Chemicals
Showing 27901–28050 of 41137 results
-
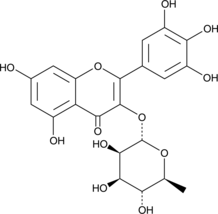
Myricetrin is a flavonoid that has been found in C. menyharthii leaf extracts and has diverse biological activities.{47426,47427} It is active against B. subtilis, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, S. aureus, and C. albicans (MIC = 0.25 mg/ml for all).{47426} Myricetrin inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and α-glucosidase in vitro (IC50s = 65 and 79 μg/ml, respectively). It inhibits LPS-induced production of TNF-α and enhances LPS-induced RANTES production in RAW 264.7 cells when used at concentrations of 0.2 and 1 mM.{47427}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26902 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
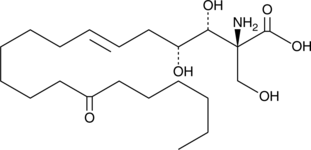
Myriocin is an amino fatty acid antibiotic derived from certain thermophylic fungi, in this case Mycelia sterilia. It is a potent immunosuppressant having 10- to 100-fold more activity than cyclosporin A.{8482} Myriocin is a potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyltransferase (Ki = 0.28 nM), the enzyme that catalyzes the first step of sphingolipid biosynthesis. {14764} It disrupts substratum adhesion of melanoma cells.{14763} It also suppresses cell proliferation in the murine cytotoxic T cell line CTLL-2 (IC50 = 15 nM) via apoptosis.{14764,2816} Myriocin suppresses replication of the hepatitis C virus in a murine model.{14762}
Brand:CaymanSKU:63150 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Myriocin is an amino fatty acid antibiotic derived from certain thermophylic fungi, in this case Mycelia sterilia. It is a potent immunosuppressant having 10- to 100-fold more activity than cyclosporin A.{8482} Myriocin is a potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyltransferase (Ki = 0.28 nM), the enzyme that catalyzes the first step of sphingolipid biosynthesis. {14764} It disrupts substratum adhesion of melanoma cells.{14763} It also suppresses cell proliferation in the murine cytotoxic T cell line CTLL-2 (IC50 = 15 nM) via apoptosis.{14764,2816} Myriocin suppresses replication of the hepatitis C virus in a murine model.{14762}
Brand:CaymanSKU:63150 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Myriocin is an amino fatty acid antibiotic derived from certain thermophylic fungi, in this case Mycelia sterilia. It is a potent immunosuppressant having 10- to 100-fold more activity than cyclosporin A.{8482} Myriocin is a potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyltransferase (Ki = 0.28 nM), the enzyme that catalyzes the first step of sphingolipid biosynthesis. {14764} It disrupts substratum adhesion of melanoma cells.{14763} It also suppresses cell proliferation in the murine cytotoxic T cell line CTLL-2 (IC50 = 15 nM) via apoptosis.{14764,2816} Myriocin suppresses replication of the hepatitis C virus in a murine model.{14762}
Brand:CaymanSKU:63150 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Myriocin is an amino fatty acid antibiotic derived from certain thermophylic fungi, in this case Mycelia sterilia. It is a potent immunosuppressant having 10- to 100-fold more activity than cyclosporin A.{8482} Myriocin is a potent inhibitor of serine palmitoyltransferase (Ki = 0.28 nM), the enzyme that catalyzes the first step of sphingolipid biosynthesis. {14764} It disrupts substratum adhesion of melanoma cells.{14763} It also suppresses cell proliferation in the murine cytotoxic T cell line CTLL-2 (IC50 = 15 nM) via apoptosis.{14764,2816} Myriocin suppresses replication of the hepatitis C virus in a murine model.{14762}
Brand:CaymanSKU:63150 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
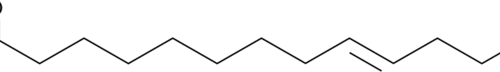
Myristelaidic acid is a 14-carbon monounsaturated ω-5 long-chain fatty acid. It is the trans isomer of myristoleic acid (Item No. 9002461). Myristelaidic acid is converted to myristelaidoyl CoA at a faster rate than myristoleic acid to myristoleoyl CoA.{36190}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22361 -Out of stock
Myristelaidic acid is a 14-carbon monounsaturated ω-5 long-chain fatty acid. It is the trans isomer of myristoleic acid (Item No. 9002461). Myristelaidic acid is converted to myristelaidoyl CoA at a faster rate than myristoleic acid to myristoleoyl CoA.{36190}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22361 -Out of stock
Myristelaidic acid is a 14-carbon monounsaturated ω-5 long-chain fatty acid. It is the trans isomer of myristoleic acid (Item No. 9002461). Myristelaidic acid is converted to myristelaidoyl CoA at a faster rate than myristoleic acid to myristoleoyl CoA.{36190}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22361 -Out of stock
Myristelaidic acid is a 14-carbon monounsaturated ω-5 long-chain fatty acid. It is the trans isomer of myristoleic acid (Item No. 9002461). Myristelaidic acid is converted to myristelaidoyl CoA at a faster rate than myristoleic acid to myristoleoyl CoA.{36190}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22361 -Out of stock
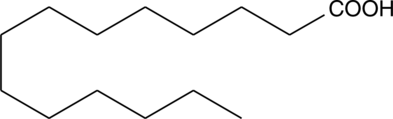
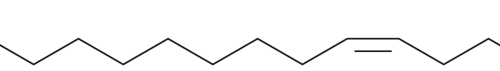
Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
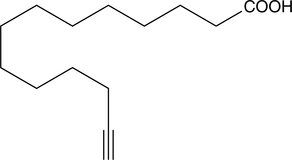
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated (14:0) fatty acid. In vivo, it is commonly added covalently to the N-terminus of proteins in a co-translational process termed N-myristoylation.{17231} The sirtuin SIRT6 removes this acyl group from myristoylated TNF-α, enhancing secretion.{22694} Myristic acid alkyne is a form of this myristic acid (Item No. 13351) with an ω-terminal alkyne. Such terminal alkyne groups can be used in linking reactions, known as click chemistry, characterized by high dependability and specificity of azide-alkyne bioconjugation reactions.{17991,17992} Click chemistry has only recently been applied to the study of lipids.{22694,16188}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated (14:0) fatty acid. In vivo, it is commonly added covalently to the N-terminus of proteins in a co-translational process termed N-myristoylation.{17231} The sirtuin SIRT6 removes this acyl group from myristoylated TNF-α, enhancing secretion.{22694} Myristic acid alkyne is a form of this myristic acid (Item No. 13351) with an ω-terminal alkyne. Such terminal alkyne groups can be used in linking reactions, known as click chemistry, characterized by high dependability and specificity of azide-alkyne bioconjugation reactions.{17991,17992} Click chemistry has only recently been applied to the study of lipids.{22694,16188}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated (14:0) fatty acid. In vivo, it is commonly added covalently to the N-terminus of proteins in a co-translational process termed N-myristoylation.{17231} The sirtuin SIRT6 removes this acyl group from myristoylated TNF-α, enhancing secretion.{22694} Myristic acid alkyne is a form of this myristic acid (Item No. 13351) with an ω-terminal alkyne. Such terminal alkyne groups can be used in linking reactions, known as click chemistry, characterized by high dependability and specificity of azide-alkyne bioconjugation reactions.{17991,17992} Click chemistry has only recently been applied to the study of lipids.{22694,16188}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated (14:0) fatty acid. In vivo, it is commonly added covalently to the N-terminus of proteins in a co-translational process termed N-myristoylation.{17231} The sirtuin SIRT6 removes this acyl group from myristoylated TNF-α, enhancing secretion.{22694} Myristic acid alkyne is a form of this myristic acid (Item No. 13351) with an ω-terminal alkyne. Such terminal alkyne groups can be used in linking reactions, known as click chemistry, characterized by high dependability and specificity of azide-alkyne bioconjugation reactions.{17991,17992} Click chemistry has only recently been applied to the study of lipids.{22694,16188}
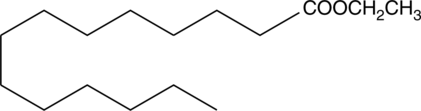
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myristic acid is a saturated fatty acid commonly found in animal and vegetable fats that is frequently used in cosmetics, soaps, perfumes, and flavorings. It increases low density lipoprotein cholesterol making it one of the most hypercholesterolemic of the saturated fatty acids.{14160} Myristic acid ethyl ester is a more hydrophobic form of the free acid. It is a marker of excessive ethanol consumption that can be isolated from the hair of an individual.{14159}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008197 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Myristic acid is a saturated fatty acid commonly found in animal and vegetable fats that is frequently used in cosmetics, soaps, perfumes, and flavorings. It increases low density lipoprotein cholesterol making it one of the most hypercholesterolemic of the saturated fatty acids.{14160} Myristic acid ethyl ester is a more hydrophobic form of the free acid. It is a marker of excessive ethanol consumption that can be isolated from the hair of an individual.{14159}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008197 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristic acid is a saturated fatty acid commonly found in animal and vegetable fats that is frequently used in cosmetics, soaps, perfumes, and flavorings. It increases low density lipoprotein cholesterol making it one of the most hypercholesterolemic of the saturated fatty acids.{14160} Myristic acid ethyl ester is a more hydrophobic form of the free acid. It is a marker of excessive ethanol consumption that can be isolated from the hair of an individual.{14159}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008197 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
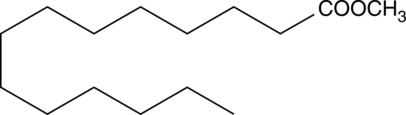
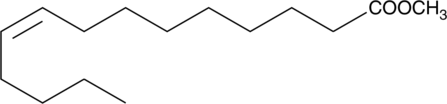
Myristic acid methyl ester is an esterified version of the free acid, which is less water soluble but more amenable for the formulation of myristate-containing diets and dietary supplements.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001867 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Myristic acid methyl ester is an esterified version of the free acid, which is less water soluble but more amenable for the formulation of myristate-containing diets and dietary supplements.
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001867 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
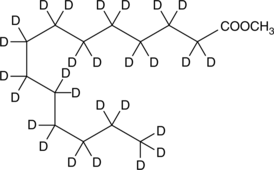
Myristic Acid methyl ester-d27 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid methyl ester (Item No. 9001867) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid methyl ester is an esterified version of the free acid, which is less water soluble but more amenable for the formulation of myristate-containing diets and dietary supplements.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28594 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristic Acid methyl ester-d27 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid methyl ester (Item No. 9001867) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid methyl ester is an esterified version of the free acid, which is less water soluble but more amenable for the formulation of myristate-containing diets and dietary supplements.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28594 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristic Acid methyl ester-d27 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid methyl ester (Item No. 9001867) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid methyl ester is an esterified version of the free acid, which is less water soluble but more amenable for the formulation of myristate-containing diets and dietary supplements.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28594 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristic Acid methyl ester-d27 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid methyl ester (Item No. 9001867) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid methyl ester is an esterified version of the free acid, which is less water soluble but more amenable for the formulation of myristate-containing diets and dietary supplements.
