Description
The NMDA receptor (NMDAR) plays an essential role in memory, neuronal development, and it has also been implicated in several disorders of the central nervous system including Alzheimer’s disease, epilepsy, and ischemic neuronal death. {14637,14639,14638} The NR1 protein can form NMDA activated channels when expressed in Xenopus oocytes but the currents in such channels are much smaller than those seen in situ. Channels with more physiological characteristics are produced when the NR1 subunit is combined with one or more of the NMDAR2 (NR2 A-D) subunits. {14636} Phosphorylation of Tyr1336 in NR2B is thought to potentiate NMDA receptor-dependent influx of calcium.{14640} Ischemia may also increase the phosphorylation of this site.
Synonyms:
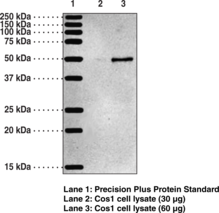
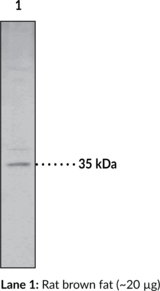
Immunogen: phosphopeptide corresponding to amino acid residues surrounding the Phospho-Tyr1336 of human NMDA Receptor NR2B Subunit
Formulation: Peptide affinity-purified antibody
Isotype:
Applications: WB
Origin: Animal/Rabbit
Stability: 365 days
Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Neuroscience|Behavioral Neuroscience|Learning & Memory||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neuroprotection|Ischemia||Research Area|Neuroscience|Seizure Disorders