Chemicals
Showing 24451–24600 of 41137 results
-
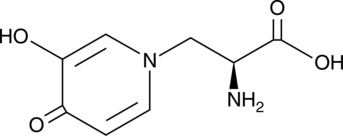
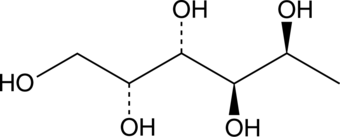
L-Fucitol is a reduced form of L-(–)-fucose (Item No. 16479). It has been used to determine the structure of E. coli and B. pallidus L-fucose isomerase.{46104,46105}
Brand:CaymanSKU:26540 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
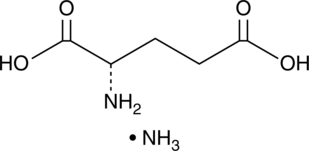
L-Glutamic acid is a non-essential amino acid and the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS.{54095} It acts on ionotropic and metabotropic receptors to induce excitatory synaptic transmission and has roles in synaptic plasticity. Excessive release of L-glutamic acid induces excitotoxicity that is associated with various human diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), stroke, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and Huntington’s disease.{54096} Excessive L-glutamic acid release, in its protonated glutamate form, also occurs during seizure activity and contributes to epileptogenesis and seizure-induced brain damage.{54097}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30377 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
L-Glutamic acid is a non-essential amino acid and the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS.{54095} It acts on ionotropic and metabotropic receptors to induce excitatory synaptic transmission and has roles in synaptic plasticity. Excessive release of L-glutamic acid induces excitotoxicity that is associated with various human diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), stroke, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and Huntington’s disease.{54096} Excessive L-glutamic acid release, in its protonated glutamate form, also occurs during seizure activity and contributes to epileptogenesis and seizure-induced brain damage.{54097}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30377 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
L-Glutamic acid is a non-essential amino acid and the primary excitatory neurotransmitter in the CNS.{54095} It acts on ionotropic and metabotropic receptors to induce excitatory synaptic transmission and has roles in synaptic plasticity. Excessive release of L-glutamic acid induces excitotoxicity that is associated with various human diseases, including amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), stroke, Parkinson’s disease, Alzheimer’s disease, and Huntington’s disease.{54096} Excessive L-glutamic acid release, in its protonated glutamate form, also occurs during seizure activity and contributes to epileptogenesis and seizure-induced brain damage.{54097}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30377 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
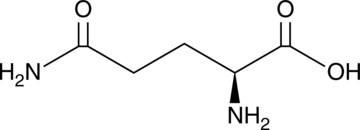
L-Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid involved in many biochemical processes. It is synthesized in vivo by glutamate and ammonia.{41351} It serves as a substrate for glutamine synthetase in neurons for the biosynthesis of the major excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters glutamate and GABA.{41350} L-Glutamine decreases adhesion of sickle red blood cells (RBCs) to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) when incubated ex vivo with patient-derived autologous plasma either alone or with LPS.{41352} It has commonly been used in cell culture media. Formulations containing L-glutamine have been used in the treatment of sickle cell disease.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23716 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-Glutamine is a non-essential amino acid involved in many biochemical processes. It is synthesized in vivo by glutamate and ammonia.{41351} It serves as a substrate for glutamine synthetase in neurons for the biosynthesis of the major excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmitters glutamate and GABA.{41350} L-Glutamine decreases adhesion of sickle red blood cells (RBCs) to human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) when incubated ex vivo with patient-derived autologous plasma either alone or with LPS.{41352} It has commonly been used in cell culture media. Formulations containing L-glutamine have been used in the treatment of sickle cell disease.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23716 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
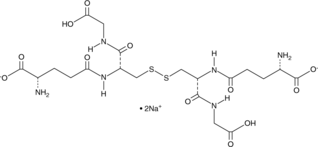
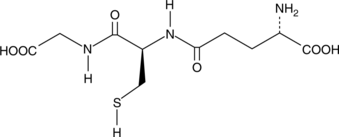
Glutathione can occur in reduced (GSH), oxidized (GSSG), or in mixed disulfide forms and is ubiquitous in multiple biological systems serving as the major thiol-disulfide redox buffer of the cell.{11632} GSSG is the oxidized form of GSH (Item No. 10007461). It can be reduced back to GSH through the NADPH-dependent enzyme glutathione reductase.{11632} GSSG functions as a hydrogen acceptor in the enzymatic determination of NADP+ and NADPH and can be a proximal donor in S-glutathionylation post translational modifications.{25273} The ratio of reduced glutathione to oxidized glutathione within cells is often used as an indicator of oxidative stress, with higher concentrations of GSSG predicting increased oxidative stress.{25274}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glutathione can occur in reduced (GSH), oxidized (GSSG), or in mixed disulfide forms and is ubiquitous in multiple biological systems serving as the major thiol-disulfide redox buffer of the cell.{11632} GSSG is the oxidized form of GSH (Item No. 10007461). It can be reduced back to GSH through the NADPH-dependent enzyme glutathione reductase.{11632} GSSG functions as a hydrogen acceptor in the enzymatic determination of NADP+ and NADPH and can be a proximal donor in S-glutathionylation post translational modifications.{25273} The ratio of reduced glutathione to oxidized glutathione within cells is often used as an indicator of oxidative stress, with higher concentrations of GSSG predicting increased oxidative stress.{25274}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glutathione can occur in reduced (GSH), oxidized (GSSG), or in mixed disulfide forms and is ubiquitous in multiple biological systems serving as the major thiol-disulfide redox buffer of the cell.{11632} GSSG is the oxidized form of GSH (Item No. 10007461). It can be reduced back to GSH through the NADPH-dependent enzyme glutathione reductase.{11632} GSSG functions as a hydrogen acceptor in the enzymatic determination of NADP+ and NADPH and can be a proximal donor in S-glutathionylation post translational modifications.{25273} The ratio of reduced glutathione to oxidized glutathione within cells is often used as an indicator of oxidative stress, with higher concentrations of GSSG predicting increased oxidative stress.{25274}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glutathione can occur in reduced (GSH), oxidized (GSSG), or in mixed disulfide forms and is ubiquitous in multiple biological systems serving as the major thiol-disulfide redox buffer of the cell.{11632} GSSG is the oxidized form of GSH (Item No. 10007461). It can be reduced back to GSH through the NADPH-dependent enzyme glutathione reductase.{11632} GSSG functions as a hydrogen acceptor in the enzymatic determination of NADP+ and NADPH and can be a proximal donor in S-glutathionylation post translational modifications.{25273} The ratio of reduced glutathione to oxidized glutathione within cells is often used as an indicator of oxidative stress, with higher concentrations of GSSG predicting increased oxidative stress.{25274}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide (γ-glutamylcysteinylglycine) widely distributed in both plants and animals.{1813,4672} GSH serves as a nucleophilic co-substrate to glutathione transferases in the detoxification of xenobiotics and is an essential electron donor to glutathione peroxidases in the reduction of hydroperoxides.{4672,165} GSH is also involved in amino acid transport and maintenance of protein sulfhydryl reduction status.{4669,4670} The concentration of GSH ranges from a few micromolar in plasma to several millimolar in tissues such as liver.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007461 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide (γ-glutamylcysteinylglycine) widely distributed in both plants and animals.{1813,4672} GSH serves as a nucleophilic co-substrate to glutathione transferases in the detoxification of xenobiotics and is an essential electron donor to glutathione peroxidases in the reduction of hydroperoxides.{4672,165} GSH is also involved in amino acid transport and maintenance of protein sulfhydryl reduction status.{4669,4670} The concentration of GSH ranges from a few micromolar in plasma to several millimolar in tissues such as liver.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007461 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide (γ-glutamylcysteinylglycine) widely distributed in both plants and animals.{1813,4672} GSH serves as a nucleophilic co-substrate to glutathione transferases in the detoxification of xenobiotics and is an essential electron donor to glutathione peroxidases in the reduction of hydroperoxides.{4672,165} GSH is also involved in amino acid transport and maintenance of protein sulfhydryl reduction status.{4669,4670} The concentration of GSH ranges from a few micromolar in plasma to several millimolar in tissues such as liver.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007461 - 25 gAvailable on backorder
Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide (γ-glutamylcysteinylglycine) widely distributed in both plants and animals.{1813,4672} GSH serves as a nucleophilic co-substrate to glutathione transferases in the detoxification of xenobiotics and is an essential electron donor to glutathione peroxidases in the reduction of hydroperoxides.{4672,165} GSH is also involved in amino acid transport and maintenance of protein sulfhydryl reduction status.{4669,4670} The concentration of GSH ranges from a few micromolar in plasma to several millimolar in tissues such as liver.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007461 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
L-Histidinol is a natural amino alcohol that serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the amino acid L-histidine in bacteria, archaebacteria, fungi, and plants.{30298,30300} It is generated from its immediate precursor, L-histidinol phosphate, by a phosphatase.{30299,30301} L-Histidinol is oxidized to L-histidinal, which in turn is oxidized to L-histidine, by a single enzyme, histidinol dehydrogenase.{30300}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Histidinol is a natural amino alcohol that serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the amino acid L-histidine in bacteria, archaebacteria, fungi, and plants.{30298,30300} It is generated from its immediate precursor, L-histidinol phosphate, by a phosphatase.{30299,30301} L-Histidinol is oxidized to L-histidinal, which in turn is oxidized to L-histidine, by a single enzyme, histidinol dehydrogenase.{30300}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
L-Histidinol is a natural amino alcohol that serves as an intermediate in the biosynthesis of the amino acid L-histidine in bacteria, archaebacteria, fungi, and plants.{30298,30300} It is generated from its immediate precursor, L-histidinol phosphate, by a phosphatase.{30299,30301} L-Histidinol is oxidized to L-histidinal, which in turn is oxidized to L-histidine, by a single enzyme, histidinol dehydrogenase.{30300}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
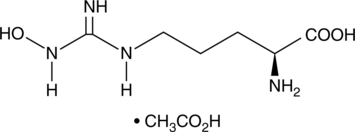
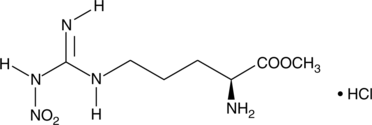
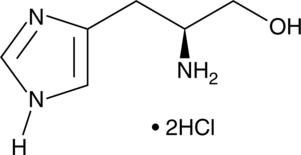
L-Homoarginine is an uncompetitive and organ-specific inhibitor of alkaline phosphatases.{36089} This non-essential amino acid inhibits human bone and liver alkaline phosphatases but has no effect on placental or intestinal isoenzymes. In vitro, L-homoarginine inhibits [3H]thymidine uptake by mouse myeloma MOPC 104E cells and inhibits proliferation of C3H/He mouse osteosarcoma cells.{36090} Pre-treatment with L-homoarginine delays in vivo tumor growth in a murine C3H/He osteosarcoma model. It also inhibits high-protein diet-induced pancreatic growth and enzyme secretion in bile-pancreatic juice-diverted rats, a model for the induction of pancreatic enzyme secretion with hypercholecystokininemia.{36091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22285 -Out of stock
L-Homoarginine is an uncompetitive and organ-specific inhibitor of alkaline phosphatases.{36089} This non-essential amino acid inhibits human bone and liver alkaline phosphatases but has no effect on placental or intestinal isoenzymes. In vitro, L-homoarginine inhibits [3H]thymidine uptake by mouse myeloma MOPC 104E cells and inhibits proliferation of C3H/He mouse osteosarcoma cells.{36090} Pre-treatment with L-homoarginine delays in vivo tumor growth in a murine C3H/He osteosarcoma model. It also inhibits high-protein diet-induced pancreatic growth and enzyme secretion in bile-pancreatic juice-diverted rats, a model for the induction of pancreatic enzyme secretion with hypercholecystokininemia.{36091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22285 -Out of stock
L-Homoarginine is an uncompetitive and organ-specific inhibitor of alkaline phosphatases.{36089} This non-essential amino acid inhibits human bone and liver alkaline phosphatases but has no effect on placental or intestinal isoenzymes. In vitro, L-homoarginine inhibits [3H]thymidine uptake by mouse myeloma MOPC 104E cells and inhibits proliferation of C3H/He mouse osteosarcoma cells.{36090} Pre-treatment with L-homoarginine delays in vivo tumor growth in a murine C3H/He osteosarcoma model. It also inhibits high-protein diet-induced pancreatic growth and enzyme secretion in bile-pancreatic juice-diverted rats, a model for the induction of pancreatic enzyme secretion with hypercholecystokininemia.{36091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22285 -Out of stock
L-Homoarginine is an uncompetitive and organ-specific inhibitor of alkaline phosphatases.{36089} This non-essential amino acid inhibits human bone and liver alkaline phosphatases but has no effect on placental or intestinal isoenzymes. In vitro, L-homoarginine inhibits [3H]thymidine uptake by mouse myeloma MOPC 104E cells and inhibits proliferation of C3H/He mouse osteosarcoma cells.{36090} Pre-treatment with L-homoarginine delays in vivo tumor growth in a murine C3H/He osteosarcoma model. It also inhibits high-protein diet-induced pancreatic growth and enzyme secretion in bile-pancreatic juice-diverted rats, a model for the induction of pancreatic enzyme secretion with hypercholecystokininemia.{36091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:22285 -Out of stock
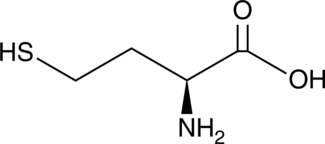
L-Homocysteine is a thiol-containing amino acid and an isomer of DL-homocysteine (Item No. 30285).{52732} It is formed via demethylation of methionine and acts as a precursor in the biosynthesis of methionine and cysteine.{52732,52733} Hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy), a disorder characterized by elevated homocysteine levels due to excessive synthesis or decreased degradation of L-homocysteine, is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke.{52732,52733,52734}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30852 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Homocysteine is a thiol-containing amino acid and an isomer of DL-homocysteine (Item No. 30285).{52732} It is formed via demethylation of methionine and acts as a precursor in the biosynthesis of methionine and cysteine.{52732,52733} Hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy), a disorder characterized by elevated homocysteine levels due to excessive synthesis or decreased degradation of L-homocysteine, is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke.{52732,52733,52734}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30852 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Homocysteine is a thiol-containing amino acid and an isomer of DL-homocysteine (Item No. 30285).{52732} It is formed via demethylation of methionine and acts as a precursor in the biosynthesis of methionine and cysteine.{52732,52733} Hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy), a disorder characterized by elevated homocysteine levels due to excessive synthesis or decreased degradation of L-homocysteine, is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke.{52732,52733,52734}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30852 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Homocysteine is a thiol-containing amino acid and an isomer of DL-homocysteine (Item No. 30285).{52732} It is formed via demethylation of methionine and acts as a precursor in the biosynthesis of methionine and cysteine.{52732,52733} Hyperhomocysteinemia (HHcy), a disorder characterized by elevated homocysteine levels due to excessive synthesis or decreased degradation of L-homocysteine, is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and stroke.{52732,52733,52734}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30852 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
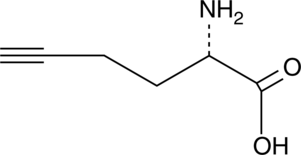
L-Homopropargyl glycine is a reactive methionine analog that contains an alkyne moiety. It is readily inserted into newly-synthesized proteins in place of methionine.{28085,28082,28083} L-Homopropargyl glycine can then be labeled or captured through click chemistry.{28082,28084} This approach represents a fast, sensitive, and non-radioactive alternative to [35S]-methionine for the detection of nascent protein synthesis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:11785 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Homopropargyl glycine is a reactive methionine analog that contains an alkyne moiety. It is readily inserted into newly-synthesized proteins in place of methionine.{28085,28082,28083} L-Homopropargyl glycine can then be labeled or captured through click chemistry.{28082,28084} This approach represents a fast, sensitive, and non-radioactive alternative to [35S]-methionine for the detection of nascent protein synthesis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:11785 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Homopropargyl glycine is a reactive methionine analog that contains an alkyne moiety. It is readily inserted into newly-synthesized proteins in place of methionine.{28085,28082,28083} L-Homopropargyl glycine can then be labeled or captured through click chemistry.{28082,28084} This approach represents a fast, sensitive, and non-radioactive alternative to [35S]-methionine for the detection of nascent protein synthesis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:11785 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Homopropargyl glycine is a reactive methionine analog that contains an alkyne moiety. It is readily inserted into newly-synthesized proteins in place of methionine.{28085,28082,28083} L-Homopropargyl glycine can then be labeled or captured through click chemistry.{28082,28084} This approach represents a fast, sensitive, and non-radioactive alternative to [35S]-methionine for the detection of nascent protein synthesis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:11785 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
L-hydroxy Arginine is a substrate for nitric oxide synthase in the catabolism of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) to form nitric oxide.{1243} It has been used as a biomarker for reduced nitric oxide formation in patients with cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome.{36792}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80300 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
L-hydroxy Arginine is a substrate for nitric oxide synthase in the catabolism of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) to form nitric oxide.{1243} It has been used as a biomarker for reduced nitric oxide formation in patients with cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome.{36792}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80300 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
L-hydroxy Arginine is a substrate for nitric oxide synthase in the catabolism of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) to form nitric oxide.{1243} It has been used as a biomarker for reduced nitric oxide formation in patients with cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome.{36792}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80300 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-hydroxy Arginine is a substrate for nitric oxide synthase in the catabolism of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) to form nitric oxide.{1243} It has been used as a biomarker for reduced nitric oxide formation in patients with cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome.{36792}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80300 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
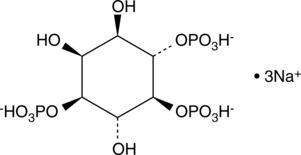
L-Iduronic acid is an epimer of glucuronic acid and a monosaccharide component of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), including heparin and chondroitin sulfate B, found on the outer cell membrane.{37572} L-Iduronic acid is conformationally flexible, which allows it to bind metal ions and may be important for the antithrombotic activity of heparin.{37573,37574} Iduronic acid-containing GAGs are selectively bound by basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), which prevents infection of Hep-2 cells with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in vitro.{37572}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21066 -Out of stock
L-Iduronic acid is an epimer of glucuronic acid and a monosaccharide component of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), including heparin and chondroitin sulfate B, found on the outer cell membrane.{37572} L-Iduronic acid is conformationally flexible, which allows it to bind metal ions and may be important for the antithrombotic activity of heparin.{37573,37574} Iduronic acid-containing GAGs are selectively bound by basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), which prevents infection of Hep-2 cells with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in vitro.{37572}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21066 -Out of stock
L-Iduronic acid is an epimer of glucuronic acid and a monosaccharide component of glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), including heparin and chondroitin sulfate B, found on the outer cell membrane.{37572} L-Iduronic acid is conformationally flexible, which allows it to bind metal ions and may be important for the antithrombotic activity of heparin.{37573,37574} Iduronic acid-containing GAGs are selectively bound by basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF), which prevents infection of Hep-2 cells with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) in vitro.{37572}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21066 -Out of stock
L-Leucine 4-methoxy-β-naphthylamide is a cell-permeable substrate for aminopeptidase M and leucine aminopeptidase that was developed for intracellular analysis of protease activities.{26798,26799}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Leucine 4-methoxy-β-naphthylamide is a cell-permeable substrate for aminopeptidase M and leucine aminopeptidase that was developed for intracellular analysis of protease activities.{26798,26799}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Leucine 4-methoxy-β-naphthylamide is a cell-permeable substrate for aminopeptidase M and leucine aminopeptidase that was developed for intracellular analysis of protease activities.{26798,26799}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Leucyl-L-Leucine methyl ester (LLME) is a lysosomal condensation product that has been reported to be cytotoxic towards natural killer cells and CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes without affecting helper T cells and B cells.{26052,26051} It has also been shown to induce death of monocytes, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and myeloid tumor cells.{26051} Upon entry into cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis, LLME undergoes a condensation process catalyzed by dipeptidyl peptidase I (DPPI) in lysosomes. This condensation leads to lysosomal rupture and DNA fragmentation in DPPI-expressing immune cells such as cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells.{26051}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Leucyl-L-Leucine methyl ester (LLME) is a lysosomal condensation product that has been reported to be cytotoxic towards natural killer cells and CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes without affecting helper T cells and B cells.{26052,26051} It has also been shown to induce death of monocytes, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and myeloid tumor cells.{26051} Upon entry into cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis, LLME undergoes a condensation process catalyzed by dipeptidyl peptidase I (DPPI) in lysosomes. This condensation leads to lysosomal rupture and DNA fragmentation in DPPI-expressing immune cells such as cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells.{26051}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Leucyl-L-Leucine methyl ester (LLME) is a lysosomal condensation product that has been reported to be cytotoxic towards natural killer cells and CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes without affecting helper T cells and B cells.{26052,26051} It has also been shown to induce death of monocytes, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, and myeloid tumor cells.{26051} Upon entry into cells via receptor-mediated endocytosis, LLME undergoes a condensation process catalyzed by dipeptidyl peptidase I (DPPI) in lysosomes. This condensation leads to lysosomal rupture and DNA fragmentation in DPPI-expressing immune cells such as cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells.{26051}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-lysine lactam is a building block.{52828,52829} It has been used in the synthesis of lysine sulfonamide HIV protease inhibitors, as well as bengamide derivatives with in vitro anticancer activity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31685 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-lysine lactam is a building block.{52828,52829} It has been used in the synthesis of lysine sulfonamide HIV protease inhibitors, as well as bengamide derivatives with in vitro anticancer activity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31685 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-lysine lactam is a building block.{52828,52829} It has been used in the synthesis of lysine sulfonamide HIV protease inhibitors, as well as bengamide derivatives with in vitro anticancer activity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31685 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
L-lysine lactam is a building block.{52828,52829} It has been used in the synthesis of lysine sulfonamide HIV protease inhibitors, as well as bengamide derivatives with in vitro anticancer activity.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31685 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Methionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an inhibitor of glutamine synthetase and a sulfoximine derivative of L-methionine.{46389} It inhibits pea glutamine synthetase by 31 to 64% when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 25 µM following preincubation with L-glutamine, an effect that is absent without L-glutamine preincubation. It also inhibits glutamine synthetase in isolated chick embryo retinas.{46390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27608 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-Methionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an inhibitor of glutamine synthetase and a sulfoximine derivative of L-methionine.{46389} It inhibits pea glutamine synthetase by 31 to 64% when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 25 µM following preincubation with L-glutamine, an effect that is absent without L-glutamine preincubation. It also inhibits glutamine synthetase in isolated chick embryo retinas.{46390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27608 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Methionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an inhibitor of glutamine synthetase and a sulfoximine derivative of L-methionine.{46389} It inhibits pea glutamine synthetase by 31 to 64% when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 25 µM following preincubation with L-glutamine, an effect that is absent without L-glutamine preincubation. It also inhibits glutamine synthetase in isolated chick embryo retinas.{46390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27608 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Methionine-(S,R)-sulfoximine is an inhibitor of glutamine synthetase and a sulfoximine derivative of L-methionine.{46389} It inhibits pea glutamine synthetase by 31 to 64% when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 25 µM following preincubation with L-glutamine, an effect that is absent without L-glutamine preincubation. It also inhibits glutamine synthetase in isolated chick embryo retinas.{46390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27608 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
L-Mimosine is a non-protein amino acid that can be isolated from certain plants and fungi. It chelates iron and copper and has been shown to reduce iron overload in animal models.{31870,31871} L-Mimosine inhibits certain enzymes that contain iron or copper, including arginase (IC50 = 3.7 µM), polyphenoloxidase, and dopamine hydroxylase.{31871,31867,31869} It also inhibits the iron-containing enzyme deoxyhypusine hydroxlase, preventing the synthesis of the eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and blocking cell cycling.{31868}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Mimosine is a non-protein amino acid that can be isolated from certain plants and fungi. It chelates iron and copper and has been shown to reduce iron overload in animal models.{31870,31871} L-Mimosine inhibits certain enzymes that contain iron or copper, including arginase (IC50 = 3.7 µM), polyphenoloxidase, and dopamine hydroxylase.{31871,31867,31869} It also inhibits the iron-containing enzyme deoxyhypusine hydroxlase, preventing the synthesis of the eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and blocking cell cycling.{31868}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Mimosine is a non-protein amino acid that can be isolated from certain plants and fungi. It chelates iron and copper and has been shown to reduce iron overload in animal models.{31870,31871} L-Mimosine inhibits certain enzymes that contain iron or copper, including arginase (IC50 = 3.7 µM), polyphenoloxidase, and dopamine hydroxylase.{31871,31867,31869} It also inhibits the iron-containing enzyme deoxyhypusine hydroxlase, preventing the synthesis of the eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and blocking cell cycling.{31868}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-L-Mimosine is a non-protein amino acid that can be isolated from certain plants and fungi. It chelates iron and copper and has been shown to reduce iron overload in animal models.{31870,31871} L-Mimosine inhibits certain enzymes that contain iron or copper, including arginase (IC50 = 3.7 µM), polyphenoloxidase, and dopamine hydroxylase.{31871,31867,31869} It also inhibits the iron-containing enzyme deoxyhypusine hydroxlase, preventing the synthesis of the eukaryotic initiation factor 5A and blocking cell cycling.{31868}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Ins(1,4,5)P3 is an isomer of the biologically important D-myo-inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate. Unlike its isomer, Ins(1,4,5)P3 does not evoke a rise in intracellular calcium when added to cells.{17407} It is not known if Ins(1,4,5)P3 can act as a competitive inhibitor of biologically-active inositol phosphates.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008426 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Ins(1,4,5)P3 is an isomer of the biologically important D-myo-inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate. Unlike its isomer, Ins(1,4,5)P3 does not evoke a rise in intracellular calcium when added to cells.{17407} It is not known if Ins(1,4,5)P3 can act as a competitive inhibitor of biologically-active inositol phosphates.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008426 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Ins(1,4,5)P3 is an isomer of the biologically important D-myo-inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate. Unlike its isomer, Ins(1,4,5)P3 does not evoke a rise in intracellular calcium when added to cells.{17407} It is not known if Ins(1,4,5)P3 can act as a competitive inhibitor of biologically-active inositol phosphates.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008426 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
L-NAME requires hydrolysis of the methyl ester by cellular esterases to become a fully functional inhibitor (L-NNA).{5433} L-NNA exhibits some selectivity for inhibition of neuronal and endothelial isoforms. It exhibits Ki values of 15 nM, 39 nM, and 4.4 µM for nNOS (bovine), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse), respectively.{5344,1857,5648} The reported Ki value for the inhibition of iNOS ranges from 4-65 µM.{1857,1901} L-NAME inhibits cGMP formation in endothelial cells with an IC50 of 3.1 µM (in the presence of 30 µM arginine) and reverses the vasodilation effects of acetylcholine in rat aorta rings with an EC50 of 0.54 µM.{1211,1855}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80210 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-NAME requires hydrolysis of the methyl ester by cellular esterases to become a fully functional inhibitor (L-NNA).{5433} L-NNA exhibits some selectivity for inhibition of neuronal and endothelial isoforms. It exhibits Ki values of 15 nM, 39 nM, and 4.4 µM for nNOS (bovine), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse), respectively.{5344,1857,5648} The reported Ki value for the inhibition of iNOS ranges from 4-65 µM.{1857,1901} L-NAME inhibits cGMP formation in endothelial cells with an IC50 of 3.1 µM (in the presence of 30 µM arginine) and reverses the vasodilation effects of acetylcholine in rat aorta rings with an EC50 of 0.54 µM.{1211,1855}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80210 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
L-NAME requires hydrolysis of the methyl ester by cellular esterases to become a fully functional inhibitor (L-NNA).{5433} L-NNA exhibits some selectivity for inhibition of neuronal and endothelial isoforms. It exhibits Ki values of 15 nM, 39 nM, and 4.4 µM for nNOS (bovine), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse), respectively.{5344,1857,5648} The reported Ki value for the inhibition of iNOS ranges from 4-65 µM.{1857,1901} L-NAME inhibits cGMP formation in endothelial cells with an IC50 of 3.1 µM (in the presence of 30 µM arginine) and reverses the vasodilation effects of acetylcholine in rat aorta rings with an EC50 of 0.54 µM.{1211,1855}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80210 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
L-NAME requires hydrolysis of the methyl ester by cellular esterases to become a fully functional inhibitor (L-NNA).{5433} L-NNA exhibits some selectivity for inhibition of neuronal and endothelial isoforms. It exhibits Ki values of 15 nM, 39 nM, and 4.4 µM for nNOS (bovine), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse), respectively.{5344,1857,5648} The reported Ki value for the inhibition of iNOS ranges from 4-65 µM.{1857,1901} L-NAME inhibits cGMP formation in endothelial cells with an IC50 of 3.1 µM (in the presence of 30 µM arginine) and reverses the vasodilation effects of acetylcholine in rat aorta rings with an EC50 of 0.54 µM.{1211,1855}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80210 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
L-NIL is a relatively selective inhibitor of iNOS. It exhibits IC50 values of 0.4-3.3 µM for iNOS as opposed to 8-38 and 17-92 µM for eNOS and nNOS, respectively.{1259,8620,26945} L-NIL effectively inhibits iNOS both in vitro and in vivo.{8487,3731,26945} L-NIL has been used to demonstrate a critical role for iNOS in the immune response to infection by the protozoan L. major.{26945,26947}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80310 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIL is a relatively selective inhibitor of iNOS. It exhibits IC50 values of 0.4-3.3 µM for iNOS as opposed to 8-38 and 17-92 µM for eNOS and nNOS, respectively.{1259,8620,26945} L-NIL effectively inhibits iNOS both in vitro and in vivo.{8487,3731,26945} L-NIL has been used to demonstrate a critical role for iNOS in the immune response to infection by the protozoan L. major.{26945,26947}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80310 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIL is a relatively selective inhibitor of iNOS. It exhibits IC50 values of 0.4-3.3 µM for iNOS as opposed to 8-38 and 17-92 µM for eNOS and nNOS, respectively.{1259,8620,26945} L-NIL effectively inhibits iNOS both in vitro and in vivo.{8487,3731,26945} L-NIL has been used to demonstrate a critical role for iNOS in the immune response to infection by the protozoan L. major.{26945,26947}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80310 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIL is a relatively selective inhibitor of iNOS. It exhibits IC50 values of 0.4-3.3 µM for iNOS as opposed to 8-38 and 17-92 µM for eNOS and nNOS, respectively.{1259,8620,26945} L-NIL effectively inhibits iNOS both in vitro and in vivo.{8487,3731,26945} L-NIL has been used to demonstrate a critical role for iNOS in the immune response to infection by the protozoan L. major.{26945,26947}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80310 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIO is a non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (bovine), and iNOS (mouse) are 1.7, 3.9, and 3.9 µM, respectively.{6358} L-NIO inhibits endothelial-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in rat aortic rings and hypotensive responses to acetylcholine and bradykinin.{1211}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80320 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIO is a non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (bovine), and iNOS (mouse) are 1.7, 3.9, and 3.9 µM, respectively.{6358} L-NIO inhibits endothelial-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in rat aortic rings and hypotensive responses to acetylcholine and bradykinin.{1211}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80320 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIO is a non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (bovine), and iNOS (mouse) are 1.7, 3.9, and 3.9 µM, respectively.{6358} L-NIO inhibits endothelial-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in rat aortic rings and hypotensive responses to acetylcholine and bradykinin.{1211}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80320 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NIO is a non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (bovine), and iNOS (mouse) are 1.7, 3.9, and 3.9 µM, respectively.{6358} L-NIO inhibits endothelial-dependent relaxation induced by acetylcholine in rat aortic rings and hypotensive responses to acetylcholine and bradykinin.{1211}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80320 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NMMA is the archetypal competitive NOS inhibitor to which other inhibitors are often compared.{5433} It is a relatively non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse) are approximately 0.18, 0.4, and 6 µM, respectively.{1415,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005031 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NMMA is the archetypal competitive NOS inhibitor to which other inhibitors are often compared.{5433} It is a relatively non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse) are approximately 0.18, 0.4, and 6 µM, respectively.{1415,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005031 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NMMA is the archetypal competitive NOS inhibitor to which other inhibitors are often compared.{5433} It is a relatively non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse) are approximately 0.18, 0.4, and 6 µM, respectively.{1415,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005031 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NMMA is the archetypal competitive NOS inhibitor to which other inhibitors are often compared.{5433} It is a relatively non-selective inhibitor of all NOS isoforms. The Ki values for nNOS (rat), eNOS (human), and iNOS (mouse) are approximately 0.18, 0.4, and 6 µM, respectively.{1415,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10005031 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
L-NNA is a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) with selectivity for the neuronal and endothelial isoforms of the enzyme. Although L-NAME is much more soluble than L-NNA in aqueous systems, a hydrolysis step is required to “activate” L-NAME, thus adding complexity to an in vivo experiment.{5433} L-NNA inhibits nNOS, eNOS, and iNOS with Ki values of 15 nM (bovine), 39 nM (human), and 4.4 µM (mouse), respectively.{1857,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80220 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
L-NNA is a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) with selectivity for the neuronal and endothelial isoforms of the enzyme. Although L-NAME is much more soluble than L-NNA in aqueous systems, a hydrolysis step is required to “activate” L-NAME, thus adding complexity to an in vivo experiment.{5433} L-NNA inhibits nNOS, eNOS, and iNOS with Ki values of 15 nM (bovine), 39 nM (human), and 4.4 µM (mouse), respectively.{1857,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80220 - 10 gAvailable on backorder
L-NNA is a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) with selectivity for the neuronal and endothelial isoforms of the enzyme. Although L-NAME is much more soluble than L-NNA in aqueous systems, a hydrolysis step is required to “activate” L-NAME, thus adding complexity to an in vivo experiment.{5433} L-NNA inhibits nNOS, eNOS, and iNOS with Ki values of 15 nM (bovine), 39 nM (human), and 4.4 µM (mouse), respectively.{1857,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80220 - 5 gAvailable on backorder
L-NNA is a competitive inhibitor of nitric oxide synthase (NOS) with selectivity for the neuronal and endothelial isoforms of the enzyme. Although L-NAME is much more soluble than L-NNA in aqueous systems, a hydrolysis step is required to “activate” L-NAME, thus adding complexity to an in vivo experiment.{5433} L-NNA inhibits nNOS, eNOS, and iNOS with Ki values of 15 nM (bovine), 39 nM (human), and 4.4 µM (mouse), respectively.{1857,5648}
Brand:CaymanSKU:80220 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
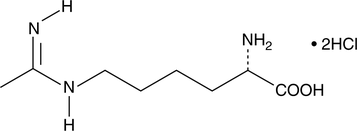
L-Ornithine is an active metabolite of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) and a non-proteinogenic amino acid.{53911} L-Ornithine is formed from arginine by arginase I during the final step of the urea cycle and acts as an alternate precursor to L-glutamate in the biosynthesis of proline. Exogenous administration of L-ornithine (111 mg/kg) delays the onset of ethanol-induced ataxia and decreases ethanol-induced sleeping time in rats.{53912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30779 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
L-Ornithine is an active metabolite of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) and a non-proteinogenic amino acid.{53911} L-Ornithine is formed from arginine by arginase I during the final step of the urea cycle and acts as an alternate precursor to L-glutamate in the biosynthesis of proline. Exogenous administration of L-ornithine (111 mg/kg) delays the onset of ethanol-induced ataxia and decreases ethanol-induced sleeping time in rats.{53912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30779 - 250 gAvailable on backorder
L-Ornithine is an active metabolite of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) and a non-proteinogenic amino acid.{53911} L-Ornithine is formed from arginine by arginase I during the final step of the urea cycle and acts as an alternate precursor to L-glutamate in the biosynthesis of proline. Exogenous administration of L-ornithine (111 mg/kg) delays the onset of ethanol-induced ataxia and decreases ethanol-induced sleeping time in rats.{53912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30779 - 50 gAvailable on backorder
L-Ornithine is an active metabolite of L-arginine (Item No. 23703) and a non-proteinogenic amino acid.{53911} L-Ornithine is formed from arginine by arginase I during the final step of the urea cycle and acts as an alternate precursor to L-glutamate in the biosynthesis of proline. Exogenous administration of L-ornithine (111 mg/kg) delays the onset of ethanol-induced ataxia and decreases ethanol-induced sleeping time in rats.{53912}
Brand:CaymanSKU:30779 - 500 gAvailable on backorder
![An uncompetitive inhibitor of alkaline phosphatases; inhibits human bone and liver alkaline phosphatases but has no effect on placental or intestinal isoenzymes; inhibits [3H]thymidine uptake by mouse myeloma MOPC 104E cells; inhibits proliferation of C3H/He mouse osteosarcoma cells in vitro; delays tumor growth in a murine C3H/He osteosarcoma model; inhibits high-protein diet-induced pancreatic growth and enzyme secretion in bile-pancreatic juice-diverted rats](https://interpriseusa.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/22285.png)