Description
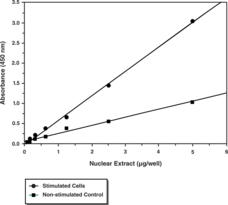
The NF-κB/Rel family of transcription factors is comprised of several structurally-related proteins that form homodimers and heterodimers and include p50/p105, p52/p100, RelA (p65), and c-Rel/NF-κB. Acting as dimers, these transcription factors bind to κB sites on DNA, thereby regulating expression of target genes. The most common Rel/NF-κB dimer in mammals contains p50-RelA (p50/p65) heterodimers and is an attractive target for potential therapeutics in human inflammation and certain other diseases. Cayman’s NF-κB (p65) Transcription Factor Assay is a non-radioactive, sensitive method for detecting human NF-κB (p65) DNA binding activity in nuclear extracts and whole cell lysates. It will not cross-react with NF-κB (p50).
Formulation:
Formal name:
Synonyms:
Host:
Imunogen:
Applications:
Clone:
Purity:
Origin: Animal/Bovine|Animal/Rabbit|Animal/Goat
Product Type|Assay Kits|ELISA||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Pattern Recognition||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|STING||Research Area|Infectious Disease