Description
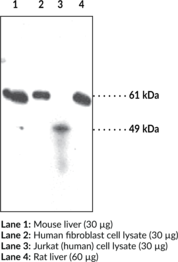
GABAA receptors are ligand-gated chloride channels that mediate the effects of the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA in the CNS.{46949,46950} They are postsynaptic heteropentameric receptors that contain protein subunits from the following isoforms: α1-6, β1-4, γ1-3, δ, ε, π, θ, and ρ1-3, arranged around a central pore. Phasic inhibitory synaptic transmission is regulated by α1β2γ2 subunit-containing GABAA receptors, the major isoform found in the brain.{46950,46951} The α subunit of GABAA receptors interfaces with a β subunit to form the GABA binding site that initiates GABA-induced action potentials and forms the benzodiazepine binding site with the γ subunit. Mutations in GABRA1, which encodes the α1 subunit isoform, are found in patients with autosomal dominant juvenile myoclonic epilepsy (JME), infantile spasms, and childhood absence epilepsy (CAE).{46950} GABRA1 expression is upregulated in ipsilateral, but not contralateral, perilesional tissue in a rat model of cortical ischemia-reperfusion injury.{55094} Cayman’s GABAA Receptor α1 Subunit Polyclonal Antibody can be used for immunohistochemistry (IHC) and Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes the GABAA receptor α1 subunit at approximately 51 kDa from mouse and rat samples.
Synonyms: GABAA Receptor Subunit α1|GABRA1|γ-Aminobutyric Acid Receptor Subunit α1
Immunogen: Fusion protein from the cytoplasmic loop of the α1 subunit of the rat GABAA receptor
Formulation: 100 µl of affinity-purified polyclonal antibody
Isotype:
Applications: IHC, WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neuroprotection|Ischemia||Research Area|Neuroscience|Seizure Disorders