Description
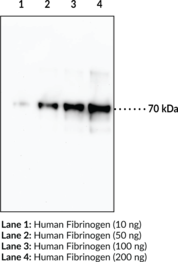
Fibrinogen is a hexameric glycoprotein that has roles in coagulation and hemostasis.{53514,53515} It is comprised of two sets of Aα, Bβ, and γ polypeptide chains encoded by FGA, FGB, and FGG, respectively, in humans.{53514} Fibrinogen is synthesized in hepatocytes and secreted into the plasma. Following thrombin-mediated cleavage of N-terminal fibrinopeptides from the Aα and Bβ chains, yielding the α and β chains, respectively, fibrinogen assembles into fibrin protofibrils and then mature fibers, which provide structure and viscoelasticity to blood clots.{53515,53516,53518} Mutations in FGA, FGB, or FGG have been found in patients with afibrinogenemia or hypofibrinogenemia.{53514} Elevated plasma fibrinogen levels are associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.{53517} Immune complexes containing citrullinated fibrinogen have been found in patients with anti-citrullinated protein antibody-positive rheumatoid arthritis.{21643} Cayman’s Fibrinogen (α chain) Monoclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot (WB) applications. The antibody recognizes the α chain of fibrinogen at 70 kDa from human samples.
Synonyms: FBG|FG|FGA
Immunogen: Human fibrinogen (α chain)
Formulation: 100 µg of protein G-purified antibody
Isotype: IgG1
Applications: WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Blood|Coagulation & Hemostasis||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity|Rheumatoid Arthritis