Chemicals
Showing 16201–16350 of 41137 results
-
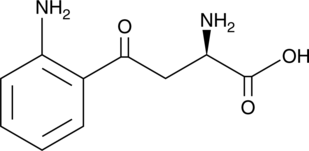
D-Kynurenine is an antagonist of hydroxycarboxylic acid receptor 3 HCA3/GPR109B (EC50 = 2.61 µM in a luciferase reporter assay) and a metabolite of D-tryptophan.{46426} It increases levels of intracellular calcium and decreases forskolin-stimulated production of cAMP in CHO cells expressing human HCA3/GPR109B when used at concentrations of 10 and 100, or 1,000 µM, respectively. D-Kynurenine (10 µM) increases expression of vimentin and decreases expression of E-cadherin in 95D lung cancer cells.{46427} It has been used as a substrate in fluorometric assays for D-amino acid oxidase activity.{46428,46429}
Brand:CaymanSKU:28254 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-Luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25836 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-Luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25836 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-Luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25836 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-Luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25836 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-Luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-Luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-Luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-Luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-Luciferin is a chemiluminescent substrate of firefly luciferase.{23396} It produces light upon oxidative decarboxylation by luciferase in the presence of ATP. D-luciferin can be employed to assay the expression of the luciferase gene linked to a promoter of interest. Alternatively, D-luciferin and luciferase can be used to assess ATP availability in cellular or biochemical assays.
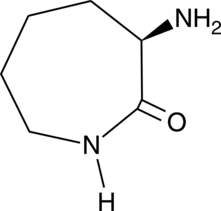
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-Lysine lactam is a chiral building block.{58111,58112} It has been used in the synthesis of a chiral antibiotic synthetic intermediate, as well as in the stereoselective synthesis of neurokinin (NK) receptor antagonists.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31684 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Lysine lactam is a chiral building block.{58111,58112} It has been used in the synthesis of a chiral antibiotic synthetic intermediate, as well as in the stereoselective synthesis of neurokinin (NK) receptor antagonists.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31684 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Lysine lactam is a chiral building block.{58111,58112} It has been used in the synthesis of a chiral antibiotic synthetic intermediate, as well as in the stereoselective synthesis of neurokinin (NK) receptor antagonists.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31684 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Lysine lactam is a chiral building block.{58111,58112} It has been used in the synthesis of a chiral antibiotic synthetic intermediate, as well as in the stereoselective synthesis of neurokinin (NK) receptor antagonists.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31684 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
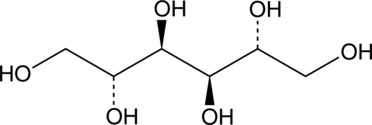
D-Mannitol (Item No. 23372) is an analytical reference standard categorized as an alcohol sugar that is used as an adulterant.{31650} It is commonly used as a cutting agent in heroin (Item Nos. 9001543 | ISO60187) and cocaine (Item Nos. 22165 | 16186 | ISO60176). This product is intended for research and forensic applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23372 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
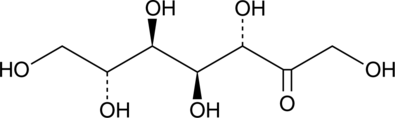
D-Glucose is phosphorylated by glucokinase and three tissue-specific hexokinases to produce glucose-6-phosphate in humans. D-Mannoheptulose is a heptose that inhibits glucokinases and hexokinases from diverse organisms through competition with D-glucose (Ki = 0.25 mM).{27136,27134,27137} It blocks glucose oxidation and glucose-mediated insulin release from pancreatic islet cells.{27135,27138} D-Mannoheptulose prevents the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate that can mediate the activation of the carbohydrate response element binding protein.{27139} By blocking glucose phosphorylation, D-mannoheptulose causes transient hyperglycemia in dogs when given at 1 g/kg but not at 8 mg/kg, although postprandial energy expenditure is increased at the lower dose.{27140}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
D-Glucose is phosphorylated by glucokinase and three tissue-specific hexokinases to produce glucose-6-phosphate in humans. D-Mannoheptulose is a heptose that inhibits glucokinases and hexokinases from diverse organisms through competition with D-glucose (Ki = 0.25 mM).{27136,27134,27137} It blocks glucose oxidation and glucose-mediated insulin release from pancreatic islet cells.{27135,27138} D-Mannoheptulose prevents the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate that can mediate the activation of the carbohydrate response element binding protein.{27139} By blocking glucose phosphorylation, D-mannoheptulose causes transient hyperglycemia in dogs when given at 1 g/kg but not at 8 mg/kg, although postprandial energy expenditure is increased at the lower dose.{27140}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
D-Glucose is phosphorylated by glucokinase and three tissue-specific hexokinases to produce glucose-6-phosphate in humans. D-Mannoheptulose is a heptose that inhibits glucokinases and hexokinases from diverse organisms through competition with D-glucose (Ki = 0.25 mM).{27136,27134,27137} It blocks glucose oxidation and glucose-mediated insulin release from pancreatic islet cells.{27135,27138} D-Mannoheptulose prevents the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate that can mediate the activation of the carbohydrate response element binding protein.{27139} By blocking glucose phosphorylation, D-mannoheptulose causes transient hyperglycemia in dogs when given at 1 g/kg but not at 8 mg/kg, although postprandial energy expenditure is increased at the lower dose.{27140}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
D-Glucose is phosphorylated by glucokinase and three tissue-specific hexokinases to produce glucose-6-phosphate in humans. D-Mannoheptulose is a heptose that inhibits glucokinases and hexokinases from diverse organisms through competition with D-glucose (Ki = 0.25 mM).{27136,27134,27137} It blocks glucose oxidation and glucose-mediated insulin release from pancreatic islet cells.{27135,27138} D-Mannoheptulose prevents the conversion of glucose to glucose-6-phosphate that can mediate the activation of the carbohydrate response element binding protein.{27139} By blocking glucose phosphorylation, D-mannoheptulose causes transient hyperglycemia in dogs when given at 1 g/kg but not at 8 mg/kg, although postprandial energy expenditure is increased at the lower dose.{27140}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
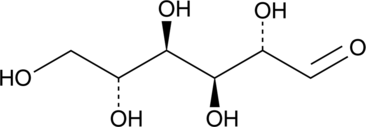
D-Mannose is an aldohexose monosaccharide and an epimer of glucose. D-Mannose is found in animals, microbes, and plants, can be used as an energy source by conversion to glucose, and can also be produced from glucose.{30551} It is converted via hexokinase to mannose-6-phosphate and then to intermediates that are incorporated into proteins via N-linked glycosylation. It decreases T cell proliferation and increases FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in vitro and prevents diabetes in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice, a model of autoimmune diabetes, when administered at a dose of 1.1 M in the drinking water.{43946} D-Mannose administration during gestation at a dose of 9 mg/ml in the drinking water rescues the embryonic lethal phenotype and prevents deficits in glycosylation in Pmm2R137H/F118L mice, a transgenic model of the congenital glycosylation disorder (CDG) PMM2-CDG, which is characterized by phosphomannomutase 2 (PMM2) gene mutations.{43947} Levels of D-mannose are reduced in the serum of patients with PMM2-CDG.{43948} Formulations containing D-mannose have been used in the treatment of mannose phosphate isomerase CDG (MPI-CDG).
Brand:CaymanSKU:27388 - 100 gAvailable on backorder
D-Mannose is an aldohexose monosaccharide and an epimer of glucose. D-Mannose is found in animals, microbes, and plants, can be used as an energy source by conversion to glucose, and can also be produced from glucose.{30551} It is converted via hexokinase to mannose-6-phosphate and then to intermediates that are incorporated into proteins via N-linked glycosylation. It decreases T cell proliferation and increases FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in vitro and prevents diabetes in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice, a model of autoimmune diabetes, when administered at a dose of 1.1 M in the drinking water.{43946} D-Mannose administration during gestation at a dose of 9 mg/ml in the drinking water rescues the embryonic lethal phenotype and prevents deficits in glycosylation in Pmm2R137H/F118L mice, a transgenic model of the congenital glycosylation disorder (CDG) PMM2-CDG, which is characterized by phosphomannomutase 2 (PMM2) gene mutations.{43947} Levels of D-mannose are reduced in the serum of patients with PMM2-CDG.{43948} Formulations containing D-mannose have been used in the treatment of mannose phosphate isomerase CDG (MPI-CDG).
Brand:CaymanSKU:27388 - 250 gAvailable on backorder
D-Mannose is an aldohexose monosaccharide and an epimer of glucose. D-Mannose is found in animals, microbes, and plants, can be used as an energy source by conversion to glucose, and can also be produced from glucose.{30551} It is converted via hexokinase to mannose-6-phosphate and then to intermediates that are incorporated into proteins via N-linked glycosylation. It decreases T cell proliferation and increases FoxP3+ T regulatory cells in vitro and prevents diabetes in non-obese diabetic (NOD) mice, a model of autoimmune diabetes, when administered at a dose of 1.1 M in the drinking water.{43946} D-Mannose administration during gestation at a dose of 9 mg/ml in the drinking water rescues the embryonic lethal phenotype and prevents deficits in glycosylation in Pmm2R137H/F118L mice, a transgenic model of the congenital glycosylation disorder (CDG) PMM2-CDG, which is characterized by phosphomannomutase 2 (PMM2) gene mutations.{43947} Levels of D-mannose are reduced in the serum of patients with PMM2-CDG.{43948} Formulations containing D-mannose have been used in the treatment of mannose phosphate isomerase CDG (MPI-CDG).
Brand:CaymanSKU:27388 - 500 gAvailable on backorder
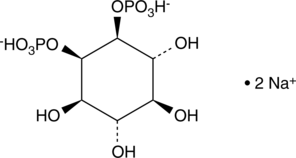
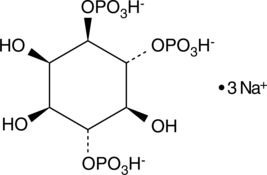
Ins(1,2)P2 (sodium salt) is one of the many inositol phosphate (InsP) isomers that could act as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8672,8344,13727} The most studied InsP Ins(1,4,5)P3, is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(1,2)P2 (tested as the D/L racemic mixture) is ~1,000-fold less potent than Ins(1,4,5)P3 at initiating Ca2+ release when injected into Xenopus oocytes.{13725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008439 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Ins(1,2)P2 (sodium salt) is one of the many inositol phosphate (InsP) isomers that could act as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8672,8344,13727} The most studied InsP Ins(1,4,5)P3, is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(1,2)P2 (tested as the D/L racemic mixture) is ~1,000-fold less potent than Ins(1,4,5)P3 at initiating Ca2+ release when injected into Xenopus oocytes.{13725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008439 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Ins(1,2)P2 (sodium salt) is one of the many inositol phosphate (InsP) isomers that could act as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8672,8344,13727} The most studied InsP Ins(1,4,5)P3, is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(1,2)P2 (tested as the D/L racemic mixture) is ~1,000-fold less potent than Ins(1,4,5)P3 at initiating Ca2+ release when injected into Xenopus oocytes.{13725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008439 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
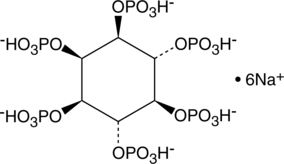
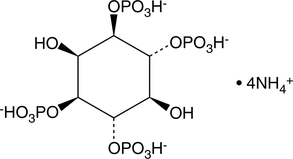
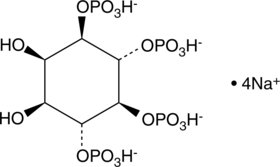
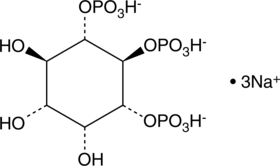
D-myo-Inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaphosphate (IP6) is a phosphate ester of inositol. It is found in mammalian cells and undergoes interconversion to other forms of inositol phosphate that act as second messengers in cell signaling.{48091} IP6 is an antioxidant that chelates iron at a molar ratio of 1:4 to reduce iron-induced hydroxy radical production and lipid peroxidation in cell-free assays.{48092} It also inhibits the formation of thiobarbituric acid reacting substances (TBARS) in cooked chicken breast when used at a concentration of 1.5 mM. IP6 inhibits proliferation of a variety of cancer cells in vitro and reduces tumor growth in rodent xenograft models.{48093} It is also known as phytic acid and is considered an anti-nutrient that binds minerals, including calcium, iron, magnesium, and zinc, in grains, legumes, oilseeds, nuts, and other plants and prevents their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals that ingest them.{48091} Formulations containing IP6 have been used in cosmetics and as preservatives in food production. Cayman’s IP6 is a highly purified product intended for use in biomedical research applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008415 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaphosphate (IP6) is a phosphate ester of inositol. It is found in mammalian cells and undergoes interconversion to other forms of inositol phosphate that act as second messengers in cell signaling.{48091} IP6 is an antioxidant that chelates iron at a molar ratio of 1:4 to reduce iron-induced hydroxy radical production and lipid peroxidation in cell-free assays.{48092} It also inhibits the formation of thiobarbituric acid reacting substances (TBARS) in cooked chicken breast when used at a concentration of 1.5 mM. IP6 inhibits proliferation of a variety of cancer cells in vitro and reduces tumor growth in rodent xenograft models.{48093} It is also known as phytic acid and is considered an anti-nutrient that binds minerals, including calcium, iron, magnesium, and zinc, in grains, legumes, oilseeds, nuts, and other plants and prevents their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals that ingest them.{48091} Formulations containing IP6 have been used in cosmetics and as preservatives in food production. Cayman’s IP6 is a highly purified product intended for use in biomedical research applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008415 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaphosphate (IP6) is a phosphate ester of inositol. It is found in mammalian cells and undergoes interconversion to other forms of inositol phosphate that act as second messengers in cell signaling.{48091} IP6 is an antioxidant that chelates iron at a molar ratio of 1:4 to reduce iron-induced hydroxy radical production and lipid peroxidation in cell-free assays.{48092} It also inhibits the formation of thiobarbituric acid reacting substances (TBARS) in cooked chicken breast when used at a concentration of 1.5 mM. IP6 inhibits proliferation of a variety of cancer cells in vitro and reduces tumor growth in rodent xenograft models.{48093} It is also known as phytic acid and is considered an anti-nutrient that binds minerals, including calcium, iron, magnesium, and zinc, in grains, legumes, oilseeds, nuts, and other plants and prevents their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals that ingest them.{48091} Formulations containing IP6 have been used in cosmetics and as preservatives in food production. Cayman’s IP6 is a highly purified product intended for use in biomedical research applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008415 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexaphosphate (IP6) is a phosphate ester of inositol. It is found in mammalian cells and undergoes interconversion to other forms of inositol phosphate that act as second messengers in cell signaling.{48091} IP6 is an antioxidant that chelates iron at a molar ratio of 1:4 to reduce iron-induced hydroxy radical production and lipid peroxidation in cell-free assays.{48092} It also inhibits the formation of thiobarbituric acid reacting substances (TBARS) in cooked chicken breast when used at a concentration of 1.5 mM. IP6 inhibits proliferation of a variety of cancer cells in vitro and reduces tumor growth in rodent xenograft models.{48093} It is also known as phytic acid and is considered an anti-nutrient that binds minerals, including calcium, iron, magnesium, and zinc, in grains, legumes, oilseeds, nuts, and other plants and prevents their absorption in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and animals that ingest them.{48091} Formulations containing IP6 have been used in cosmetics and as preservatives in food production. Cayman’s IP6 is a highly purified product intended for use in biomedical research applications.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008415 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,3-phosphate (Ins(1,3)P) is a member of the inositol phosphate (InsP) molecular family that play critical roles as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8672,8344} The most studied InsP, Ins(1,4,5)P3 is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(1,3)P2 can be dephosphorylated to Ins(1)P by inositol polyphosphate 3-phosphatase and further dephosphorylated to inositol by inositol monophosphatase.{8344}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008443 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,3-phosphate (Ins(1,3)P) is a member of the inositol phosphate (InsP) molecular family that play critical roles as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8672,8344} The most studied InsP, Ins(1,4,5)P3 is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(1,3)P2 can be dephosphorylated to Ins(1)P by inositol polyphosphate 3-phosphatase and further dephosphorylated to inositol by inositol monophosphatase.{8344}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008443 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,3-phosphate (Ins(1,3)P) is a member of the inositol phosphate (InsP) molecular family that play critical roles as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8672,8344} The most studied InsP, Ins(1,4,5)P3 is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(1,3)P2 can be dephosphorylated to Ins(1)P by inositol polyphosphate 3-phosphatase and further dephosphorylated to inositol by inositol monophosphatase.{8344}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008443 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
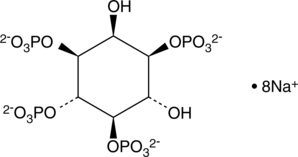
D-myo-Inositol-1,3,4,5-tetraphosphate (Ins(1,3,4,5)-P4) is formed by the phosphorylation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 by inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate 3-kinase.{783,1769} Ins(1,3,4,5)-P4 increases intracellular calcium levels by two distinct mechanisms: opening calcium channels on both the endoplasmic reticulum to release calcium from internal stores and on the plasma membrane to allow the influx of calcium from outside the cell.{831}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60980 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,3,4,5-tetraphosphate (Ins(1,3,4,5)-P4) is formed by the phosphorylation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 by inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate 3-kinase.{783,1769} Ins(1,3,4,5)-P4 increases intracellular calcium levels by two distinct mechanisms: opening calcium channels on both the endoplasmic reticulum to release calcium from internal stores and on the plasma membrane to allow the influx of calcium from outside the cell.{831}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60980 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,3,4,5-tetraphosphate (Ins(1,3,4,5)-P4) is formed by the phosphorylation of Ins(1,4,5)P3 by inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate 3-kinase.{783,1769} Ins(1,3,4,5)-P4 increases intracellular calcium levels by two distinct mechanisms: opening calcium channels on both the endoplasmic reticulum to release calcium from internal stores and on the plasma membrane to allow the influx of calcium from outside the cell.{831}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60980 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
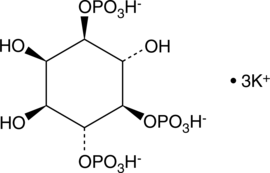
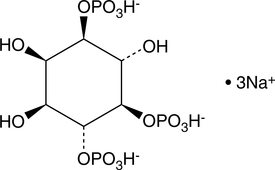
The inositol phosphates (IPs) are a family of molecules produced by altering the phosphorylation status of each of the six carbons on the cyclic inositol structure. They act as second messengers, regulating a wide array of cellular functions. D-myo-inositol-1,3,4,6-tetraphosphate(Ins(1,3,4,6)-P4) largely acts an intermediate, serving as substrate for inositol-1,3,4,6-tetraphosphate 5-kinase to produce inositol-1,3,4,5,6-pentaphosphate, or inositol-1,3,4,6-tetraphosphate 2-kinase to give inositol-1,2,3,4,6-pentaphosphate.{16515} These inositol pentaphosphates can be further phosphorylated to produce inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate, or phytic acid, which serves diverse roles in eukaryotic tissues. Ins(1,3,4,6)-P4 is a poor activator of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphospate receptor in vitro.{5630} Other functions of this IP remain to be elucidated.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008442 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
The inositol phosphates (IPs) are a family of molecules produced by altering the phosphorylation status of each of the six carbons on the cyclic inositol structure. They act as second messengers, regulating a wide array of cellular functions. D-myo-inositol-1,3,4,6-tetraphosphate(Ins(1,3,4,6)-P4) largely acts an intermediate, serving as substrate for inositol-1,3,4,6-tetraphosphate 5-kinase to produce inositol-1,3,4,5,6-pentaphosphate, or inositol-1,3,4,6-tetraphosphate 2-kinase to give inositol-1,2,3,4,6-pentaphosphate.{16515} These inositol pentaphosphates can be further phosphorylated to produce inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate, or phytic acid, which serves diverse roles in eukaryotic tissues. Ins(1,3,4,6)-P4 is a poor activator of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphospate receptor in vitro.{5630} Other functions of this IP remain to be elucidated.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008442 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
The inositol phosphates (IPs) are a family of molecules produced by altering the phosphorylation status of each of the six carbons on the cyclic inositol structure. They act as second messengers, regulating a wide array of cellular functions. D-myo-inositol-1,3,4,6-tetraphosphate(Ins(1,3,4,6)-P4) largely acts an intermediate, serving as substrate for inositol-1,3,4,6-tetraphosphate 5-kinase to produce inositol-1,3,4,5,6-pentaphosphate, or inositol-1,3,4,6-tetraphosphate 2-kinase to give inositol-1,2,3,4,6-pentaphosphate.{16515} These inositol pentaphosphates can be further phosphorylated to produce inositol-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexakisphosphate, or phytic acid, which serves diverse roles in eukaryotic tissues. Ins(1,3,4,6)-P4 is a poor activator of the inositol 1,4,5-trisphospate receptor in vitro.{5630} Other functions of this IP remain to be elucidated.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008442 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC) mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} It binds to one of several Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptors, each containing a calcium channel domain. Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to the receptor results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60960 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC) mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} It binds to one of several Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptors, each containing a calcium channel domain. Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to the receptor results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60960 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC) mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} It binds to one of several Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptors, each containing a calcium channel domain. Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to the receptor results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60960 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC) mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} It binds to one of several Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptors, each containing a calcium channel domain. Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to the receptor results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096}
Brand:CaymanSKU:60960 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} It binds to one of several Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptors, each containing a calcium channel domain. Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to the receptor results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008205 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} It binds to one of several Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptors, each containing a calcium channel domain. Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to the receptor results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008205 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5-triphosphate (Ins(1,4,5)P3) is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidyl inositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} It binds to one of several Ins(1,4,5)P3 receptors, each containing a calcium channel domain. Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to the receptor results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008205 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5,6-tetrahosphate (sodium salt) (Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4) is one of several different inositol oligophosphate isomers implicated in signal transduction. Production of Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 by intestinal epithelial cells increases approximately 2-14 fold, depending on the strain and incubation time, following infection with Salmonella. D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5,6-tetraphosphate (sodium salt) (Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4) is one of several different inositol oligophosphate isomers implicated in signal transduction. Production of Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 by intestinal epithelial cells increases approximately 2-14 fold, depending on the strain and incubation time, following infection with Salmonella.{13729} Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 antagonizes epidermal growth factor (EGF) signalling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway.{13729} Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 (tested as the D/L racemic mixture) is ~1,000-fold less potent than Ins(1,4,5)-P3 at initiating Ca2+ release when injected into Xenopus oocytes.{13725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007783 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5,6-tetrahosphate (sodium salt) (Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4) is one of several different inositol oligophosphate isomers implicated in signal transduction. Production of Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 by intestinal epithelial cells increases approximately 2-14 fold, depending on the strain and incubation time, following infection with Salmonella. D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5,6-tetraphosphate (sodium salt) (Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4) is one of several different inositol oligophosphate isomers implicated in signal transduction. Production of Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 by intestinal epithelial cells increases approximately 2-14 fold, depending on the strain and incubation time, following infection with Salmonella.{13729} Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 antagonizes epidermal growth factor (EGF) signalling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway.{13729} Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 (tested as the D/L racemic mixture) is ~1,000-fold less potent than Ins(1,4,5)-P3 at initiating Ca2+ release when injected into Xenopus oocytes.{13725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007783 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5,6-tetrahosphate (sodium salt) (Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4) is one of several different inositol oligophosphate isomers implicated in signal transduction. Production of Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 by intestinal epithelial cells increases approximately 2-14 fold, depending on the strain and incubation time, following infection with Salmonella. D-myo-Inositol-1,4,5,6-tetraphosphate (sodium salt) (Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4) is one of several different inositol oligophosphate isomers implicated in signal transduction. Production of Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 by intestinal epithelial cells increases approximately 2-14 fold, depending on the strain and incubation time, following infection with Salmonella.{13729} Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 antagonizes epidermal growth factor (EGF) signalling through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway.{13729} Ins(1,4,5,6)-P4 (tested as the D/L racemic mixture) is ~1,000-fold less potent than Ins(1,4,5)-P3 at initiating Ca2+ release when injected into Xenopus oocytes.{13725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007783 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,6-phosphate (Ins(1,4,6)-P3) is a member of the inositol phosphate (InsP) family that play critical roles as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8672,8344} The most studied InsP, Ins(1,4,5)-P3, is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)-P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(1,4,6)-P3 (tested as the meso compound) is 9-fold less potent than Ins(1,4,5)-P3 at initiating Ca2+ release when injected into Xenopus oocytes.{13725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008427 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,6-phosphate (Ins(1,4,6)-P3) is a member of the inositol phosphate (InsP) family that play critical roles as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8672,8344} The most studied InsP, Ins(1,4,5)-P3, is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)-P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(1,4,6)-P3 (tested as the meso compound) is 9-fold less potent than Ins(1,4,5)-P3 at initiating Ca2+ release when injected into Xenopus oocytes.{13725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008427 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-1,4,6-phosphate (Ins(1,4,6)-P3) is a member of the inositol phosphate (InsP) family that play critical roles as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8672,8344} The most studied InsP, Ins(1,4,5)-P3, is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-biphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)-P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(1,4,6)-P3 (tested as the meso compound) is 9-fold less potent than Ins(1,4,5)-P3 at initiating Ca2+ release when injected into Xenopus oocytes.{13725}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008427 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
The inositol phosphates are a family of mono- to poly-phosphorylated compounds that act as messengers, regulating cellular functions including cell cycling, apoptosis, differentiation, andmotility.{8344,8672} D-myo-Inositol-1,5,6-triphosphate is an intermediate compound, produced by the dephosphorylation of various inositol-tetrakisphosphate forms. The triphosphate can be further metabolized to produce inositol-biphosphate mediators. The biological roles of D-myo-inositol-1,5,6-triphosphate remain to be determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008422 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
The inositol phosphates are a family of mono- to poly-phosphorylated compounds that act as messengers, regulating cellular functions including cell cycling, apoptosis, differentiation, andmotility.{8344,8672} D-myo-Inositol-1,5,6-triphosphate is an intermediate compound, produced by the dephosphorylation of various inositol-tetrakisphosphate forms. The triphosphate can be further metabolized to produce inositol-biphosphate mediators. The biological roles of D-myo-inositol-1,5,6-triphosphate remain to be determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008422 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
The inositol phosphates are a family of mono- to poly-phosphorylated compounds that act as messengers, regulating cellular functions including cell cycling, apoptosis, differentiation, andmotility.{8344,8672} D-myo-Inositol-1,5,6-triphosphate is an intermediate compound, produced by the dephosphorylation of various inositol-tetrakisphosphate forms. The triphosphate can be further metabolized to produce inositol-biphosphate mediators. The biological roles of D-myo-inositol-1,5,6-triphosphate remain to be determined.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008422 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
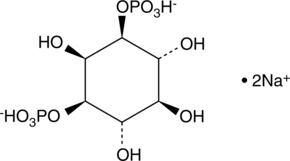
D-myo-Inositol-4-phosphate (Ins(4)P1) is a member of the inositol phosphate (InsP) molecular family that play critical roles as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8344,8672} The most studied InsP, Ins(1,4,5)P3, is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-diphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(4)P1 can be formed by dephosphorylation of Ins(1,4)P2 by inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase or dephosphorylated to inositol by inositol monophosphatase.{8344}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008437 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-4-phosphate (Ins(4)P1) is a member of the inositol phosphate (InsP) molecular family that play critical roles as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8344,8672} The most studied InsP, Ins(1,4,5)P3, is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-diphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(4)P1 can be formed by dephosphorylation of Ins(1,4)P2 by inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase or dephosphorylated to inositol by inositol monophosphatase.{8344}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008437 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
D-myo-Inositol-4-phosphate (Ins(4)P1) is a member of the inositol phosphate (InsP) molecular family that play critical roles as small, soluble second messengers in the transmission of cellular signals.{8344,8672} The most studied InsP, Ins(1,4,5)P3, is a second messenger produced in cells by phospholipase C (PLC)-mediated hydrolysis of phosphatidylinositol-4,5-diphosphate.{2429,5714} Binding of Ins(1,4,5)P3 to its receptor on the endoplasmic reticulum results in opening of the calcium channels and an increase in intracellular calcium.{5714,4096} Ins(4)P1 can be formed by dephosphorylation of Ins(1,4)P2 by inositol polyphosphate 1-phosphatase or dephosphorylated to inositol by inositol monophosphatase.{8344}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10008437 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
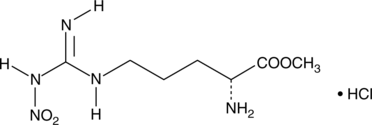
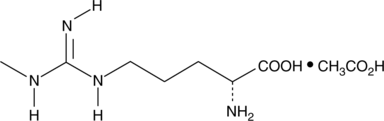
N(G)-Nitro-D-arginine methyl ester (D-NAME) is the less active enantiomer of the nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME; Item No. 80210). D-NAME was initially thought to be inactive and was often used as a negative control for L-NAME.{33894,33892} Later studies showed that D-NAME (40 mg/kg/day in rats) can have similar but less pronounced effects as L-NAME (40 mg/kg/day in rats) in the cardiovascular system, particularly at long-term timepoints.{33891} D-NAME (3-10 µg/mouse) had no effect on nociception in mice assessed using the tail flick test.{33893}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21687 -Out of stock
N(G)-Nitro-D-arginine methyl ester (D-NAME) is the less active enantiomer of the nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME; Item No. 80210). D-NAME was initially thought to be inactive and was often used as a negative control for L-NAME.{33894,33892} Later studies showed that D-NAME (40 mg/kg/day in rats) can have similar but less pronounced effects as L-NAME (40 mg/kg/day in rats) in the cardiovascular system, particularly at long-term timepoints.{33891} D-NAME (3-10 µg/mouse) had no effect on nociception in mice assessed using the tail flick test.{33893}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21687 -Out of stock
N(G)-Nitro-D-arginine methyl ester (D-NAME) is the less active enantiomer of the nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME; Item No. 80210). D-NAME was initially thought to be inactive and was often used as a negative control for L-NAME.{33894,33892} Later studies showed that D-NAME (40 mg/kg/day in rats) can have similar but less pronounced effects as L-NAME (40 mg/kg/day in rats) in the cardiovascular system, particularly at long-term timepoints.{33891} D-NAME (3-10 µg/mouse) had no effect on nociception in mice assessed using the tail flick test.{33893}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21687 -Out of stock
N(G)-Nitro-D-arginine methyl ester (D-NAME) is the less active enantiomer of the nitric oxide (NO) synthase inhibitor N(G)-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME; Item No. 80210). D-NAME was initially thought to be inactive and was often used as a negative control for L-NAME.{33894,33892} Later studies showed that D-NAME (40 mg/kg/day in rats) can have similar but less pronounced effects as L-NAME (40 mg/kg/day in rats) in the cardiovascular system, particularly at long-term timepoints.{33891} D-NAME (3-10 µg/mouse) had no effect on nociception in mice assessed using the tail flick test.{33893}
Brand:CaymanSKU:21687 -Out of stock
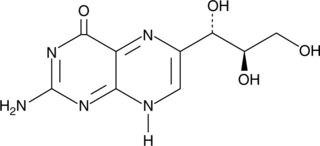
Neopterin is a pyrazino-pyrimidine compound derived from GTP that represents an intermediate product in the synthetic pathway of biopterin and is an essential cofactor in neurotransmitter synthesis.{1268} Neopterin is released from macrophages upon immune stimulation with interferon-γ from activated T cells.{22214} It is routinely used as a biochemical tool to screen for and monitor the progression of certain diseases accompanied by hyperimmune stimulation.{22214}
Brand:CaymanSKU:12057 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Neopterin is a pyrazino-pyrimidine compound derived from GTP that represents an intermediate product in the synthetic pathway of biopterin and is an essential cofactor in neurotransmitter synthesis.{1268} Neopterin is released from macrophages upon immune stimulation with interferon-γ from activated T cells.{22214} It is routinely used as a biochemical tool to screen for and monitor the progression of certain diseases accompanied by hyperimmune stimulation.{22214}
Brand:CaymanSKU:12057 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Neopterin is a pyrazino-pyrimidine compound derived from GTP that represents an intermediate product in the synthetic pathway of biopterin and is an essential cofactor in neurotransmitter synthesis.{1268} Neopterin is released from macrophages upon immune stimulation with interferon-γ from activated T cells.{22214} It is routinely used as a biochemical tool to screen for and monitor the progression of certain diseases accompanied by hyperimmune stimulation.{22214}
Brand:CaymanSKU:12057 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
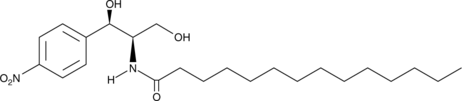
D-NMAPPD is an inhibitor of ceramidase.{12571} It induces cell death in SW403 colon adenocarcinoma cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner but has no effect on viability of rat hepatocytes, Kupffer cells, or sinusoidal endothelial cells when used at a concentration of 100 mM. D-NMAPPD increases intracellular ceramide accumulation and cytochrome C release and induces apoptosis in SW403 cells, effects that can be prevented by the caspase-3 inhibitor Ac-DEVD-CHO (Item No. 10017). In vivo, D-NMAPPD (75 mg/kg) reduces tumor growth and the number of hepatic metastases in SW403 and LoVo colon cancer mouse xenograft models.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006305 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
D-NMAPPD is an inhibitor of ceramidase.{12571} It induces cell death in SW403 colon adenocarcinoma cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner but has no effect on viability of rat hepatocytes, Kupffer cells, or sinusoidal endothelial cells when used at a concentration of 100 mM. D-NMAPPD increases intracellular ceramide accumulation and cytochrome C release and induces apoptosis in SW403 cells, effects that can be prevented by the caspase-3 inhibitor Ac-DEVD-CHO (Item No. 10017). In vivo, D-NMAPPD (75 mg/kg) reduces tumor growth and the number of hepatic metastases in SW403 and LoVo colon cancer mouse xenograft models.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006305 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
D-NMAPPD is an inhibitor of ceramidase.{12571} It induces cell death in SW403 colon adenocarcinoma cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner but has no effect on viability of rat hepatocytes, Kupffer cells, or sinusoidal endothelial cells when used at a concentration of 100 mM. D-NMAPPD increases intracellular ceramide accumulation and cytochrome C release and induces apoptosis in SW403 cells, effects that can be prevented by the caspase-3 inhibitor Ac-DEVD-CHO (Item No. 10017). In vivo, D-NMAPPD (75 mg/kg) reduces tumor growth and the number of hepatic metastases in SW403 and LoVo colon cancer mouse xenograft models.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006305 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
D-NMAPPD is an inhibitor of ceramidase.{12571} It induces cell death in SW403 colon adenocarcinoma cells in a time- and concentration-dependent manner but has no effect on viability of rat hepatocytes, Kupffer cells, or sinusoidal endothelial cells when used at a concentration of 100 mM. D-NMAPPD increases intracellular ceramide accumulation and cytochrome C release and induces apoptosis in SW403 cells, effects that can be prevented by the caspase-3 inhibitor Ac-DEVD-CHO (Item No. 10017). In vivo, D-NMAPPD (75 mg/kg) reduces tumor growth and the number of hepatic metastases in SW403 and LoVo colon cancer mouse xenograft models.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006305 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
D-NMMA is the inactive enantiomer of the competitive NOS inhibitor, L-NMMA (Item No. 10005031). It fails to inhibit NOS at concentrations as high as 100 μM and thus, may be used to explore non-specific effects of L-NMMA.{22192,22191}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-NMMA is the inactive enantiomer of the competitive NOS inhibitor, L-NMMA (Item No. 10005031). It fails to inhibit NOS at concentrations as high as 100 μM and thus, may be used to explore non-specific effects of L-NMMA.{22192,22191}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-NMMA is the inactive enantiomer of the competitive NOS inhibitor, L-NMMA (Item No. 10005031). It fails to inhibit NOS at concentrations as high as 100 μM and thus, may be used to explore non-specific effects of L-NMMA.{22192,22191}
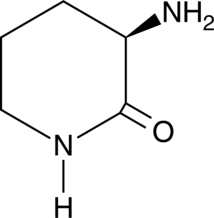
Brand:CaymanSKU:-D-Ornithine lactam is a building block.{52761,52762} It has been used in the synthesis of hepatitis C virus (HCV) non-structural protein 5B (NS5B) inhibitors, as well as αVβ3 integrin receptor antagonists.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31680 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Ornithine lactam is a building block.{52761,52762} It has been used in the synthesis of hepatitis C virus (HCV) non-structural protein 5B (NS5B) inhibitors, as well as αVβ3 integrin receptor antagonists.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31680 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Ornithine lactam is a building block.{52761,52762} It has been used in the synthesis of hepatitis C virus (HCV) non-structural protein 5B (NS5B) inhibitors, as well as αVβ3 integrin receptor antagonists.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31680 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
D-Ornithine lactam is a building block.{52761,52762} It has been used in the synthesis of hepatitis C virus (HCV) non-structural protein 5B (NS5B) inhibitors, as well as αVβ3 integrin receptor antagonists.
Brand:CaymanSKU:31680 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
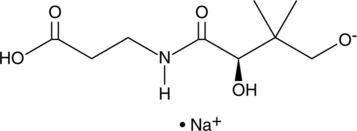
Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is a precursor in the biosynthesis of coenzyme A (Item No. 16147), which is an essential cofactor functioning as an acyl group carrier and carbonyl-activating group for the citric acid cycle and fatty acid metabolism.{18938,18936} Two enantiomers of pantothenic acid exist, D- or L-form. D-Pantothenic acid (sodium salt) is a sodium salt form of the biologically active enantiomer of vitamin B5 and is used in the synthesis of coenzyme A.{28305} The L-form of pantothenic acid is biologically inactive and has been shown to act as an antagonist of D-pantothenic acid.{28304}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is a precursor in the biosynthesis of coenzyme A (Item No. 16147), which is an essential cofactor functioning as an acyl group carrier and carbonyl-activating group for the citric acid cycle and fatty acid metabolism.{18938,18936} Two enantiomers of pantothenic acid exist, D- or L-form. D-Pantothenic acid (sodium salt) is a sodium salt form of the biologically active enantiomer of vitamin B5 and is used in the synthesis of coenzyme A.{28305} The L-form of pantothenic acid is biologically inactive and has been shown to act as an antagonist of D-pantothenic acid.{28304}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
Pantothenic acid (vitamin B5) is a precursor in the biosynthesis of coenzyme A (Item No. 16147), which is an essential cofactor functioning as an acyl group carrier and carbonyl-activating group for the citric acid cycle and fatty acid metabolism.{18938,18936} Two enantiomers of pantothenic acid exist, D- or L-form. D-Pantothenic acid (sodium salt) is a sodium salt form of the biologically active enantiomer of vitamin B5 and is used in the synthesis of coenzyme A.{28305} The L-form of pantothenic acid is biologically inactive and has been shown to act as an antagonist of D-pantothenic acid.{28304}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder