Chemicals
Showing 20101–20250 of 41137 results
-
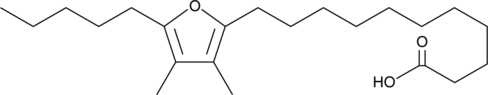
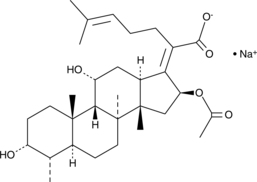
Furan fatty acid F6 is a furan fatty acid originally isolated from E. lucius (Northern pike).{38340,38341} Furan fatty acid F6 pre-treatment prevents cell death from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in rat brain C6 astroglioma cells in a dose-dependent manner.{38342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003082 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Furan fatty acid F6 is a furan fatty acid originally isolated from E. lucius (Northern pike).{38340,38341} Furan fatty acid F6 pre-treatment prevents cell death from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in rat brain C6 astroglioma cells in a dose-dependent manner.{38342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003082 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Furan fatty acid F6 is a furan fatty acid originally isolated from E. lucius (Northern pike).{38340,38341} Furan fatty acid F6 pre-treatment prevents cell death from hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in rat brain C6 astroglioma cells in a dose-dependent manner.{38342}
Brand:CaymanSKU:9003082 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Furegrelate is a potent inhibitor of thromboxane synthase with little effect on other enzymes essential for arachidonate metabolism. The IC50 value is 15 nM for human platelet microsomal thromboxane synthase.{1227,1228}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70540 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Furegrelate is a potent inhibitor of thromboxane synthase with little effect on other enzymes essential for arachidonate metabolism. The IC50 value is 15 nM for human platelet microsomal thromboxane synthase.{1227,1228}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70540 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Furegrelate is a potent inhibitor of thromboxane synthase with little effect on other enzymes essential for arachidonate metabolism. The IC50 value is 15 nM for human platelet microsomal thromboxane synthase.{1227,1228}
Brand:CaymanSKU:70540 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Furin is a proprotein convertase, converting precursor proteins to functional proteins within the Golgi/trans-Golgi secretory pathway. Furin inhibitor I is a selective, irreversible, and cell-permeable competitive inhibitor of proprotein convertases, including furin/SPC1 (Ki = ~1 nM), SPC2/PC2 (Ki = 0.36 nM), SPC3/PC1/PC3 (Ki = 2.0 nM), SPC4/PACE4 (Ki = 3.6 nM), SPC6/PC5/PC6, and SPC7/LPC/PC7/PC8 (Ki = 0.12 nM).{24090,24089} Because furin activates viral glycoproteins, this inhibitor is a useful antiviral agent.{24087} In addition, it inhibits furin-dependent pro-MMP-2 activation in mononuclear inflammatory cells.{24088}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Furin is a proprotein convertase, converting precursor proteins to functional proteins within the Golgi/trans-Golgi secretory pathway. Furin inhibitor I is a selective, irreversible, and cell-permeable competitive inhibitor of proprotein convertases, including furin/SPC1 (Ki = ~1 nM), SPC2/PC2 (Ki = 0.36 nM), SPC3/PC1/PC3 (Ki = 2.0 nM), SPC4/PACE4 (Ki = 3.6 nM), SPC6/PC5/PC6, and SPC7/LPC/PC7/PC8 (Ki = 0.12 nM).{24090,24089} Because furin activates viral glycoproteins, this inhibitor is a useful antiviral agent.{24087} In addition, it inhibits furin-dependent pro-MMP-2 activation in mononuclear inflammatory cells.{24088}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Furin is a proprotein convertase, converting precursor proteins to functional proteins within the Golgi/trans-Golgi secretory pathway. Furin inhibitor I is a selective, irreversible, and cell-permeable competitive inhibitor of proprotein convertases, including furin/SPC1 (Ki = ~1 nM), SPC2/PC2 (Ki = 0.36 nM), SPC3/PC1/PC3 (Ki = 2.0 nM), SPC4/PACE4 (Ki = 3.6 nM), SPC6/PC5/PC6, and SPC7/LPC/PC7/PC8 (Ki = 0.12 nM).{24090,24089} Because furin activates viral glycoproteins, this inhibitor is a useful antiviral agent.{24087} In addition, it inhibits furin-dependent pro-MMP-2 activation in mononuclear inflammatory cells.{24088}
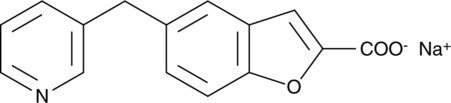
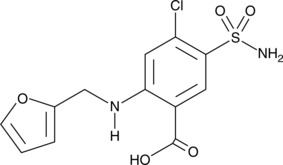
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Furosemide is a loop diuretic and an inhibitor of the Na+/K+/2Cl- (NKCC) cotransporters, NKCC1 and NKCC2 (Kis = ~10 µM for both).{23244,28297} In vivo, furosemide (0.1 mg/kg, p.o.) increases diuresis in beagle dogs.{52809} Furosemide (30 mg/kg) reduces ventricular collagen deposition and fibrosis in a rat model of dilated cardiomyopathy.{52810} It is also an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase I (CAI), CAII, and CAIII (Kis = 0.052-0.065 µM) and organic ion transporter 1 (OAT1; Ki = 9.5 µM), as well as a GABAA receptor antagonist.{23242,29296,29298} This product is also available as an analytical reference standard (Item No. 26298).
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Furosemide (Item No. 26298) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a diuretic.{33139} Formulations containing diuretics, including furosemide, have been misused in sports for weight reduction and as masking agents in humans and to prevent exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage in racehorses.{33139,46102} This product is intended for use in analytical forensic applications. This product is also available as a general research tool (Item No. 17273).
Brand:CaymanSKU:26298 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Furosemide is a loop diuretic and an inhibitor of the Na+/K+/2Cl- (NKCC) cotransporters, NKCC1 and NKCC2 (Kis = ~10 µM for both).{23244,28297} In vivo, furosemide (0.1 mg/kg, p.o.) increases diuresis in beagle dogs.{52809} Furosemide (30 mg/kg) reduces ventricular collagen deposition and fibrosis in a rat model of dilated cardiomyopathy.{52810} It is also an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase I (CAI), CAII, and CAIII (Kis = 0.052-0.065 µM) and organic ion transporter 1 (OAT1; Ki = 9.5 µM), as well as a GABAA receptor antagonist.{23242,29296,29298} This product is also available as an analytical reference standard (Item No. 26298).
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Furosemide (Item No. 26298) is an analytical reference standard categorized as a diuretic.{33139} Formulations containing diuretics, including furosemide, have been misused in sports for weight reduction and as masking agents in humans and to prevent exercise-induced pulmonary hemorrhage in racehorses.{33139,46102} This product is intended for use in analytical forensic applications. This product is also available as a general research tool (Item No. 17273).
