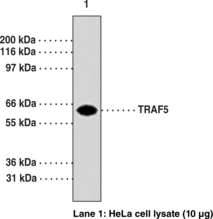
Description
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-induced signaling is mediated through association of TNF receptor (TNFR) with adaptor proteins, such as TNF receptor-associated factors (TRAFs). TRAFs form a family of cytoplasmic adapter proteins that mediate signal transduction from many members of the TNF-receptor superfamily (e.g., RANK, CD30, CD40, etc.) and the interleukin-1 receptor. The carboxy-terminal region of TRAFs is required for self-association and interaction with receptor cytoplasmic domains following ligand-induced oligomerization. Recent molecular cloning studies have led to identification of seven TRAFs (TRAF1-TRAF7).{19431,18761,19383,19384,19385} Human TRAF5 is a 557-amino acid protein. TRAF5 is implicated in NF-kB and c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase activation by members of the TNF receptor superfamily, including CD27, CD30, CD40, and lymphotoxin-β receptor. Targeted disruption of TRAF5 gene causes defects in CD40-CD27 mediated lymphocyte activation.{19385}
Synonyms:
Immunogen: fusion protein corresponding to amino acids 77-186 of human TRAF5
Formulation: 100 µg of protein G-purified IgG in 200 µl PBS containing 0.05% BSA and 0.05% sodium azide
Isotype:
Applications: WB
Origin: Animal/Mouse
Stability: 180 days
Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity