Description
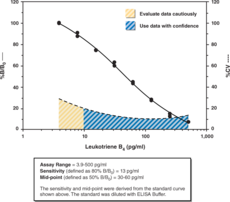
LTB4 is synthesized from arachidonic acid by the combined action of 5-LO and LTA4 hydrolase. LTB4 has long been recognized as a potent mediator of inflammation. It stimulates a number of leukocyte functions, including aggregation, stimulation of ion fluxes, enhancement of lysosomal enzyme release, superoxide anion production, chemotaxis, and chemokinesis. In subnanomolar ranges ,(3.9 x 10-10 M), LTB4 causes chemotaxis and chemokinesis in human PMNLs. At higher concentrations, (1.0 x 10-7 M), LTB4 leads to neutrophil aggregation and degranulation as well as superoxide anion production. Plasma levels of LTB4 increase from 100 ng/ml following leukocyte stimulation. LTB4 is metabolized in leukocytes and hepatocytes to less active 20-hydroxy and 20-carboxy LTB4 and is not excreted in the urine.
Formulation:
Formal name:
Synonyms: LTB4 EIA Kit
Host:
Imunogen:
Applications:
Clone:
Purity:
Origin: Animal/Mouse|Animal/Bovine|Animal/Eel|Animal/Rabbit
Application|ELISA||Product Type|Assay Kits|ELISA||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Inflammatory Lipid Mediators|Leukotrienes||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Lipoxygenase Pathways