Cayman
Showing 13651–13800 of 45550 results
-
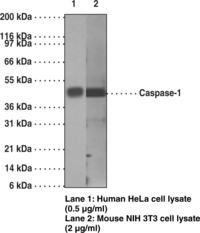
Caspases are a family of cysteine proteases that are key mediators of programmed cell death or apoptosis.{1642} The precursor form of all caspases is composed of a prodomain and large and small catalytic subunits. The active forms of caspases are generated by several stimuli including ligand-receptor interactions, growth factor deprivation and inhibitors of cellular functions. All known caspases require cleavage adjacent to aspartates to liberate one large and one small subunit, which associate into a tetramer to form the active enzyme. Caspase-1 is similar to the cell death gene CED-3 of C. elegans and regulates multiple proinflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-1β and interferon-γ-inducing factor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13907 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: synthetic peptide corresponding to human caspase-1 within the region of amino acids 371-390 • Host: mouse, clone 14F468 • Isotype: IgG1κ • Cross Reactivity: (+) human and mouse caspase-1 • Application(s): IHC (paraffin-embedded sections) and WB • Caspase-1 is similar to the cell death gene CED-3 of C. elegans and regulates multiple proinflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-1β and interferon-γ-inducing factor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13907- 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: synthetic peptide corresponding to human caspase-1 within the region of amino acids 371-390 • Host: mouse, clone 14F468 • Isotype: IgG1κ • Cross Reactivity: (+) human and mouse caspase-1 • Application(s): IHC (paraffin-embedded sections) and WB • Caspase-1 is similar to the cell death gene CED-3 of C. elegans and regulates multiple proinflammatory cytokines, including interleukin-1β and interferon-γ-inducing factor.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13907- 1 eaCaspases are a family of cysteine proteases that are key mediators of programmed cell death or apoptosis.{18384} The precursor form of all caspases is composed of a prodomain and large and small catalytic subunits. The active forms of caspases are generated by several stimuli including ligand-receptor interactions, growth factor deprivation, and inhibitors of cellular functions. All known caspases require cleavage adjacent to aspartates to liberate one large and one small subunit, which associate into an a2b2 tetramer to form the active enzyme. Caspase-14 has a conserved active site pentapeptide, QACRG. However, no proteolytic or biological activities have been identified so far. Its high expression in embryonic tissues and limited expression in adult tissues suggests that it may have some role during ontogenesis.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13916 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: synthetic peptide corresponding to mouse caspase-14 amino acids 2-18 • Host: mouse • Cross Reactivity: (+) human and mouse caspase-14 • Application(s): FC (intracellular) and WB • Caspase-14 has a conserved active site pentapeptide, QACRG. However, no proteolytic or biological activities have been identified so far.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13916- 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: synthetic peptide corresponding to mouse caspase-14 amino acids 2-18 • Host: mouse • Cross Reactivity: (+) human and mouse caspase-14 • Application(s): FC (intracellular) and WB • Caspase-14 has a conserved active site pentapeptide, QACRG. However, no proteolytic or biological activities have been identified so far.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13916- 1 eaImmunogen: Synthetic peptide from an internal region of human caspase-3 • Host: Rabbit • Species Reactivity: (+) Human and mouse; other species not tested • Cross Reactivity: (+) Caspase-2 (proform and active subunits) • Application(s): WB and IHC •
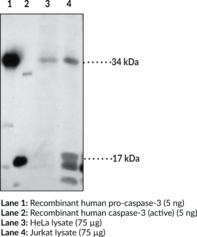
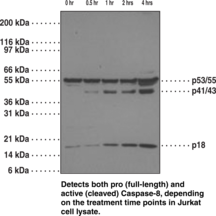
Brand:CaymanSKU:160745- 1 eaApoptosis is associated with many diseases and is induced by a family of cell death receptors and their ligands. Cell death signals are transduced by death domain containing adapter molecules and members of the caspase family of proteases. Caspase-3 is a key effector caspase in the apoptosis cascade.{7216,6292} The enzyme is efficiently activated by caspase-8, caspase-9, and granzyme B resulting in 17 and 12 kDa active subunits formed from the 34 kDa proenzyme.{7216, 8444} The substrates of caspase-3 are numerous and include pro- and anti-apoptotic proteins, downstream components of the apoptotic machinery (for example, ICAD), as well as structural and homeostatic proteins.{7216,6292} DNA fragmentation and the morphological changes associated with this final stage of apoptosis appears to be dependent upon caspase-3.{6291} Caspase-3 is expressed in a variety of tissues and cells.{8444,8443}
Brand:CaymanSKU:160745 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide from an internal region of human caspase-3 • Host: Rabbit • Species Reactivity: (+) Human and mouse; other species not tested • Cross Reactivity: (+) Caspase-2 (proform and active subunits) • Application(s): WB and IHC •
Brand:CaymanSKU:160745- 1 eaAvailable on backorder
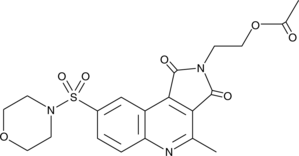
Caspase-3 inhibitor VII is a 4-methylated pyrroloquinoline that reversibly inhibits caspase-3 (IC50 = 23 nM).{34501} It displays anti-apoptotic activity in Jurkat T cells treated with staurosporine (Item No. 81590).{34501}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Caspase-3 inhibitor VII is a 4-methylated pyrroloquinoline that reversibly inhibits caspase-3 (IC50 = 23 nM).{34501} It displays anti-apoptotic activity in Jurkat T cells treated with staurosporine (Item No. 81590).{34501}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Caspase-3 inhibitor VII is a 4-methylated pyrroloquinoline that reversibly inhibits caspase-3 (IC50 = 23 nM).{34501} It displays anti-apoptotic activity in Jurkat T cells treated with staurosporine (Item No. 81590).{34501}
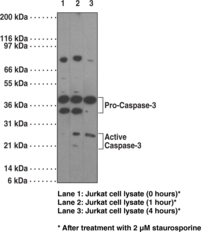
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Caspases are a family of cysteine proteases that are key mediators of programmed cell death or apoptosis.{18384} The precursor form of all caspases is composed of a prodomain and large and small catalytic subunits. The active forms of caspases are generated by several stimuli including ligand-receptor interactions, growth factor deprivation, and inhibitors of cellular functions. All known caspases require cleavage adjacent to aspartates to liberate one large and one small subunit, which associate into a tetramer to form the active enzyme. The gene for caspase-3 also known as Yama, CPP32, and apopain codes for a 32 kDa protein.{8444,18385,18386} Caspase-3 cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) to a specific 85 kDa form observed during apoptosis and is inhibitable by the CrmA protein. Other caspase-3 substrates include DNA-PK, actin, GAS2, and pro-caspase-6.{6292} Caspase-3 is activated by cleavage events at Asp28/Ser29 (between N-terminal pro-domain) and Asp175/Ser176 (between large and small subunits) to generate a large subunit of 17 kDa and a small subunit of 12 kDa.{18385}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13909 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: recombinant full-length human caspase-3 • Host: mouse, clone 31A1067• Isotype: IgG1κ • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat caspase-3 • Application(s): IHC (frozen and paraffin-embedded sections) and WB • Caspase-3 cleaves the death substrate PARP to a specific 85 kDa form observed during apoptosis and is inhibitable by the CrmA protein. Other caspase-3 substrates include DNA-PK, actin, GAS2, procaspase-6, etc.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13909- 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: recombinant full-length human caspase-3 • Host: mouse, clone 31A1067• Isotype: IgG1κ • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat caspase-3 • Application(s): IHC (frozen and paraffin-embedded sections) and WB • Caspase-3 cleaves the death substrate PARP to a specific 85 kDa form observed during apoptosis and is inhibitable by the CrmA protein. Other caspase-3 substrates include DNA-PK, actin, GAS2, procaspase-6, etc.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13909- 1 eaCaspases are a family of cysteine proteases that are key mediators of programmed cell death or apoptosis.{18384} The precursor form of all caspases is composed of a prodomain and large and small catalytic subunits. The active forms of caspases are generated by several stimuli including ligand-receptor interactions, growth factor deprivation, and inhibitors of cellular functions. All known caspases require cleavage adjacent to aspartates to liberate one large and one small subunit, which associate into an a2b2 tetramer to form the active enzyme. The gene for caspase-3, also known as yama, CPP32, and apopain, codes for a 32 kDa protein.{8444,18385,18386} Caspase-3 cleaves the death substrate poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) to a specific 85 kDa form observed during apoptosis and is inhibitable by the CrmA protein. Other caspase-3 substrates include DNA-PK, actin, GAS2, procaspase-6, etc.{6292} Caspase-3 is activated by cleavage events at Asp28/Ser29 (between N-terminal pro-domain) and Asp175/Ser176 (between large and small subunits) to generate a large subunit of 17 kDa and a small subunit of 12 kDa.{18385}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13911 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: recombinant full-length human caspase-3 • Host: mouse, clone 31A893 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human caspase-3 • Application(s): WB • Caspase-3 cleaves the death substrate PARP to a specific 85 kDa form observed during apoptosis and is inhibitable by the CrmA protein. Other caspase-3 substrates include DNA-PK, actin, GAS2, procaspase-6, etc.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13911- 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: recombinant full-length human caspase-3 • Host: mouse, clone 31A893 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human caspase-3 • Application(s): WB • Caspase-3 cleaves the death substrate PARP to a specific 85 kDa form observed during apoptosis and is inhibitable by the CrmA protein. Other caspase-3 substrates include DNA-PK, actin, GAS2, procaspase-6, etc.
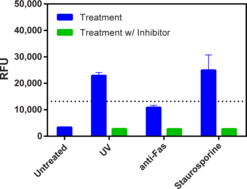
Brand:CaymanSKU:13911- 1 eaCayman’s Caspase-3/7 Fluorescence Assay Kit employs a specific substrate, N-Ac-DEVD-N’-MC-R110, which upon cleavage by active caspase-3 or caspase-7, generates a highly fluorescent product that can be measured using excitation and emission wavelengths of 485 and 535 nm, respectively. The kit is simple to use and can be easily adapted to high throughput screening for therapeutic compounds regulating activation of caspase-3 or -7. Active caspase-3 is included in the kit for use as a positive control. The caspase-3/7 inhibitor, N-Ac-DEVD-CHO, is also included in the kit for verifying the specificity of the substrate.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009135 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
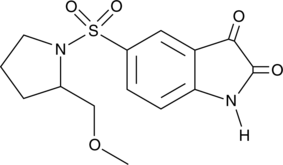
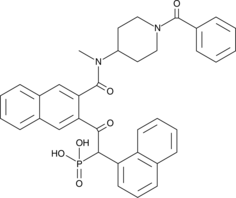
Caspase-3/7 inhibitor I is a potent, reversible, isatin sulfonamide-based inhibitor of caspase-3 (Ki(app) = 60 nM; IC50 = 120 nM) and caspase-7 (Ki(app) = 170 nM).{8115} It is a weaker inhibitor of caspase-9 (Ki(app) = 3.1 μM) and caspase-1, caspase-2, caspase-4, caspase-6, and caspase-8 (Ki(app)s ≥25 μM).{8115,8929} Caspase-3/7 inhibitor I inhibits apoptosis in camptothecin-treated Jurkat cells (IC50 = ~50 µM) and in chondrocytes (44% inhibition at 10 µM and 98% inhibition at 50 µM).{8929} The basis for the unique selectivity of this compound for caspases 3 and 7 involves the recognition of three distinct hydrophobic residues in the S2 pocket surrounding the catalytic cysteine residue.{8115}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Caspase-3/7 inhibitor I is a potent, reversible, isatin sulfonamide-based inhibitor of caspase-3 (Ki(app) = 60 nM; IC50 = 120 nM) and caspase-7 (Ki(app) = 170 nM).{8115} It is a weaker inhibitor of caspase-9 (Ki(app) = 3.1 μM) and caspase-1, caspase-2, caspase-4, caspase-6, and caspase-8 (Ki(app)s ≥25 μM).{8115,8929} Caspase-3/7 inhibitor I inhibits apoptosis in camptothecin-treated Jurkat cells (IC50 = ~50 µM) and in chondrocytes (44% inhibition at 10 µM and 98% inhibition at 50 µM).{8929} The basis for the unique selectivity of this compound for caspases 3 and 7 involves the recognition of three distinct hydrophobic residues in the S2 pocket surrounding the catalytic cysteine residue.{8115}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Cayman’s Caspase-4 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit provides a robust and easy-to-use platform for identifying novel inhibitors of human caspase-4, a major upstream effector of non-canonical inflammasome activation. The assay uses a caspase-4-specific fluorogenic substrate, Ac-LEVD-AFC. Caspase-4 cleaves this substrate generating free AFC, which can be easily quantified using a fluorescence plate reader at excitation and emission wavelengths of 400 and 505 nm, respectively. The potent and reversible caspase-4 inhibitor AC-LEVD-CHO is included as a positive control.
Brand:CaymanSKU:701820 - 384 wellsAvailable on backorder
Cayman’s Caspase-6 Inhibitor Screening Assay Kit provides a robust and easy-to-use platform for identifying novel inhibitors of human caspase-6, a cysteine protease implicated in multiple neurodegenerative disorders. The assay uses a caspase-6-specific fluorogenic substrate, Z-VEID-AFC. Caspase-6 cleaves this substrate generating free AFC, which can be easily quantified using a fluorescence plate reader at excitation and emission wavelengths of 400 and 505 nm, respectively. The potent and reversible caspase-6 inhibitor Ac-VEID-CHO is included as a positive control and inhibits caspase-6 with an IC50 value of 12 nM.
Brand:CaymanSKU:701890 - 384 wellsAvailable on backorder
Caspases are a family of cysteine proteases that are key mediators of programmed cell death or apoptosis.{18384} The precursor form of all caspases is composed of a prodomain and large and small catalytic subunits. The active forms of caspases are generated by several stimuli including ligand-receptor interactions, growth factor deprivation, and inhibitors of cellular functions. All known caspases require cleavage adjacent to aspartates to liberate one large and one small subunit, which associate into an a2b2 tetramer to form the active enzyme. Caspase-8 (FLICE) forms a direct link between the activation of CD95 and the caspase pathway. Overexpression of caspase-8 induces apoptosis, which can be blocked by inhibitors specific for the ICE family.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13913 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: human caspase-8 amino acids PVETDSEEQP • Host: mouse, clone 90A992 • Isotype: IgG1 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, chimpanzee, and Rhesus monkey caspase-8 • Application(s): FC, IHC (paraffin-embedded tissue), and WB • Caspase-8 forms a direct link between the activation of CD95 and the caspase pathway. Overexpression of caspase-8 induces apoptosis, which can be blocked by inhibitors specific for the ICE family.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13913- 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: human caspase-8 amino acids PVETDSEEQP • Host: mouse, clone 90A992 • Isotype: IgG1 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, chimpanzee, and Rhesus monkey caspase-8 • Application(s): FC, IHC (paraffin-embedded tissue), and WB • Caspase-8 forms a direct link between the activation of CD95 and the caspase pathway. Overexpression of caspase-8 induces apoptosis, which can be blocked by inhibitors specific for the ICE family.
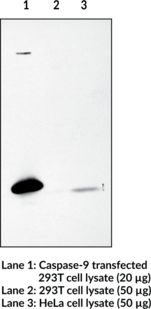
Brand:CaymanSKU:13913- 1 eaCaspase-9 and Apaf-1 bind to each other, which leads to caspase activation. Activated caspase-9 cleaves and activates caspase-3, one of the key proteases responsible for the proteolytic cleavage of many proteins in apoptosis. Caspase-9 plays a central role in cell death induced by a wide variety of apoptosis inducers including TNFa, TRAIL, anti-CD95, FADD, and TRADD. Caspase-9 is expressed in a variety of human tissues. Recently, a novel isoform of rat caspase-9 has been identified in which the C-terminus of full-length caspase-9 is replaced with an alternative peptide sequence. This protein, called Caspase-9 (CTD) (where CTD is carboxyl-terminal divergent) is expressed in multiple tissues, with the relative highest levels observed in ovary and heart. The variant C-terminus of CTD in rat is derived from an alternative exon of the rat caspase-9 gene. CTD was found primarily in the cytoplasm and was not detected in the nucleus. CTD proenzyme is not processed in the cells and lacks apoptotic activity. The CTD-transfected cells are resistant to caspase induction by cytochrome c, suggesting the CTD acts as a dominant-negative variant.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13915 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: mixture of synthetic peptides corresponding to rat caspase-9 amino acids 345-359 and 366-383 • Host: rabbit • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat caspase-9 • Application(s): WB • CTD is a novel isoform of rat caspase-9 in which the C-terminus of full-length caspase-9 is replaced with an alternative peptide sequence. It is found primarily in the cytoplasm and was not detected in the nucleus. CTD proenzyme is not processed in the cells and lacks apoptotic activity. The CTD-transfected cells are resistant to caspase induction by cytochrome c, suggesting the CTD acts as a dominant-negative variant.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13915- 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: mixture of synthetic peptides corresponding to rat caspase-9 amino acids 345-359 and 366-383 • Host: rabbit • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat caspase-9 • Application(s): WB • CTD is a novel isoform of rat caspase-9 in which the C-terminus of full-length caspase-9 is replaced with an alternative peptide sequence. It is found primarily in the cytoplasm and was not detected in the nucleus. CTD proenzyme is not processed in the cells and lacks apoptotic activity. The CTD-transfected cells are resistant to caspase induction by cytochrome c, suggesting the CTD acts as a dominant-negative variant.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13915- 1 eaAntigen: human caspase-9 amino acids 299-318 • Host: rabbit • Application(s): WB • Caspase-9 is activated by granzyme B, CPP32, or by binding Apaf-1. Activated caspase-9 cleaves and activates caspase-3, playing a central role in cell death induced by a wide variety of apoptosis inducers including TNF-α, TRAIL, anti-CD95, FADD, and TRADD.
Brand:CaymanSKU:160790- 1 eaApoptosis is related to many diseases and is induced by a family of cell death receptors and their ligands. Cell death signals are transduced by death domain containing adapter molecules and members of the caspase family of proteases. A novel member in the caspase family was recently identified and designated ICE-LAP6, Mch6, and Apaf3.{6864,6865,6874} Caspase-9 and Apaf-1 bind to each other, which leads to caspase-9 activation.{6874} Caspase-9 is also activated by granzyme B and CPP32.{6864,6865} Activated caspase-9 cleaves and activates caspase-3, one of the key proteases responsible for the proteolytic cleavage of many key proteins in apoptosis.{6874} Caspase-9 plays a central role in cell death induced by a wide variety of apoptosis inducers including TNF-α, TRAIL, anti-CD-95, FADD, and TRADD.{6863} Caspase-9 is expressed in a variety of human tissues.{6864,6865}
Brand:CaymanSKU:160790 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Antigen: human caspase-9 amino acids 299-318 • Host: rabbit • Application(s): WB • Caspase-9 is activated by granzyme B, CPP32, or by binding Apaf-1. Activated caspase-9 cleaves and activates caspase-3, playing a central role in cell death induced by a wide variety of apoptosis inducers including TNF-α, TRAIL, anti-CD95, FADD, and TRADD.
Brand:CaymanSKU:160790- 1 eaAvailable on backorder
Caspofungin is an antifungal compound that is classified as an echinocandin, as it acts by noncompetititvely inhibiting the enzyme 1,3-β glucan synthase and preventing the synthesis of glucan in the fungal cell wall.{26520} It is effective against disseminated or invasive aspergillosis and candidiasis in mice.{26517,26521} Caspofungin has a 50% minimum effective concentration against Aspergillus spp. of 0.015 µg/ml.{26518} It does not antagonize other antifungal compounds, like amphotericin B, and, in some cases, may show additive or synergistic activity.{26520,26521,20805}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Caspofungin is an antifungal compound that is classified as an echinocandin, as it acts by noncompetititvely inhibiting the enzyme 1,3-β glucan synthase and preventing the synthesis of glucan in the fungal cell wall.{26520} It is effective against disseminated or invasive aspergillosis and candidiasis in mice.{26517,26521} Caspofungin has a 50% minimum effective concentration against Aspergillus spp. of 0.015 µg/ml.{26518} It does not antagonize other antifungal compounds, like amphotericin B, and, in some cases, may show additive or synergistic activity.{26520,26521,20805}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Caspofungin is an antifungal compound that is classified as an echinocandin, as it acts by noncompetititvely inhibiting the enzyme 1,3-β glucan synthase and preventing the synthesis of glucan in the fungal cell wall.{26520} It is effective against disseminated or invasive aspergillosis and candidiasis in mice.{26517,26521} Caspofungin has a 50% minimum effective concentration against Aspergillus spp. of 0.015 µg/ml.{26518} It does not antagonize other antifungal compounds, like amphotericin B, and, in some cases, may show additive or synergistic activity.{26520,26521,20805}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Caspofungin is an antifungal compound that is classified as an echinocandin, as it acts by noncompetititvely inhibiting the enzyme 1,3-β glucan synthase and preventing the synthesis of glucan in the fungal cell wall.{26520} It is effective against disseminated or invasive aspergillosis and candidiasis in mice.{26517,26521} Caspofungin has a 50% minimum effective concentration against Aspergillus spp. of 0.015 µg/ml.{26518} It does not antagonize other antifungal compounds, like amphotericin B, and, in some cases, may show additive or synergistic activity.{26520,26521,20805}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Glucosidases catalyze the cleavage of individual glucosyl residues from various glycoconjugates, including complex carbohydrates and glycoproteins. Castanospermine is an inhibitor of both α- and β-glucosidases, inhibiting lysosomal and neutral α-glucosidases with Ki values of 0.1 and 10 μM, respectively, and lysosomal and cytosolic β-glucosidases with Ki values of 7 and 40 μM, respectively.{20414} It is effective both in vitro and in vivo.{20410,20409} Through its effects on glucosidases, castanospermine blocks N-linked glycosylation during post-translational modification of proteins, affecting protein trafficking and cell functions that are dependent on glycosylation, including angiogenesis.{20409,20411} Castanospermine also interferes with viral replication and infection that is dependent on glucosidase activity.{16269,20412,20413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11313 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Glucosidases catalyze the cleavage of individual glucosyl residues from various glycoconjugates, including complex carbohydrates and glycoproteins. Castanospermine is an inhibitor of both α- and β-glucosidases, inhibiting lysosomal and neutral α-glucosidases with Ki values of 0.1 and 10 μM, respectively, and lysosomal and cytosolic β-glucosidases with Ki values of 7 and 40 μM, respectively.{20414} It is effective both in vitro and in vivo.{20410,20409} Through its effects on glucosidases, castanospermine blocks N-linked glycosylation during post-translational modification of proteins, affecting protein trafficking and cell functions that are dependent on glycosylation, including angiogenesis.{20409,20411} Castanospermine also interferes with viral replication and infection that is dependent on glucosidase activity.{16269,20412,20413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11313 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Glucosidases catalyze the cleavage of individual glucosyl residues from various glycoconjugates, including complex carbohydrates and glycoproteins. Castanospermine is an inhibitor of both α- and β-glucosidases, inhibiting lysosomal and neutral α-glucosidases with Ki values of 0.1 and 10 μM, respectively, and lysosomal and cytosolic β-glucosidases with Ki values of 7 and 40 μM, respectively.{20414} It is effective both in vitro and in vivo.{20410,20409} Through its effects on glucosidases, castanospermine blocks N-linked glycosylation during post-translational modification of proteins, affecting protein trafficking and cell functions that are dependent on glycosylation, including angiogenesis.{20409,20411} Castanospermine also interferes with viral replication and infection that is dependent on glucosidase activity.{16269,20412,20413}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11313 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Casticin is a flavonol isolated from A. annua, V. trifolia, and V. agnus-castus that decreases proliferation in K562, HL-60, and Kasumi-1 leukemia cell lines (IC50s = 5.95, 4.82, and 15.56 µM, respectively).{38024} It blocks TGF-β/SMAD signaling in LX2 cells preventing activation, inhibiting proliferation, and inducing apoptosis of these hepatic stellate cells.{38025} In a mouse model of liver fibrosis, casticin (20 mg/kg) decreases TGF-β1 mRNA and phosphorylated SMAD (p-SMAD) levels. Casticin induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and breast cancer cells.{27628,27627} It also downregulates Twist and prevents the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human HCC SMMC-7721 cells.{27268}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Casticin is a flavonol isolated from A. annua, V. trifolia, and V. agnus-castus that decreases proliferation in K562, HL-60, and Kasumi-1 leukemia cell lines (IC50s = 5.95, 4.82, and 15.56 µM, respectively).{38024} It blocks TGF-β/SMAD signaling in LX2 cells preventing activation, inhibiting proliferation, and inducing apoptosis of these hepatic stellate cells.{38025} In a mouse model of liver fibrosis, casticin (20 mg/kg) decreases TGF-β1 mRNA and phosphorylated SMAD (p-SMAD) levels. Casticin induces apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and breast cancer cells.{27628,27627} It also downregulates Twist and prevents the epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in human HCC SMMC-7721 cells.{27268}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Brand:CaymanSKU:707010 - 1 eaAvailable on backorder
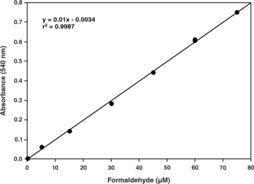
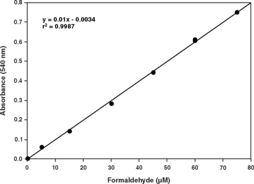
Catalase (EC 1.11.1.6; 2H2O2 oxidoreductase) is an ubiquitous antioxidant enzyme that is present in most aerobic cells. Catalase (CAT) is involved in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a reactive oxygen species (ROS), which is a toxic product of both normal aerobic metabolism and pathogenic ROS production. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of two molecules of H2O2 to molecular oxygen and two molecules of water (catalytic activity). CAT also demonstrates peroxidatic activity, in which low molecular weight alcohols can serve as electron donors. While the aliphatic alcohols serve as specific substrates for CAT, other enzymes with peroxidatic activity do not utilize these substrates. In humans, the highest levels of catalase are found in liver, kidney, and erythrocytes, where it is believed to account for the majority of hydrogen peroxide decomposition. The Cayman Chemical Catalase Assay Kit utilizes the peroxidatic function of CAT for determination of enzyme activity. The method is based on the reaction of the enzyme with methanol in the presence of an optimal concentration of H2O2. The formaldehyde produced is measured spectrophotometrically with 4-amino-3-hydrazino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole (Purpald) as the chromogen.{9608,1446} Purpald specifically forms a bicyclic heterocycle with aldehydes, which upon oxidation changes from colorless to a purple color.{9608,1446} The assay can be used to measure CAT activity in plasma, serum, erythrocyte lysates, tissue homogenates, and cell lysates.
Brand:CaymanSKU:707002 - 480 wellsAvailable on backorder
Catalase (EC 1.11.1.6; 2H2O2 oxidoreductase) is an ubiquitous antioxidant enzyme that is present in most aerobic cells. Catalase (CAT) is involved in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a reactive oxygen species (ROS), which is a toxic product of both normal aerobic metabolism and pathogenic ROS production. This enzyme catalyzes the conversion of two molecules of H2O2 to molecular oxygen and two molecules of water (catalytic activity). CAT also demonstrates peroxidatic activity, in which low molecular weight alcohols can serve as electron donors. While the aliphatic alcohols serve as specific substrates for CAT, other enzymes with peroxidatic activity do not utilize these substrates. In humans, the highest levels of catalase are found in liver, kidney, and erythrocytes, where it is believed to account for the majority of hydrogen peroxide decomposition. The Cayman Chemical Catalase Assay Kit utilizes the peroxidatic function of CAT for determination of enzyme activity. The method is based on the reaction of the enzyme with methanol in the presence of an optimal concentration of H2O2. The formaldehyde produced is measured spectrophotometrically with 4-amino-3-hydrazino-5-mercapto-1,2,4-triazole (Purpald) as the chromogen.{9608,1446} Purpald specifically forms a bicyclic heterocycle with aldehydes, which upon oxidation changes from colorless to a purple color.{9608,1446} The assay can be used to measure CAT activity in plasma, serum, erythrocyte lysates, tissue homogenates, and cell lysates.
Brand:CaymanSKU:707002 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
Catalase (CAT) is a ubiquitous antioxidant enzyme involved in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a toxic product of both normal aerobic metabolism and pathogenic ROS production. It catalyzes the conversion of two molecules of H2O2 to molecular oxygen and two molecules of water (catalytic activity). CAT also demonstrates peroxidatic activity, in which low molecular weight alcohols can serve as electron donors. While aliphatic alcohols serve as specific substrates for CAT, other enzymes with peroxidatic activity do not utilize these substrates. Cayman’s Catalase Assay Kit utilizes the peroxidatic function of CAT for determination of enzyme activity in plasma, serum, erythrocyte lysates, tissue homogenates, and cell lysates. The method is based on the reaction of the enzyme with methanol in the presence of an optimal concentration of H2O2. The formaldehyde produced is measured colorimetrically with Purpald, a chromogen that specifically forms a bicyclic heterocycle with aldehydes, which upon oxidation changes from colorless to a purple color.
Brand:CaymanSKU:700910 - 480 wellsAvailable on backorder
Catalase (CAT) is a ubiquitous antioxidant enzyme involved in the detoxification of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a toxic product of both normal aerobic metabolism and pathogenic ROS production. It catalyzes the conversion of two molecules of H2O2 to molecular oxygen and two molecules of water (catalytic activity). CAT also demonstrates peroxidatic activity, in which low molecular weight alcohols can serve as electron donors. While aliphatic alcohols serve as specific substrates for CAT, other enzymes with peroxidatic activity do not utilize these substrates. Cayman’s Catalase Assay Kit utilizes the peroxidatic function of CAT for determination of enzyme activity in plasma, serum, erythrocyte lysates, tissue homogenates, and cell lysates. The method is based on the reaction of the enzyme with methanol in the presence of an optimal concentration of H2O2. The formaldehyde produced is measured colorimetrically with Purpald, a chromogen that specifically forms a bicyclic heterocycle with aldehydes, which upon oxidation changes from colorless to a purple color.
Brand:CaymanSKU:700910 - 96 wellsAvailable on backorder
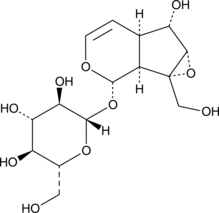
Catalpol is an iridoid glycoside that has been isolated from R. glutinosa and has diverse biological activities, including anti-apoptotic, pro-angiogenic, and radioprotective properties.{41802} It protects against mitochondrial pathway-dependent apoptosis in PC12 rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells and H9c2 rat embryonic ventricular myocardial cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM.{41800,41801} Catalpol pretreatment reduces apoptosis and improves viability in AHH-1 human lymphocyte cells exposed to ionizing radiation and reduces intestinal damage induced by radiation in mice when used at concentrations and doses ranging from of 25 to 100 µg/ml and 25 to 100 mg/kg, respectively.{41799} In a rat model of stroke, catalpol (5 mg/kg, i.p.) increases the expression of erythropoietin and VEGF and improves angiogenesis in the brain.{41803}
Brand:CaymanSKU:24925 - 1 gAvailable on backorder
Catalpol is an iridoid glycoside that has been isolated from R. glutinosa and has diverse biological activities, including anti-apoptotic, pro-angiogenic, and radioprotective properties.{41802} It protects against mitochondrial pathway-dependent apoptosis in PC12 rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells and H9c2 rat embryonic ventricular myocardial cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM.{41800,41801} Catalpol pretreatment reduces apoptosis and improves viability in AHH-1 human lymphocyte cells exposed to ionizing radiation and reduces intestinal damage induced by radiation in mice when used at concentrations and doses ranging from of 25 to 100 µg/ml and 25 to 100 mg/kg, respectively.{41799} In a rat model of stroke, catalpol (5 mg/kg, i.p.) increases the expression of erythropoietin and VEGF and improves angiogenesis in the brain.{41803}
Brand:CaymanSKU:24925 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Catalpol is an iridoid glycoside that has been isolated from R. glutinosa and has diverse biological activities, including anti-apoptotic, pro-angiogenic, and radioprotective properties.{41802} It protects against mitochondrial pathway-dependent apoptosis in PC12 rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells and H9c2 rat embryonic ventricular myocardial cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM.{41800,41801} Catalpol pretreatment reduces apoptosis and improves viability in AHH-1 human lymphocyte cells exposed to ionizing radiation and reduces intestinal damage induced by radiation in mice when used at concentrations and doses ranging from of 25 to 100 µg/ml and 25 to 100 mg/kg, respectively.{41799} In a rat model of stroke, catalpol (5 mg/kg, i.p.) increases the expression of erythropoietin and VEGF and improves angiogenesis in the brain.{41803}
Brand:CaymanSKU:24925 - 250 mgAvailable on backorder
Catalpol is an iridoid glycoside that has been isolated from R. glutinosa and has diverse biological activities, including anti-apoptotic, pro-angiogenic, and radioprotective properties.{41802} It protects against mitochondrial pathway-dependent apoptosis in PC12 rat adrenal pheochromocytoma cells and H9c2 rat embryonic ventricular myocardial cells when used at a concentration of 10 µM.{41800,41801} Catalpol pretreatment reduces apoptosis and improves viability in AHH-1 human lymphocyte cells exposed to ionizing radiation and reduces intestinal damage induced by radiation in mice when used at concentrations and doses ranging from of 25 to 100 µg/ml and 25 to 100 mg/kg, respectively.{41799} In a rat model of stroke, catalpol (5 mg/kg, i.p.) increases the expression of erythropoietin and VEGF and improves angiogenesis in the brain.{41803}
Brand:CaymanSKU:24925 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Vinca alkaloids are an important class of cell cycle-dependent antimitotic agents. Catharanthine is a precursor of the vinblastine and vincristine group of alkaloids found in the Vinca plant, C. roseus that have been used widely in chemotherapy regimens.{22468} It is biologically active in synergy with similar indole alkaloids and can be used as starting material for the synthesis of vinblastine and vincristine.{22469,22467}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11695 - 100 mgAvailable on backorder
Vinca alkaloids are an important class of cell cycle-dependent antimitotic agents. Catharanthine is a precursor of the vinblastine and vincristine group of alkaloids found in the Vinca plant, C. roseus that have been used widely in chemotherapy regimens.{22468} It is biologically active in synergy with similar indole alkaloids and can be used as starting material for the synthesis of vinblastine and vincristine.{22469,22467}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11695 - 50 mgAvailable on backorder
Vinca alkaloids are an important class of cell cycle-dependent antimitotic agents. Catharanthine is a precursor of the vinblastine and vincristine group of alkaloids found in the Vinca plant, C. roseus that have been used widely in chemotherapy regimens.{22468} It is biologically active in synergy with similar indole alkaloids and can be used as starting material for the synthesis of vinblastine and vincristine.{22469,22467}
Brand:CaymanSKU:11695 - 500 mgAvailable on backorder
Cathepsin G inhibitor I is a potent and selective inhibitor of cathepsin G (IC50 = 53 nM).{25673} It weakly inhibits or has no effect on related proteases, including chymotrypsin, thrombin, plasmin, trypsin, tryptase, and elastase.{25673}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Cathepsin G inhibitor I is a potent and selective inhibitor of cathepsin G (IC50 = 53 nM).{25673} It weakly inhibits or has no effect on related proteases, including chymotrypsin, thrombin, plasmin, trypsin, tryptase, and elastase.{25673}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Cathepsin G inhibitor I is a potent and selective inhibitor of cathepsin G (IC50 = 53 nM).{25673} It weakly inhibits or has no effect on related proteases, including chymotrypsin, thrombin, plasmin, trypsin, tryptase, and elastase.{25673}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Cathepsin L inhibitor is a potent inhibitor of cathepsin L (IC50 = 0.85 nM).{41143} It is selective for cathepsin L over calpain II and cathepsin B (IC50s = 184, and 85.1 nM, respectively). It is trypanocidal with an ED50 value of 45 nM against T. brucei that is well below the ED50 value of 21,500 nM for human HL-60 cells.{41145} Cathepsin L inhibitor completely suppresses osteoclastic pit formation on femur slices isolated from bovine cortical bone at a concentration of 1 μg/ml.{41143},{41144} In vivo, cathepsin L inhibitor (2.5-10 mg/kg) inhibits bone loss in a mouse model of osteoporosis in a dose-dependent manner.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23249 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Cathepsin L inhibitor is a potent inhibitor of cathepsin L (IC50 = 0.85 nM).{41143} It is selective for cathepsin L over calpain II and cathepsin B (IC50s = 184, and 85.1 nM, respectively). It is trypanocidal with an ED50 value of 45 nM against T. brucei that is well below the ED50 value of 21,500 nM for human HL-60 cells.{41145} Cathepsin L inhibitor completely suppresses osteoclastic pit formation on femur slices isolated from bovine cortical bone at a concentration of 1 μg/ml.{41143},{41144} In vivo, cathepsin L inhibitor (2.5-10 mg/kg) inhibits bone loss in a mouse model of osteoporosis in a dose-dependent manner.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23249 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Cathepsin L inhibitor is a potent inhibitor of cathepsin L (IC50 = 0.85 nM).{41143} It is selective for cathepsin L over calpain II and cathepsin B (IC50s = 184, and 85.1 nM, respectively). It is trypanocidal with an ED50 value of 45 nM against T. brucei that is well below the ED50 value of 21,500 nM for human HL-60 cells.{41145} Cathepsin L inhibitor completely suppresses osteoclastic pit formation on femur slices isolated from bovine cortical bone at a concentration of 1 μg/ml.{41143},{41144} In vivo, cathepsin L inhibitor (2.5-10 mg/kg) inhibits bone loss in a mouse model of osteoporosis in a dose-dependent manner.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23249 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder
Cathepsin L inhibitor is a potent inhibitor of cathepsin L (IC50 = 0.85 nM).{41143} It is selective for cathepsin L over calpain II and cathepsin B (IC50s = 184, and 85.1 nM, respectively). It is trypanocidal with an ED50 value of 45 nM against T. brucei that is well below the ED50 value of 21,500 nM for human HL-60 cells.{41145} Cathepsin L inhibitor completely suppresses osteoclastic pit formation on femur slices isolated from bovine cortical bone at a concentration of 1 μg/ml.{41143},{41144} In vivo, cathepsin L inhibitor (2.5-10 mg/kg) inhibits bone loss in a mouse model of osteoporosis in a dose-dependent manner.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23249 - 5 mgAvailable on backorder
Ion channels are integral membrane proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of living cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient.{17533} They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells because their main function is to regulate the flow of ions across this membrane. Whereas some ion channels permit the passage of ions based on charge, others conduct based on a ionic species, such as sodium or potassium. Furthermore, in some ion channels, the passage is governed by a gate which is controlled by chemical or electrical signals, temperature, or mechanical forces. There are a few main classifications of gated ion channels. There are voltage-gated ion channels, ligand-gated, other gating systems, and finally those that are classified differently, having more exotic characteristics. The first are voltage-gated ion channels which open and close in response to membrane potential. These are then seperated into sodium, calcium, potassium, proton, transient receptor, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, each of which is responsible for a unique role. Ligand-gated ion channels are also known as ionotropic receptors, and they open in response to specific ligand molecules binding to the extracellular domain of the receptor protein. The other gated classifications include activation and inactivation by second messengers, inward-rectifier potassium channels, calcium-activated potassium channels, two-pore-domain potassium channels, light-gated channels, mechano-sensitive ion channels, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Finally, the other classifications are based on less normal characteristics such as two-pore channels, and transient receptor potential channels.{17535} Specifically, Cav1.2 is a cardiac L-type calcium channel and is important for excitation and contraction of the heart.{17551} It may be associated with a variant of Long QT syndrome called Timothy’s syndrome{17552,17553} and also with Brugada syndrome. Some references also suggest it is related to bipolar disease as well.{17553}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13702 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: fusion protein amino acids 1,507-1,733 • Isotype: IgG2b • Host: mouse, clone S57-46 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cav1.2 • Application(s): ICC, IF, IHC, and WB • Cav1.2 is a cardiac L-type calcium channel important for excitation and contraction of the heart.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13702- 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: fusion protein amino acids 1,507-1,733 • Isotype: IgG2b • Host: mouse, clone S57-46 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cav1.2 • Application(s): ICC, IF, IHC, and WB • Cav1.2 is a cardiac L-type calcium channel important for excitation and contraction of the heart.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13702- 100 µgIon channels are integral membrane proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of living cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient.{17533} They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells because their main function is to regulate the flow of ions across this membrane. Whereas some ion channels permit the passage of ions based on charge, others conduct based on a ionic species, such as sodium or potassium. Furthermore, in some ion channels, the passage is governed by a gate which is controlled by chemical or electrical signals, temperature, or mechanical forces. There are a few main classifications of gated ion channels. There are voltage-gated ion channels, ligand-gated, other gating systems, and finally those that are classified differently, having more exotic characteristics. The first are voltage-gated ion channels which open and close in response to membrane potential. These are then seperated into sodium, calcium, potassium, proton, transient receptor, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, each of which is responsible for a unique role. Ligand-gated ion channels are also known as ionotropic receptors, and they open in response to specific ligand molecules binding to the extracellular domain of the receptor protein. The other gated classifications include activation and inactivation by second messengers, inward-rectifier potassium channels, calcium-activated potassium channels, two-pore-domain potassium channels, light-gated channels, mechano-sensitive ion channels, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Finally, the other classifications are based on less normal characteristics such as two-pore channels, and transient receptor potential channels.{17535} Specifically, Cav1.3, also known as the calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L type, α1D subunit (CACNA1D), is a human gene. Cav1.3 subunits are primarily expressed in neurons and neuroendocrine cells. Some studies suggest however that Cav1.3 is also found in the atria, and may figure prominently in atrial arrhythmias.{17540} Cav1.3 also carries the primary sensory receptors of the mammalian cochlea, and are also expressed in the electromotile outer hair cells.{17541}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13703 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: fusion protein amino acids 2,025-2,161 (C-terminal) of rat Cav1.3 • Isotype: IgG1 • Host: mouse, clone S38-8 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cav1.3 • Application(s): ICC, IF, IHC, and WB • Cav1.3 subunits are primarily expressed in neurons and neuroendocrine cells and potentially in heart atria and may figure prominently in atrial arrhythmias. Cav1.3 also carries the primary sensory receptors of the mammalian cochlea and also expressed in the electromotile outer hair cells.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13703- 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: fusion protein amino acids 2,025-2,161 (C-terminal) of rat Cav1.3 • Isotype: IgG1 • Host: mouse, clone S38-8 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cav1.3 • Application(s): ICC, IF, IHC, and WB • Cav1.3 subunits are primarily expressed in neurons and neuroendocrine cells and potentially in heart atria and may figure prominently in atrial arrhythmias. Cav1.3 also carries the primary sensory receptors of the mammalian cochlea and also expressed in the electromotile outer hair cells.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13703- 100 µgIon channels are integral membrane proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of living cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient.{17533} They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells and their main function is to regulate the flow of ions across this membrane. Whereas some ion channels permit the passage of ions based on charge, others conduct based on a ionic species, such as sodium or potassium. Furthermore, in some ion channels, the passage is governed by a gate which is controlled by chemical or electrical signals, temperature, or mechanical forces. There are a few main classifications of gated ion channels. There are voltage-gated ion channels, ligand-gated, other gating systems, and finally those that are classified differently, having more exotic characteristics. The first are voltage-gated ion channels which open and close in response to membrane potential. These are then seperated into sodium, calcium, potassium, proton, transient receptor, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, each of which is responsible for a unique role. Ligand-gated ion channels are also known as ionotropic receptors and they open in response to specific ligand molecules binding to the extracellular domain of the receptor protein. The other gated classifications include activation and inactivation by second messengers, inward-rectifier potassium channels, calcium-activated potassium channels, two-pore-domain potassium channels, light-gated channels, mechano-sensitive ion channels, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Finally, the other classifications are based on less normal characteristics such as two-pore channels and transient receptor potential channels.{17535} Cav1.3, also known as the calcium channel, voltage-dependent, L-type, α1D subunit (CACNA1D), is a human gene. Cav1.3 subunits are primarily expressed in neurons and neuroendocine cells. Some studies suggest however that Cav1.3 is also found in the atria and may figure prominently in atrial arrhythmias.{17540} Cav1.3 also carries the primary sensory receptors of the mammalian cochlea and are also expressed in the electromotile outer hair cells.{17541}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13706 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: fusion protein amino acids 859-875 (N-terminal) of human Cav1.3 • Isotype: IgG2a • Host: mouse, clone S48A-9 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cav1.3 • Application(s): ICC, IHC, and WB • Cav1.3 subunits are primarily expressed in neurons and neuroendocrine cells and potentially in heart atria and may figure prominently in atrial arrhythmias. Cav1.3 also carries the primary sensory receptors of the mammalian cochlea and also expressed in the electromotile outer hair cells.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13706- 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: fusion protein amino acids 859-875 (N-terminal) of human Cav1.3 • Isotype: IgG2a • Host: mouse, clone S48A-9 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cav1.3 • Application(s): ICC, IHC, and WB • Cav1.3 subunits are primarily expressed in neurons and neuroendocrine cells and potentially in heart atria and may figure prominently in atrial arrhythmias. Cav1.3 also carries the primary sensory receptors of the mammalian cochlea and also expressed in the electromotile outer hair cells.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13706- 100 µgIon channels are integral membrane proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of living cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient.{17533} They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells and their main function is to regulate the flow of ions across this membrane. Whereas some ion channels permit the passage of ions based on charge, others conduct based on a ionic species, such as sodium or potassium. Furthermore, in some ion channels, the passage is governed by a gate which is controlled by chemical or electrical signals, temperature, or mechanical forces. There are a few main classifications of gated ion channels. There are voltage-gated ion channels, ligand-gated, other gating systems, and finally those that are classified differently, having more exotic characteristics. The first are voltage-gated ion channels which open and close in response to membrane potential. These are then seperated into sodium, calcium, potassium, proton, transient receptor, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, each of which is responsible for a unique role. Ligand-gated ion channels are also known as ionotropic receptors and they open in response to specific ligand molecules binding to the extracellular domain of the receptor protein. The other gated classifications include activation and inactivation by second messengers, inward-rectifier potassium channels, calcium-activated potassium channels, two-pore-domain potassium channels, light-gated channels, mechano-sensitive ion channels, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Finally, the other classifications are based on less normal characteristics such as two-pore channels and transient receptor potential channels.{17535} Cav3.2 is a protein which in humans is encoded by the CACNA1H gene. Studies suggest certain mutations in this gene lead to childhood absence epilepsy.{17596,17598} Studies also suggest that the up-regulations of Cav3.2 may participate in the progession of prostate cancer toward an androgen-independent stage.{17599}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13704 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: fusion protein amino acids 1,019-1,293 (II-III loop) human Cav3.2 • Isotype: IgG1 • Host: mouse, clone S55-10 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cav3.2 • Application(s): ICC, IHC, and WB • Cav3.2 is a protein encoded by the CACNA1H gene, which is associated with childhood absence epilepsy. Studies suggest that the up-regulations of Cav3.2 may participate in the progession of prostate cancer toward an androgen-independent stage.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13704- 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: fusion protein amino acids 1,019-1,293 (II-III loop) human Cav3.2 • Isotype: IgG1 • Host: mouse, clone S55-10 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cav3.2 • Application(s): ICC, IHC, and WB • Cav3.2 is a protein encoded by the CACNA1H gene, which is associated with childhood absence epilepsy. Studies suggest that the up-regulations of Cav3.2 may participate in the progession of prostate cancer toward an androgen-independent stage.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13704- 100 µgIon channels are integral membrane proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of living cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient.{17533} They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells because their main function is to regulate the flow of ions across this membrane. Whereas some ion channels permit the passage of ions based on charge, others conduct based on a ionic species, such as sodium or potassium. Furthermore, in some ion channels, the passage is governed by a gate which is controlled by chemical or electrical signals, temperature, or mechanical forces. There are a few main classifications of gated ion channels. There are voltage-gated ion channels, ligand-gated, other gating systems, and finally those that are classified differently, having more exotic characteristics. The first are voltage-gated ion channels which open and close in response to membrane potential. These are then spearated into sodium, calcium, potassium, proton, transient receptor, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, each of which is responsible for a unique role. Ligand-gated ion channels are also known as ionotropic receptors, and they open in response to specific ligand molecules binding to the extracellular domain of the receptor protein. The other gated classifications include activation and inactivation by second messengers, inward-rectifier potassium channels, calcium-activated potassium channels, two-pore-domain potassium channels, light-gated channels, mechano-sensitive ion channels, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Finally, the other classifications are based on less normal characteristics such as two-pore channels, and transient receptor potential channels.{17535} Calcium channel, voltage-dependent, β1 subunit, also known as CACNB1, is a human gene. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the calcium channel β subunit family. It plays an important role in the calcium channel by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the α1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation. Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and three transcript variants encoding three distinct isoforms have been identified.{17535,17536}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13700 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: rat Cavβ1 amino acids 19-34 • Isotype: IgG2a • Host: mouse, clone S7-18 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cavβ1 • Application(s): ICC, IHC, and WB • Cavβ1 plays an important role in the calcium channel by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the α1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13700- 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: rat Cavβ1 amino acids 19-34 • Isotype: IgG2a • Host: mouse, clone S7-18 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cavβ1 • Application(s): ICC, IHC, and WB • Cavβ1 plays an important role in the calcium channel by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the α1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13700- 100 µgIon channels are integral membrane proteins that help establish and control the small voltage gradient across the plasma membrane of living cells by allowing the flow of ions down their electrochemical gradient.{17533} They are present in the membranes that surround all biological cells because their main function is to regulate the flow of ions across this membrane. Whereas some ion channels permit the passage of ions based on charge, others conduct based on a ionic species, such as sodium or potassium. Furthermore, in some ion channels, the passage is governed by a gate which is controlled by chemical or electrical signals, temperature, or mechanical forces. There are a few main classifications of gated ion channels. There are voltage-gated ion channels, ligand-gated, other gating systems, and finally those that are classified differently, having more exotic characteristics. The first are voltage-gated ion channels which open and close in response to membrane potential. These are then seperated into sodium, calcium, potassium, proton, transient receptor, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels, each of which is responsible for a unique role. Ligand-gated ion channels are also known as ionotropic receptors, and they open in response to specific ligand molecules binding to the extracellular domain of the receptor protein. The other gated classifications include activation and inactivation by second messengers, inward-rectifier potassium channels, calcium-activated potassium channels, two-pore-domain potassium channels, light-gated channels, mechano-sensitive ion channels, and cyclic nucleotide-gated channels. Finally, the other classifications are based on less normal characteristics such as two-pore channels, and transient receptor potential channels.{17535} Specifically, this gene encodes a member of the β subunit family, a protein in the voltage-dependent calcium channel complex. Calcium channels mediate the influx of calcium ions into the cell upon membrane polarization and consist of a complex of α1, α3/δ, β, and γ subunits in a 1:1:1:1 ratio. Various versions of each of these subunits exist, either expressed from similar genes or the result of alternative splicing. The protein described in this record plays an important role in calcium channel function by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the a1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation. Certain mutations in this gene have been associated with idiopathic generalized epilepsy (IGE) and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME). Alternate transcriptional splice variants of this gene, encoding different isoforms, have been characterized.{17542,17543}
Brand:CaymanSKU:13701 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: rat Cavβ4 amino acids 458-474 • Isotype: IgG1 • Host: mouse, clone S10-7 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cavβ4 • Application(s): ICC, IF, IHC, and WB • Cavβ4 plays an important role in calcium channel function by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the α1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13701- 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Antigen: rat Cavβ4 amino acids 458-474 • Isotype: IgG1 • Host: mouse, clone S10-7 • Cross Reactivity: (+) human, mouse, and rat Cavβ4 • Application(s): ICC, IF, IHC, and WB • Cavβ4 plays an important role in calcium channel function by modulating G protein inhibition, increasing peak calcium current, controlling the α1 subunit membrane targeting and shifting the voltage dependence of activation and inactivation.
Brand:CaymanSKU:13701- 100 µgProstaglandins are rapidly inactivated in vivo by the action of 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-hydroxy PGDH). This enzyme oxidizes the 15-hydroxyl group and hydrogenates the 13,14-double bond, producing 13,14-dihydro-15 keto metabolites with greatly reduced biological activity. CAY10397 is a selective inhibitor of 15-hydroxy PGDH with an IC50 of approximately 10 µM.{8455} CAY10397 acts to prolong the lifetime and activity of endogenously produced prostaglandins both in cell culture and in vivo.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70130 - 1 mgAvailable on backorder
Prostaglandins are rapidly inactivated in vivo by the action of 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-hydroxy PGDH). This enzyme oxidizes the 15-hydroxyl group and hydrogenates the 13,14-double bond, producing 13,14-dihydro-15 keto metabolites with greatly reduced biological activity. CAY10397 is a selective inhibitor of 15-hydroxy PGDH with an IC50 of approximately 10 µM.{8455} CAY10397 acts to prolong the lifetime and activity of endogenously produced prostaglandins both in cell culture and in vivo.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70130 - 10 mgAvailable on backorder
Prostaglandins are rapidly inactivated in vivo by the action of 15-hydroxy prostaglandin dehydrogenase (15-hydroxy PGDH). This enzyme oxidizes the 15-hydroxyl group and hydrogenates the 13,14-double bond, producing 13,14-dihydro-15 keto metabolites with greatly reduced biological activity. CAY10397 is a selective inhibitor of 15-hydroxy PGDH with an IC50 of approximately 10 µM.{8455} CAY10397 acts to prolong the lifetime and activity of endogenously produced prostaglandins both in cell culture and in vivo.
Brand:CaymanSKU:70130 - 25 mgAvailable on backorder