Chemicals
Showing 25201–25350 of 41137 results
-
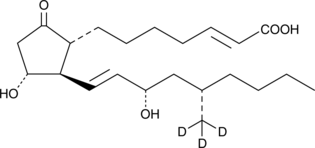
Limaprost-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of limaprost (Item No. 13810) by GC- or LC-MS. Limaprost is an analog of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1; Item No. 13010) with structural modifications intended to give it a prolonged half-life and greater potency. Limaprost is orally active in both rats and guinea pigs at doses of 100 µg/kg as an inhibitor of ADP and collagen-induced platelet aggregation. Limaprost is 10-1,000 times more potent than PGE1 as an inhibitor of platelet adhesiveness measured in vitro. Intra-coronary injection (100 ng/kg) or intravenous injection (3 µg/kg) in anesthetized dogs causes vasodilation and increased coronary blood flow by 60-80%. Significant hypotensive effects were seen at 100 and 300 µg/kg orally in rats.{6808}
Brand:CaymanSKU:25416 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
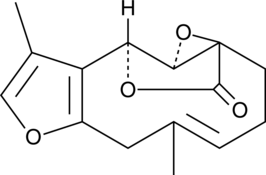
Limonin is the first described limonoid, which are naturally occurring tetranortriterpenoids that impart bitter flavor in citrus fruits. Compounds belonging to this group have reported anti-proliferative and proapoptotic activity on several cancer cell lines as well as pesticidal, anti-malarial, anti-microbial, and anti-HIV activity.{27612}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Limonin is the first described limonoid, which are naturally occurring tetranortriterpenoids that impart bitter flavor in citrus fruits. Compounds belonging to this group have reported anti-proliferative and proapoptotic activity on several cancer cell lines as well as pesticidal, anti-malarial, anti-microbial, and anti-HIV activity.{27612}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Limonin is the first described limonoid, which are naturally occurring tetranortriterpenoids that impart bitter flavor in citrus fruits. Compounds belonging to this group have reported anti-proliferative and proapoptotic activity on several cancer cell lines as well as pesticidal, anti-malarial, anti-microbial, and anti-HIV activity.{27612}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Limonin is the first described limonoid, which are naturally occurring tetranortriterpenoids that impart bitter flavor in citrus fruits. Compounds belonging to this group have reported anti-proliferative and proapoptotic activity on several cancer cell lines as well as pesticidal, anti-malarial, anti-microbial, and anti-HIV activity.{27612}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Lin28 1632 is a small molecule inhibitor of the interaction between the RNA binding protein Lin28 and let-7 precursor RNA (IC50 = 8 μM in a competition ELISA).{41072} It increases levels of endogenous let-7 miRNAs and decreases Lin28 expression in a dose-dependent manner in murine embryonic stem cells (mESCs). Lin28 1632 inhibits clonogenic growth of 22Rv1, PC3, DU145, and Huh7 cancer cells and decreases tumor-sphere formation by 22Rv1 and Huh7 cells in vitro. It also binds bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) and CREB-binding protein (CBP/CREBBP) bromodomains (Kds = 7 and 25 μM, respectively).
Brand:CaymanSKU:22401 -Out of stock
Lin28 1632 is a small molecule inhibitor of the interaction between the RNA binding protein Lin28 and let-7 precursor RNA (IC50 = 8 μM in a competition ELISA).{41072} It increases levels of endogenous let-7 miRNAs and decreases Lin28 expression in a dose-dependent manner in murine embryonic stem cells (mESCs). Lin28 1632 inhibits clonogenic growth of 22Rv1, PC3, DU145, and Huh7 cancer cells and decreases tumor-sphere formation by 22Rv1 and Huh7 cells in vitro. It also binds bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) and CREB-binding protein (CBP/CREBBP) bromodomains (Kds = 7 and 25 μM, respectively).
Brand:CaymanSKU:22401 -Out of stock
Lin28 1632 is a small molecule inhibitor of the interaction between the RNA binding protein Lin28 and let-7 precursor RNA (IC50 = 8 μM in a competition ELISA).{41072} It increases levels of endogenous let-7 miRNAs and decreases Lin28 expression in a dose-dependent manner in murine embryonic stem cells (mESCs). Lin28 1632 inhibits clonogenic growth of 22Rv1, PC3, DU145, and Huh7 cancer cells and decreases tumor-sphere formation by 22Rv1 and Huh7 cells in vitro. It also binds bromodomain-containing protein 4 (BRD4) and CREB-binding protein (CBP/CREBBP) bromodomains (Kds = 7 and 25 μM, respectively).
Brand:CaymanSKU:22401 -Out of stock
Linaclotide is a peptide agonist of the guanylate cyclase C receptor (Ki = 16.4 nM in a radioligand binding assay using mouse intestinal mucosa).{40472} Luminal exposure to 5 μg of linaclotide stimulates fluid secretion and cGMP concentration in jejunal loops isolated from wild-type mice but not guanylate cyclase C receptor-null mice. Linaclotide (100 μg/kg) increases intestinal transit rate in wild-type mice. It also reduces the number of phosphorylated ERK-positive dorsal horn neurons in the thoracolumbar spinal cord, a marker of nociceptive signaling, following noxious colorectal distension and mechanical hypersensitivity in a mouse model of TNBS-induced colitis.{40473} Formulations containing linaclotide have been used for the treatment of constipation and pain associated with irritable bowel syndrome.
Brand:CaymanSKU:24085 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Linaclotide is a peptide agonist of the guanylate cyclase C receptor (Ki = 16.4 nM in a radioligand binding assay using mouse intestinal mucosa).{40472} Luminal exposure to 5 μg of linaclotide stimulates fluid secretion and cGMP concentration in jejunal loops isolated from wild-type mice but not guanylate cyclase C receptor-null mice. Linaclotide (100 μg/kg) increases intestinal transit rate in wild-type mice. It also reduces the number of phosphorylated ERK-positive dorsal horn neurons in the thoracolumbar spinal cord, a marker of nociceptive signaling, following noxious colorectal distension and mechanical hypersensitivity in a mouse model of TNBS-induced colitis.{40473} Formulations containing linaclotide have been used for the treatment of constipation and pain associated with irritable bowel syndrome.
Brand:CaymanSKU:24085 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Linaclotide is a peptide agonist of the guanylate cyclase C receptor (Ki = 16.4 nM in a radioligand binding assay using mouse intestinal mucosa).{40472} Luminal exposure to 5 μg of linaclotide stimulates fluid secretion and cGMP concentration in jejunal loops isolated from wild-type mice but not guanylate cyclase C receptor-null mice. Linaclotide (100 μg/kg) increases intestinal transit rate in wild-type mice. It also reduces the number of phosphorylated ERK-positive dorsal horn neurons in the thoracolumbar spinal cord, a marker of nociceptive signaling, following noxious colorectal distension and mechanical hypersensitivity in a mouse model of TNBS-induced colitis.{40473} Formulations containing linaclotide have been used for the treatment of constipation and pain associated with irritable bowel syndrome.
Brand:CaymanSKU:24085 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Linaclotide is a peptide agonist of the guanylate cyclase C receptor (Ki = 16.4 nM in a radioligand binding assay using mouse intestinal mucosa).{40472} Luminal exposure to 5 μg of linaclotide stimulates fluid secretion and cGMP concentration in jejunal loops isolated from wild-type mice but not guanylate cyclase C receptor-null mice. Linaclotide (100 μg/kg) increases intestinal transit rate in wild-type mice. It also reduces the number of phosphorylated ERK-positive dorsal horn neurons in the thoracolumbar spinal cord, a marker of nociceptive signaling, following noxious colorectal distension and mechanical hypersensitivity in a mouse model of TNBS-induced colitis.{40473} Formulations containing linaclotide have been used for the treatment of constipation and pain associated with irritable bowel syndrome.
Brand:CaymanSKU:24085 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
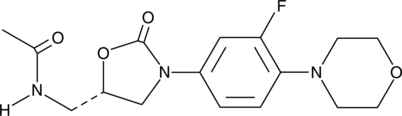
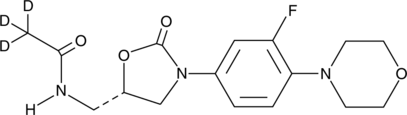
Linagliptin is a potent inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) with an IC50 value of 1 nM for human recombinant DPP-4.{41123} It is selective, with ≥10,000-fold selectivity for DPP-4 over a panel of 11 peptidases and proteases. Linagliptin (3 mg/kg) inhibits 90% of plasma DPP-4 activity in rat. It also dose-dependently decreases plasma glucose and increases plasma levels of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and insulin in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Oral administration of linagliptin reduces HbA1c levels in mice with high-fat diet- and low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes.{41124} Formulations containing linagliptin have been used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.{41125}
Brand:CaymanSKU:23306 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Linagliptin is a potent inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) with an IC50 value of 1 nM for human recombinant DPP-4.{41123} It is selective, with ≥10,000-fold selectivity for DPP-4 over a panel of 11 peptidases and proteases. Linagliptin (3 mg/kg) inhibits 90% of plasma DPP-4 activity in rat. It also dose-dependently decreases plasma glucose and increases plasma levels of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and insulin in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Oral administration of linagliptin reduces HbA1c levels in mice with high-fat diet- and low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes.{41124} Formulations containing linagliptin have been used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.{41125}
Brand:CaymanSKU:23306 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Linagliptin is a potent inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP-4) with an IC50 value of 1 nM for human recombinant DPP-4.{41123} It is selective, with ≥10,000-fold selectivity for DPP-4 over a panel of 11 peptidases and proteases. Linagliptin (3 mg/kg) inhibits 90% of plasma DPP-4 activity in rat. It also dose-dependently decreases plasma glucose and increases plasma levels of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and insulin in Zucker diabetic fatty rats. Oral administration of linagliptin reduces HbA1c levels in mice with high-fat diet- and low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes.{41124} Formulations containing linagliptin have been used for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus.{41125}
Brand:CaymanSKU:23306 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
Linamarin is a glucoside of acetone cyanohydrin found in the leaves and roots of cassava, lima beans, and flax.{32190} It is thought to function in the transport of nitrogen from plant leaves to roots in young plants but also serves as a plant defense mechanism. Linamarin is converted to toxic hydrocyanic acid or prussic acid when it comes into contact with linamarase, an enzyme that is released when the cells of cassava roots are ruptured.{32189}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20532 -Available on backorder
Linamarin is a glucoside of acetone cyanohydrin found in the leaves and roots of cassava, lima beans, and flax.{32190} It is thought to function in the transport of nitrogen from plant leaves to roots in young plants but also serves as a plant defense mechanism. Linamarin is converted to toxic hydrocyanic acid or prussic acid when it comes into contact with linamarase, an enzyme that is released when the cells of cassava roots are ruptured.{32189}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20532 -Available on backorder
Linamarin is a glucoside of acetone cyanohydrin found in the leaves and roots of cassava, lima beans, and flax.{32190} It is thought to function in the transport of nitrogen from plant leaves to roots in young plants but also serves as a plant defense mechanism. Linamarin is converted to toxic hydrocyanic acid or prussic acid when it comes into contact with linamarase, an enzyme that is released when the cells of cassava roots are ruptured.{32189}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20532 -Available on backorder
Linamarin is a glucoside of acetone cyanohydrin found in the leaves and roots of cassava, lima beans, and flax.{32190} It is thought to function in the transport of nitrogen from plant leaves to roots in young plants but also serves as a plant defense mechanism. Linamarin is converted to toxic hydrocyanic acid or prussic acid when it comes into contact with linamarase, an enzyme that is released when the cells of cassava roots are ruptured.{32189}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20532 -Available on backorder
Linarin is a flavonoid glycoside that has been found in various fruits and vegetables and has diverse biological activities.{45217,45218,45219} It potentiates cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-induced ligand (TRAIL) in U87MG human glioma cells.{45217} In vivo, linarin potentiates TRAIL-induced tumor cell apoptosis and reduction of tumor growth in a U87MG mouse xenograft model. Linarin (12.5-50 mg/kg) reduces pulmonary platelet count, edema, and macrophage, polymorphonuclear leukocyte, and lymphocyte infiltration, as well as inhibits TXNIP/NLRP3, MAPK, and NF-κB signaling in a mouse model of LPS-induced acute lung injury.{45218} It also inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and induces dyskinesia recovery by 74.5 and 88%, respectively, in a zebrafish model of Alzheimer’s disease when administered in tank water at a concentration of 50 μg/ml.{45219}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26900 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Linarin is a flavonoid glycoside that has been found in various fruits and vegetables and has diverse biological activities.{45217,45218,45219} It potentiates cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-induced ligand (TRAIL) in U87MG human glioma cells.{45217} In vivo, linarin potentiates TRAIL-induced tumor cell apoptosis and reduction of tumor growth in a U87MG mouse xenograft model. Linarin (12.5-50 mg/kg) reduces pulmonary platelet count, edema, and macrophage, polymorphonuclear leukocyte, and lymphocyte infiltration, as well as inhibits TXNIP/NLRP3, MAPK, and NF-κB signaling in a mouse model of LPS-induced acute lung injury.{45218} It also inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and induces dyskinesia recovery by 74.5 and 88%, respectively, in a zebrafish model of Alzheimer’s disease when administered in tank water at a concentration of 50 μg/ml.{45219}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26900 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Linarin is a flavonoid glycoside that has been found in various fruits and vegetables and has diverse biological activities.{45217,45218,45219} It potentiates cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-induced ligand (TRAIL) in U87MG human glioma cells.{45217} In vivo, linarin potentiates TRAIL-induced tumor cell apoptosis and reduction of tumor growth in a U87MG mouse xenograft model. Linarin (12.5-50 mg/kg) reduces pulmonary platelet count, edema, and macrophage, polymorphonuclear leukocyte, and lymphocyte infiltration, as well as inhibits TXNIP/NLRP3, MAPK, and NF-κB signaling in a mouse model of LPS-induced acute lung injury.{45218} It also inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and induces dyskinesia recovery by 74.5 and 88%, respectively, in a zebrafish model of Alzheimer’s disease when administered in tank water at a concentration of 50 μg/ml.{45219}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26900 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Linarin is a flavonoid glycoside that has been found in various fruits and vegetables and has diverse biological activities.{45217,45218,45219} It potentiates cytotoxicity and apoptosis induced by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-induced ligand (TRAIL) in U87MG human glioma cells.{45217} In vivo, linarin potentiates TRAIL-induced tumor cell apoptosis and reduction of tumor growth in a U87MG mouse xenograft model. Linarin (12.5-50 mg/kg) reduces pulmonary platelet count, edema, and macrophage, polymorphonuclear leukocyte, and lymphocyte infiltration, as well as inhibits TXNIP/NLRP3, MAPK, and NF-κB signaling in a mouse model of LPS-induced acute lung injury.{45218} It also inhibits acetylcholinesterase (AChE) and induces dyskinesia recovery by 74.5 and 88%, respectively, in a zebrafish model of Alzheimer’s disease when administered in tank water at a concentration of 50 μg/ml.{45219}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26900 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Lincomycin is a lincosamide antibiotic first isolated from S. lincolnensis. It has a spectrum and mechanism of action similar to erythromycin (Item No. 16486), a macrolide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis and is effective against a host of bacterial genera, including Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Haemophilus (MIC90s range from 0.015-2.0 mg/l).{22680,22758} Lincomycin is closely related to clindamycin (Item No. 15006), a lincosamide antibiotic that is used for serious infections and in the prevention of emerging infections in burns.{22532,22529,22530,22528}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21526 -Out of stock
Lincomycin is a lincosamide antibiotic first isolated from S. lincolnensis. It has a spectrum and mechanism of action similar to erythromycin (Item No. 16486), a macrolide antibiotic that inhibits bacterial protein synthesis and is effective against a host of bacterial genera, including Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and Haemophilus (MIC90s range from 0.015-2.0 mg/l).{22680,22758} Lincomycin is closely related to clindamycin (Item No. 15006), a lincosamide antibiotic that is used for serious infections and in the prevention of emerging infections in burns.{22532,22529,22530,22528}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21526 -Out of stock
Linderane is a sesquiterpene that has been found in L. aggregata.{45215,45216} It inhibits the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP2C9 (Ki = 1.26 μM) in an irreversible and NADPH-dependent manner.{45215} Linderane decreases phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck1) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6pc) gene expression, cAMP concentration, and CREB phosphorylation, increases phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) activity, and inhibits gluconeogenesis in rat primary hepatocytes.{45216} In vivo, linderane (50 mg/kg twice per day) decreases serum and hepatic triglyceride levels, as well as random-fed and fasting blood glucose levels in ob/ob mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27479 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Linderane is a sesquiterpene that has been found in L. aggregata.{45215,45216} It inhibits the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP2C9 (Ki = 1.26 μM) in an irreversible and NADPH-dependent manner.{45215} Linderane decreases phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck1) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6pc) gene expression, cAMP concentration, and CREB phosphorylation, increases phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) activity, and inhibits gluconeogenesis in rat primary hepatocytes.{45216} In vivo, linderane (50 mg/kg twice per day) decreases serum and hepatic triglyceride levels, as well as random-fed and fasting blood glucose levels in ob/ob mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27479 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Linderane is a sesquiterpene that has been found in L. aggregata.{45215,45216} It inhibits the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP2C9 (Ki = 1.26 μM) in an irreversible and NADPH-dependent manner.{45215} Linderane decreases phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck1) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6pc) gene expression, cAMP concentration, and CREB phosphorylation, increases phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) activity, and inhibits gluconeogenesis in rat primary hepatocytes.{45216} In vivo, linderane (50 mg/kg twice per day) decreases serum and hepatic triglyceride levels, as well as random-fed and fasting blood glucose levels in ob/ob mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27479 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Linderane is a sesquiterpene that has been found in L. aggregata.{45215,45216} It inhibits the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP2C9 (Ki = 1.26 μM) in an irreversible and NADPH-dependent manner.{45215} Linderane decreases phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase (Pck1) and glucose-6-phosphatase (G6pc) gene expression, cAMP concentration, and CREB phosphorylation, increases phosphodiesterase 3 (PDE3) activity, and inhibits gluconeogenesis in rat primary hepatocytes.{45216} In vivo, linderane (50 mg/kg twice per day) decreases serum and hepatic triglyceride levels, as well as random-fed and fasting blood glucose levels in ob/ob mice.
Brand:CaymanSKU:27479 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Linezolid is a synthetic oxazolidinone antibiotic with activity against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria, including resistant strains of several species, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), penicillin-resistant pneumococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, various anaerobic bacteria, and several mycobacteria and streptococci (MICs = 2-4 mg/ml).{22653} Linezolid inhibits protein synthesis by binding to domain V of the 23S ribosomal RNA of the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. In vivo, linezolid (50 mg/kg) reduces pulmonary MRSA load in spontaneously breathing and mechanically ventilated rabbits.{36681} Formulations containing linezolid have been used to treat MRSA infections.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Linezolid is a synthetic oxazolidinone antibiotic with activity against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria, including resistant strains of several species, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), penicillin-resistant pneumococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, various anaerobic bacteria, and several mycobacteria and streptococci (MICs = 2-4 mg/ml).{22653} Linezolid inhibits protein synthesis by binding to domain V of the 23S ribosomal RNA of the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. In vivo, linezolid (50 mg/kg) reduces pulmonary MRSA load in spontaneously breathing and mechanically ventilated rabbits.{36681} Formulations containing linezolid have been used to treat MRSA infections.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Linezolid is a synthetic oxazolidinone antibiotic with activity against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria, including resistant strains of several species, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), penicillin-resistant pneumococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, various anaerobic bacteria, and several mycobacteria and streptococci (MICs = 2-4 mg/ml).{22653} Linezolid inhibits protein synthesis by binding to domain V of the 23S ribosomal RNA of the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. In vivo, linezolid (50 mg/kg) reduces pulmonary MRSA load in spontaneously breathing and mechanically ventilated rabbits.{36681} Formulations containing linezolid have been used to treat MRSA infections.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Linezolid is a synthetic oxazolidinone antibiotic with activity against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria, including resistant strains of several species, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), penicillin-resistant pneumococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, various anaerobic bacteria, and several mycobacteria and streptococci (MICs = 2-4 mg/ml).{22653} Linezolid inhibits protein synthesis by binding to domain V of the 23S ribosomal RNA of the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. In vivo, linezolid (50 mg/kg) reduces pulmonary MRSA load in spontaneously breathing and mechanically ventilated rabbits.{36681} Formulations containing linezolid have been used to treat MRSA infections.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Linezolid-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linezolid (Item No. 15012) by GC- or LC-MS. Linezolid is a synthetic oxazolidinone antibiotic with activity against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria, including resistant strains of several species, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), penicillin-resistant pneumococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, various anaerobic bacteria, and several mycobacteria and streptococci (MICs = 2-4 mg/ml).{22653} Linezolid inhibits protein synthesis by binding to domain V of the 23S ribosomal RNA of the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. In vivo, linezolid (50 mg/kg) reduces pulmonary MRSA load in spontaneously breathing and mechanically ventilated rabbits.{36681} Formulations containing linezolid have been used to treat MRSA infections.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25038 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Linezolid-d3 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linezolid (Item No. 15012) by GC- or LC-MS. Linezolid is a synthetic oxazolidinone antibiotic with activity against a wide range of Gram-positive bacteria, including resistant strains of several species, such as methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), penicillin-resistant pneumococci, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, various anaerobic bacteria, and several mycobacteria and streptococci (MICs = 2-4 mg/ml).{22653} Linezolid inhibits protein synthesis by binding to domain V of the 23S ribosomal RNA of the 50S subunit of bacterial ribosomes. In vivo, linezolid (50 mg/kg) reduces pulmonary MRSA load in spontaneously breathing and mechanically ventilated rabbits.{36681} Formulations containing linezolid have been used to treat MRSA infections.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25038 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
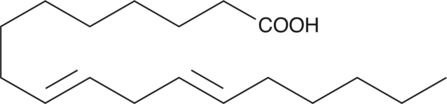
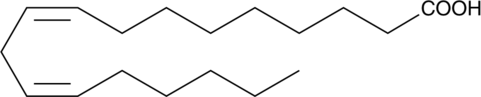
Linoelaidic acid is the all-trans fatty acid homolog of linoleic acid. Trans-fatty acids are generally not detected in raw food oils, but constitute up to 25% of the unsaturated fat in partially hydrogenated oils.{5470}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90160 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Linoelaidic acid is the all-trans fatty acid homolog of linoleic acid. Trans-fatty acids are generally not detected in raw food oils, but constitute up to 25% of the unsaturated fat in partially hydrogenated oils.{5470}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90160 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoelaidic acid is the all-trans fatty acid homolog of linoleic acid. Trans-fatty acids are generally not detected in raw food oils, but constitute up to 25% of the unsaturated fat in partially hydrogenated oils.{5470}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90160 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoelaidic acid is the all-trans fatty acid homolog of linoleic acid. Trans-fatty acids are generally not detected in raw food oils, but constitute up to 25% of the unsaturated fat in partially hydrogenated oils.{5470}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90160 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
Linoelaidic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of linoelaidic acid (Item No. 90160). It has been found in H. sabdariffa essential oil as well as biodiesel produced from sea mango seed oil.{49143,49144}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26732 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoelaidic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of linoelaidic acid (Item No. 90160). It has been found in H. sabdariffa essential oil as well as biodiesel produced from sea mango seed oil.{49143,49144}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26732 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
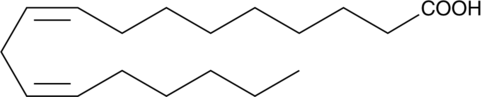
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90150 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90150 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90150 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90150 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128} Linoleic acid (peroxide free) contains the antioxidant BHT (Item No. 89910). BHT-free linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 21909) is also available.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90150.1 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128} Linoleic acid (peroxide free) contains the antioxidant BHT (Item No. 89910). BHT-free linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 21909) is also available.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90150.1 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128} Linoleic acid (peroxide free) contains the antioxidant BHT (Item No. 89910). BHT-free linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 21909) is also available.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90150.1 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128} Linoleic acid (peroxide free) contains the antioxidant BHT (Item No. 89910). BHT-free linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 21909) is also available.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90150.1 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21909 -Out of stock
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21909 -Out of stock
Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21909 -Out of stock
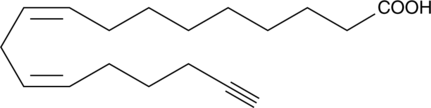
Linoleic acid alkyne is an ω-alkyne derivative of linoleic acid (Item No. 90150). The ω-alkyne moiety allows Cu(I)-catalyzed cycloaddition chemistry with other molecules containing an azide group.{33415,33416} Linoleic acid alkyne has been used in experiments focusing on the biological roles of linoleic acid.{26526,33418} Alternatively, this modified lipid can be used to synthesize other alkyne-containing products, such as glycerophospholipids, for click chemistry.{33417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10541 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid alkyne is an ω-alkyne derivative of linoleic acid (Item No. 90150). The ω-alkyne moiety allows Cu(I)-catalyzed cycloaddition chemistry with other molecules containing an azide group.{33415,33416} Linoleic acid alkyne has been used in experiments focusing on the biological roles of linoleic acid.{26526,33418} Alternatively, this modified lipid can be used to synthesize other alkyne-containing products, such as glycerophospholipids, for click chemistry.{33417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10541 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid alkyne is an ω-alkyne derivative of linoleic acid (Item No. 90150). The ω-alkyne moiety allows Cu(I)-catalyzed cycloaddition chemistry with other molecules containing an azide group.{33415,33416} Linoleic acid alkyne has been used in experiments focusing on the biological roles of linoleic acid.{26526,33418} Alternatively, this modified lipid can be used to synthesize other alkyne-containing products, such as glycerophospholipids, for click chemistry.{33417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10541 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid alkyne is an ω-alkyne derivative of linoleic acid (Item No. 90150). The ω-alkyne moiety allows Cu(I)-catalyzed cycloaddition chemistry with other molecules containing an azide group.{33415,33416} Linoleic acid alkyne has been used in experiments focusing on the biological roles of linoleic acid.{26526,33418} Alternatively, this modified lipid can be used to synthesize other alkyne-containing products, such as glycerophospholipids, for click chemistry.{33417}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10541 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
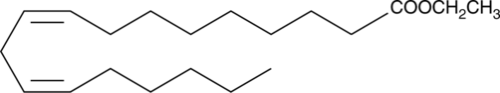
Linoleic acid ethyl ester is an esterified form of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909). It is active against the bacteria S. mutans, A. actinomycetemcomitans, P. gingivalis, S. gordonii, and S. sanguis and the fungus C. albicans when used at a concentration of 25 µg/ml.{53851} Linoleic acid ethyl ester (5 and 10 µM) inhibits LPS-induced production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010), IL-6, and TNF-α in RAW 264.7 cells.{53852} Formulations containing linoleic acid ethyl ester have been used in cosmetics for the treatment of acne.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008198 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid ethyl ester is an esterified form of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909). It is active against the bacteria S. mutans, A. actinomycetemcomitans, P. gingivalis, S. gordonii, and S. sanguis and the fungus C. albicans when used at a concentration of 25 µg/ml.{53851} Linoleic acid ethyl ester (5 and 10 µM) inhibits LPS-induced production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010), IL-6, and TNF-α in RAW 264.7 cells.{53852} Formulations containing linoleic acid ethyl ester have been used in cosmetics for the treatment of acne.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008198 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid ethyl ester is an esterified form of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909). It is active against the bacteria S. mutans, A. actinomycetemcomitans, P. gingivalis, S. gordonii, and S. sanguis and the fungus C. albicans when used at a concentration of 25 µg/ml.{53851} Linoleic acid ethyl ester (5 and 10 µM) inhibits LPS-induced production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010), IL-6, and TNF-α in RAW 264.7 cells.{53852} Formulations containing linoleic acid ethyl ester have been used in cosmetics for the treatment of acne.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008198 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid ethyl ester is an esterified form of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909). It is active against the bacteria S. mutans, A. actinomycetemcomitans, P. gingivalis, S. gordonii, and S. sanguis and the fungus C. albicans when used at a concentration of 25 µg/ml.{53851} Linoleic acid ethyl ester (5 and 10 µM) inhibits LPS-induced production of nitric oxide (NO), prostaglandin E2 (PGE2; Item No. 14010), IL-6, and TNF-α in RAW 264.7 cells.{53852} Formulations containing linoleic acid ethyl ester have been used in cosmetics for the treatment of acne.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008198 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
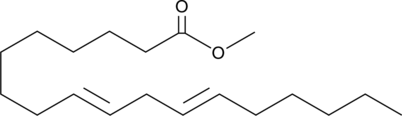
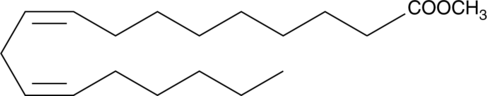
Linoleic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909). It has been found in several types of animal fat biodiesel and biodiesel synthesized from beef tallow, soybean oil, and babassu oil blends.{48244,48265} It has been used as a substrate to measure the antioxidant activity of β-carotene (Item No. 16837) against free radical-induced lipid peroxidation.{56142}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20603 -Available on backorder
Linoleic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909). It has been found in several types of animal fat biodiesel and biodiesel synthesized from beef tallow, soybean oil, and babassu oil blends.{48244,48265} It has been used as a substrate to measure the antioxidant activity of β-carotene (Item No. 16837) against free radical-induced lipid peroxidation.{56142}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20603 -Available on backorder
Linoleic acid methyl ester is an esterified form of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909). It has been found in several types of animal fat biodiesel and biodiesel synthesized from beef tallow, soybean oil, and babassu oil blends.{48244,48265} It has been used as a substrate to measure the antioxidant activity of β-carotene (Item No. 16837) against free radical-induced lipid peroxidation.{56142}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20603 -Available on backorder
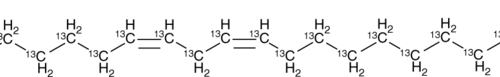
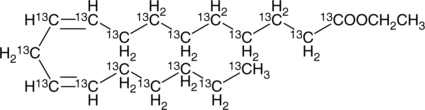
Linoleic Acid-13C18 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) by GC- or LC-MS. Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31159 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic Acid-13C18 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) by GC- or LC-MS. Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31159 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid-13C18 ethyl ester is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleic acid ethyl ester (Item No. 10008198) by GC- or LC-MS. Linoleic acid ethyl ester is an esterified form of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909). Linoleic acid is an essential fatty acid and one of the most abundant polyunsaturated fatty acids in the Western diet.{52085} Deficiencies in linoleic acid are linked to defective wound healing, growth retardation, and dermatitis.{1017,2418} Linoleic acid is metabolized in both plants and animals to form 9(S)- and 13(S)-HODE.{770}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28750 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid-13C18 ethyl ester is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleic acid ethyl ester (Item No. 10008198) by GC- or LC-MS. Linoleic acid ethyl ester is an esterified form of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909). Linoleic acid is an essential fatty acid and one of the most abundant polyunsaturated fatty acids in the Western diet.{52085} Deficiencies in linoleic acid are linked to defective wound healing, growth retardation, and dermatitis.{1017,2418} Linoleic acid is metabolized in both plants and animals to form 9(S)- and 13(S)-HODE.{770}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28750 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid-13C18 ethyl ester is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleic acid ethyl ester (Item No. 10008198) by GC- or LC-MS. Linoleic acid ethyl ester is an esterified form of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909). Linoleic acid is an essential fatty acid and one of the most abundant polyunsaturated fatty acids in the Western diet.{52085} Deficiencies in linoleic acid are linked to defective wound healing, growth retardation, and dermatitis.{1017,2418} Linoleic acid is metabolized in both plants and animals to form 9(S)- and 13(S)-HODE.{770}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28750 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
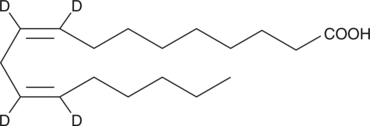
Linoleic acid-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) by GC- or LC-MS. Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390150 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) by GC- or LC-MS. Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390150 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleic acid-d4 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleic acid (Item Nos. 90150 | 90150.1 | 21909) by GC- or LC-MS. Linoleic acid is an essential ω-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA).{52085} It is the most abundant PUFA in a variety of foods, and dietary sources of linoleic acid include vegetable oils, meats, nuts, seeds, and eggs. Linoleic acid (30 μM) increases migration of IEC-6 rat intestinal epithelial cells in a wound healing assay.{56127} Rats fed a linoleate-deficient diet exhibit decreased body weight and an increased ratio of eicosatrienoate to arachidonate in liver and serum phospholipids compared with rats fed a control diet, as well as mild scaling of forepaw skin.{56128}
Brand:CaymanSKU:390150 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
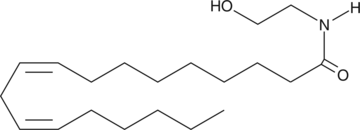
Linoleoyl ethanolamide is an endocannabinoid detected in porcine brain and murine peritoneal macrophages which contains linoleate in place of the arachidonate moiety of arachidonyl ethanolamide (AEA).{11172,11151} It has weak affinity for the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and CB2 receptors, exhibiting Ki values of 10 µM and 25 µM, respectively.{7422} However, it is only approximately 4-fold less potent than AEA at causing catalepsy in mice (ED50 of 26.5 mg/kg).{11177} In addition, linoleoyl ethanolamide increases ERK phosphorylation and AP-1-dependent transcription approximately 1.5 fold at 15 µM in a CB-receptor-independent manner.{11152} However, cellular toxicity is readily apparent at concentrations of 10-20 µM. Linoleoyl ethanolamide inhibits human fatty acid amide hydrolase-dependent hydrolysis of AEA with a Ki value of 9.0 µM, but also is hydrolyzed effectively by the enzyme.{7251,3922}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90155 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleoyl ethanolamide is an endocannabinoid detected in porcine brain and murine peritoneal macrophages which contains linoleate in place of the arachidonate moiety of arachidonyl ethanolamide (AEA).{11172,11151} It has weak affinity for the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and CB2 receptors, exhibiting Ki values of 10 µM and 25 µM, respectively.{7422} However, it is only approximately 4-fold less potent than AEA at causing catalepsy in mice (ED50 of 26.5 mg/kg).{11177} In addition, linoleoyl ethanolamide increases ERK phosphorylation and AP-1-dependent transcription approximately 1.5 fold at 15 µM in a CB-receptor-independent manner.{11152} However, cellular toxicity is readily apparent at concentrations of 10-20 µM. Linoleoyl ethanolamide inhibits human fatty acid amide hydrolase-dependent hydrolysis of AEA with a Ki value of 9.0 µM, but also is hydrolyzed effectively by the enzyme.{7251,3922}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90155 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleoyl ethanolamide is an endocannabinoid detected in porcine brain and murine peritoneal macrophages which contains linoleate in place of the arachidonate moiety of arachidonyl ethanolamide (AEA).{11172,11151} It has weak affinity for the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and CB2 receptors, exhibiting Ki values of 10 µM and 25 µM, respectively.{7422} However, it is only approximately 4-fold less potent than AEA at causing catalepsy in mice (ED50 of 26.5 mg/kg).{11177} In addition, linoleoyl ethanolamide increases ERK phosphorylation and AP-1-dependent transcription approximately 1.5 fold at 15 µM in a CB-receptor-independent manner.{11152} However, cellular toxicity is readily apparent at concentrations of 10-20 µM. Linoleoyl ethanolamide inhibits human fatty acid amide hydrolase-dependent hydrolysis of AEA with a Ki value of 9.0 µM, but also is hydrolyzed effectively by the enzyme.{7251,3922}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90155 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleoyl ethanolamide is an endocannabinoid detected in porcine brain and murine peritoneal macrophages which contains linoleate in place of the arachidonate moiety of arachidonyl ethanolamide (AEA).{11172,11151} It has weak affinity for the cannabinoid 1 (CB1) and CB2 receptors, exhibiting Ki values of 10 µM and 25 µM, respectively.{7422} However, it is only approximately 4-fold less potent than AEA at causing catalepsy in mice (ED50 of 26.5 mg/kg).{11177} In addition, linoleoyl ethanolamide increases ERK phosphorylation and AP-1-dependent transcription approximately 1.5 fold at 15 µM in a CB-receptor-independent manner.{11152} However, cellular toxicity is readily apparent at concentrations of 10-20 µM. Linoleoyl ethanolamide inhibits human fatty acid amide hydrolase-dependent hydrolysis of AEA with a Ki value of 9.0 µM, but also is hydrolyzed effectively by the enzyme.{7251,3922}
Brand:CaymanSKU:90155 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
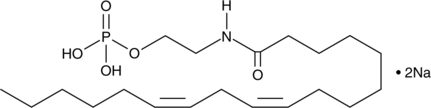
Linoleoyl ethanolamide phosphate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of linoleoyl ethanolamide (Item No. 90155) that can be generated through phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine.{24249} Linoleoyl ethanolamide phosphate, along with other endogenous N-acylethanolamines, is thought to play a role in the regulation of food intake by selective prolongation of feeding latency and post-meal interval.{24250}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001837 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleoyl ethanolamide phosphate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of linoleoyl ethanolamide (Item No. 90155) that can be generated through phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine.{24249} Linoleoyl ethanolamide phosphate, along with other endogenous N-acylethanolamines, is thought to play a role in the regulation of food intake by selective prolongation of feeding latency and post-meal interval.{24250}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001837 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleoyl ethanolamide phosphate is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of linoleoyl ethanolamide (Item No. 90155) that can be generated through phospholipase C-mediated hydrolysis of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine.{24249} Linoleoyl ethanolamide phosphate, along with other endogenous N-acylethanolamines, is thought to play a role in the regulation of food intake by selective prolongation of feeding latency and post-meal interval.{24250}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9001837 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
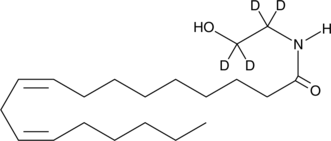
Linoleoyl ethanolamide-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleoyl ethanolamide (Item No. 90155) by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Linoleoyl ethanolamide is an endocannabinoid detected in porcine brain and murine peritoneal macrophages which contains linoleate in place of the arachidonate moiety of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA).{11172,11151} It has weak affinity for the central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors, exhibiting Ki values of 10 µM and 25 µM, respectively.{7422} However, it is only approximately 4-fold less potent than AEA at causing catalepsy in mice (ED50 of 26.5 mg/kg).{11177} In addition, linoleoyl ethanolamide increases ERK phosphorylation and AP-1-dependent transcription approximately 1.5-fold at 15 µM in a CB-receptor-independent manner.{11152} However, cellular toxicity is readily apparent at concentrations of 10-20 µM. Linoleoyl ethanolamide inhibits human fatty acid amide hydrolase-dependent hydrolysis of AEA with a Ki value of 9.0 µM, but also is hydrolyzed effectively by the enzyme.{7251,3922}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000553 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Linoleoyl ethanolamide-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleoyl ethanolamide (Item No. 90155) by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Linoleoyl ethanolamide is an endocannabinoid detected in porcine brain and murine peritoneal macrophages which contains linoleate in place of the arachidonate moiety of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA).{11172,11151} It has weak affinity for the central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors, exhibiting Ki values of 10 µM and 25 µM, respectively.{7422} However, it is only approximately 4-fold less potent than AEA at causing catalepsy in mice (ED50 of 26.5 mg/kg).{11177} In addition, linoleoyl ethanolamide increases ERK phosphorylation and AP-1-dependent transcription approximately 1.5-fold at 15 µM in a CB-receptor-independent manner.{11152} However, cellular toxicity is readily apparent at concentrations of 10-20 µM. Linoleoyl ethanolamide inhibits human fatty acid amide hydrolase-dependent hydrolysis of AEA with a Ki value of 9.0 µM, but also is hydrolyzed effectively by the enzyme.{7251,3922}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000553 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Linoleoyl ethanolamide-d4 contains four deuterium atoms at the hydroxyethyl 1,1′,2, and 2′ positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of linoleoyl ethanolamide (Item No. 90155) by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Linoleoyl ethanolamide is an endocannabinoid detected in porcine brain and murine peritoneal macrophages which contains linoleate in place of the arachidonate moiety of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA).{11172,11151} It has weak affinity for the central cannabinoid (CB1) and peripheral cannabinoid (CB2) receptors, exhibiting Ki values of 10 µM and 25 µM, respectively.{7422} However, it is only approximately 4-fold less potent than AEA at causing catalepsy in mice (ED50 of 26.5 mg/kg).{11177} In addition, linoleoyl ethanolamide increases ERK phosphorylation and AP-1-dependent transcription approximately 1.5-fold at 15 µM in a CB-receptor-independent manner.{11152} However, cellular toxicity is readily apparent at concentrations of 10-20 µM. Linoleoyl ethanolamide inhibits human fatty acid amide hydrolase-dependent hydrolysis of AEA with a Ki value of 9.0 µM, but also is hydrolyzed effectively by the enzyme.{7251,3922}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9000553 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder