Chemicals
Showing 28051–28200 of 41137 results
-
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Different quorum sensing molecules are produced at different times in bacterial population growth and have distinct cellular effects mediated through changes in gene expression.{16591,16592} N-3-hydroxyoctanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule secreted by various bacteria.{20835,20837} This lactone can have activating or suppressing effects on gene expression and biofilm formation, respectively.{20833,20836} N-3-hydroxyoctanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is produced via lactonolysis from 3-oxooctanoyl-homoserine lactone, altering quorum sensing or contributing to quorum quenching.{20832}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001150 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Different quorum sensing molecules are produced at different times in bacterial population growth and have distinct cellular effects mediated through changes in gene expression.{16591,16592} N-3-hydroxyoctanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a small diffusible signaling molecule secreted by various bacteria.{20835,20837} This lactone can have activating or suppressing effects on gene expression and biofilm formation, respectively.{20833,20836} N-3-hydroxyoctanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is produced via lactonolysis from 3-oxooctanoyl-homoserine lactone, altering quorum sensing or contributing to quorum quenching.{20832}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001150 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
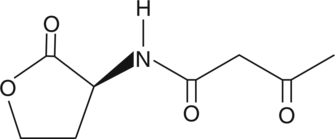
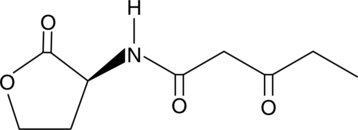
N-3-oxo-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a bacterial quorum-sensing signaling molecule.{59066} It induces expression of rhiI in R. leguminosarum, a gene with roles in the interaction of the rhizosphere with legumes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13024 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-3-oxo-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a bacterial quorum-sensing signaling molecule.{59066} It induces expression of rhiI in R. leguminosarum, a gene with roles in the interaction of the rhizosphere with legumes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13024 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-3-oxo-butyryl-L-Homoserine lactone is a bacterial quorum-sensing signaling molecule.{59066} It induces expression of rhiI in R. leguminosarum, a gene with roles in the interaction of the rhizosphere with legumes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13024 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
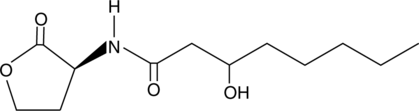
N-3-oxo-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a quorum-sensing signaling molecule that is produced by bacteria in response to increasing cell density.{53177} It increases expression of the bacterial conjugation gene tra in A. tumefaciens in a reporter cell assay. N-3-oxo-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone (100 nM) induces adventitious root formation and increases expression of the auxin-response genes AUX22c and AUX22d and the cell division genes CDC2, ARC, and CDPK in mung bean seedlings.{53178} It decreases expression of glucanase genes in A. thaliana when used at a concentration of 6 µM.{53179}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13026 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-3-oxo-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a quorum-sensing signaling molecule that is produced by bacteria in response to increasing cell density.{53177} It increases expression of the bacterial conjugation gene tra in A. tumefaciens in a reporter cell assay. N-3-oxo-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone (100 nM) induces adventitious root formation and increases expression of the auxin-response genes AUX22c and AUX22d and the cell division genes CDC2, ARC, and CDPK in mung bean seedlings.{53178} It decreases expression of glucanase genes in A. thaliana when used at a concentration of 6 µM.{53179}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13026 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
N-3-oxo-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a quorum-sensing signaling molecule that is produced by bacteria in response to increasing cell density.{53177} It increases expression of the bacterial conjugation gene tra in A. tumefaciens in a reporter cell assay. N-3-oxo-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone (100 nM) induces adventitious root formation and increases expression of the auxin-response genes AUX22c and AUX22d and the cell division genes CDC2, ARC, and CDPK in mung bean seedlings.{53178} It decreases expression of glucanase genes in A. thaliana when used at a concentration of 6 µM.{53179}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13026 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-3-oxo-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a quorum-sensing signaling molecule that is produced by bacteria in response to increasing cell density.{53177} It increases expression of the bacterial conjugation gene tra in A. tumefaciens in a reporter cell assay. N-3-oxo-decanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone (100 nM) induces adventitious root formation and increases expression of the auxin-response genes AUX22c and AUX22d and the cell division genes CDC2, ARC, and CDPK in mung bean seedlings.{53178} It decreases expression of glucanase genes in A. thaliana when used at a concentration of 6 µM.{53179}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13026 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{13433} A promising field of study involves controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules.{13433} N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C12-HSL) is one of the AHLs frequently identified in extracts of respiratory secretions from cystic fibrosis patients infected with P. aeruginosa and/or strains of the B. cepacia complex.{14095} 3-oxo-C12-HSL activates the transcription factors NF-κB and AP-2 to induce interleukin-8 production in human lung fibroblasts and epithelial cells, possibly contributing to the neutrophil infiltration and inflammation found in P. aeruginosa infections.{14252}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007895 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{13433} A promising field of study involves controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules.{13433} N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C12-HSL) is one of the AHLs frequently identified in extracts of respiratory secretions from cystic fibrosis patients infected with P. aeruginosa and/or strains of the B. cepacia complex.{14095} 3-oxo-C12-HSL activates the transcription factors NF-κB and AP-2 to induce interleukin-8 production in human lung fibroblasts and epithelial cells, possibly contributing to the neutrophil infiltration and inflammation found in P. aeruginosa infections.{14252}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007895 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{13433} A promising field of study involves controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules.{13433} N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C12-HSL) is one of the AHLs frequently identified in extracts of respiratory secretions from cystic fibrosis patients infected with P. aeruginosa and/or strains of the B. cepacia complex.{14095} 3-oxo-C12-HSL activates the transcription factors NF-κB and AP-2 to induce interleukin-8 production in human lung fibroblasts and epithelial cells, possibly contributing to the neutrophil infiltration and inflammation found in P. aeruginosa infections.{14252}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007895 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{13433} A promising field of study involves controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules.{13433} N-3-oxo-dodecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C12-HSL) is one of the AHLs frequently identified in extracts of respiratory secretions from cystic fibrosis patients infected with P. aeruginosa and/or strains of the B. cepacia complex.{14095} 3-oxo-C12-HSL activates the transcription factors NF-κB and AP-2 to induce interleukin-8 production in human lung fibroblasts and epithelial cells, possibly contributing to the neutrophil infiltration and inflammation found in P. aeruginosa infections.{14252}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007895 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
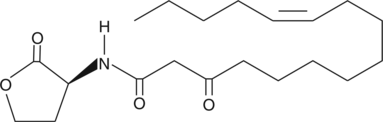
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} An unspecified positional and geometric isomer of 3-oxo-C16:1-(L)-HSL is produced by the F2/5 strain of A. vitis, the bacterium responsible for grape crown gall and its resulting loss of agricultural productivity.{15400}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011238 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} An unspecified positional and geometric isomer of 3-oxo-C16:1-(L)-HSL is produced by the F2/5 strain of A. vitis, the bacterium responsible for grape crown gall and its resulting loss of agricultural productivity.{15400}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011238 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} An unspecified positional and geometric isomer of 3-oxo-C16:1-(L)-HSL is produced by the F2/5 strain of A. vitis, the bacterium responsible for grape crown gall and its resulting loss of agricultural productivity.{15400}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011238 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} An unspecified positional and geometric isomer of 3-oxo-C16:1-(L)-HSL is produced by the F2/5 strain of A. vitis, the bacterium responsible for grape crown gall and its resulting loss of agricultural productivity.{15400}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011238 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
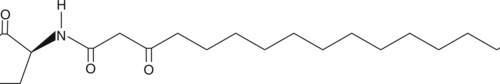
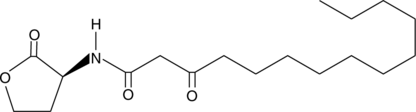
N-3-oxo-hexadecanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is an unusual, substituted, long-chain N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) produced by some bacteria, including strains of Agrobacterium vitis and Pseudomonas.{33650,33651} Like other AHLs, this C16-containing form is thought to be involved in quorum sensing. Substituted, long-chain AHLs, including N-3-oxo-tetradecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (Item No. 13063), prime for systemic acquired resistance to pathogen attack in plants.{33652}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13062 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-3-oxo-hexadecanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is an unusual, substituted, long-chain N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) produced by some bacteria, including strains of Agrobacterium vitis and Pseudomonas.{33650,33651} Like other AHLs, this C16-containing form is thought to be involved in quorum sensing. Substituted, long-chain AHLs, including N-3-oxo-tetradecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (Item No. 13063), prime for systemic acquired resistance to pathogen attack in plants.{33652}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13062 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
N-3-oxo-hexadecanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is an unusual, substituted, long-chain N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) produced by some bacteria, including strains of Agrobacterium vitis and Pseudomonas.{33650,33651} Like other AHLs, this C16-containing form is thought to be involved in quorum sensing. Substituted, long-chain AHLs, including N-3-oxo-tetradecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (Item No. 13063), prime for systemic acquired resistance to pathogen attack in plants.{33652}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-3-oxo-hexadecanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is an unusual, substituted, long-chain N-acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) produced by some bacteria, including strains of Agrobacterium vitis and Pseudomonas.{33650,33651} Like other AHLs, this C16-containing form is thought to be involved in quorum sensing. Substituted, long-chain AHLs, including N-3-oxo-tetradecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (Item No. 13063), prime for systemic acquired resistance to pathogen attack in plants.{33652}
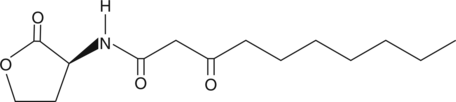
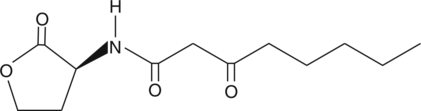
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} In the gram-negative bacterium A. tumefaciens, N-3-oxo-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactone promotes the expression of the transcriptional activator (and LuxR homolog) TraR.{16347}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011206 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} In the gram-negative bacterium A. tumefaciens, N-3-oxo-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactone promotes the expression of the transcriptional activator (and LuxR homolog) TraR.{16347}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011206 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} In the gram-negative bacterium A. tumefaciens, N-3-oxo-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactone promotes the expression of the transcriptional activator (and LuxR homolog) TraR.{16347}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011206 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} In the gram-negative bacterium A. tumefaciens, N-3-oxo-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactone promotes the expression of the transcriptional activator (and LuxR homolog) TraR.{16347}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10011206 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
N-3-oxo-pentanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a chain-shortened derivative of the bacterial quorum sensing signaling molecule N-3-oxo-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (Item No. 10011206).{39321} It inhibits binding of the autoinducer N-3-oxo-hexanoyl homoserine lactone to E. coli containing the transcription factor LuxR when used at a concentration of 230 nM.{53505} It acts as an autoinducer to activate the V. fischeri luminescence system in E. coli when used at concentrations ranging from 20 to 200 nM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-3-oxo-pentanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a chain-shortened derivative of the bacterial quorum sensing signaling molecule N-3-oxo-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (Item No. 10011206).{39321} It inhibits binding of the autoinducer N-3-oxo-hexanoyl homoserine lactone to E. coli containing the transcription factor LuxR when used at a concentration of 230 nM.{53505} It acts as an autoinducer to activate the V. fischeri luminescence system in E. coli when used at concentrations ranging from 20 to 200 nM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-3-oxo-pentanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a chain-shortened derivative of the bacterial quorum sensing signaling molecule N-3-oxo-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (Item No. 10011206).{39321} It inhibits binding of the autoinducer N-3-oxo-hexanoyl homoserine lactone to E. coli containing the transcription factor LuxR when used at a concentration of 230 nM.{53505} It acts as an autoinducer to activate the V. fischeri luminescence system in E. coli when used at concentrations ranging from 20 to 200 nM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-3-oxo-pentanoyl-L-Homoserine lactone is a chain-shortened derivative of the bacterial quorum sensing signaling molecule N-3-oxo-octanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (Item No. 10011206).{39321} It inhibits binding of the autoinducer N-3-oxo-hexanoyl homoserine lactone to E. coli containing the transcription factor LuxR when used at a concentration of 230 nM.{53505} It acts as an autoinducer to activate the V. fischeri luminescence system in E. coli when used at concentrations ranging from 20 to 200 nM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} 3-oxo-C14:1-Δ7cis-(L)-HSL is a bacterial quorum sensing compound that possesses antimicrobial activity, the ability to inhibit biofilm formation, and exhibits immune suppressive activity.{17157,16341} This compound is structurally related to other 3-oxo-monounsaturated (N-acylated homoserine lactones) AHLs such as 3-oxo-C16:1-Δ11cis-(L)-HSL (Catalog No. 10011238).
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} 3-oxo-C14:1-Δ7cis-(L)-HSL is a bacterial quorum sensing compound that possesses antimicrobial activity, the ability to inhibit biofilm formation, and exhibits immune suppressive activity.{17157,16341} This compound is structurally related to other 3-oxo-monounsaturated (N-acylated homoserine lactones) AHLs such as 3-oxo-C16:1-Δ11cis-(L)-HSL (Catalog No. 10011238).
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} 3-oxo-C14:1-Δ7cis-(L)-HSL is a bacterial quorum sensing compound that possesses antimicrobial activity, the ability to inhibit biofilm formation, and exhibits immune suppressive activity.{17157,16341} This compound is structurally related to other 3-oxo-monounsaturated (N-acylated homoserine lactones) AHLs such as 3-oxo-C16:1-Δ11cis-(L)-HSL (Catalog No. 10011238).
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density.{15370} This regulatory process manifests itself with a variety of phenotypes including biofilm formation and virulence factor production.{13434} Coordinated gene expression is achieved by the production, release, and detection of small diffusible signal molecules called autoinducers. The N-acylated homoserine lactones (AHLs) comprise one such class of autoinducers, each of which generally consists of a fatty acid coupled with homoserine lactone (HSL). Regulation of bacterial quorum sensing signaling systems to inhibit pathogenesis represents a new approach to antimicrobial therapy in the treatment of infectious diseases.{15369} AHLs vary in acyl group length (C4-C18), in the substitution of C3 (hydrogen, hydroxyl, or oxo group), and in the presence or absence of one or more carbon-carbon double bonds in the fatty acid chain. These differences confer signal specificity through the affinity of transcriptional regulators of the LuxR family.{15398} 3-oxo-C14:1-Δ7cis-(L)-HSL is a bacterial quorum sensing compound that possesses antimicrobial activity, the ability to inhibit biofilm formation, and exhibits immune suppressive activity.{17157,16341} This compound is structurally related to other 3-oxo-monounsaturated (N-acylated homoserine lactones) AHLs such as 3-oxo-C16:1-Δ11cis-(L)-HSL (Catalog No. 10011238).
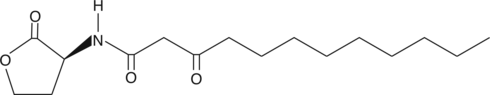
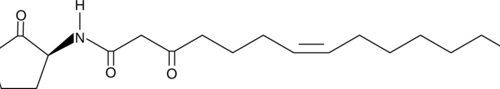
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by the synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-3-oxo-tetradecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C14-HSL) is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and affecting cellular metabolism in bacteria.{16305,16307,16308} It appears later than shorter acyl chain AHLs in developing biofilms{16593} and, like other long chain 3-oxo-AHLs, stimulates the production of putisolvin,{16612} which in turn, inhibits biofilm formation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by the synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-3-oxo-tetradecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C14-HSL) is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and affecting cellular metabolism in bacteria.{16305,16307,16308} It appears later than shorter acyl chain AHLs in developing biofilms{16593} and, like other long chain 3-oxo-AHLs, stimulates the production of putisolvin,{16612} which in turn, inhibits biofilm formation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by the synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-3-oxo-tetradecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C14-HSL) is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and affecting cellular metabolism in bacteria.{16305,16307,16308} It appears later than shorter acyl chain AHLs in developing biofilms{16593} and, like other long chain 3-oxo-AHLs, stimulates the production of putisolvin,{16612} which in turn, inhibits biofilm formation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Quorum sensing is a regulatory system used by bacteria for controlling gene expression in response to increasing cell density. Controlling bacterial infections by quenching their quorum sensing systems is a promising field of study. The expression of specific target genes, such as transcriptional regulators belonging to the LuxIR family of proteins, is coordinated by the synthesis of diffusible acylhomoserine lactone (AHL) molecules. N-3-oxo-tetradecanoyl-L-homoserine lactone (3-oxo-C14-HSL) is a small diffusible signaling molecule involved in quorum sensing, thereby controlling gene expression and affecting cellular metabolism in bacteria.{16305,16307,16308} It appears later than shorter acyl chain AHLs in developing biofilms{16593} and, like other long chain 3-oxo-AHLs, stimulates the production of putisolvin,{16612} which in turn, inhibits biofilm formation.
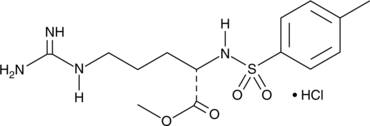
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-4-Tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester (TAME) is a synthetic substrate of serine proteases, including thrombin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, and kallikreins.{28529,28531,28530} It can be used to evaluate serine proteases from diverse sources.{28532} TAME also binds to and inhibits anaphase-promoting complex, a ubiquitin ligase, in Xenopus egg extract.{28533,28534}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-4-Tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester (TAME) is a synthetic substrate of serine proteases, including thrombin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, and kallikreins.{28529,28531,28530} It can be used to evaluate serine proteases from diverse sources.{28532} TAME also binds to and inhibits anaphase-promoting complex, a ubiquitin ligase, in Xenopus egg extract.{28533,28534}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-4-Tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester (TAME) is a synthetic substrate of serine proteases, including thrombin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, and kallikreins.{28529,28531,28530} It can be used to evaluate serine proteases from diverse sources.{28532} TAME also binds to and inhibits anaphase-promoting complex, a ubiquitin ligase, in Xenopus egg extract.{28533,28534}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-4-Tosyl-L-arginine methyl ester (TAME) is a synthetic substrate of serine proteases, including thrombin, trypsin, chymotrypsin, and kallikreins.{28529,28531,28530} It can be used to evaluate serine proteases from diverse sources.{28532} TAME also binds to and inhibits anaphase-promoting complex, a ubiquitin ligase, in Xenopus egg extract.{28533,28534}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
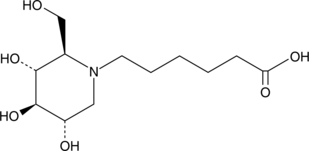
1-Deoxynojirimycin (Item No. 10011718) is a glucose analog that potently inhibits α-glucosidase I and II. N-5-Carboxypentyl-1-deoxynojirimycin is a ligand used for the purification of glucosidase I and II.{29032,29034} The carboxypentyl groups allows linkage of the inhibitor with resins for affinity chromatography.{29032,29033} N-5-Carboxypentyl-1-deoxynojirimycin is at least as potent an inhibitor of glucosidase as 1-deoxynojirimycin (Kis = 0.45 and 2.1 µM, respectively, for pig liver glucosidase I).{29031}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
1-Deoxynojirimycin (Item No. 10011718) is a glucose analog that potently inhibits α-glucosidase I and II. N-5-Carboxypentyl-1-deoxynojirimycin is a ligand used for the purification of glucosidase I and II.{29032,29034} The carboxypentyl groups allows linkage of the inhibitor with resins for affinity chromatography.{29032,29033} N-5-Carboxypentyl-1-deoxynojirimycin is at least as potent an inhibitor of glucosidase as 1-deoxynojirimycin (Kis = 0.45 and 2.1 µM, respectively, for pig liver glucosidase I).{29031}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
1-Deoxynojirimycin (Item No. 10011718) is a glucose analog that potently inhibits α-glucosidase I and II. N-5-Carboxypentyl-1-deoxynojirimycin is a ligand used for the purification of glucosidase I and II.{29032,29034} The carboxypentyl groups allows linkage of the inhibitor with resins for affinity chromatography.{29032,29033} N-5-Carboxypentyl-1-deoxynojirimycin is at least as potent an inhibitor of glucosidase as 1-deoxynojirimycin (Kis = 0.45 and 2.1 µM, respectively, for pig liver glucosidase I).{29031}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
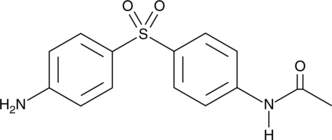
N-acetyl Dapsone is a metabolite of dapsone, an anti-inflammatory and antibacterial compound that is widely used in the treatment of leprosy, malaria, acne, and various immune disorders.{28213} Dapsone is acetylated in the liver to monoacetyldapsone, the major metabolite, and other mono and diacetyl derivatives, and subsequently deacetylated back to diaminodiphenylsulfone (dapsone) until a state of equilibrium is achieved.{28213}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-acetyl Dapsone is a metabolite of dapsone, an anti-inflammatory and antibacterial compound that is widely used in the treatment of leprosy, malaria, acne, and various immune disorders.{28213} Dapsone is acetylated in the liver to monoacetyldapsone, the major metabolite, and other mono and diacetyl derivatives, and subsequently deacetylated back to diaminodiphenylsulfone (dapsone) until a state of equilibrium is achieved.{28213}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-acetyl Dapsone is a metabolite of dapsone, an anti-inflammatory and antibacterial compound that is widely used in the treatment of leprosy, malaria, acne, and various immune disorders.{28213} Dapsone is acetylated in the liver to monoacetyldapsone, the major metabolite, and other mono and diacetyl derivatives, and subsequently deacetylated back to diaminodiphenylsulfone (dapsone) until a state of equilibrium is achieved.{28213}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
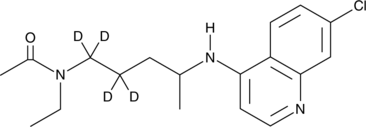
N-acetyl Desethylchloroquine-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of N-acetyl desethylchloroquine by GC- or LC-MS. N-acetyl Desethylchloroquine is a minor metabolite of chloroquine (Item No. 14194).{54268,54269}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30908 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl Desethylchloroquine-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of N-acetyl desethylchloroquine by GC- or LC-MS. N-acetyl Desethylchloroquine is a minor metabolite of chloroquine (Item No. 14194).{54268,54269}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30908 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl Desethylchloroquine-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of N-acetyl desethylchloroquine by GC- or LC-MS. N-acetyl Desethylchloroquine is a minor metabolite of chloroquine (Item No. 14194).{54268,54269}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30908 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
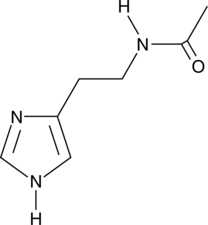
N-acetyl Histamine is a histamine metabolite that is formed via acetyl-CoA-dependent N-acetylation of histamine by AANATL7 in D. melanogaster, polyamine N-acetyltransferase in F. hepatica, and the arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferases aaNAT2 and aaNAT5b in A. aegypti.{41784} It selectively inhibits sweet-almond β-glucosidase over yeast α-glucosidase in vitro (Kis = 0.035 and 20 mM, respectively).{41783} It also inhibits human glutaminyl cyclase (IC50 = 17 μM).{41785} N-acetyl Histamine has no effect on eosinophil activity and has been used as a negative control for histamine mediation of anaphylaxis.{41786}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25118 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl Histamine is a histamine metabolite that is formed via acetyl-CoA-dependent N-acetylation of histamine by AANATL7 in D. melanogaster, polyamine N-acetyltransferase in F. hepatica, and the arylalkylamine N-acetyltransferases aaNAT2 and aaNAT5b in A. aegypti.{41784} It selectively inhibits sweet-almond β-glucosidase over yeast α-glucosidase in vitro (Kis = 0.035 and 20 mM, respectively).{41783} It also inhibits human glutaminyl cyclase (IC50 = 17 μM).{41785} N-acetyl Histamine has no effect on eosinophil activity and has been used as a negative control for histamine mediation of anaphylaxis.{41786}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25118 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
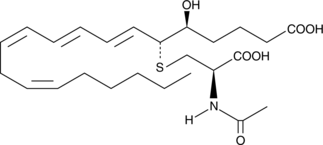
N-acetyl LTE4 is the major inactive metabolite of LTE4 found in bile. This route of metabolism is prominent in the rat, but of minor importance in humans.{544,546} N-acetyl LTE4 is 100 times less potent than LTC4 as a vasoconstricting agent.{546} In healthy human subjects urinary excretion of N-acetyl LTE4 is about 1.5 nmol/mol creatinine, which is considerably less than that of LTE4 (12 nmol/mol creatinine).{307}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20420 -Available on backorder
N-acetyl LTE4 is the major inactive metabolite of LTE4 found in bile. This route of metabolism is prominent in the rat, but of minor importance in humans.{544,546} N-acetyl LTE4 is 100 times less potent than LTC4 as a vasoconstricting agent.{546} In healthy human subjects urinary excretion of N-acetyl LTE4 is about 1.5 nmol/mol creatinine, which is considerably less than that of LTE4 (12 nmol/mol creatinine).{307}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20420 -Available on backorder
N-acetyl LTE4 is the major inactive metabolite of LTE4 found in bile. This route of metabolism is prominent in the rat, but of minor importance in humans.{544,546} N-acetyl LTE4 is 100 times less potent than LTC4 as a vasoconstricting agent.{546} In healthy human subjects urinary excretion of N-acetyl LTE4 is about 1.5 nmol/mol creatinine, which is considerably less than that of LTE4 (12 nmol/mol creatinine).{307}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20420 -Available on backorder
N-acetyl Sulfamethoxazole is a metabolite of sulfamethoxazole, an antibiotic with antiviral activity, that can be detected in urine.{27032,28148}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
N-acetyl Sulfamethoxazole is a metabolite of sulfamethoxazole, an antibiotic with antiviral activity, that can be detected in urine.{27032,28148}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
N-acetyl Sulfamethoxazole is a metabolite of sulfamethoxazole, an antibiotic with antiviral activity, that can be detected in urine.{27032,28148}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
N-acetyl Sulfamethoxazole is a metabolite of sulfamethoxazole, an antibiotic with antiviral activity, that can be detected in urine.{27032,28148}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
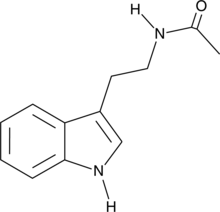
N-acetyl Tryptamine is a structural analog of melatonin (5-methoxy-N-acetyltryptamine; Item No. 14427) that binds the melatonin MT2 receptor (Ki = 41 nM).{30340} It acts as a melatonin receptor antagonist in frog skin and chicken retina and as a partial agonist in rabbit retina.{30338,30339,26017} N-acetyl Tryptamine is also a reaction product of assays for serotonin N-acetyltransferase, the penultimate enzyme in the melatonin biosynthetic pathway.{30337}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-acetyl Tryptamine is a structural analog of melatonin (5-methoxy-N-acetyltryptamine; Item No. 14427) that binds the melatonin MT2 receptor (Ki = 41 nM).{30340} It acts as a melatonin receptor antagonist in frog skin and chicken retina and as a partial agonist in rabbit retina.{30338,30339,26017} N-acetyl Tryptamine is also a reaction product of assays for serotonin N-acetyltransferase, the penultimate enzyme in the melatonin biosynthetic pathway.{30337}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-acetyl Tryptamine is a structural analog of melatonin (5-methoxy-N-acetyltryptamine; Item No. 14427) that binds the melatonin MT2 receptor (Ki = 41 nM).{30340} It acts as a melatonin receptor antagonist in frog skin and chicken retina and as a partial agonist in rabbit retina.{30338,30339,26017} N-acetyl Tryptamine is also a reaction product of assays for serotonin N-acetyltransferase, the penultimate enzyme in the melatonin biosynthetic pathway.{30337}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-acetyl Tryptamine is a structural analog of melatonin (5-methoxy-N-acetyltryptamine; Item No. 14427) that binds the melatonin MT2 receptor (Ki = 41 nM).{30340} It acts as a melatonin receptor antagonist in frog skin and chicken retina and as a partial agonist in rabbit retina.{30338,30339,26017} N-acetyl Tryptamine is also a reaction product of assays for serotonin N-acetyltransferase, the penultimate enzyme in the melatonin biosynthetic pathway.{30337}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
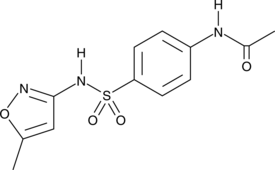
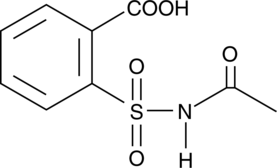
N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a structural analog of aspirin that acts as a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX) with a COX-2 selectivity index of 0.23.{13010} In vitro studies showed that N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a more potent inhibitor of COX-1/COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 µM and 0.25 µM, respectively, than aspirin with IC50 values of 0.35 µM and 2.4 µM, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008284 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a structural analog of aspirin that acts as a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX) with a COX-2 selectivity index of 0.23.{13010} In vitro studies showed that N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a more potent inhibitor of COX-1/COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 µM and 0.25 µM, respectively, than aspirin with IC50 values of 0.35 µM and 2.4 µM, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008284 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a structural analog of aspirin that acts as a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX) with a COX-2 selectivity index of 0.23.{13010} In vitro studies showed that N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a more potent inhibitor of COX-1/COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 µM and 0.25 µM, respectively, than aspirin with IC50 values of 0.35 µM and 2.4 µM, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008284 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a structural analog of aspirin that acts as a non-selective inhibitor of cyclooxygenase (COX) with a COX-2 selectivity index of 0.23.{13010} In vitro studies showed that N-acetyl-2-carboxy Benzenesulfonamide is a more potent inhibitor of COX-1/COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 µM and 0.25 µM, respectively, than aspirin with IC50 values of 0.35 µM and 2.4 µM, respectively.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008284 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl-2,3-dehydro-2-Deoxyneuraminic acid (DANA) is an inhibitor of human neuraminidases (sialidases) NEU1-4 (IC50s = 143, 43, 61, and 74 μM, respectively).{38566} In vivo, DANA (30 μl of a 5 mM solution) reduces latency to first seizure and increases seizure duration in a rat model of potassium-induced seizures.{38567}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19939 -Available on backorder
N-acetyl-2,3-dehydro-2-Deoxyneuraminic acid (DANA) is an inhibitor of human neuraminidases (sialidases) NEU1-4 (IC50s = 143, 43, 61, and 74 μM, respectively).{38566} In vivo, DANA (30 μl of a 5 mM solution) reduces latency to first seizure and increases seizure duration in a rat model of potassium-induced seizures.{38567}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19939 -Available on backorder
N-acetyl-2,3-dehydro-2-Deoxyneuraminic acid (DANA) is an inhibitor of human neuraminidases (sialidases) NEU1-4 (IC50s = 143, 43, 61, and 74 μM, respectively).{38566} In vivo, DANA (30 μl of a 5 mM solution) reduces latency to first seizure and increases seizure duration in a rat model of potassium-induced seizures.{38567}
Brand:CaymanSKU:19939 -Available on backorder
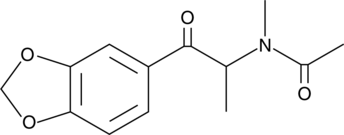
N-acetyl-3,4-Methylenedioxymethcathinone (N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC) is an acetylated analog of methylone (Item No. 10986), the MDMA-type designer drug that has been detected in products marketed as bath salts, plant food, and tablets.{19508,19756} The biological actions of N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC are unknown. This product is intended for forensic and research purposes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001492 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl-3,4-Methylenedioxymethcathinone (N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC) is an acetylated analog of methylone (Item No. 10986), the MDMA-type designer drug that has been detected in products marketed as bath salts, plant food, and tablets.{19508,19756} The biological actions of N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC are unknown. This product is intended for forensic and research purposes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001492 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl-3,4-Methylenedioxymethcathinone (N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC) is an acetylated analog of methylone (Item No. 10986), the MDMA-type designer drug that has been detected in products marketed as bath salts, plant food, and tablets.{19508,19756} The biological actions of N-acetyl-3,4-MDMC are unknown. This product is intended for forensic and research purposes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001492 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
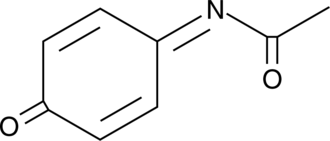
N-Acetyl-4-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) is a cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2E1 metabolite of acetaminophen that can be toxic to the liver when acetaminophen is consumed in large doses.{7361} At therapeutic doses of acetaminophen, NAPQI is inactivated by conjugation with glutathione. However, following toxic doses of acetaminophen, available liver reserves of glutathione are quickly depleted due to clearance of excess NAPQI, which enables hepatic proteins to become covalently modified by reactive metabolites and eventually results in hepatocyte necrosis.{7361}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-Acetyl-4-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) is a cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2E1 metabolite of acetaminophen that can be toxic to the liver when acetaminophen is consumed in large doses.{7361} At therapeutic doses of acetaminophen, NAPQI is inactivated by conjugation with glutathione. However, following toxic doses of acetaminophen, available liver reserves of glutathione are quickly depleted due to clearance of excess NAPQI, which enables hepatic proteins to become covalently modified by reactive metabolites and eventually results in hepatocyte necrosis.{7361}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-Acetyl-4-benzoquinone imine (NAPQI) is a cytochrome P450 3A4 and 2E1 metabolite of acetaminophen that can be toxic to the liver when acetaminophen is consumed in large doses.{7361} At therapeutic doses of acetaminophen, NAPQI is inactivated by conjugation with glutathione. However, following toxic doses of acetaminophen, available liver reserves of glutathione are quickly depleted due to clearance of excess NAPQI, which enables hepatic proteins to become covalently modified by reactive metabolites and eventually results in hepatocyte necrosis.{7361}
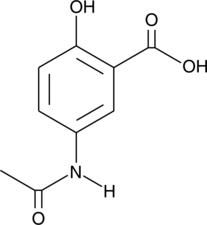
Brand:CaymanSKU:-N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid is a metabolite of the anti-inflammatory agent 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA; Item No. 70265) and its prodrug form, sulfasalazine (Item No. 15025).{42753,8455} It is formed in the liver, intestinal lumen, and colonic epithelial cells via N-acetyltransferases.{42754} It reduces IFN-γ binding to colonic epithelial cells by 24% when used at a concentration of 10 mM.{42756} N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid (100 µM) scavenges 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; Item No. 14805) radicals in a cell-free assay and inhibits base hydroxylation in DNA stimulated by hydroxy radicals.{42753,42755} Unlike sulfasalazine, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid does not inhibit 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (PGDH).{8455} Urinary levels of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid have been used as a marker of 5-ASA adherence in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.{42757}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27618 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid is a metabolite of the anti-inflammatory agent 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA; Item No. 70265) and its prodrug form, sulfasalazine (Item No. 15025).{42753,8455} It is formed in the liver, intestinal lumen, and colonic epithelial cells via N-acetyltransferases.{42754} It reduces IFN-γ binding to colonic epithelial cells by 24% when used at a concentration of 10 mM.{42756} N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid (100 µM) scavenges 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; Item No. 14805) radicals in a cell-free assay and inhibits base hydroxylation in DNA stimulated by hydroxy radicals.{42753,42755} Unlike sulfasalazine, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid does not inhibit 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (PGDH).{8455} Urinary levels of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid have been used as a marker of 5-ASA adherence in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.{42757}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27618 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid is a metabolite of the anti-inflammatory agent 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA; Item No. 70265) and its prodrug form, sulfasalazine (Item No. 15025).{42753,8455} It is formed in the liver, intestinal lumen, and colonic epithelial cells via N-acetyltransferases.{42754} It reduces IFN-γ binding to colonic epithelial cells by 24% when used at a concentration of 10 mM.{42756} N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid (100 µM) scavenges 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; Item No. 14805) radicals in a cell-free assay and inhibits base hydroxylation in DNA stimulated by hydroxy radicals.{42753,42755} Unlike sulfasalazine, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid does not inhibit 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (PGDH).{8455} Urinary levels of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid have been used as a marker of 5-ASA adherence in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.{42757}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27618 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid is a metabolite of the anti-inflammatory agent 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA; Item No. 70265) and its prodrug form, sulfasalazine (Item No. 15025).{42753,8455} It is formed in the liver, intestinal lumen, and colonic epithelial cells via N-acetyltransferases.{42754} It reduces IFN-γ binding to colonic epithelial cells by 24% when used at a concentration of 10 mM.{42756} N-acetyl-5-Aminosalicylic acid (100 µM) scavenges 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH; Item No. 14805) radicals in a cell-free assay and inhibits base hydroxylation in DNA stimulated by hydroxy radicals.{42753,42755} Unlike sulfasalazine, N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid does not inhibit 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (PGDH).{8455} Urinary levels of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid have been used as a marker of 5-ASA adherence in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.{42757}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27618 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
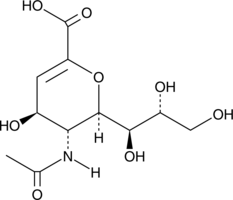
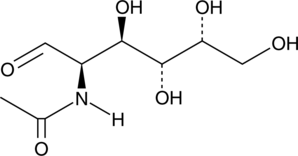
N-acetyl-D-Galactosamine (GalNAc) is an amino sugar derivative of galactose and a component of O-GalNAc glycans.{61099,61100} It is transferred from UDP-GalNAc to the hydroxy group of protein serine or threonine residues by polypeptide GalNAc transferase, forming the Tn antigen, during the first step of mucin-type O-glycosylation.{61101,61100} GalNAc has been used as a targeting moiety for liver-targeted delivery of oligonucleotides.{61099}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31728 - 1 gAvailable on backorder