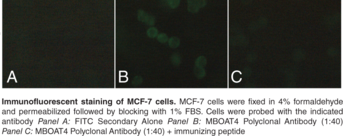
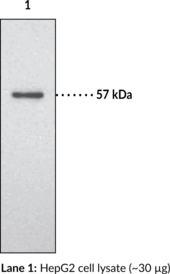
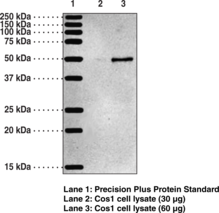
Description
Membrane bound O-acyl transferases (MBOATs) are a group of conserved, multiple transmembrane spanning enzymes involved in many biological functions including lipid biosynthesis, embryogenesis, nutrient sensing, and membrane lipid remodeling. This group of proteins is associated with pathologies such as diabetes, obesity, atherosclerosis, and Alzheimer’s disease.{27302} MBOAT4 is responsible for the octanoylination of ghrelin at serine 3, and can use a number of fatty acids as substrates including octanoic acid, decanoic acid, and tetradecanoic acid.{15759} Increases in the expression of MBOAT4 are dependent on preproghrelin expression during insulin-induced adipogenesis.{29964} Cayman’s MBOAT4 Polyclonal Antibody detects MBOAT in MCF-7 and RT-4 cells by flow cytometry and immunofluorescence in human samples.
Synonyms: Ghrelin O-Acyltransferase|GOAT|Membrane-bound O-Acyltransferase Domain-containing Protein 4
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide from the internal intracellular region of human MBOAT4
Formulation: 500 µl of peptide affinity-purified antibody
Isotype:
Applications: FC and IF
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|Flow Cytometry||Application|Immunofluorescence||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases|Atherosclerosis||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Diabetes||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Obesity||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease