Description
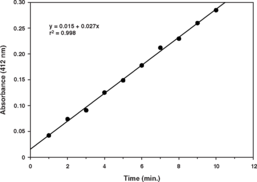
PAF-AH catalyzes the hydrolysis of the potent biologically-active phospholipid PAF, generating inactive lyso-PAF. Cayman’s PAF-AH assay kit provides an accurate and convenient method for measurement of PAF-AH activity. The assay uses 2-thio PAF which serves as a substrate for PAF-AH. Upon hydrolysis of the acetyl thioester bond at the sn-2 position by PAF-AH, free thiols are detected using Ellman’s reagent.
Formulation:
Formal name:
Synonyms: Lp-PLA2|PAF-AH
Host:
Imunogen:
Applications:
Clone:
Purity:
Origin:
Product Type|Assay Kits|Colorimetric Assays||Product Type|Assay Kits|Enzyme Activity||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Blood|Coagulation & Hemostasis||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Lipids & Lipoproteins|Lipoproteins