Brand:CaymanSKU:26298 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
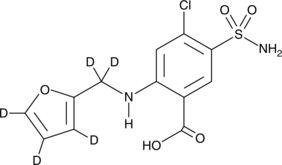
Furosemide-d5 is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of furosemide (Item No. 17273) by GC- or LC-MS. Furosemide is a loop diuretic and an inhibitor of the Na+/K+/2Cl- (NKCC) cotransporters, NKCC1 and NKCC2 (Kis = ~10 µM for both).{23244,28297} In vivo, furosemide (0.1 mg/kg, p.o.) increases diuresis in beagle dogs.{52809} Furosemide (30 mg/kg) reduces ventricular collagen deposition and fibrosis in a rat model of dilated cardiomyopathy.{52810} It is also an inhibitor of carbonic anhydrase I (CAI), CAII, and CAIII (Kis = 0.052-0.065 µM) and organic ion transporter 1 (OAT1; Ki = 9.5 µM), as well as a GABAA receptor antagonist.{23242,29296,29298}
Brand:CaymanSKU:31789 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
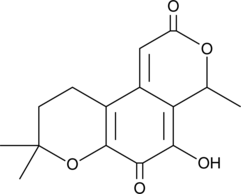
Fusapyrone is a broad-spectrum antifungal metabolite first isolated from Fusarium species. It has been investigated for use in the control of postharvest crop diseases such as inhibiting the growth of ochratoxin-producing strains of Aspergillus section Nigri in wine grapes.{32285}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20751 -Available on backorder
Fusapyrone is a broad-spectrum antifungal metabolite first isolated from Fusarium species. It has been investigated for use in the control of postharvest crop diseases such as inhibiting the growth of ochratoxin-producing strains of Aspergillus section Nigri in wine grapes.{32285}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20751 -Available on backorder
Fusarenon X is a type B trichothecene mycotoxin typically derived from Fusarium species. It is primarily found in contaminated cereals.{31924} Fusarenon X inhibits protein synthesis, which leads to disruption of DNA synthesis.{31924} As this occurs in actively proliferating cells, fusarenon X causes immunosuppression, intestinal malabsorption, developmental toxicity, and genotoxicity.{31924} Fusarenon X can be metabolized to fusarenon X-glucoside by infected plants.{29047}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11432 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Fusarenon X is a type B trichothecene mycotoxin typically derived from Fusarium species. It is primarily found in contaminated cereals.{31924} Fusarenon X inhibits protein synthesis, which leads to disruption of DNA synthesis.{31924} As this occurs in actively proliferating cells, fusarenon X causes immunosuppression, intestinal malabsorption, developmental toxicity, and genotoxicity.{31924} Fusarenon X can be metabolized to fusarenon X-glucoside by infected plants.{29047}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11432 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Fusarenon X is a type B trichothecene mycotoxin typically derived from Fusarium species. It is primarily found in contaminated cereals.{31924} Fusarenon X inhibits protein synthesis, which leads to disruption of DNA synthesis.{31924} As this occurs in actively proliferating cells, fusarenon X causes immunosuppression, intestinal malabsorption, developmental toxicity, and genotoxicity.{31924} Fusarenon X can be metabolized to fusarenon X-glucoside by infected plants.{29047}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11432 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
Fusarenon X is a type B trichothecene mycotoxin typically derived from Fusarium species. It is primarily found in contaminated cereals.{31924} Fusarenon X inhibits protein synthesis, which leads to disruption of DNA synthesis.{31924} As this occurs in actively proliferating cells, fusarenon X causes immunosuppression, intestinal malabsorption, developmental toxicity, and genotoxicity.{31924} Fusarenon X can be metabolized to fusarenon X-glucoside by infected plants.{29047}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11432 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
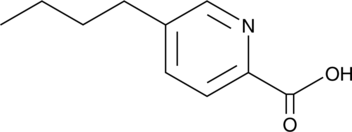
Fusaric acid is a picolinic acid derivative first isolated from fungi of the genus Fusarium.{29046} It is transformed to an N-methylamide derivative by many plant species infected by the mold.{29047} Both fusaric acid and fusaric acid methylamide are thought to contribute to the toxicoses developed from ingesting mold-infested feeds.{29047,29048} Fusaric acid can also synergize the toxicity of trichothecenes in certain assays.{29048}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Fusaric acid is a picolinic acid derivative first isolated from fungi of the genus Fusarium.{29046} It is transformed to an N-methylamide derivative by many plant species infected by the mold.{29047} Both fusaric acid and fusaric acid methylamide are thought to contribute to the toxicoses developed from ingesting mold-infested feeds.{29047,29048} Fusaric acid can also synergize the toxicity of trichothecenes in certain assays.{29048}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Fusaric acid is a picolinic acid derivative first isolated from fungi of the genus Fusarium.{29046} It is transformed to an N-methylamide derivative by many plant species infected by the mold.{29047} Both fusaric acid and fusaric acid methylamide are thought to contribute to the toxicoses developed from ingesting mold-infested feeds.{29047,29048} Fusaric acid can also synergize the toxicity of trichothecenes in certain assays.{29048}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Fusaric acid is a picolinic acid derivative first isolated from fungi of the genus Fusarium.{29046} It is transformed to an N-methylamide derivative by many plant species infected by the mold.{29047} Both fusaric acid and fusaric acid methylamide are thought to contribute to the toxicoses developed from ingesting mold-infested feeds.{29047,29048} Fusaric acid can also synergize the toxicity of trichothecenes in certain assays.{29048}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Fusarisetin A is a pentacyclic fungal metabolite first isolated from Fusarium species. At 3-30 µg/ml, it is reported to inhibit acinar morphogenesis, cell migration, and invasion in a 3D-matrigel assay system designed to study tumor cell motility.{32292}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20692 -Available on backorder
Fusarisetin A is a pentacyclic fungal metabolite first isolated from Fusarium species. At 3-30 µg/ml, it is reported to inhibit acinar morphogenesis, cell migration, and invasion in a 3D-matrigel assay system designed to study tumor cell motility.{32292}
Brand:CaymanSKU:20692 -Available on backorder
Fuscin is a quinonoid fungal metabolite originally isolated from O. fuscum that has diverse biological activities.{46199,46200,46201} It inhibits binding of the ADP/ATP translocase inhibitor atractyloside (Item No. 14804) to rat liver mitochondria in an ADP-dependent manner when used at a concentration of 50 μM in a radioligand binding assay.{46199} Fuscin (20 μM) reduces the glutathione content of rat liver mitochondria to 28% of controls and inhibits NADH oxidation in sonicated pigeon heart mitochondria preparations in a concentration-dependent manner.{46200} It competes with macrophage inflammatory protein 1α (MIP-1α) for binding to CCR5 chemokine receptors in vitro with an IC50 value of 21 μM.{46201}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27485 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Fuscin is a quinonoid fungal metabolite originally isolated from O. fuscum that has diverse biological activities.{46199,46200,46201} It inhibits binding of the ADP/ATP translocase inhibitor atractyloside (Item No. 14804) to rat liver mitochondria in an ADP-dependent manner when used at a concentration of 50 μM in a radioligand binding assay.{46199} Fuscin (20 μM) reduces the glutathione content of rat liver mitochondria to 28% of controls and inhibits NADH oxidation in sonicated pigeon heart mitochondria preparations in a concentration-dependent manner.{46200} It competes with macrophage inflammatory protein 1α (MIP-1α) for binding to CCR5 chemokine receptors in vitro with an IC50 value of 21 μM.{46201}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27485 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Fuscin is a quinonoid fungal metabolite originally isolated from O. fuscum that has diverse biological activities.{46199,46200,46201} It inhibits binding of the ADP/ATP translocase inhibitor atractyloside (Item No. 14804) to rat liver mitochondria in an ADP-dependent manner when used at a concentration of 50 μM in a radioligand binding assay.{46199} Fuscin (20 μM) reduces the glutathione content of rat liver mitochondria to 28% of controls and inhibits NADH oxidation in sonicated pigeon heart mitochondria preparations in a concentration-dependent manner.{46200} It competes with macrophage inflammatory protein 1α (MIP-1α) for binding to CCR5 chemokine receptors in vitro with an IC50 value of 21 μM.{46201}
Brand:CaymanSKU:27485 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
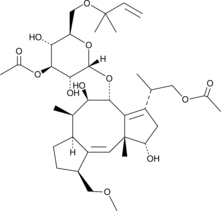
Fusicoccin is a phytotoxin originally isolated from F. amygdali that induces death of tomato plants when used at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 0.2 μg/ml.{43094} Topical administration of fusicoccin to tobacco (N. tabacum), sorghum (S. bicolor), cucumber (C. sativa), lucerne (M. sativa), and pokeweed (P. Americana) induces permanent opening of leaf stomata and wilting.{43095} Fusicoccin binds to the preformed complex between plasma membrane H+-ATPase and a 14-3-3 protein in plants to stabilize and activate the enzyme leading to dysregulated solute transport and control of transmembrane electric potential.{43096} It also stabilizes eukaryotic 14-3-3 protein interactions with binding partners containing a C-terminal 14-3-3 recognition motif, also known as a mode 3 motif, such as ERα, GPIbα, TASK3, CTFR, and p53 in vitro.{43097} Fusicoccin stimulates cortical neurite outgrowth in a 14-3-3 protein-dependent manner (EC50 = 29 μM).{43098} In vivo, topical administration of fusicoccin to the injury site reduces collapse and retraction of severed axons in a mouse model of spinal cord injury.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25020 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Fusidic acid is a fusidane antibiotic originally isolated from F. coccineum.{54000} It is active against the Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus, S. pyogenes, C. diphtheriae, B. subtilis, and C. tetani (MIC50s = 0.01-20 µg/ml) but not the Gram-negative bacteria E. coli, S. typhimurium, and P. vulgaris or the fungi C. albicans and A. fumigatus (MIC50s = >100 µg/ml for all).{54001} Fusidic acid inhibits ribosomal recycling and protein translocation, processes mediated by elongation factor G (EF-G), in isolated E. coli ribosomes (IC50s = ~0.1 and ~200 µM, respectively).{54002} Topical administration of fusidic acid (2%) reduces the number of skin colony forming units (CFUs) and levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in a mouse model of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) skin wound infection.{54003}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Fusidic acid is a fusidane antibiotic originally isolated from F. coccineum.{54000} It is active against the Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus, S. pyogenes, C. diphtheriae, B. subtilis, and C. tetani (MIC50s = 0.01-20 µg/ml) but not the Gram-negative bacteria E. coli, S. typhimurium, and P. vulgaris or the fungi C. albicans and A. fumigatus (MIC50s = >100 µg/ml for all).{54001} Fusidic acid inhibits ribosomal recycling and protein translocation, processes mediated by elongation factor G (EF-G), in isolated E. coli ribosomes (IC50s = ~0.1 and ~200 µM, respectively).{54002} Topical administration of fusidic acid (2%) reduces the number of skin colony forming units (CFUs) and levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in a mouse model of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) skin wound infection.{54003}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Fusidic acid is a fusidane antibiotic originally isolated from F. coccineum.{54000} It is active against the Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus, S. pyogenes, C. diphtheriae, B. subtilis, and C. tetani (MIC50s = 0.01-20 µg/ml) but not the Gram-negative bacteria E. coli, S. typhimurium, and P. vulgaris or the fungi C. albicans and A. fumigatus (MIC50s = >100 µg/ml for all).{54001} Fusidic acid inhibits ribosomal recycling and protein translocation, processes mediated by elongation factor G (EF-G), in isolated E. coli ribosomes (IC50s = ~0.1 and ~200 µM, respectively).{54002} Topical administration of fusidic acid (2%) reduces the number of skin colony forming units (CFUs) and levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in a mouse model of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) skin wound infection.{54003}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Fusidic acid is a fusidane antibiotic originally isolated from F. coccineum.{54000} It is active against the Gram-positive bacteria S. aureus, S. pyogenes, C. diphtheriae, B. subtilis, and C. tetani (MIC50s = 0.01-20 µg/ml) but not the Gram-negative bacteria E. coli, S. typhimurium, and P. vulgaris or the fungi C. albicans and A. fumigatus (MIC50s = >100 µg/ml for all).{54001} Fusidic acid inhibits ribosomal recycling and protein translocation, processes mediated by elongation factor G (EF-G), in isolated E. coli ribosomes (IC50s = ~0.1 and ~200 µM, respectively).{54002} Topical administration of fusidic acid (2%) reduces the number of skin colony forming units (CFUs) and levels of TNF-α and IL-6 in a mouse model of methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA) skin wound infection.{54003}
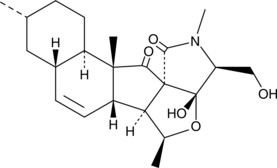
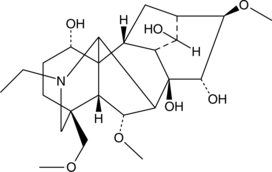
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Fuziline is a diterpene alkaloid that has been found in A. lateralis and has cardioprotective activity.{54422} It reduces sodium pentobarbital-induced cell death in primary neonatal rat cardiomyocytes when used at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 10 µM. Fuziline (0.5 µM) reduces the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptosis induced by isoproterenol (Item No. 15592) in H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes.{54421} In vivo, fuziline (3 and 10 mg/kg) reduces isoproterenol-induced myocardial necrosis and fibrosis in rats.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30889 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Fuziline is a diterpene alkaloid that has been found in A. lateralis and has cardioprotective activity.{54422} It reduces sodium pentobarbital-induced cell death in primary neonatal rat cardiomyocytes when used at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 10 µM. Fuziline (0.5 µM) reduces the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptosis induced by isoproterenol (Item No. 15592) in H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes.{54421} In vivo, fuziline (3 and 10 mg/kg) reduces isoproterenol-induced myocardial necrosis and fibrosis in rats.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30889 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Fuziline is a diterpene alkaloid that has been found in A. lateralis and has cardioprotective activity.{54422} It reduces sodium pentobarbital-induced cell death in primary neonatal rat cardiomyocytes when used at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 10 µM. Fuziline (0.5 µM) reduces the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptosis induced by isoproterenol (Item No. 15592) in H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes.{54421} In vivo, fuziline (3 and 10 mg/kg) reduces isoproterenol-induced myocardial necrosis and fibrosis in rats.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30889 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Fuziline is a diterpene alkaloid that has been found in A. lateralis and has cardioprotective activity.{54422} It reduces sodium pentobarbital-induced cell death in primary neonatal rat cardiomyocytes when used at concentrations ranging from 0.1 to 10 µM. Fuziline (0.5 µM) reduces the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and apoptosis induced by isoproterenol (Item No. 15592) in H9c2 rat cardiomyocytes.{54421} In vivo, fuziline (3 and 10 mg/kg) reduces isoproterenol-induced myocardial necrosis and fibrosis in rats.
