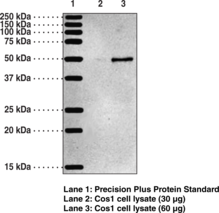
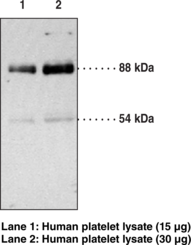
Description
NeuN, also known as FOX3 and RNA binding protein fox-1 homolog 3 (Rbfox3), is a pre-mRNA alternative splicing regulator encoded by RBFOX3 in humans.{53699,53701} It is expressed in mature neurons of the brain and spinal cord and is commonly used as a neuronal marker to quantify the number of new neurons generated during adult neurogenesis or the extent of therapeutic neuroprotection in animal models of neurodegenerative disease.{53702,53700} There are two subtypes of NeuN, a 46 kDa nuclear form and 48 kDa cytoplasmic form. Cytosolic NeuN is increased in the lumbar spinal cord in a mouse model of amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) compared with control animals.{53701} Exon deletions and truncations of NeuN are found in patients with Rolandic epilepsy and RBFOX3 is located within the apparently balanced chromosomal rearrangement (ABCR) regions of chromosomes in patients with developmental delays and speech disorders.{53700} Cayman’s NeuN Monoclonal Antibody can be used for immunocytochemistry (ICC), immunohistochemistry (IHC), and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes nuclear and cytosolic NeuN at approximately 46 and 48 kDa, respectively.
Synonyms: FOX3|Rbfox3|RNA Binding Protein Fox-1 Homolog 3
Immunogen: Recombinant protein from the N-terminus of human NeuN
Formulation: 100 µl of Protein G-purified mouse monoclonal antibody
Isotype: IgG2a
Applications: ICC, IHC, and WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|Immunocytochemistry||Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders||Research Area|Neuroscience|Seizure Disorders