Brand:CaymanSKU:28594 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
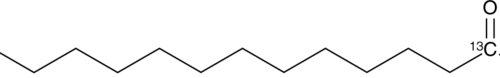
Myristic acid-13C is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid (Item No. 13351) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29463 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristic acid-13C is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid (Item No. 13351) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29463 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
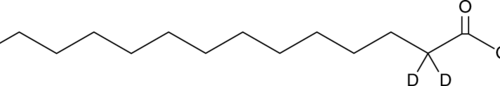
Myristic acid-d2 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid (Item No. 13351) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29411 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristic acid-d2 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid (Item No. 13351) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29411 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristic acid-d2 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid (Item No. 13351) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29411 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristic acid-d2 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid (Item No. 13351) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29411 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
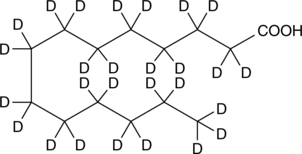
Myristic acid-d27 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid (Item No. 13351) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003317 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristic acid-d27 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid (Item No. 13351) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003317 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristic acid-d27 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristic acid (Item No. 13351) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristic acid is a 14-carbon saturated fatty acid. It is incorporated into myristoyl coenzyme A (myristoyl-CoA) and transferred by N-myristoyltransferase to the N-terminal glycine of certain proteins either during translation to modify protein activity or post-translationally in apoptotic cells.{41877,41878}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003317 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
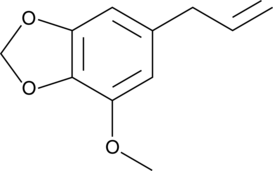
Myristicin is an alkenylbenzene present in small amounts in the essential oil of nutmeg that is reported to act as a serotonin receptor antagonist, a weak monamine oxidase inhibitor, and to produce hallucinogenic effects.{24226} Abuse of myristicin has led to fatal poisoning, which has prompted improved methods for HPLC determination of myristicin in human plasma.{24440} This product is intended for forensic and research purposes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myristicin is an alkenylbenzene present in small amounts in the essential oil of nutmeg that is reported to act as a serotonin receptor antagonist, a weak monamine oxidase inhibitor, and to produce hallucinogenic effects.{24226} Abuse of myristicin has led to fatal poisoning, which has prompted improved methods for HPLC determination of myristicin in human plasma.{24440} This product is intended for forensic and research purposes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myristicin is an alkenylbenzene present in small amounts in the essential oil of nutmeg that is reported to act as a serotonin receptor antagonist, a weak monamine oxidase inhibitor, and to produce hallucinogenic effects.{24226} Abuse of myristicin has led to fatal poisoning, which has prompted improved methods for HPLC determination of myristicin in human plasma.{24440} This product is intended for forensic and research purposes.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myristoleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid found in the fruit extract of S. repens and in dairy extracts.{14760, 14761} It induces apoptosis and necrosis in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells at a rate of 8.8% and 8.1%, respectively.{14760} Myristoleic acid inhibits C. albicans germination in vitro with a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 9 µM.{14761} Furthermore, myristoleic acid inhibits osteogenesis in vitro via interference with cytoskeletal rearrangement and prevents RANKL-induced bone loss and osteoclast formation in mice.{39234}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002461 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid found in the fruit extract of S. repens and in dairy extracts.{14760, 14761} It induces apoptosis and necrosis in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells at a rate of 8.8% and 8.1%, respectively.{14760} Myristoleic acid inhibits C. albicans germination in vitro with a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 9 µM.{14761} Furthermore, myristoleic acid inhibits osteogenesis in vitro via interference with cytoskeletal rearrangement and prevents RANKL-induced bone loss and osteoclast formation in mice.{39234}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002461 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoleic acid is a monounsaturated fatty acid found in the fruit extract of S. repens and in dairy extracts.{14760, 14761} It induces apoptosis and necrosis in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells at a rate of 8.8% and 8.1%, respectively.{14760} Myristoleic acid inhibits C. albicans germination in vitro with a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 9 µM.