Brand:CaymanSKU:30889 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
FX1 is an inhibitor of the transcription factor B cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6; IC50 = ~35 μM).{43297} It is selective for BCL6 over a panel of 50 kinases at a concentration of 10 μM. FX1 (50 μM) reduces recruitment of the BCL6 corepressor proteins SMRT and BCOR to the BCL6 target loci CDKN1A, CD69, and CXCR4 in a ChIP assay. It represses growth of Farage, SUDLH-6, DOHH-2, OCI-Ly7, RCK8, SUDHL-4, OCI-Ly1, and SC-1 BCL6-dependent cell lines (GI50s = 16-54 μM) but not OCI-LY1-B50, Karpas 433, OCI-Ly19, or Toledo BCL6-independent cell lines (GI50s = >125 μM). In vivo, FX1 (50 mg/kg) reduces tumor volume in an HBL-1 large B cell lymphoma mouse xenograft model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23908 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
FX1 is an inhibitor of the transcription factor B cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6; IC50 = ~35 μM).{43297} It is selective for BCL6 over a panel of 50 kinases at a concentration of 10 μM. FX1 (50 μM) reduces recruitment of the BCL6 corepressor proteins SMRT and BCOR to the BCL6 target loci CDKN1A, CD69, and CXCR4 in a ChIP assay. It represses growth of Farage, SUDLH-6, DOHH-2, OCI-Ly7, RCK8, SUDHL-4, OCI-Ly1, and SC-1 BCL6-dependent cell lines (GI50s = 16-54 μM) but not OCI-LY1-B50, Karpas 433, OCI-Ly19, or Toledo BCL6-independent cell lines (GI50s = >125 μM). In vivo, FX1 (50 mg/kg) reduces tumor volume in an HBL-1 large B cell lymphoma mouse xenograft model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23908 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
FX1 is an inhibitor of the transcription factor B cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6; IC50 = ~35 μM).{43297} It is selective for BCL6 over a panel of 50 kinases at a concentration of 10 μM. FX1 (50 μM) reduces recruitment of the BCL6 corepressor proteins SMRT and BCOR to the BCL6 target loci CDKN1A, CD69, and CXCR4 in a ChIP assay. It represses growth of Farage, SUDLH-6, DOHH-2, OCI-Ly7, RCK8, SUDHL-4, OCI-Ly1, and SC-1 BCL6-dependent cell lines (GI50s = 16-54 μM) but not OCI-LY1-B50, Karpas 433, OCI-Ly19, or Toledo BCL6-independent cell lines (GI50s = >125 μM). In vivo, FX1 (50 mg/kg) reduces tumor volume in an HBL-1 large B cell lymphoma mouse xenograft model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23908 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
FX1 is an inhibitor of the transcription factor B cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6; IC50 = ~35 μM).{43297} It is selective for BCL6 over a panel of 50 kinases at a concentration of 10 μM. FX1 (50 μM) reduces recruitment of the BCL6 corepressor proteins SMRT and BCOR to the BCL6 target loci CDKN1A, CD69, and CXCR4 in a ChIP assay. It represses growth of Farage, SUDLH-6, DOHH-2, OCI-Ly7, RCK8, SUDHL-4, OCI-Ly1, and SC-1 BCL6-dependent cell lines (GI50s = 16-54 μM) but not OCI-LY1-B50, Karpas 433, OCI-Ly19, or Toledo BCL6-independent cell lines (GI50s = >125 μM). In vivo, FX1 (50 mg/kg) reduces tumor volume in an HBL-1 large B cell lymphoma mouse xenograft model.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23908 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Wnt signaling proteins are small secreted proteins that are active in embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and tumorigenesis.{17947,14336,13185} Wnt proteins initiate cell signaling by binding Frizzled (Fz) receptors, a family of G protein-coupled receptors. FzM1 is an allosteric ligand of Fz4.{30790} At 10 µM, it inhibits nuclear translocation of β-catenin in U87MG glioma cells treated with lithium chloride, a GSK3 inhibitor that enhances the Wnt canonical signaling pathway.{30790} FzM1 impairs the ability of U87MG cells to form neurospheres in culture and stimulates the differentiation of Caco-2 epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma cells.{30790}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Wnt signaling proteins are small secreted proteins that are active in embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and tumorigenesis.{17947,14336,13185} Wnt proteins initiate cell signaling by binding Frizzled (Fz) receptors, a family of G protein-coupled receptors. FzM1 is an allosteric ligand of Fz4.{30790} At 10 µM, it inhibits nuclear translocation of β-catenin in U87MG glioma cells treated with lithium chloride, a GSK3 inhibitor that enhances the Wnt canonical signaling pathway.{30790} FzM1 impairs the ability of U87MG cells to form neurospheres in culture and stimulates the differentiation of Caco-2 epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma cells.{30790}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Wnt signaling proteins are small secreted proteins that are active in embryonic development, tissue homeostasis, and tumorigenesis.{17947,14336,13185} Wnt proteins initiate cell signaling by binding Frizzled (Fz) receptors, a family of G protein-coupled receptors. FzM1 is an allosteric ligand of Fz4.{30790} At 10 µM, it inhibits nuclear translocation of β-catenin in U87MG glioma cells treated with lithium chloride, a GSK3 inhibitor that enhances the Wnt canonical signaling pathway.{30790} FzM1 impairs the ability of U87MG cells to form neurospheres in culture and stimulates the differentiation of Caco-2 epithelial colorectal adenocarcinoma cells.{30790}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
GPR30 is a transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) localized to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that binds estradiol with high affinity, activating multiple intracellular signaling pathways.{13111} G-1 is a nonsteroidal, high-affinity, selective agonist of GPR30 that binds with a Ki value of 11 nM. Competitive binding studies in endoplasmic reticulum α- (ERα-) and ERβ-expressing cells yielded Ki values for estradiol of 0.30 and 0.38 nM, respectively, with no substantial binding of G-1 at 1 µM.{14210} The discovery of G-1, a compound that does not bind classical ERs, should facilitate further physiological experiments to define the role of GPR30 in vivo.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008933 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
GPR30 is a transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) localized to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that binds estradiol with high affinity, activating multiple intracellular signaling pathways.{13111} G-1 is a nonsteroidal, high-affinity, selective agonist of GPR30 that binds with a Ki value of 11 nM. Competitive binding studies in endoplasmic reticulum α- (ERα-) and ERβ-expressing cells yielded Ki values for estradiol of 0.30 and 0.38 nM, respectively, with no substantial binding of G-1 at 1 µM.{14210} The discovery of G-1, a compound that does not bind classical ERs, should facilitate further physiological experiments to define the role of GPR30 in vivo.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008933 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
