Description
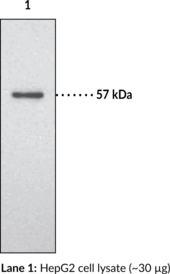
Hormone-sensitive lipase (HSL) catalyzes the hydrolysis of tri-, di-, and monoacylglycerols, as well as cholesterol esters and thus mobilizes fatty acid and provides a primary source of energy in mammals.{13168} The enzyme is highly expressed in adipose tissue and steroidogenic tissues, and less abundantly in skeletal muscle, heart, brain, pancreatic beta cells, adrenal gland, ovaries, testes, and macrophages. Its presence in various tissues indicates the enzyme plays diverse roles including those in steroidogenesis and spermatogenesis, foam cell formation in atherosclerosis, and diabetic pathology.{13168,13167} Human HSL cDNA encodes a 775 amino acid protein with an estimated molecular size of 84 kDa.{13169} A second, larger isoform encoded by a unique testis mRNA was later identified.{13171,13166} Cayman’s HSL Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot applications. The antibody recognizes HSL at 86 kDa from human, mouse, and rat samples.
Synonyms: HSL|LIPE
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide from the C-terminal region of human HSL receptor
Formulation: Peptide affinity-purified IgG
Isotype:
Applications: WB
Origin: Animal/Rabbit
Stability: 365 days
Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases|Atherosclerosis||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Lipids & Lipoproteins|Cholesterol Metabolism||Research Area|Endocrinology & Metabolism|Metabolic Diseases|Diabetes