17417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Of the different types of nitric oxide synthases (NOS), the inducible (iNOS) form contributes to inflammation and immune response while the constitutively-expressed endothelial (eNOS) enzyme plays important roles in regulating vascular tone. N-Benzylacetamidine is a potent inhibitor of iNOS (IC50 = 0.20 μM), with over 1,000-fold selectivity compared to eNOS (IC50 = 350 µM).{17417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Of the different types of nitric oxide synthases (NOS), the inducible (iNOS) form contributes to inflammation and immune response while the constitutively-expressed endothelial (eNOS) enzyme plays important roles in regulating vascular tone. N-Benzylacetamidine is a potent inhibitor of iNOS (IC50 = 0.20 μM), with over 1,000-fold selectivity compared to eNOS (IC50 = 350 µM).{17417}
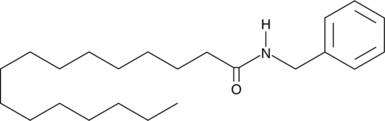
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-Benzylpalmitamide is a long-chain fatty acid amide (macamide or macaene) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant and is structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} N-Benzylpalmitamide has been the most frequently isolated of the 19 macamides currently identified. While many macamides have been identified as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), N-benzylpalmitamide displays only moderate FAAH inhibitory activity (44% inhibition at 500 µM).{28386} Additionally, many members of this family demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28387}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002235 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Benzylpalmitamide is a long-chain fatty acid amide (macamide or macaene) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant and is structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} N-Benzylpalmitamide has been the most frequently isolated of the 19 macamides currently identified. While many macamides have been identified as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), N-benzylpalmitamide displays only moderate FAAH inhibitory activity (44% inhibition at 500 µM).{28386} Additionally, many members of this family demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28387}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002235 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Benzylpalmitamide is a long-chain fatty acid amide (macamide or macaene) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant and is structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} N-Benzylpalmitamide has been the most frequently isolated of the 19 macamides currently identified. While many macamides have been identified as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), N-benzylpalmitamide displays only moderate FAAH inhibitory activity (44% inhibition at 500 µM).{28386} Additionally, many members of this family demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28387}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002235 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Benzylpalmitamide is a long-chain fatty acid amide (macamide or macaene) isolated from the maca (L. meyenii) plant and is structurally related to cannabinoids.{28386} N-Benzylpalmitamide has been the most frequently isolated of the 19 macamides currently identified. While many macamides have been identified as potent inhibitors of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH), N-benzylpalmitamide displays only moderate FAAH inhibitory activity (44% inhibition at 500 µM).{28386} Additionally, many members of this family demonstrate selective antiproliferative activity against diverse cancer cell lines.{28387}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002235 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Boc Ketamine (Item No. 9003561) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an arylcyclohexylamine. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003561 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Boc Ketamine (Item No. 9003561) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an arylcyclohexylamine. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003561 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Boc Norketamine (Item No. 9003560) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an arylcyclohexylamine. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003560 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-Boc Norketamine (Item No. 9003560) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an arylcyclohexylamine. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003560 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
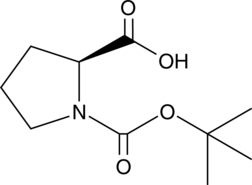
N-Boc-L-proline is a synthetic intermediate.{49607,49608} It has been used in the synthesis of enantioselective catalysts for aldol reactions and hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30386 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
N-Boc-L-proline is a synthetic intermediate.{49607,49608} It has been used in the synthesis of enantioselective catalysts for aldol reactions and hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30386 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
N-Boc-L-proline is a synthetic intermediate.{49607,49608} It has been used in the synthesis of enantioselective catalysts for aldol reactions and hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS5A inhibitors.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30386 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
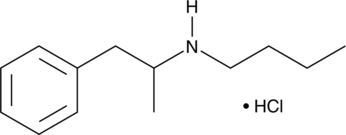
N-butyl Amphetamine (hydrochloride) (Item No. 23547) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an amphetamine.{26035} This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23547 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-butyl Amphetamine (hydrochloride) (Item No. 23547) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an amphetamine.{26035} This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23547 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
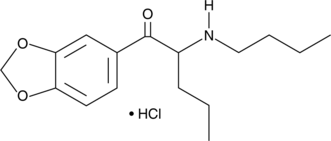
N-butyl Pentylone (hydrochloride) (Item No. 26701) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a cathinone. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26701 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-butyl Pentylone (hydrochloride) (Item No. 26701) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a cathinone. This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26701 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
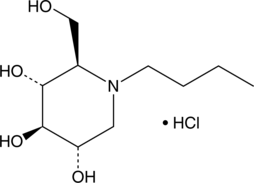
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin (NB-DNJ) is an iminosugar that inhibits ceramide-specific glucosyltransferase and β-glucosidase 2 (IC50s = 32 and 81 μM, respectively, for rat recombinant enzymes).{38202} The addition of NB-DNJ to growth medium for COS-7 cells expressing wild-type, S364R, N370S, V15M, or M123T glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme deficient in Spanish populations with the sphingolipid storage disorder Gaucher disease, leads to a 2.1-, 1.3-, 2.3-, 3.6,- or 9.9-fold increase in enzyme activity.{38203} NB-DNJ also inhibits HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with IC50 values of 282 and 211 μM, respectively.{38204} Formulations containing NB-DNJ have been used for the treatment of Gaucher disease and juvenile Sandhoff disease.{38205}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21065 -Out of stock
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin (NB-DNJ) is an iminosugar that inhibits ceramide-specific glucosyltransferase and β-glucosidase 2 (IC50s = 32 and 81 μM, respectively, for rat recombinant enzymes).{38202} The addition of NB-DNJ to growth medium for COS-7 cells expressing wild-type, S364R, N370S, V15M, or M123T glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme deficient in Spanish populations with the sphingolipid storage disorder Gaucher disease, leads to a 2.1-, 1.3-, 2.3-, 3.6,- or 9.9-fold increase in enzyme activity.{38203} NB-DNJ also inhibits HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with IC50 values of 282 and 211 μM, respectively.{38204} Formulations containing NB-DNJ have been used for the treatment of Gaucher disease and juvenile Sandhoff disease.{38205}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21065 -Out of stock
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin (NB-DNJ) is an iminosugar that inhibits ceramide-specific glucosyltransferase and β-glucosidase 2 (IC50s = 32 and 81 μM, respectively, for rat recombinant enzymes).{38202} The addition of NB-DNJ to growth medium for COS-7 cells expressing wild-type, S364R, N370S, V15M, or M123T glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme deficient in Spanish populations with the sphingolipid storage disorder Gaucher disease, leads to a 2.1-, 1.3-, 2.3-, 3.6,- or 9.9-fold increase in enzyme activity.{38203} NB-DNJ also inhibits HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with IC50 values of 282 and 211 μM, respectively.{38204} Formulations containing NB-DNJ have been used for the treatment of Gaucher disease and juvenile Sandhoff disease.{38205}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21065 -Out of stock
N-Butyldeoxynojirimycin (NB-DNJ) is an iminosugar that inhibits ceramide-specific glucosyltransferase and β-glucosidase 2 (IC50s = 32 and 81 μM, respectively, for rat recombinant enzymes).{38202} The addition of NB-DNJ to growth medium for COS-7 cells expressing wild-type, S364R, N370S, V15M, or M123T glucocerebrosidase, an enzyme deficient in Spanish populations with the sphingolipid storage disorder Gaucher disease, leads to a 2.1-, 1.3-, 2.3-, 3.6,- or 9.9-fold increase in enzyme activity.{38203} NB-DNJ also inhibits HIV-1 and HIV-2 infection of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) with IC50 values of 282 and 211 μM, respectively.{38204} Formulations containing NB-DNJ have been used for the treatment of Gaucher disease and juvenile Sandhoff disease.{38205}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21065 -Out of stock
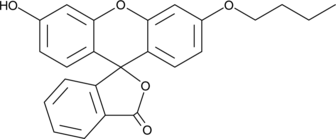
N-Butylfluorescein is a fluorescent compound that displays excitation/emission maxima of 467/512 nm, respectively.{48518} It has been used in the synthesis of butyl fluorescein myo-inositol phosphate (butyl FLIP), a fluorogenic substrate of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC).{48519}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20909 -Out of stock
N-Butylfluorescein is a fluorescent compound that displays excitation/emission maxima of 467/512 nm, respectively.{48518} It has been used in the synthesis of butyl fluorescein myo-inositol phosphate (butyl FLIP), a fluorogenic substrate of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC).{48519}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20909 -Out of stock
N-Butylfluorescein is a fluorescent compound that displays excitation/emission maxima of 467/512 nm, respectively.{48518} It has been used in the synthesis of butyl fluorescein myo-inositol phosphate (butyl FLIP), a fluorogenic substrate of phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI-PLC).{48519}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20909 -Out of stock
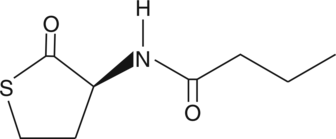
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone is an analog of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone, the small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and cellular metabolism.{16309} N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone induces violacein expression in C. violaceum mutants usually not able to produce AHLs.{16309,16308}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011204 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone is an analog of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone, the small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and cellular metabolism.{16309} N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone induces violacein expression in C. violaceum mutants usually not able to produce AHLs.{16309,16308}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011204 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone is an analog of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone, the small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and cellular metabolism.{16309} N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone induces violacein expression in C. violaceum mutants usually not able to produce AHLs.{16309,16308}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011204 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone is an analog of N-butyryl-L-homoserine lactone, the small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and cellular metabolism.{16309} N-butyryl-L-Homocysteine thio-lactone induces violacein expression in C. violaceum mutants usually not able to produce AHLs.{16309,16308}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011204 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
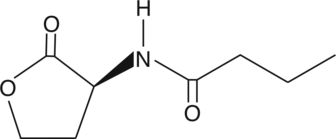
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, controlling gene expression, and cellular metabolism.{13434} The diverse applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence in general, infection prevention, and formation of biofilms.{13433,14086,14087,14088,14089,14093}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007898 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, controlling gene expression, and cellular metabolism.{13434} The diverse applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence in general, infection prevention, and formation of biofilms.{13433,14086,14087,14088,14089,14093}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007898 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, controlling gene expression, and cellular metabolism.{13434} The diverse applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence in general, infection prevention, and formation of biofilms.{13433,14086,14087,14088,14089,14093}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007898 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, controlling gene expression, and cellular metabolism.{13434} The diverse applications of this molecule include regulation of virulence in general, infection prevention, and formation of biofilms.{13433,14086,14087,14088,14089,14093}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007898 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
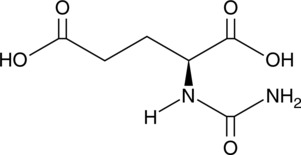
N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid is an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1), the first enzyme in the urea cycle.{38610} It is a structural analog of N-acetyl-glutamate, an endogenous CPS1 activator. N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid (500 mg/kg) reduces 2-ketoisocaproate-induced hyperammonemia in a mouse model of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency.{38609} It inhibits cell proliferation of a variety of cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 5 to 7.5 nM.{38608} It also inhibits tumor growth by 80 and 82% in orthotopic mouse models of pancreatic and triple-negative breast cancer, respectively, when administered at a dose of 120 mg/kg per day for 10 days. Formulations containing N-carbamyl-L-glutamic acid have been used in the treatment of primary N-acetyl-glutamate synthase deficiency.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23512 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid is an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1), the first enzyme in the urea cycle.{38610} It is a structural analog of N-acetyl-glutamate, an endogenous CPS1 activator. N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid (500 mg/kg) reduces 2-ketoisocaproate-induced hyperammonemia in a mouse model of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency.{38609} It inhibits cell proliferation of a variety of cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 5 to 7.5 nM.{38608} It also inhibits tumor growth by 80 and 82% in orthotopic mouse models of pancreatic and triple-negative breast cancer, respectively, when administered at a dose of 120 mg/kg per day for 10 days. Formulations containing N-carbamyl-L-glutamic acid have been used in the treatment of primary N-acetyl-glutamate synthase deficiency.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23512 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid is an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1), the first enzyme in the urea cycle.{38610} It is a structural analog of N-acetyl-glutamate, an endogenous CPS1 activator. N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid (500 mg/kg) reduces 2-ketoisocaproate-induced hyperammonemia in a mouse model of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency.{38609} It inhibits cell proliferation of a variety of cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 5 to 7.5 nM.{38608} It also inhibits tumor growth by 80 and 82% in orthotopic mouse models of pancreatic and triple-negative breast cancer, respectively, when administered at a dose of 120 mg/kg per day for 10 days. Formulations containing N-carbamyl-L-glutamic acid have been used in the treatment of primary N-acetyl-glutamate synthase deficiency.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23512 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid is an activator of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1), the first enzyme in the urea cycle.{38610} It is a structural analog of N-acetyl-glutamate, an endogenous CPS1 activator. N-Carbamyl-L-glutamic acid (500 mg/kg) reduces 2-ketoisocaproate-induced hyperammonemia in a mouse model of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-CoA lyase deficiency.{38609} It inhibits cell proliferation of a variety of cancer cell lines with IC50 values ranging from 5 to 7.5 nM.{38608} It also inhibits tumor growth by 80 and 82% in orthotopic mouse models of pancreatic and triple-negative breast cancer, respectively, when administered at a dose of 120 mg/kg per day for 10 days. Formulations containing N-carbamyl-L-glutamic acid have been used in the treatment of primary N-acetyl-glutamate synthase deficiency.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23512 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C16:1-Δ9-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a quorum sensing signaling molecule in strains of S. meliloti.{15835,15834,15833,15828} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012673 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C16:1-Δ9-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a quorum sensing signaling molecule in strains of S. meliloti.{15835,15834,15833,15828} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012673 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C16:1-Δ9-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a quorum sensing signaling molecule in strains of S. meliloti.{15835,15834,15833,15828} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012673 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C16:1-Δ9-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a quorum sensing signaling molecule in strains of S. meliloti.{15835,15834,15833,15828} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012673 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C18:1-Δ9 cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that may have antimicrobial activity{15832} and thus, might be used to inhibit pathogenesis by regulating bacerial quorum sensing signaling.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012674 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C18:1-Δ9 cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that may have antimicrobial activity{15832} and thus, might be used to inhibit pathogenesis by regulating bacerial quorum sensing signaling.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012674 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C18:1-Δ9 cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that may have antimicrobial activity{15832} and thus, might be used to inhibit pathogenesis by regulating bacerial quorum sensing signaling.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012674 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C18:1-Δ9 cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that may have antimicrobial activity{15832} and thus, might be used to inhibit pathogenesis by regulating bacerial quorum sensing signaling.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012674 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C14:1-Δ9-cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a signaling molecule in the quorum sensing of A. vitis.{15831} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therpy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012672 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C14:1-Δ9-cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a signaling molecule in the quorum sensing of A. vitis.{15831} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therpy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012672 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C14:1-Δ9-cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a signaling molecule in the quorum sensing of A. vitis.{15831} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therpy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012672 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory process used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group) and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} C14:1-Δ9-cis-(L)-HSL is a long-chain AHL that functions as a signaling molecule in the quorum sensing of A. vitis.{15831} Regulating bacterial quorum sensing signaling can be used to inhibit pathogenesis and thus, represents a new approach to antimicrobial therpy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10012672 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
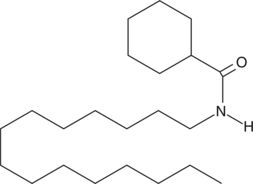
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic palmitoyl ethanolamidase (PEAase) that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonylpentadecylamine is a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase, inhibiting the enzyme with an IC50 of 4.5 µM, while failing to inhibit FAAH even at 100 µM.{13342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007739 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic palmitoyl ethanolamidase (PEAase) that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonylpentadecylamine is a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase, inhibiting the enzyme with an IC50 of 4.5 µM, while failing to inhibit FAAH even at 100 µM.{13342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007739 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic palmitoyl ethanolamidase (PEAase) that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonylpentadecylamine is a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase, inhibiting the enzyme with an IC50 of 4.5 µM, while failing to inhibit FAAH even at 100 µM.{13342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007739 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Numerous analogs of fatty acyl ethanolamides potentiate the intrinsic biological activity of endocannabinoids.{10254} This potentiation is ascribed either to inhibition of AEA reuptake into neurons, or inhibition of fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) within the neurons. {10647} However, Ueda has recently cloned another amidase, the acidic palmitoyl ethanolamidase (PEAase) that promotes the hydrolysis of palmitoylethanolamide.{9989} N-Cyclohexanecarbonylpentadecylamine is a selective inhibitor of acidic PEAase, inhibiting the enzyme with an IC50 of 4.5 µM, while failing to inhibit FAAH even at 100 µM.{13342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007739 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder