Chemicals
Showing 24751–24900 of 41137 results
-
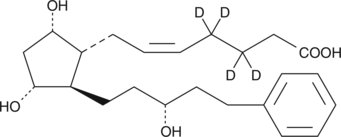
Latanoprost (free acid)-d4 (Lat-FA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the 3, 3, 4, and 4 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Lat-FA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Latanoprost is an F-series prostaglandin (PG) analog which has been approved for use as an ocular hypotensive drug.{1107} It is the isopropyl ester of a PGF2α analog containing an aromatic group (17-phenyl) in the ω-chain. As an isopropyl ester, latanoprost acts as a prodrug which is converted to Lat-FA by endogenous esterase enzymes. Lat-FA is a potent FP receptor agonist with an EC50 value of 3.6 nM for human FP receptors, which is twice the potency of PGF2α and more than 200 times more potent latanoprost.{8322} The efficacy of PG analog esters for the treatment of glaucoma correlates closely with the FP receptor binding affinity of the free acid.{3802} However, Lat-FA is more irritating and less effective than the prodrug latanoprost when applied directly to the eyes of human glaucoma patients.{5358}
Brand:CaymanSKU:316811 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Latanoprost (free acid)-d4 (Lat-FA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the 3, 3, 4, and 4 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Lat-FA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Latanoprost is an F-series prostaglandin (PG) analog which has been approved for use as an ocular hypotensive drug.{1107} It is the isopropyl ester of a PGF2α analog containing an aromatic group (17-phenyl) in the ω-chain. As an isopropyl ester, latanoprost acts as a prodrug which is converted to Lat-FA by endogenous esterase enzymes. Lat-FA is a potent FP receptor agonist with an EC50 value of 3.6 nM for human FP receptors, which is twice the potency of PGF2α and more than 200 times more potent latanoprost.{8322} The efficacy of PG analog esters for the treatment of glaucoma correlates closely with the FP receptor binding affinity of the free acid.{3802} However, Lat-FA is more irritating and less effective than the prodrug latanoprost when applied directly to the eyes of human glaucoma patients.{5358}
Brand:CaymanSKU:316811 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Latanoprost (free acid)-d4 (Lat-FA-d4) contains four deuterium atoms at the 3, 3, 4, and 4 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Lat-FA by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Latanoprost is an F-series prostaglandin (PG) analog which has been approved for use as an ocular hypotensive drug.{1107} It is the isopropyl ester of a PGF2α analog containing an aromatic group (17-phenyl) in the ω-chain. As an isopropyl ester, latanoprost acts as a prodrug which is converted to Lat-FA by endogenous esterase enzymes. Lat-FA is a potent FP receptor agonist with an EC50 value of 3.6 nM for human FP receptors, which is twice the potency of PGF2α and more than 200 times more potent latanoprost.{8322} The efficacy of PG analog esters for the treatment of glaucoma correlates closely with the FP receptor binding affinity of the free acid.{3802} However, Lat-FA is more irritating and less effective than the prodrug latanoprost when applied directly to the eyes of human glaucoma patients.{5358}
Brand:CaymanSKU:316811 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
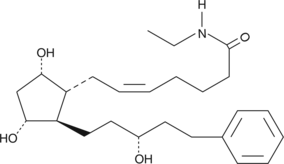
Latanoprost ethyl amide (Lat-NEt) is a latanoprost analog in which the C-1 carboxyl group has been modified to an N-ethyl amide. Prostaglandin esters have been shown to have ocular hypotensive activity.{8837} Prostaglandin N-ethyl amides were recently introduced as alternative prostaglandin ocular hypotensive prodrugs.{8941} Although it has been claimed that prostaglandin ethyl amides are not converted to the free acids in vivo,{8641} studies in our laboratories have shown that bovine and human corneal tissue converts the N-ethyl amides of various prostaglandins to the free acids with a conversion rate of about 2.5 µg/g corneal tissue/hr.{9311} Lat-NEt would be expected to show the typical intraocular effects of Latanoprost free acid, but with the much slower hydrolysis pharmacokinetics of the prostaglandin N-amides.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Latanoprost ethyl amide (Lat-NEt) is a latanoprost analog in which the C-1 carboxyl group has been modified to an N-ethyl amide. Prostaglandin esters have been shown to have ocular hypotensive activity.{8837} Prostaglandin N-ethyl amides were recently introduced as alternative prostaglandin ocular hypotensive prodrugs.{8941} Although it has been claimed that prostaglandin ethyl amides are not converted to the free acids in vivo,{8641} studies in our laboratories have shown that bovine and human corneal tissue converts the N-ethyl amides of various prostaglandins to the free acids with a conversion rate of about 2.5 µg/g corneal tissue/hr.{9311} Lat-NEt would be expected to show the typical intraocular effects of Latanoprost free acid, but with the much slower hydrolysis pharmacokinetics of the prostaglandin N-amides.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Latanoprost ethyl amide (Lat-NEt) is a latanoprost analog in which the C-1 carboxyl group has been modified to an N-ethyl amide. Prostaglandin esters have been shown to have ocular hypotensive activity.{8837} Prostaglandin N-ethyl amides were recently introduced as alternative prostaglandin ocular hypotensive prodrugs.{8941} Although it has been claimed that prostaglandin ethyl amides are not converted to the free acids in vivo,{8641} studies in our laboratories have shown that bovine and human corneal tissue converts the N-ethyl amides of various prostaglandins to the free acids with a conversion rate of about 2.5 µg/g corneal tissue/hr.{9311} Lat-NEt would be expected to show the typical intraocular effects of Latanoprost free acid, but with the much slower hydrolysis pharmacokinetics of the prostaglandin N-amides.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
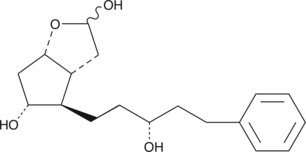
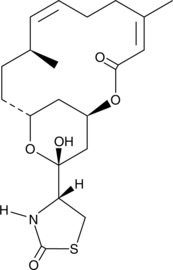
Latanoprost is an F-series prostaglandin analog which has been approved for use as an ocular hypotensive drug. Latanoprost lactol is an intermediate in the synthesis of latanoprost. Latanoprost lactol can be converted to the free acid of latanoprost by Wittig reaction with commercially available reagents.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70049 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Latanoprost is an F-series prostaglandin analog which has been approved for use as an ocular hypotensive drug. Latanoprost lactol is an intermediate in the synthesis of latanoprost. Latanoprost lactol can be converted to the free acid of latanoprost by Wittig reaction with commercially available reagents.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70049 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Latanoprost is an F-series prostaglandin analog which has been approved for use as an ocular hypotensive drug. Latanoprost lactol is an intermediate in the synthesis of latanoprost. Latanoprost lactol can be converted to the free acid of latanoprost by Wittig reaction with commercially available reagents.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70049 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
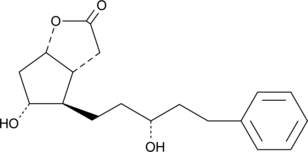
Latanoprost is an F-series prostaglandin analog which has been approved for use as an ocular hypotensive drug. Latanoprost lactone diol is an intermediate in the synthesis of latanoprost Latanoprost lactone diol can be converted to the free acid of latanoprost by reduction with DIBAL followed by Wittig reaction with commercially available reagents.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70039 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Latanoprost is an F-series prostaglandin analog which has been approved for use as an ocular hypotensive drug. Latanoprost lactone diol is an intermediate in the synthesis of latanoprost Latanoprost lactone diol can be converted to the free acid of latanoprost by reduction with DIBAL followed by Wittig reaction with commercially available reagents.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70039 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Latanoprost is an F-series prostaglandin analog which has been approved for use as an ocular hypotensive drug. Latanoprost lactone diol is an intermediate in the synthesis of latanoprost Latanoprost lactone diol can be converted to the free acid of latanoprost by reduction with DIBAL followed by Wittig reaction with commercially available reagents.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70039 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
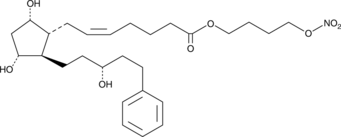
Latanoprostene bunod is a nitric oxide-donating prostaglandin F2α (FP) receptor agonist that is converted to latanoprost (free acid) (Item No. 16811) and nitric oxide (NO) in vivo.{43936} It induces cGMP accumulation in PC12 and HEK293 cells (EC50s = 1.6 and 9.2 μM, respectively). Topical administration of latanoprostene bunod (0.036% solution) reduces intraocular pressure (IOP) in canine and rabbit models of glaucoma. It also decreases IOP in a cynomolgus monkey model of laser-induced ocular hypertension.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25830 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Latanoprostene bunod is a nitric oxide-donating prostaglandin F2α (FP) receptor agonist that is converted to latanoprost (free acid) (Item No. 16811) and nitric oxide (NO) in vivo.{43936} It induces cGMP accumulation in PC12 and HEK293 cells (EC50s = 1.6 and 9.2 μM, respectively). Topical administration of latanoprostene bunod (0.036% solution) reduces intraocular pressure (IOP) in canine and rabbit models of glaucoma. It also decreases IOP in a cynomolgus monkey model of laser-induced ocular hypertension.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25830 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Latanoprostene bunod is a nitric oxide-donating prostaglandin F2α (FP) receptor agonist that is converted to latanoprost (free acid) (Item No. 16811) and nitric oxide (NO) in vivo.{43936} It induces cGMP accumulation in PC12 and HEK293 cells (EC50s = 1.6 and 9.2 μM, respectively). Topical administration of latanoprostene bunod (0.036% solution) reduces intraocular pressure (IOP) in canine and rabbit models of glaucoma. It also decreases IOP in a cynomolgus monkey model of laser-induced ocular hypertension.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25830 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Latanoprostene bunod is a nitric oxide-donating prostaglandin F2α (FP) receptor agonist that is converted to latanoprost (free acid) (Item No. 16811) and nitric oxide (NO) in vivo.{43936} It induces cGMP accumulation in PC12 and HEK293 cells (EC50s = 1.6 and 9.2 μM, respectively). Topical administration of latanoprostene bunod (0.036% solution) reduces intraocular pressure (IOP) in canine and rabbit models of glaucoma. It also decreases IOP in a cynomolgus monkey model of laser-induced ocular hypertension.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25830 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
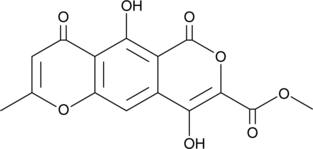
Lateropyrone is a fungal metabolite produced by Fusarium species.{46078} It has been found in freshly harvested and stored sugar beet crops in Europe.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26463 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Lateropyrone is a fungal metabolite produced by Fusarium species.{46078} It has been found in freshly harvested and stored sugar beet crops in Europe.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26463 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
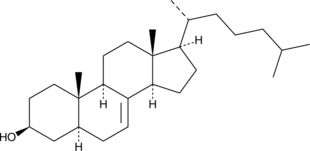
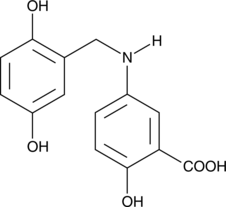
Lathosterol is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.{42408,42409} Serum levels of lathosterol correlate with cholesterol synthesis and have been used as biomarkers of excess cholesterol production. Lathosterol accumulates in lathosterolosis, a disorder characterized by a deficiency of lathosterol 5-desaturase, the enzyme that converts lathosterol to 7-dehydro cholesterol (Item No. 14612).{42410}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003102 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Lathosterol is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.{42408,42409} Serum levels of lathosterol correlate with cholesterol synthesis and have been used as biomarkers of excess cholesterol production. Lathosterol accumulates in lathosterolosis, a disorder characterized by a deficiency of lathosterol 5-desaturase, the enzyme that converts lathosterol to 7-dehydro cholesterol (Item No. 14612).{42410}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003102 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Lathosterol is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.{42408,42409} Serum levels of lathosterol correlate with cholesterol synthesis and have been used as biomarkers of excess cholesterol production. Lathosterol accumulates in lathosterolosis, a disorder characterized by a deficiency of lathosterol 5-desaturase, the enzyme that converts lathosterol to 7-dehydro cholesterol (Item No. 14612).{42410}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003102 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Lathosterol is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of cholesterol.{42408,42409} Serum levels of lathosterol correlate with cholesterol synthesis and have been used as biomarkers of excess cholesterol production. Lathosterol accumulates in lathosterolosis, a disorder characterized by a deficiency of lathosterol 5-desaturase, the enzyme that converts lathosterol to 7-dehydro cholesterol (Item No. 14612).{42410}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003102 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Actin disruption is used to study cell functions in vitro (e.g., migration, endocytosis) and in vivo (e.g., tumor cell invasion). Latrunculin A is a bioactive 2-thiazolidinone macrolide derived from sponges that sequesters G-actin and prevents F-actin assembly. It binds monomeric actin with 1:1 stoichiometry and can be used to block actin polymerization both in vitro (Kd = 0.2 μM) and in cells (0.5 μM, 30 min).{{15842,15843,15838} Latrunculin A (1-10 μM) causes depolymerization of tumor cell cytoskeleton within ten minutes.{15841} Overnight treatment of cells with latrunculin A (10 μM) strongly suppresses actin synthesis.{15839} Prolonged cell treatment blocks dexamethasone-induced changes in actin cytoskeleton with no effect on cell viability.{15840}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010630 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Actin disruption is used to study cell functions in vitro (e.g., migration, endocytosis) and in vivo (e.g., tumor cell invasion). Latrunculin A is a bioactive 2-thiazolidinone macrolide derived from sponges that sequesters G-actin and prevents F-actin assembly. It binds monomeric actin with 1:1 stoichiometry and can be used to block actin polymerization both in vitro (Kd = 0.2 μM) and in cells (0.5 μM, 30 min).{{15842,15843,15838} Latrunculin A (1-10 μM) causes depolymerization of tumor cell cytoskeleton within ten minutes.{15841} Overnight treatment of cells with latrunculin A (10 μM) strongly suppresses actin synthesis.{15839} Prolonged cell treatment blocks dexamethasone-induced changes in actin cytoskeleton with no effect on cell viability.{15840}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010630 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
Actin disruption is used to study cell functions in vitro (e.g., migration, endocytosis) and in vivo (e.g., tumor cell invasion). Latrunculin A is a bioactive 2-thiazolidinone macrolide derived from sponges that sequesters G-actin and prevents F-actin assembly. It binds monomeric actin with 1:1 stoichiometry and can be used to block actin polymerization both in vitro (Kd = 0.2 μM) and in cells (0.5 μM, 30 min).{{15842,15843,15838} Latrunculin A (1-10 μM) causes depolymerization of tumor cell cytoskeleton within ten minutes.{15841} Overnight treatment of cells with latrunculin A (10 μM) strongly suppresses actin synthesis.{15839} Prolonged cell treatment blocks dexamethasone-induced changes in actin cytoskeleton with no effect on cell viability.{15840}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010630 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
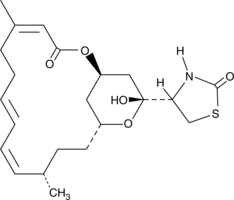
The latrunculins are commonly used to experimentally disrupt the actin cytoskeleton of cells. Latrunculin B causes concentration-dependent changes in cell shape and actin organization. It sequesters G-actin and prevents F-actin assembly. It binds monomeric actin with 1:1 stoichiometry and can be used to block actin polymerization both in vitro and in cells (Kd = 60 nM).{16723} The short-term effects of latrunculin B are comparable to those of latrunculin A, although latrunculin B is slightly less potent.{16724} However, latrunculin B is gradually inactivated by serum so that induced changes are transient in the continued presence of the compound. For this reason, latrunculin B may have fewer unwanted effects than latrunculin A and may be preferred for short-term studies.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010631 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
The latrunculins are commonly used to experimentally disrupt the actin cytoskeleton of cells. Latrunculin B causes concentration-dependent changes in cell shape and actin organization. It sequesters G-actin and prevents F-actin assembly. It binds monomeric actin with 1:1 stoichiometry and can be used to block actin polymerization both in vitro and in cells (Kd = 60 nM).{16723} The short-term effects of latrunculin B are comparable to those of latrunculin A, although latrunculin B is slightly less potent.{16724} However, latrunculin B is gradually inactivated by serum so that induced changes are transient in the continued presence of the compound. For this reason, latrunculin B may have fewer unwanted effects than latrunculin A and may be preferred for short-term studies.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010631 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
The latrunculins are commonly used to experimentally disrupt the actin cytoskeleton of cells. Latrunculin B causes concentration-dependent changes in cell shape and actin organization. It sequesters G-actin and prevents F-actin assembly. It binds monomeric actin with 1:1 stoichiometry and can be used to block actin polymerization both in vitro and in cells (Kd = 60 nM).{16723} The short-term effects of latrunculin B are comparable to those of latrunculin A, although latrunculin B is slightly less potent.{16724} However, latrunculin B is gradually inactivated by serum so that induced changes are transient in the continued presence of the compound. For this reason, latrunculin B may have fewer unwanted effects than latrunculin A and may be preferred for short-term studies.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010631 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
The latrunculins are commonly used to experimentally disrupt the actin cytoskeleton of cells. Latrunculin B causes concentration-dependent changes in cell shape and actin organization. It sequesters G-actin and prevents F-actin assembly. It binds monomeric actin with 1:1 stoichiometry and can be used to block actin polymerization both in vitro and in cells (Kd = 60 nM).{16723} The short-term effects of latrunculin B are comparable to those of latrunculin A, although latrunculin B is slightly less potent.{16724} However, latrunculin B is gradually inactivated by serum so that induced changes are transient in the continued presence of the compound. For this reason, latrunculin B may have fewer unwanted effects than latrunculin A and may be preferred for short-term studies.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010631 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
LAU159 is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of α6β3γ2 subunit-containing GABAA receptors.{52055} It selectively increases GABA-induced currents in X. laevis oocytes expressing α6β3γ2 over α1β3γ2, α2β3γ2, α3β3γ2, α4β3γ2, and α5β3γ2 subunit-containing receptors at 10 μM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26336 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
LAU159 is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of α6β3γ2 subunit-containing GABAA receptors.{52055} It selectively increases GABA-induced currents in X. laevis oocytes expressing α6β3γ2 over α1β3γ2, α2β3γ2, α3β3γ2, α4β3γ2, and α5β3γ2 subunit-containing receptors at 10 μM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26336 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
LAU159 is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of α6β3γ2 subunit-containing GABAA receptors.{52055} It selectively increases GABA-induced currents in X. laevis oocytes expressing α6β3γ2 over α1β3γ2, α2β3γ2, α3β3γ2, α4β3γ2, and α5β3γ2 subunit-containing receptors at 10 μM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26336 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
LAU159 is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of α6β3γ2 subunit-containing GABAA receptors.{52055} It selectively increases GABA-induced currents in X. laevis oocytes expressing α6β3γ2 over α1β3γ2, α2β3γ2, α3β3γ2, α4β3γ2, and α5β3γ2 subunit-containing receptors at 10 μM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:26336 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Laurdan is a membrane-permeable fluorescent probe that displays spectral sensitivity to the phospholipid phase of the cell membrane to which it is bound.{37064} Quantitation of generalized polarization (GP) of laurdan can be used to identify phospholipid phase. When excited at 340 nm, GP values are 0.6 and -0.2 for gel phase and liquid crystalline phase, respectively. GP does not change with polar head group or pH (in the range 4-10); it changes only with phase state.
Brand:CaymanSKU:19706 -Available on backorder
Laurdan is a membrane-permeable fluorescent probe that displays spectral sensitivity to the phospholipid phase of the cell membrane to which it is bound.{37064} Quantitation of generalized polarization (GP) of laurdan can be used to identify phospholipid phase. When excited at 340 nm, GP values are 0.6 and -0.2 for gel phase and liquid crystalline phase, respectively. GP does not change with polar head group or pH (in the range 4-10); it changes only with phase state.
Brand:CaymanSKU:19706 -Available on backorder
Laurdan is a membrane-permeable fluorescent probe that displays spectral sensitivity to the phospholipid phase of the cell membrane to which it is bound.{37064} Quantitation of generalized polarization (GP) of laurdan can be used to identify phospholipid phase. When excited at 340 nm, GP values are 0.6 and -0.2 for gel phase and liquid crystalline phase, respectively. GP does not change with polar head group or pH (in the range 4-10); it changes only with phase state.
Brand:CaymanSKU:19706 -Available on backorder
Laurdan is a membrane-permeable fluorescent probe that displays spectral sensitivity to the phospholipid phase of the cell membrane to which it is bound.{37064} Quantitation of generalized polarization (GP) of laurdan can be used to identify phospholipid phase. When excited at 340 nm, GP values are 0.6 and -0.2 for gel phase and liquid crystalline phase, respectively. GP does not change with polar head group or pH (in the range 4-10); it changes only with phase state.
Brand:CaymanSKU:19706 -Available on backorder
Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006626 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006626 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006626 - 250 gAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006626 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
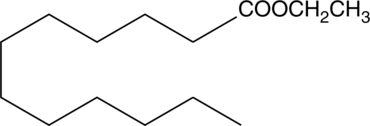
Lauric acid is a common 12-carbon saturated fatty acid plentiful in coconut and other nut oils. Saturated fatty acids induce the expression of cyclooxygenase-2, an effect that is significant at 25 µM in RAW 264.7 cells, with lauric acid being the most potent of the C:8-18 fatty acids.{10646} Lauric acid ethyl ester is a more lipophilic and less toxic form of the free acid. It is one of the medium-chain fatty acid ethyl esters that is released during the anaerobic fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae along with the free acid.{14124}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008203 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid is a common 12-carbon saturated fatty acid plentiful in coconut and other nut oils. Saturated fatty acids induce the expression of cyclooxygenase-2, an effect that is significant at 25 µM in RAW 264.7 cells, with lauric acid being the most potent of the C:8-18 fatty acids.{10646} Lauric acid ethyl ester is a more lipophilic and less toxic form of the free acid. It is one of the medium-chain fatty acid ethyl esters that is released during the anaerobic fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae along with the free acid.{14124}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008203 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid is a common 12-carbon saturated fatty acid plentiful in coconut and other nut oils. Saturated fatty acids induce the expression of cyclooxygenase-2, an effect that is significant at 25 µM in RAW 264.7 cells, with lauric acid being the most potent of the C:8-18 fatty acids.{10646} Lauric acid ethyl ester is a more lipophilic and less toxic form of the free acid. It is one of the medium-chain fatty acid ethyl esters that is released during the anaerobic fermentation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae along with the free acid.{14124}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008203 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
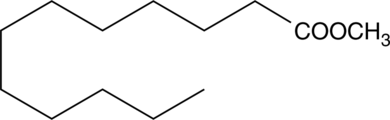
Lauric acid methyl ester is an esterified version of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626), which is a common 12-carbon saturated fatty acid. Lauric acid methyl ester was a major component (35.5%) of biodiesel made from crude fat extracted from black soldier flies, with oleinic acid methyl ester (23.6%) and palmitic acid methyl ester (14.8%; Item No. 10007358) as lesser components.{38297} It has also been used in the transesterification of starches and as an internal standard for GC- and LC-MS.{38296,38298}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20608 -Available on backorder
Lauric acid methyl ester is an esterified version of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626), which is a common 12-carbon saturated fatty acid. Lauric acid methyl ester was a major component (35.5%) of biodiesel made from crude fat extracted from black soldier flies, with oleinic acid methyl ester (23.6%) and palmitic acid methyl ester (14.8%; Item No. 10007358) as lesser components.{38297} It has also been used in the transesterification of starches and as an internal standard for GC- and LC-MS.{38296,38298}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20608 -Available on backorder
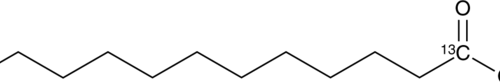
Lauric acid-13C is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29462 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid-13C is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29462 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid-13C is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29462 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
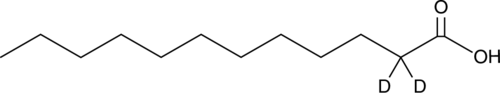
Lauric acid-d2 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29410 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid-d2 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29410 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid-d2 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29410 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid-d2 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a medium-chain saturated fatty acid. It has been found at high levels in coconut oil.{53245} Lauric acid induces the activation of NF-κB and the expression of COX-2, inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), and IL-1α in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 µM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:29410 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
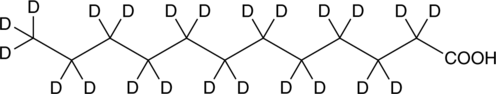
Lauric acid-d23 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a common 12-carbon saturated fatty acid that has been found in A. mollis.{39978} It induces COX-2 expression and COX-2 reporter gene activity in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 mM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28080 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid-d23 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a common 12-carbon saturated fatty acid that has been found in A. mollis.{39978} It induces COX-2 expression and COX-2 reporter gene activity in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 mM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28080 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid-d23 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a common 12-carbon saturated fatty acid that has been found in A. mollis.{39978} It induces COX-2 expression and COX-2 reporter gene activity in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 mM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28080 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauric acid-d23 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of lauric acid (Item No. 10006626) by GC- or LC-MS. Lauric acid is a common 12-carbon saturated fatty acid that has been found in A. mollis.{39978} It induces COX-2 expression and COX-2 reporter gene activity in RAW 264.7 cells when used at a concentration of 25 mM.{10646}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28080 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
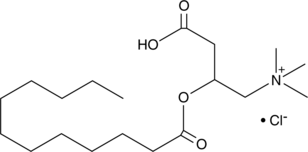
Lauroyl-DL-carnitine is a zwitterionic, long-chain acylcarnitine used to improve in vivo absorption of certain hydrophilic compounds, especially through mucosal membranes.{26713,26715,26714}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Lauroyl-DL-carnitine is a zwitterionic, long-chain acylcarnitine used to improve in vivo absorption of certain hydrophilic compounds, especially through mucosal membranes.{26713,26715,26714}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Lauroyl-DL-carnitine is a zwitterionic, long-chain acylcarnitine used to improve in vivo absorption of certain hydrophilic compounds, especially through mucosal membranes.{26713,26715,26714}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Lauroyl-DL-carnitine is a zwitterionic, long-chain acylcarnitine used to improve in vivo absorption of certain hydrophilic compounds, especially through mucosal membranes.{26713,26715,26714}
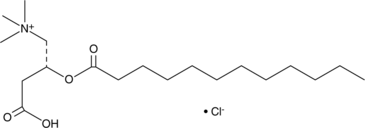
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Lauroyl-L-carnitine is an acylcarnitine and a surfactant.{43575} It has been used to permeabilize porcine enterocytes for delivery of the polar fluorescent probe lucifer yellow (Item No. 25573).
Brand:CaymanSKU:26550 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauroyl-L-carnitine is an acylcarnitine and a surfactant.{43575} It has been used to permeabilize porcine enterocytes for delivery of the polar fluorescent probe lucifer yellow (Item No. 25573).
Brand:CaymanSKU:26550 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauroyl-L-carnitine is an acylcarnitine and a surfactant.{43575} It has been used to permeabilize porcine enterocytes for delivery of the polar fluorescent probe lucifer yellow (Item No. 25573).
Brand:CaymanSKU:26550 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Lauroyl-L-carnitine is an acylcarnitine and a surfactant.{43575} It has been used to permeabilize porcine enterocytes for delivery of the polar fluorescent probe lucifer yellow (Item No. 25573).
Brand:CaymanSKU:26550 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin A is a selective inhibitor of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-associated tyrosine kinase (IC50 = 11 nM) that was first isolated from a Streptomyces culture filtrate.{16076,32582} It does not inhibit protein kinase A (PKA), PKC, or PI3K (IC50s > 100 µM).{32582} It has been used to differentiate rat mesenchymal stem cells, to inhibit NMDA-stimulated cGMP production, and to inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis.{28437,16078,25113}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010268 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin A is a selective inhibitor of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-associated tyrosine kinase (IC50 = 11 nM) that was first isolated from a Streptomyces culture filtrate.{16076,32582} It does not inhibit protein kinase A (PKA), PKC, or PI3K (IC50s > 100 µM).{32582} It has been used to differentiate rat mesenchymal stem cells, to inhibit NMDA-stimulated cGMP production, and to inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis.{28437,16078,25113}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010268 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin A is a selective inhibitor of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-associated tyrosine kinase (IC50 = 11 nM) that was first isolated from a Streptomyces culture filtrate.{16076,32582} It does not inhibit protein kinase A (PKA), PKC, or PI3K (IC50s > 100 µM).{32582} It has been used to differentiate rat mesenchymal stem cells, to inhibit NMDA-stimulated cGMP production, and to inhibit VEGF-induced angiogenesis.{28437,16078,25113}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010268 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin B is a competitive inhibitor of glucose transporter 1 (Glut1; Ki = 15 µM).{46352} It is also an inhibitor of the interaction between HIV-1 integrase and LEDGF/p75 (IC50 = 94.07 µM).{46353} Lavendustin B is a weak inhibitor of tyrosine kinases (IC50 = 0.49 µg/ml) and has been used as a negative control for the protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor lavendustin A (Item No. 10010268).{16076,46354,46355}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27311 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin B is a competitive inhibitor of glucose transporter 1 (Glut1; Ki = 15 µM).{46352} It is also an inhibitor of the interaction between HIV-1 integrase and LEDGF/p75 (IC50 = 94.07 µM).{46353} Lavendustin B is a weak inhibitor of tyrosine kinases (IC50 = 0.49 µg/ml) and has been used as a negative control for the protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor lavendustin A (Item No. 10010268).{16076,46354,46355}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27311 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin B is a competitive inhibitor of glucose transporter 1 (Glut1; Ki = 15 µM).{46352} It is also an inhibitor of the interaction between HIV-1 integrase and LEDGF/p75 (IC50 = 94.07 µM).{46353} Lavendustin B is a weak inhibitor of tyrosine kinases (IC50 = 0.49 µg/ml) and has been used as a negative control for the protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor lavendustin A (Item No. 10010268).{16076,46354,46355}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27311 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin B is a competitive inhibitor of glucose transporter 1 (Glut1; Ki = 15 µM).{46352} It is also an inhibitor of the interaction between HIV-1 integrase and LEDGF/p75 (IC50 = 94.07 µM).{46353} Lavendustin B is a weak inhibitor of tyrosine kinases (IC50 = 0.49 µg/ml) and has been used as a negative control for the protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor lavendustin A (Item No. 10010268).{16076,46354,46355}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27311 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin C, a derivative of a Streptomyces griseolavendus butyl acetate extract, is a potent inhibitor of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-associated tyrosine kinase with an IC50 value of 0.012 µM.{16076} Lavendustin C also inhibits pp60c-src(+) kinase and Ca2+ calmodulin-dependent kinase II with IC50 values of 0.5 and 0.2 µM, respectively.{16078} At a concentration of 10-150 µM, lavendustin C inhibits tyrosine kinase-associated neutrophil degranulation and superoxide generation.{16077}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010329 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin C, a derivative of a Streptomyces griseolavendus butyl acetate extract, is a potent inhibitor of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-associated tyrosine kinase with an IC50 value of 0.012 µM.{16076} Lavendustin C also inhibits pp60c-src(+) kinase and Ca2+ calmodulin-dependent kinase II with IC50 values of 0.5 and 0.2 µM, respectively.{16078} At a concentration of 10-150 µM, lavendustin C inhibits tyrosine kinase-associated neutrophil degranulation and superoxide generation.{16077}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010329 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin C, a derivative of a Streptomyces griseolavendus butyl acetate extract, is a potent inhibitor of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-associated tyrosine kinase with an IC50 value of 0.012 µM.{16076} Lavendustin C also inhibits pp60c-src(+) kinase and Ca2+ calmodulin-dependent kinase II with IC50 values of 0.5 and 0.2 µM, respectively.{16078} At a concentration of 10-150 µM, lavendustin C inhibits tyrosine kinase-associated neutrophil degranulation and superoxide generation.{16077}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010329 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Lavendustin C, a derivative of a Streptomyces griseolavendus butyl acetate extract, is a potent inhibitor of epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor-associated tyrosine kinase with an IC50 value of 0.012 µM.{16076} Lavendustin C also inhibits pp60c-src(+) kinase and Ca2+ calmodulin-dependent kinase II with IC50 values of 0.5 and 0.2 µM, respectively.{16078} At a concentration of 10-150 µM, lavendustin C inhibits tyrosine kinase-associated neutrophil degranulation and superoxide generation.{16077}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010329 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
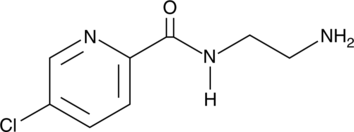
Monoamine oxidases, MAO-A and MAO-B, regulate the intracellular concentrations of biogenic monoamines such as 5-hydroxytryptamine and dopamine via oxidative deamination. Inhibitors of MAO-A are widely used for the therapy of affective disorders, whereas MAO-B inhibitors have clinical efficacy in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.{21368} Lazabemide is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) with IC50 values of 0.48 and 1.5 μM measured in platelets of human subjects ages 19-36 and 60-78, respectively.{21370} It is structurally similar to the MAO-B preferential substrate phenylethylamine and can be oxidized by MAO-B, forming tightly, but reversibly, bound adducts with the active site of the enzyme.{21369} The selectivity of lazabemide for MAO-B inhibition has been demonstrated in both in vitro and ex vivo conditions and it was evaluated in clinical trials for possible neuroprotective actions in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.{21368}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11640 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Monoamine oxidases, MAO-A and MAO-B, regulate the intracellular concentrations of biogenic monoamines such as 5-hydroxytryptamine and dopamine via oxidative deamination. Inhibitors of MAO-A are widely used for the therapy of affective disorders, whereas MAO-B inhibitors have clinical efficacy in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.{21368} Lazabemide is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) with IC50 values of 0.48 and 1.5 μM measured in platelets of human subjects ages 19-36 and 60-78, respectively.{21370} It is structurally similar to the MAO-B preferential substrate phenylethylamine and can be oxidized by MAO-B, forming tightly, but reversibly, bound adducts with the active site of the enzyme.{21369} The selectivity of lazabemide for MAO-B inhibition has been demonstrated in both in vitro and ex vivo conditions and it was evaluated in clinical trials for possible neuroprotective actions in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.{21368}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11640 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Monoamine oxidases, MAO-A and MAO-B, regulate the intracellular concentrations of biogenic monoamines such as 5-hydroxytryptamine and dopamine via oxidative deamination. Inhibitors of MAO-A are widely used for the therapy of affective disorders, whereas MAO-B inhibitors have clinical efficacy in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.{21368} Lazabemide is a reversible inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B (MAO-B) with IC50 values of 0.48 and 1.5 μM measured in platelets of human subjects ages 19-36 and 60-78, respectively.{21370} It is structurally similar to the MAO-B preferential substrate phenylethylamine and can be oxidized by MAO-B, forming tightly, but reversibly, bound adducts with the active site of the enzyme.{21369} The selectivity of lazabemide for MAO-B inhibition has been demonstrated in both in vitro and ex vivo conditions and it was evaluated in clinical trials for possible neuroprotective actions in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.{21368}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11640 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
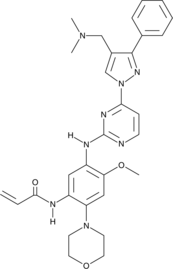
Lazertinib is an irreversible inhibitor of mutant EGFRs (IC50s = 1.7, 2, and 3.3 nM for EGFRL858R/T790M, EGFRDel19/T790M, and EGFRDel19, respectively).{52289} It is selective for mutant EGFRs over wild-type EGFR, HER2, and HER4 (IC50s = 76, 364, and 1,017 nM, respectively). Lazertinib reduces viability of Ba/F3 cells expressing mutant EGFRs (IC50s = 3.3-5.7 nM). In vivo, lazertinib (1, 3, and 10 mg/kg) reduces tumor volume in an EGFRT790M mutant H1975 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) mouse xenograft model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29670 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Lazertinib is an irreversible inhibitor of mutant EGFRs (IC50s = 1.7, 2, and 3.3 nM for EGFRL858R/T790M, EGFRDel19/T790M, and EGFRDel19, respectively).{52289} It is selective for mutant EGFRs over wild-type EGFR, HER2, and HER4 (IC50s = 76, 364, and 1,017 nM, respectively). Lazertinib reduces viability of Ba/F3 cells expressing mutant EGFRs (IC50s = 3.3-5.7 nM). In vivo, lazertinib (1, 3, and 10 mg/kg) reduces tumor volume in an EGFRT790M mutant H1975 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) mouse xenograft model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:29670 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder