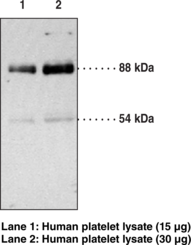
Description
The cysteinyl leukotrienes (cysLTs; LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4) contract airway and pulmonary vascular smooth muscle, increase vascular permeability, and stimulate mucus secretion, thereby playing a major role in asthma.{3956,2069,3483,4157} LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4 mediate their actions via at least two receptors designated CysLT1 and CysLT2.{3956} Cloning of the human CysLT2 receptor reveals it is a 346 amino acid protein with 38% homology to the CysLT1 receptor.{8519,7174} The rank order of binding for leukotrienes to the cloned receptor, as determined using a radioligand binding assay, is LTC4 = LTD4 >> LTE4.{8519} The mRNA for the human CysLT2 receptor is expressed in lung macrophages, airway smooth muscle, cardiac Purkinje cells, adrenal medulla cells, peripheral blood leukocytes, spleen, placenta, and brain.{8519,9059}
Synonyms: Cysteinyl-Leukotriene Receptor 2
Immunogen: Synthetic peptide from the C-terminal region of human CysLT2 Receptor
Formulation: Peptide affinity-purified polyclonal antibody
Isotype:
Applications: ELISA, FC, IHC, and WB
Origin: Animal/Rabbit
Stability: 365 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Flow Cytometry||Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Vasculature|Smooth Muscle Cells||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Lipoxygenase Pathways