GPR30 is a transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) localized to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that binds estradiol with high affinity, activating multiple intracellular signaling pathways.{13111} G-1 is a nonsteroidal, high-affinity, selective agonist of GPR30 that binds with a Ki value of 11 nM. Competitive binding studies in endoplasmic reticulum α- (ERα-) and ERβ-expressing cells yielded Ki values for estradiol of 0.30 and 0.38 nM, respectively, with no substantial binding of G-1 at 1 µM.{14210} The discovery of G-1, a compound that does not bind classical ERs, should facilitate further physiological experiments to define the role of GPR30 in vivo.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008933 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
GPR30 is a transmembrane G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) localized to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) that binds estradiol with high affinity, activating multiple intracellular signaling pathways.{13111} G-1 is a nonsteroidal, high-affinity, selective agonist of GPR30 that binds with a Ki value of 11 nM. Competitive binding studies in endoplasmic reticulum α- (ERα-) and ERβ-expressing cells yielded Ki values for estradiol of 0.30 and 0.38 nM, respectively, with no substantial binding of G-1 at 1 µM.{14210} The discovery of G-1, a compound that does not bind classical ERs, should facilitate further physiological experiments to define the role of GPR30 in vivo.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008933 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), or GPR30, specifically binds natural and man-made estrogens.{23445} It is thought to be involved in estrogen-sensitive cancers.{23445,23446} GPER knockout mice are fertile, although they exhibit thymic atrophy, impaired glucose tolerance, and altered bone growth.{23445} G-15 is a cell-permeable non-steroidal antagonist of GPER (Ki = 20 nM).{23444} It displays low affinity cross-reactivity with the classical estrogen receptor (ER), ERα, so that at doses greater than 1 µM it is capable of mediating limited ER-dependent transcriptional activity.{23443} G-15 antagonizes the anti-depressive effects of estrogen in vivo.{23444}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), or GPR30, specifically binds natural and man-made estrogens.{23445} It is thought to be involved in estrogen-sensitive cancers.{23445,23446} GPER knockout mice are fertile, although they exhibit thymic atrophy, impaired glucose tolerance, and altered bone growth.{23445} G-15 is a cell-permeable non-steroidal antagonist of GPER (Ki = 20 nM).{23444} It displays low affinity cross-reactivity with the classical estrogen receptor (ER), ERα, so that at doses greater than 1 µM it is capable of mediating limited ER-dependent transcriptional activity.{23443} G-15 antagonizes the anti-depressive effects of estrogen in vivo.{23444}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), or GPR30, specifically binds natural and man-made estrogens.{23445} It is thought to be involved in estrogen-sensitive cancers.{23445,23446} GPER knockout mice are fertile, although they exhibit thymic atrophy, impaired glucose tolerance, and altered bone growth.{23445} G-15 is a cell-permeable non-steroidal antagonist of GPER (Ki = 20 nM).{23444} It displays low affinity cross-reactivity with the classical estrogen receptor (ER), ERα, so that at doses greater than 1 µM it is capable of mediating limited ER-dependent transcriptional activity.{23443} G-15 antagonizes the anti-depressive effects of estrogen in vivo.{23444}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), or GPR30, specifically binds natural and man-made estrogens.{23445} It is thought to be involved in estrogen-sensitive cancers.{23445,23446} GPER knockout mice are fertile, although they exhibit thymic atrophy, impaired glucose tolerance, and altered bone growth.{23445} G-15 is a cell-permeable non-steroidal antagonist of GPER (Ki = 20 nM).{23444} It displays low affinity cross-reactivity with the classical estrogen receptor (ER), ERα, so that at doses greater than 1 µM it is capable of mediating limited ER-dependent transcriptional activity.{23443} G-15 antagonizes the anti-depressive effects of estrogen in vivo.{23444}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), or GPR30, specifically binds natural and man-made estrogens.{23445} It is thought to be involved in estrogen-sensitive cancers.{23445,23446} GPER knockout mice are fertile, although they exhibit thymic atrophy, impaired glucose tolerance, and altered bone growth.{23445} G-36 is a cell-permeable non-steroidal antagonist of GPER, inhibiting activation by either 17β-estradiol (Item No. 10006315) or the GPER-selective agonist G-1 (Item No. 10008933) (IC50 = 112 and 165 nM, respectively).{23443} It has no detectable binding activity to either ERα or ERβ.{23443} G-36 blocks the activation of PI3K or calcium mobilization triggered by estrogen through GPER and it suppresses ERK activation by estrogen or G-1 but not by EGF.{23443} G-36 can be used in combination with GPER-selective agonists, like G-1, to distinguish the roles of GPER from those of ERα and ERβ in complex biological systems.{23443,24423}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), or GPR30, specifically binds natural and man-made estrogens.{23445} It is thought to be involved in estrogen-sensitive cancers.{23445,23446} GPER knockout mice are fertile, although they exhibit thymic atrophy, impaired glucose tolerance, and altered bone growth.{23445} G-36 is a cell-permeable non-steroidal antagonist of GPER, inhibiting activation by either 17β-estradiol (Item No. 10006315) or the GPER-selective agonist G-1 (Item No. 10008933) (IC50 = 112 and 165 nM, respectively).{23443} It has no detectable binding activity to either ERα or ERβ.{23443} G-36 blocks the activation of PI3K or calcium mobilization triggered by estrogen through GPER and it suppresses ERK activation by estrogen or G-1 but not by EGF.{23443} G-36 can be used in combination with GPER-selective agonists, like G-1, to distinguish the roles of GPER from those of ERα and ERβ in complex biological systems.{23443,24423}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), or GPR30, specifically binds natural and man-made estrogens.{23445} It is thought to be involved in estrogen-sensitive cancers.{23445,23446} GPER knockout mice are fertile, although they exhibit thymic atrophy, impaired glucose tolerance, and altered bone growth.{23445} G-36 is a cell-permeable non-steroidal antagonist of GPER, inhibiting activation by either 17β-estradiol (Item No. 10006315) or the GPER-selective agonist G-1 (Item No. 10008933) (IC50 = 112 and 165 nM, respectively).{23443} It has no detectable binding activity to either ERα or ERβ.{23443} G-36 blocks the activation of PI3K or calcium mobilization triggered by estrogen through GPER and it suppresses ERK activation by estrogen or G-1 but not by EGF.{23443} G-36 can be used in combination with GPER-selective agonists, like G-1, to distinguish the roles of GPER from those of ERα and ERβ in complex biological systems.{23443,24423}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-G protein-coupled estrogen receptor (GPER), or GPR30, specifically binds natural and man-made estrogens.{23445} It is thought to be involved in estrogen-sensitive cancers.{23445,23446} GPER knockout mice are fertile, although they exhibit thymic atrophy, impaired glucose tolerance, and altered bone growth.{23445} G-36 is a cell-permeable non-steroidal antagonist of GPER, inhibiting activation by either 17β-estradiol (Item No. 10006315) or the GPER-selective agonist G-1 (Item No. 10008933) (IC50 = 112 and 165 nM, respectively).{23443} It has no detectable binding activity to either ERα or ERβ.{23443} G-36 blocks the activation of PI3K or calcium mobilization triggered by estrogen through GPER and it suppresses ERK activation by estrogen or G-1 but not by EGF.{23443} G-36 can be used in combination with GPER-selective agonists, like G-1, to distinguish the roles of GPER from those of ERα and ERβ in complex biological systems.{23443,24423}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-G-418 Sulfate is an aminoglycosidic antibiotic that is related to gentamicin. It is toxic to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as it blocks protein elongation during translation. G-418 is commonly used for the selection of cells that are genetically engineered with a plasmid containing the neo (neor) gene, which provides resistance to G-418. In mammalian cells, selection is commonly performed using 400 mg/L G-418, followed by 200 mg/L for culture maintenance; optimal concentrations may depend on cell type or plasmid and should be empirically determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-G-418 Sulfate is an aminoglycosidic antibiotic that is related to gentamicin. It is toxic to both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, as it blocks protein elongation during translation. G-418 is commonly used for the selection of cells that are genetically engineered with a plasmid containing the neo (neor) gene, which provides resistance to G-418. In mammalian cells, selection is commonly performed using 400 mg/L G-418, followed by 200 mg/L for culture maintenance; optimal concentrations may depend on cell type or plasmid and should be empirically determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-G-5555 is an inhibitor of p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1; Ki = 3.7 nM), a non-receptor serine/threonine kinase involved in tumorigenesis.{37400} It is selective for PAK1 over the majority of targets in a panel of 235 kinases but does inhibit PAK2, PAK3, KHS1, LCK, MST3, MST4, SIK2, and YSK1 by greater than 70% with IC50 values ranging from 9 to 52 nM. G-5555 inhibits phosphorylation of MEK, a downstream target of PAK1, in EBC1 cells (IC50 = 69 nM). G-5555 (10, 20, and 30 mg/kg) dose-dependently reduces phosphorylation of MEK in tumors from an H292 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) mouse xenograft model. G-5555 inhibits hERG channels less than 50% at a concentration of 10 μM, indicating the potential for a low risk of QT interval prolongation and potentially fatal arrhythmias.{37401}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21469 -Out of stock
G-5555 is an inhibitor of p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1; Ki = 3.7 nM), a non-receptor serine/threonine kinase involved in tumorigenesis.{37400} It is selective for PAK1 over the majority of targets in a panel of 235 kinases but does inhibit PAK2, PAK3, KHS1, LCK, MST3, MST4, SIK2, and YSK1 by greater than 70% with IC50 values ranging from 9 to 52 nM. G-5555 inhibits phosphorylation of MEK, a downstream target of PAK1, in EBC1 cells (IC50 = 69 nM). G-5555 (10, 20, and 30 mg/kg) dose-dependently reduces phosphorylation of MEK in tumors from an H292 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) mouse xenograft model. G-5555 inhibits hERG channels less than 50% at a concentration of 10 μM, indicating the potential for a low risk of QT interval prolongation and potentially fatal arrhythmias.{37401}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21469 -Out of stock
G-5555 is an inhibitor of p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1; Ki = 3.7 nM), a non-receptor serine/threonine kinase involved in tumorigenesis.{37400} It is selective for PAK1 over the majority of targets in a panel of 235 kinases but does inhibit PAK2, PAK3, KHS1, LCK, MST3, MST4, SIK2, and YSK1 by greater than 70% with IC50 values ranging from 9 to 52 nM. G-5555 inhibits phosphorylation of MEK, a downstream target of PAK1, in EBC1 cells (IC50 = 69 nM). G-5555 (10, 20, and 30 mg/kg) dose-dependently reduces phosphorylation of MEK in tumors from an H292 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) mouse xenograft model. G-5555 inhibits hERG channels less than 50% at a concentration of 10 μM, indicating the potential for a low risk of QT interval prolongation and potentially fatal arrhythmias.{37401}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21469 -Out of stock
G-5555 is an inhibitor of p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1; Ki = 3.7 nM), a non-receptor serine/threonine kinase involved in tumorigenesis.{37400} It is selective for PAK1 over the majority of targets in a panel of 235 kinases but does inhibit PAK2, PAK3, KHS1, LCK, MST3, MST4, SIK2, and YSK1 by greater than 70% with IC50 values ranging from 9 to 52 nM. G-5555 inhibits phosphorylation of MEK, a downstream target of PAK1, in EBC1 cells (IC50 = 69 nM). G-5555 (10, 20, and 30 mg/kg) dose-dependently reduces phosphorylation of MEK in tumors from an H292 non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) mouse xenograft model. G-5555 inhibits hERG channels less than 50% at a concentration of 10 μM, indicating the potential for a low risk of QT interval prolongation and potentially fatal arrhythmias.{37401}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21469 -Out of stock
G-749 is an inhibitor of Fms-like tyrosine receptor kinase 3 (FLT3) with IC50 values ranging from 2.1 to 38.1 nM for wild-type and mutant (constitutively active) FLT3s in Ba/F3 cells expressing recombinant receptors.{38271} It also inhibits growth of human leukemia cell lines that express FLT3-ITD mutant kinase (IC50s = 3.5 and 7.5 nM for MV4-11 and Molm-14 cells, respectively) but has no effect on cells that lack FLT3 expression or that express wild-type FLT3. G-749 reduces tumor growth and increases survival in a dose-dependent manner in MV4-11 and Molm-14 murine leukemia xenograft models. It reduces growth of bone marrow blasts derived from acute myeloid leukemia patients, showing more potent inhibition of blasts expressing the FLT3-ITD mutant receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22139 -Out of stock
G-749 is an inhibitor of Fms-like tyrosine receptor kinase 3 (FLT3) with IC50 values ranging from 2.1 to 38.1 nM for wild-type and mutant (constitutively active) FLT3s in Ba/F3 cells expressing recombinant receptors.{38271} It also inhibits growth of human leukemia cell lines that express FLT3-ITD mutant kinase (IC50s = 3.5 and 7.5 nM for MV4-11 and Molm-14 cells, respectively) but has no effect on cells that lack FLT3 expression or that express wild-type FLT3. G-749 reduces tumor growth and increases survival in a dose-dependent manner in MV4-11 and Molm-14 murine leukemia xenograft models. It reduces growth of bone marrow blasts derived from acute myeloid leukemia patients, showing more potent inhibition of blasts expressing the FLT3-ITD mutant receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22139 -Out of stock
G-749 is an inhibitor of Fms-like tyrosine receptor kinase 3 (FLT3) with IC50 values ranging from 2.1 to 38.1 nM for wild-type and mutant (constitutively active) FLT3s in Ba/F3 cells expressing recombinant receptors.{38271} It also inhibits growth of human leukemia cell lines that express FLT3-ITD mutant kinase (IC50s = 3.5 and 7.5 nM for MV4-11 and Molm-14 cells, respectively) but has no effect on cells that lack FLT3 expression or that express wild-type FLT3. G-749 reduces tumor growth and increases survival in a dose-dependent manner in MV4-11 and Molm-14 murine leukemia xenograft models. It reduces growth of bone marrow blasts derived from acute myeloid leukemia patients, showing more potent inhibition of blasts expressing the FLT3-ITD mutant receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22139 -Out of stock
G-749 is an inhibitor of Fms-like tyrosine receptor kinase 3 (FLT3) with IC50 values ranging from 2.1 to 38.1 nM for wild-type and mutant (constitutively active) FLT3s in Ba/F3 cells expressing recombinant receptors.{38271} It also inhibits growth of human leukemia cell lines that express FLT3-ITD mutant kinase (IC50s = 3.5 and 7.5 nM for MV4-11 and Molm-14 cells, respectively) but has no effect on cells that lack FLT3 expression or that express wild-type FLT3. G-749 reduces tumor growth and increases survival in a dose-dependent manner in MV4-11 and Molm-14 murine leukemia xenograft models. It reduces growth of bone marrow blasts derived from acute myeloid leukemia patients, showing more potent inhibition of blasts expressing the FLT3-ITD mutant receptor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22139 -Out of stock
G007-LK is an inhibitor of the tankyrases TNKS1 and TNKS2 (IC50s = 46 and 25 nM, respectively).{40726} It is selective for TNKS1 and TNKS2 over a panel of 90 kinases, 16 phosphatases, and 73 G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) when used at a concentration of 10 µM. G007-LK inhibits colony formation of COLO 320 DM and SW403 colorectal cancer cell lines when used at a concentration of 200 µM, as well as human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells in a dose-dependent manner.{40727,40728} It increases expression of intestinal differentiation markers in COLO 320 DM and HCT15 cells when used at a concentration of 100 nM. G007-LK inhibits Wnt3A-induced signaling in human HEK293 and mouse 10T1/2 cells.{40727} G007-LK (20 mg/kg, i.p., twice daily) also inhibits tumor growth in COLO 320 DM and SW403 mouse xenograft models, however, it leads to intestinal toxicity when administered at a dose of 30 mg/kg twice daily, leading to moribundity and death.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22934 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
G007-LK is an inhibitor of the tankyrases TNKS1 and TNKS2 (IC50s = 46 and 25 nM, respectively).{40726} It is selective for TNKS1 and TNKS2 over a panel of 90 kinases, 16 phosphatases, and 73 G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) when used at a concentration of 10 µM. G007-LK inhibits colony formation of COLO 320 DM and SW403 colorectal cancer cell lines when used at a concentration of 200 µM, as well as human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells in a dose-dependent manner.{40727,40728} It increases expression of intestinal differentiation markers in COLO 320 DM and HCT15 cells when used at a concentration of 100 nM. G007-LK inhibits Wnt3A-induced signaling in human HEK293 and mouse 10T1/2 cells.{40727} G007-LK (20 mg/kg, i.p., twice daily) also inhibits tumor growth in COLO 320 DM and SW403 mouse xenograft models, however, it leads to intestinal toxicity when administered at a dose of 30 mg/kg twice daily, leading to moribundity and death.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22934 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
G007-LK is an inhibitor of the tankyrases TNKS1 and TNKS2 (IC50s = 46 and 25 nM, respectively).{40726} It is selective for TNKS1 and TNKS2 over a panel of 90 kinases, 16 phosphatases, and 73 G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) when used at a concentration of 10 µM. G007-LK inhibits colony formation of COLO 320 DM and SW403 colorectal cancer cell lines when used at a concentration of 200 µM, as well as human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells in a dose-dependent manner.{40727,40728} It increases expression of intestinal differentiation markers in COLO 320 DM and HCT15 cells when used at a concentration of 100 nM. G007-LK inhibits Wnt3A-induced signaling in human HEK293 and mouse 10T1/2 cells.{40727} G007-LK (20 mg/kg, i.p., twice daily) also inhibits tumor growth in COLO 320 DM and SW403 mouse xenograft models, however, it leads to intestinal toxicity when administered at a dose of 30 mg/kg twice daily, leading to moribundity and death.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22934 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
G007-LK is an inhibitor of the tankyrases TNKS1 and TNKS2 (IC50s = 46 and 25 nM, respectively).{40726} It is selective for TNKS1 and TNKS2 over a panel of 90 kinases, 16 phosphatases, and 73 G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) when used at a concentration of 10 µM. G007-LK inhibits colony formation of COLO 320 DM and SW403 colorectal cancer cell lines when used at a concentration of 200 µM, as well as human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells in a dose-dependent manner.{40727,40728} It increases expression of intestinal differentiation markers in COLO 320 DM and HCT15 cells when used at a concentration of 100 nM. G007-LK inhibits Wnt3A-induced signaling in human HEK293 and mouse 10T1/2 cells.{40727} G007-LK (20 mg/kg, i.p., twice daily) also inhibits tumor growth in COLO 320 DM and SW403 mouse xenograft models, however, it leads to intestinal toxicity when administered at a dose of 30 mg/kg twice daily, leading to moribundity and death.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22934 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
G10 is an indirect activator of stimulator of interferon genes (STING) signaling.{37248} It induces transcription of genes dependent on IRF3 and IFN, which are activated by STING, but has no effect on non-STING activated NF-κB-dependent transcription of IL-8, IL-1β, or MIP-1α in human fibroblasts. However, G10 does increase expression of NF-κB-dependent genes in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and human umbilical microvascular endothelial cells (HUMECs). In vitro, it prevents replication of the chikungunya and Venezuelan equine encephalitis alphaviruses (IC90s = 8.01 and 24.57 µM, respectively). G10 (100 µM) increases phosphorylation of IRF3, which is lost in cells lacking STING.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22353 -Out of stock
G10 is an indirect activator of stimulator of interferon genes (STING) signaling.{37248} It induces transcription of genes dependent on IRF3 and IFN, which are activated by STING, but has no effect on non-STING activated NF-κB-dependent transcription of IL-8, IL-1β, or MIP-1α in human fibroblasts. However, G10 does increase expression of NF-κB-dependent genes in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and human umbilical microvascular endothelial cells (HUMECs). In vitro, it prevents replication of the chikungunya and Venezuelan equine encephalitis alphaviruses (IC90s = 8.01 and 24.57 µM, respectively). G10 (100 µM) increases phosphorylation of IRF3, which is lost in cells lacking STING.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22353 -Out of stock
G10 is an indirect activator of stimulator of interferon genes (STING) signaling.{37248} It induces transcription of genes dependent on IRF3 and IFN, which are activated by STING, but has no effect on non-STING activated NF-κB-dependent transcription of IL-8, IL-1β, or MIP-1α in human fibroblasts. However, G10 does increase expression of NF-κB-dependent genes in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and human umbilical microvascular endothelial cells (HUMECs). In vitro, it prevents replication of the chikungunya and Venezuelan equine encephalitis alphaviruses (IC90s = 8.01 and 24.57 µM, respectively). G10 (100 µM) increases phosphorylation of IRF3, which is lost in cells lacking STING.
Brand:CaymanSKU:22353 -Out of stock
G244-LM is an inhibitor of Wnt signaling.{40727} It inhibits Wnt3a-induced signaling in HEK293 human and 10T1/2 mouse cells in a reporter assay. It also inhibits Wnt signaling and colony formation in COLO-320DM and SW403, but not HCT-15 or DLD-1, colorectal cancer cells when used at a concentration of 0.2 µM for seven to 13 days. G244-LM inhibits growth of mouse intestinal organoids (IC50 = 0.11 µM) and organoid spheroids cultured from small intestine adenomas isolated from ApcMin mice, which exhibit constitutively activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21876 -Out of stock
G244-LM is an inhibitor of Wnt signaling.{40727} It inhibits Wnt3a-induced signaling in HEK293 human and 10T1/2 mouse cells in a reporter assay. It also inhibits Wnt signaling and colony formation in COLO-320DM and SW403, but not HCT-15 or DLD-1, colorectal cancer cells when used at a concentration of 0.2 µM for seven to 13 days. G244-LM inhibits growth of mouse intestinal organoids (IC50 = 0.11 µM) and organoid spheroids cultured from small intestine adenomas isolated from ApcMin mice, which exhibit constitutively activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21876 -Out of stock
G244-LM is an inhibitor of Wnt signaling.{40727} It inhibits Wnt3a-induced signaling in HEK293 human and 10T1/2 mouse cells in a reporter assay. It also inhibits Wnt signaling and colony formation in COLO-320DM and SW403, but not HCT-15 or DLD-1, colorectal cancer cells when used at a concentration of 0.2 µM for seven to 13 days. G244-LM inhibits growth of mouse intestinal organoids (IC50 = 0.11 µM) and organoid spheroids cultured from small intestine adenomas isolated from ApcMin mice, which exhibit constitutively activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21876 -Out of stock
G244-LM is an inhibitor of Wnt signaling.{40727} It inhibits Wnt3a-induced signaling in HEK293 human and 10T1/2 mouse cells in a reporter assay. It also inhibits Wnt signaling and colony formation in COLO-320DM and SW403, but not HCT-15 or DLD-1, colorectal cancer cells when used at a concentration of 0.2 µM for seven to 13 days. G244-LM inhibits growth of mouse intestinal organoids (IC50 = 0.11 µM) and organoid spheroids cultured from small intestine adenomas isolated from ApcMin mice, which exhibit constitutively activated Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
Brand:CaymanSKU:21876 -Out of stock
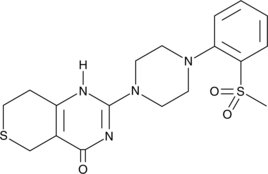
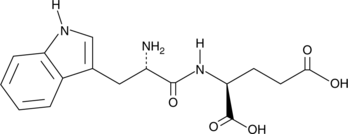
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) is a nuclear receptor with key roles in adipocyte differentiation and glucose homeostasis.{18294,14553} G3335 is a cell-permeable dipeptide that potently antagonizes PPARγ (Kd = 8.34 µM).{28551} It reversibly and competitively blocks activation of PPARγ by rosiglitazone (IC50 = 8-32 µM).{28551} G3335 is active in vivo, abolishing the protective effects of rosiglitazone in experimental spinal cord injury in rats.{28550} G3335 has also been used to evaluate the role of PPARγ in neurotoxicity studies.{28549,28552}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) is a nuclear receptor with key roles in adipocyte differentiation and glucose homeostasis.{18294,14553} G3335 is a cell-permeable dipeptide that potently antagonizes PPARγ (Kd = 8.34 µM).{28551} It reversibly and competitively blocks activation of PPARγ by rosiglitazone (IC50 = 8-32 µM).{28551} G3335 is active in vivo, abolishing the protective effects of rosiglitazone in experimental spinal cord injury in rats.{28550} G3335 has also been used to evaluate the role of PPARγ in neurotoxicity studies.{28549,28552}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ (PPARγ) is a nuclear receptor with key roles in adipocyte differentiation and glucose homeostasis.{18294,14553} G3335 is a cell-permeable dipeptide that potently antagonizes PPARγ (Kd = 8.34 µM).{28551} It reversibly and competitively blocks activation of PPARγ by rosiglitazone (IC50 = 8-32 µM).{28551} G3335 is active in vivo, abolishing the protective effects of rosiglitazone in experimental spinal cord injury in rats.{28550} G3335 has also been used to evaluate the role of PPARγ in neurotoxicity studies.{28549,28552}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder