Description
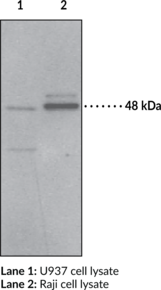
Immunogen: synthetic peptide from the N-terminal region of human protein PAF receptor • Host: rabbit • Species Reactivity: (+) Human and green monkey PAF receptor • Application(s): FC, IHC, and WB • PAF is a biologically active phospholipid whose biological effects include activation of platelets, polymorphonuclear leukocytes, monocytes, and macrophages. PAF increases vascular permeability, decreases cardiac output, induces hypotension, and stimulates uterine contraction.
Synonyms: Platelet-activating Factor Receptor
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide from the N-terminal region of human PAF receptor
Formulation: 500 µl of peptide affinity-purified antibody
Isotype:
Applications: FC, IHC, and WB
Origin: Animal/Rabbit
Stability: 365 days
Application|Flow Cytometry||Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Blood|Coagulation & Hemostasis||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Glycerophospholipids