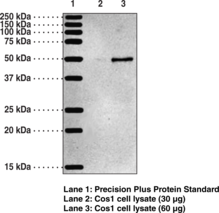
Description
Methylation of DNA at cytosine residues plays an important role in regulation of gene expression, genomic imprinting and is essential for mammalian development. Hypermethylation of CpG islands in tumor suppressor genes or hypomethylation of bulk genomic DNA may be linked with development of cancer. To date, three families of mammalian DNA methyltransferase genes have been identified which include DNMT1, DNMT2, and DNMT3. DNMT1 is constitutively expressed in proliferating cells and inactivation of this gene causes global demethylation of genomic DNA and embryonic lethality. DNMT2 is expressed at low levels in adult tissues and its inactivation does not affect DNA methylation or maintenance of methylation. The DNMT3 family members, DNMT3a, and DNMT3b are strongly expressed in embryonic stem (ES) cells but their expression is down regulated in differentiating ES cells and is low in adult somatic tissue. Recently, it has been shown that naturally occurring mutations of DNMT3b gene occurs in patients with a rare autosomal recessive disorder, termed ICF (immunodeficiency, centromeric instability, and facial anomalies) syndrome.
Synonyms: DNMT3a
Immunogen: recombinant mouse DNMT3a expressed in bacteria
Formulation: 100 μg of Protein G purified IgG in 200 μl PBS containing 0.05% sodium azide
Isotype: IgG1
Applications: ELISA
Origin: Animal/Mouse
Stability: 180 days
Application|ELISA||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Writers|DNA/RNA Methylation