{14761} Furthermore, myristoleic acid inhibits osteogenesis in vitro via interference with cytoskeletal rearrangement and prevents RANKL-induced bone loss and osteoclast formation in mice.{39234}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002461 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoleic acid is a cytotoxic component from the fruit extract of S. repens.{14760} It induces apoptosis and necrosis in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells at a rate of 8.8% and 8.1%, respectively.{14760} Furthermore, myristoleic acid found in the by-products for making cheese is one of three fatty acids that are most active at inhibiting Candida albicans germination.{14761} It has a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 9 µM in vivo.{14762} Myristoleic acid methyl ester is a more hydrophobic form of the free acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008581 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Myristoleic acid is a cytotoxic component from the fruit extract of S. repens.{14760} It induces apoptosis and necrosis in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells at a rate of 8.8% and 8.1%, respectively.{14760} Furthermore, myristoleic acid found in the by-products for making cheese is one of three fatty acids that are most active at inhibiting Candida albicans germination.{14761} It has a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 9 µM in vivo.{14762} Myristoleic acid methyl ester is a more hydrophobic form of the free acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008581 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoleic acid is a cytotoxic component from the fruit extract of S. repens.{14760} It induces apoptosis and necrosis in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells at a rate of 8.8% and 8.1%, respectively.{14760} Furthermore, myristoleic acid found in the by-products for making cheese is one of three fatty acids that are most active at inhibiting Candida albicans germination.{14761} It has a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 9 µM in vivo.{14762} Myristoleic acid methyl ester is a more hydrophobic form of the free acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008581 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoleic acid is a cytotoxic component from the fruit extract of S. repens.{14760} It induces apoptosis and necrosis in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells at a rate of 8.8% and 8.1%, respectively.{14760} Furthermore, myristoleic acid found in the by-products for making cheese is one of three fatty acids that are most active at inhibiting Candida albicans germination.{14761} It has a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 9 µM in vivo.{14762} Myristoleic acid methyl ester is a more hydrophobic form of the free acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008581 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
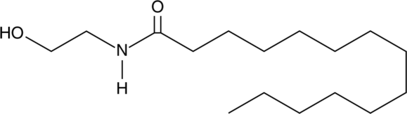
Myristoyl ethanolamide is a member of the family of fatty N-acyl ethanolamines collectively called endocannabinoids.{1202,1712,13153} Myristic acid is typically detected at low levels in rat cerebrospinal fluid, however the specific role and relative importance of its ethanolamine metabolite have not been yet determined.{22439}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001742 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoyl ethanolamide is a member of the family of fatty N-acyl ethanolamines collectively called endocannabinoids.{1202,1712,13153} Myristic acid is typically detected at low levels in rat cerebrospinal fluid, however the specific role and relative importance of its ethanolamine metabolite have not been yet determined.{22439}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001742 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoyl ethanolamide is a member of the family of fatty N-acyl ethanolamines collectively called endocannabinoids.{1202,1712,13153} Myristic acid is typically detected at low levels in rat cerebrospinal fluid, however the specific role and relative importance of its ethanolamine metabolite have not been yet determined.{22439}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001742 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoyl ethanolamide is a member of the family of fatty N-acyl ethanolamines collectively called endocannabinoids.{1202,1712,13153} Myristic acid is typically detected at low levels in rat cerebrospinal fluid, however the specific role and relative importance of its ethanolamine metabolite have not been yet determined.{22439}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001742 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
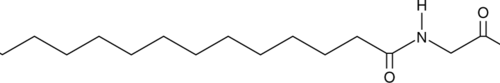
Myristoyl-Gly-OH is a lipidated amino acid and fatty amide. It has been used as an immunogen to raise antibodies against myristoylated proteins and as a synthetic intermediate in the synthesis of lipopeptides.{60100,60101}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30107 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoyl-Gly-OH is a lipidated amino acid and fatty amide. It has been used as an immunogen to raise antibodies against myristoylated proteins and as a synthetic intermediate in the synthesis of lipopeptides.{60100,60101}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30107 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoyl-Gly-OH is a lipidated amino acid and fatty amide. It has been used as an immunogen to raise antibodies against myristoylated proteins and as a synthetic intermediate in the synthesis of lipopeptides.{60100,60101}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30107 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoyl-Gly-OH is a lipidated amino acid and fatty amide. It has been used as an immunogen to raise antibodies against myristoylated proteins and as a synthetic intermediate in the synthesis of lipopeptides.{60100,60101}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30107 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
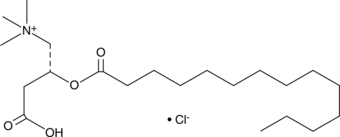
Myristoyl-L-carnitine is a naturally occurring long-chain acylcarnitine.{42563} Plasma levels of myristoyl-L-carnitine are decreased in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and increased in patients with end-stage renal disease.{42563,42564}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26559 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoyl-L-carnitine is a naturally occurring long-chain acylcarnitine.{42563} Plasma levels of myristoyl-L-carnitine are decreased in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and increased in patients with end-stage renal disease.{42563,42564}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26559 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoyl-L-carnitine is a naturally occurring long-chain acylcarnitine.{42563} Plasma levels of myristoyl-L-carnitine are decreased in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and increased in patients with end-stage renal disease.{42563,42564}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26559 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
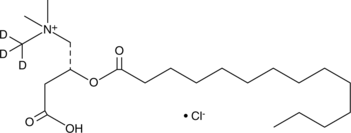
Myristoyl-L-carnitine-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristoyl-L-carnitine (Item No. 26559) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristoyl-L-carnitine is a naturally occurring long-chain acylcarnitine.{42563} Plasma levels of myristoyl-L-carnitine are decreased in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and increased in patients with end-stage renal disease.{42563,42564}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26581 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Myristoyl-L-carnitine-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of myristoyl-L-carnitine (Item No. 26559) by GC- or LC-MS. Myristoyl-L-carnitine is a naturally occurring long-chain acylcarnitine.{42563} Plasma levels of myristoyl-L-carnitine are decreased in patients with chronic fatigue syndrome and increased in patients with end-stage renal disease.{42563,42564}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26581 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
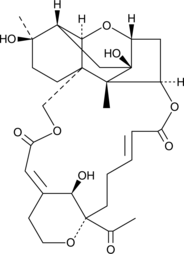
Myrothecine A is a trichothecene mycotoxin that has been found in M. roridum and has anticancer activities.{48753,48754} It inhibits proliferation of A549, MCF-7, HepG2, and SMMC-7721 cancer cells (IC50s = 95, 70, 60, and 25 µM, respectively).{48753} Myrothecine A (50 µM) induces G1 cell cycle arrest in HepG2 cells, as well as increases Bax and cleaved caspase-3, -5, and -8 levels and induces apoptosis in SMMC-7721 cells.{48753,48754}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28193 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
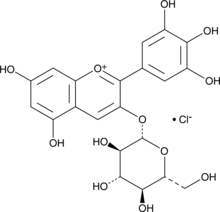
Myrtillin is a natural anthocyanin found in plants. It is the 3-glucoside of delphinidin. Anthocyanins, including myrtillin, are potent antioxidants.{26210,26209,23825}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myrtillin is a natural anthocyanin found in plants. It is the 3-glucoside of delphinidin. Anthocyanins, including myrtillin, are potent antioxidants.{26210,26209,23825}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myrtillin is a natural anthocyanin found in plants. It is the 3-glucoside of delphinidin. Anthocyanins, including myrtillin, are potent antioxidants.{26210,26209,23825}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myrtillin is a natural anthocyanin found in plants. It is the 3-glucoside of delphinidin. Anthocyanins, including myrtillin, are potent antioxidants.{26210,26209,23825}
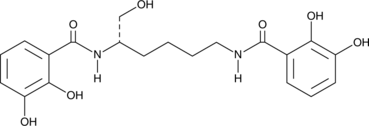
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Myxochelin A is a microbial metabolite that has been found in A. disciformis and has diverse biological activities.{53609} It is active against Gram-positive bacteria, including B. cereus, S. aureus, and M. luteus, but not Gram-negative bacteria or fungi in an agar diffusion assay when used at a concentration of 80 µg/disc. Myxochelin A inhibits 5-lipoxygenase (5-LO) activity with an IC50 value of 1.9 µM for the recombinant human enzyme.{53610} It is cytotoxic to 26-L5 colon cancer cells when used at a concentration of 3 µg/ml.{53611}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26422 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
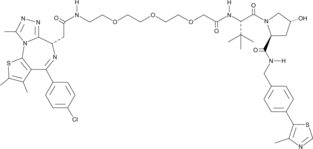
MZ1 is a hybrid compound that drives the selective proteasomal degradation of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4).{33482} It is characterized as a proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) and contains JQ-1, which binds bromo- and extra-terminal (BET) proteins, linked to a ligand for the E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL. MZ1 induces the selective degradation of BRD4 in HeLa cells when used at 0.1-0.5 µM.{33482} At concentrations of 2-10 µM, MZ1 causes the removal of BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4.{33482} BRD protein removal is evident within four hours of adding MZ1 and persists for at least 48 hours, unless MZ1 is removed.{33482}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21622 -Out of stock
MZ1 is a hybrid compound that drives the selective proteasomal degradation of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4).{33482} It is characterized as a proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) and contains JQ-1, which binds bromo- and extra-terminal (BET) proteins, linked to a ligand for the E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL. MZ1 induces the selective degradation of BRD4 in HeLa cells when used at 0.1-0.5 µM.{33482} At concentrations of 2-10 µM, MZ1 causes the removal of BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4.{33482} BRD protein removal is evident within four hours of adding MZ1 and persists for at least 48 hours, unless MZ1 is removed.{33482}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21622 -Out of stock
MZ1 is a hybrid compound that drives the selective proteasomal degradation of bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4).{33482} It is characterized as a proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) and contains JQ-1, which binds bromo- and extra-terminal (BET) proteins, linked to a ligand for the E3 ubiquitin ligase VHL. MZ1 induces the selective degradation of BRD4 in HeLa cells when used at 0.1-0.5 µM.{33482} At concentrations of 2-10 µM, MZ1 causes the removal of BRD2, BRD3, and BRD4.{33482} BRD protein removal is evident within four hours of adding MZ1 and persists for at least 48 hours, unless MZ1 is removed.{33482}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21622 -Out of stock
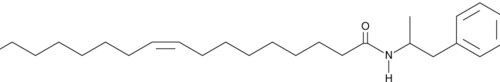
N-(1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)oleamide binds to the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptor with a Ki value of 365 nM in a radioligand binding assay using rat brain homogenate.{36053} It has an EC50 value of 698 nM for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in a luciferase reporter assay and, in rats, it decreases food intake. It does not inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002954 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)oleamide binds to the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptor with a Ki value of 365 nM in a radioligand binding assay using rat brain homogenate.{36053} It has an EC50 value of 698 nM for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in a luciferase reporter assay and, in rats, it decreases food intake. It does not inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002954 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
N-(1-(3,4-Dihydroxyphenyl)propan-2-yl)oleamide binds to the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptor with a Ki value of 365 nM in a radioligand binding assay using rat brain homogenate.{36053} It has an EC50 value of 698 nM for the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor α (PPARα) in a luciferase reporter assay and, in rats, it decreases food intake. It does not inhibit fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH).
Brand:CaymanSKU:9002954 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
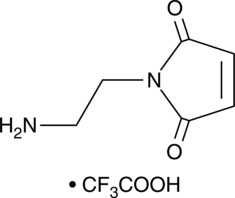
N-(2-Aminoethyl)maleimide is a thiol-reactive cross-linking agent.{52503,52504} It has been used in the synthesis of maleimide-functionalized heparin hydrogels in the development of growth factor delivery systems and radiotracers for thiol-mediated protein labelling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30530 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
N-(2-Aminoethyl)maleimide is a thiol-reactive cross-linking agent.{52503,52504} It has been used in the synthesis of maleimide-functionalized heparin hydrogels in the development of growth factor delivery systems and radiotracers for thiol-mediated protein labelling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30530 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-Aminoethyl)maleimide is a thiol-reactive cross-linking agent.{52503,52504} It has been used in the synthesis of maleimide-functionalized heparin hydrogels in the development of growth factor delivery systems and radiotracers for thiol-mediated protein labelling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30530 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
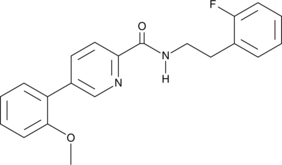
N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide is an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) signaling (IC50 = 0.32 μM in a cell-based hypoxia responsive element (HRE) reporter assay under hypoxic conditions).{50774} It inhibits hypoxia-induced increases in HIF-1α levels in MDA-MB-231, SKOV3, and HeLa cells in a concentration-dependent manner. N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide also inhibits hypoxia-induced VEGF expression and capillary-like tube formation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and inhibits migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in wound healing and transwell assays under hypoxic conditions. It also reduces lung metastasis in an MDA-MB-231 mouse xenograft model when administered at doses of 15 and 30 mg/kg every other day.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29740 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide is an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) signaling (IC50 = 0.32 μM in a cell-based hypoxia responsive element (HRE) reporter assay under hypoxic conditions).{50774} It inhibits hypoxia-induced increases in HIF-1α levels in MDA-MB-231, SKOV3, and HeLa cells in a concentration-dependent manner. N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide also inhibits hypoxia-induced VEGF expression and capillary-like tube formation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and inhibits migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in wound healing and transwell assays under hypoxic conditions. It also reduces lung metastasis in an MDA-MB-231 mouse xenograft model when administered at doses of 15 and 30 mg/kg every other day.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29740 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide is an inhibitor of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF-1) signaling (IC50 = 0.32 μM in a cell-based hypoxia responsive element (HRE) reporter assay under hypoxic conditions).{50774} It inhibits hypoxia-induced increases in HIF-1α levels in MDA-MB-231, SKOV3, and HeLa cells in a concentration-dependent manner. N-(2-Fluorophenethyl)-5-(2-methoxyphenyl)picolinamide also inhibits hypoxia-induced VEGF expression and capillary-like tube formation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) and inhibits migration and invasion of MDA-MB-231 cells in wound healing and transwell assays under hypoxic conditions. It also reduces lung metastasis in an MDA-MB-231 mouse xenograft model when administered at doses of 15 and 30 mg/kg every other day.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29740 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
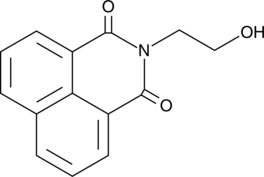
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is an N-substituted 1,8-naphthalimide used as a fluorescent probe and as a precursor for protection of amine groups.{28744} It is used to detect nucleic acids and their precursors, which quench the fluorescence of N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-naphthalimide.{41257} Nucleic acids quench the fluorescence most strongly followed by nucleosides and nucleobases, of which purine bases quench more strongly than pyrimidine bases. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is electroactive and forms adducts with 1,3-dihydroxy benzene and 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene.{28744} N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide displays excitation spectra of 330-333 and 344-347 nm with emission spectra of 366-378 nm in solvents of varying polarities, with a higher Stokes shift in less polar solvents.{41256}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is an N-substituted 1,8-naphthalimide used as a fluorescent probe and as a precursor for protection of amine groups.{28744} It is used to detect nucleic acids and their precursors, which quench the fluorescence of N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-naphthalimide.{41257} Nucleic acids quench the fluorescence most strongly followed by nucleosides and nucleobases, of which purine bases quench more strongly than pyrimidine bases. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is electroactive and forms adducts with 1,3-dihydroxy benzene and 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene.{28744} N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide displays excitation spectra of 330-333 and 344-347 nm with emission spectra of 366-378 nm in solvents of varying polarities, with a higher Stokes shift in less polar solvents.{41256}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is an N-substituted 1,8-naphthalimide used as a fluorescent probe and as a precursor for protection of amine groups.{28744} It is used to detect nucleic acids and their precursors, which quench the fluorescence of N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-naphthalimide.{41257} Nucleic acids quench the fluorescence most strongly followed by nucleosides and nucleobases, of which purine bases quench more strongly than pyrimidine bases. N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide is electroactive and forms adducts with 1,3-dihydroxy benzene and 1,3,5-trihydroxybenzene.{28744} N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-Naphthalimide displays excitation spectra of 330-333 and 344-347 nm with emission spectra of 366-378 nm in solvents of varying polarities, with a higher Stokes shift in less polar solvents.{41256}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
N-(2-phenylethyl)-indomethacin amide (N-2PIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-2PIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 and 0.125 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is over 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant and ovine COX-1. N-2PIA shows anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and cancer chemopreventive activity in various experimental models.{8243}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70272 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-phenylethyl)-indomethacin amide (N-2PIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-2PIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 and 0.125 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is over 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant and ovine COX-1. N-2PIA shows anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and cancer chemopreventive activity in various experimental models.{8243}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70272 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
N-(2-phenylethyl)-indomethacin amide (N-2PIA) is one of several aromatic amides of indomethacin reported to be potent and selective reversible inhibitors of COX-2.{8243} N-2PIA inhibits human recombinant and ovine COX-2 with IC50 values of 0.06 and 0.125 µM, respectively.{8243,8513} It is over 400 times less potent as an inhibitor of human recombinant and ovine COX-1. N-2PIA shows anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and cancer chemopreventive activity in various experimental models.{8243}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70272 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder