Cayman
Showing 751–900 of 45550 results
-
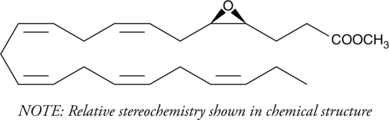
(±)17(18)-EpETE methyl ester is an analog of the eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) metabolite (±)17(18)-EpETE (Item No. 50861) that is more lipid soluble.
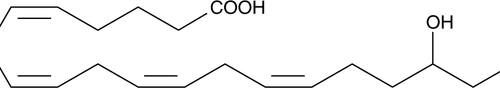
Brand:CaymanSKU:-(±)17(18)-EpETE-Ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide.{40186} It is formed from the endocannabinoid eicosapentaenoic ethanolamide (EPEA) via cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases and hydrolyzed by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). It is endogenously produced in LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglia cells and in BV-2 microglia cells supplemented with EPEA, an effect that can be reduced by the CYP inhibitor ketoconazole. (±)17(18)-EpETE-ethanolamide decreases IL-6 and nitrite production induced by LPS in BV-2 microglia and increases the production of IL-10. It inhibits platelet aggregation induced by arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607) when used at a concentration of 50 µM but not aggregation induced by ADP (Item Nos. 16778 | 21121), collagen, or ristocetin. It also induces relaxation of preconstricted bovine coronary arteries (ED50 = 1.1 µM) and inhibits VEGF-stimulated tubulogenesis in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs). (±)17(18)-EpETE-ethanolamide is the predominant EPEA metabolite found in rat brain, and it has also been found in rat heart, kidney, spleen, and liver, as well as in pig brain. It activates cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and CB2 with EC50 values of 18.5 and 1.4 nM, respectively, in a β-arrestin recruitment assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25920 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)17(18)-EpETE-Ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide.{40186} It is formed from the endocannabinoid eicosapentaenoic ethanolamide (EPEA) via cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases and hydrolyzed by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). It is endogenously produced in LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglia cells and in BV-2 microglia cells supplemented with EPEA, an effect that can be reduced by the CYP inhibitor ketoconazole. (±)17(18)-EpETE-ethanolamide decreases IL-6 and nitrite production induced by LPS in BV-2 microglia and increases the production of IL-10. It inhibits platelet aggregation induced by arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607) when used at a concentration of 50 µM but not aggregation induced by ADP (Item Nos. 16778 | 21121), collagen, or ristocetin. It also induces relaxation of preconstricted bovine coronary arteries (ED50 = 1.1 µM) and inhibits VEGF-stimulated tubulogenesis in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs). (±)17(18)-EpETE-ethanolamide is the predominant EPEA metabolite found in rat brain, and it has also been found in rat heart, kidney, spleen, and liver, as well as in pig brain. It activates cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and CB2 with EC50 values of 18.5 and 1.4 nM, respectively, in a β-arrestin recruitment assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25920 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)17(18)-EpETE-Ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide.{40186} It is formed from the endocannabinoid eicosapentaenoic ethanolamide (EPEA) via cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases and hydrolyzed by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). It is endogenously produced in LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglia cells and in BV-2 microglia cells supplemented with EPEA, an effect that can be reduced by the CYP inhibitor ketoconazole. (±)17(18)-EpETE-ethanolamide decreases IL-6 and nitrite production induced by LPS in BV-2 microglia and increases the production of IL-10. It inhibits platelet aggregation induced by arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607) when used at a concentration of 50 µM but not aggregation induced by ADP (Item Nos. 16778 | 21121), collagen, or ristocetin. It also induces relaxation of preconstricted bovine coronary arteries (ED50 = 1.1 µM) and inhibits VEGF-stimulated tubulogenesis in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs). (±)17(18)-EpETE-ethanolamide is the predominant EPEA metabolite found in rat brain, and it has also been found in rat heart, kidney, spleen, and liver, as well as in pig brain. It activates cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and CB2 with EC50 values of 18.5 and 1.4 nM, respectively, in a β-arrestin recruitment assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25920 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)17(18)-EpETE-Ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide.{40186} It is formed from the endocannabinoid eicosapentaenoic ethanolamide (EPEA) via cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases and hydrolyzed by soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) and fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH). It is endogenously produced in LPS-stimulated BV-2 microglia cells and in BV-2 microglia cells supplemented with EPEA, an effect that can be reduced by the CYP inhibitor ketoconazole. (±)17(18)-EpETE-ethanolamide decreases IL-6 and nitrite production induced by LPS in BV-2 microglia and increases the production of IL-10. It inhibits platelet aggregation induced by arachidonic acid (Item Nos. 90010 | 90010.1 | 10006607) when used at a concentration of 50 µM but not aggregation induced by ADP (Item Nos. 16778 | 21121), collagen, or ristocetin. It also induces relaxation of preconstricted bovine coronary arteries (ED50 = 1.1 µM) and inhibits VEGF-stimulated tubulogenesis in human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs). (±)17(18)-EpETE-ethanolamide is the predominant EPEA metabolite found in rat brain, and it has also been found in rat heart, kidney, spleen, and liver, as well as in pig brain. It activates cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and CB2 with EC50 values of 18.5 and 1.4 nM, respectively, in a β-arrestin recruitment assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25920 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)18-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item Nos. 90110 | 90110.1 | 21908).{53027} 18-HEPE levels are increased in the plasma and heart, as well as in the supernatant of cultured peritoneal macrophages isolated from fat-1 transgenic mice that are capable of endogenously producing ω-3 fatty acids from ω-6 fatty acids.{53024,53025,53026} It reduces increases in cardiac fibrosis and the expression of Nppa, Col1a1, Tgfb1, Cx3cl1, and Adgre1 induced by transverse aortic constriction in a mouse model of cardiac hypertrophy when administered at doses of 1 and 5 µg.{53025}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32840 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)18-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item Nos. 90110 | 90110.1 | 21908).{53027} 18-HEPE levels are increased in the plasma and heart, as well as in the supernatant of cultured peritoneal macrophages isolated from fat-1 transgenic mice that are capable of endogenously producing ω-3 fatty acids from ω-6 fatty acids.{53024,53025,53026} It reduces increases in cardiac fibrosis and the expression of Nppa, Col1a1, Tgfb1, Cx3cl1, and Adgre1 induced by transverse aortic constriction in a mouse model of cardiac hypertrophy when administered at doses of 1 and 5 µg.{53025}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32840 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)18-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item Nos. 90110 | 90110.1 | 21908).{53027} 18-HEPE levels are increased in the plasma and heart, as well as in the supernatant of cultured peritoneal macrophages isolated from fat-1 transgenic mice that are capable of endogenously producing ω-3 fatty acids from ω-6 fatty acids.{53024,53025,53026} It reduces increases in cardiac fibrosis and the expression of Nppa, Col1a1, Tgfb1, Cx3cl1, and Adgre1 induced by transverse aortic constriction in a mouse model of cardiac hypertrophy when administered at doses of 1 and 5 µg.{53025}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32840 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)18-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item Nos. 90110 | 90110.1 | 21908).{53027} 18-HEPE levels are increased in the plasma and heart, as well as in the supernatant of cultured peritoneal macrophages isolated from fat-1 transgenic mice that are capable of endogenously producing ω-3 fatty acids from ω-6 fatty acids.{53024,53025,53026} It reduces increases in cardiac fibrosis and the expression of Nppa, Col1a1, Tgfb1, Cx3cl1, and Adgre1 induced by transverse aortic constriction in a mouse model of cardiac hypertrophy when administered at doses of 1 and 5 µg.{53025}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32840 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)18-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item Nos. 90110 | 90110.1 | 21908).{53027} 18-HEPE levels are increased in the plasma and heart, as well as in the supernatant of cultured peritoneal macrophages isolated from fat-1 transgenic mice that are capable of endogenously producing ω-3 fatty acids from ω-6 fatty acids.{53024,53025,53026} It reduces increases in cardiac fibrosis and the expression of Nppa, Col1a1, Tgfb1, Cx3cl1, and Adgre1 induced by transverse aortic constriction in a mouse model of cardiac hypertrophy when administered at doses of 1 and 5 µg.{53025} (±)18-HEPE MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of (±)18-HEPE (Item No. 32840) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This (±)18-HEPE MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:23567 - 10 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)18-HETE is the racemic version of a cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolite of arachidonic acid. When formed by the CYP2E1 isoform, 18-HETE is comprised 100% of the (R) isomer.{15766} 18(R)-HETE dose-dependently stimulates vasodilation of the rabbit kidney, whereas 18(S)-HETE does not affect perfusion pressure.{3825} 18-HETE has negligible effects on ATPase activity.{3825} 18(R)-HETE at 1 µM completely blocks 20-HETE-induced vasoconstriction of renal arterioles.{15772}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010638 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)18-HETE is the racemic version of a cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolite of arachidonic acid. When formed by the CYP2E1 isoform, 18-HETE is comprised 100% of the (R) isomer.{15766} 18(R)-HETE dose-dependently stimulates vasodilation of the rabbit kidney, whereas 18(S)-HETE does not affect perfusion pressure.{3825} 18-HETE has negligible effects on ATPase activity.{3825} 18(R)-HETE at 1 µM completely blocks 20-HETE-induced vasoconstriction of renal arterioles.{15772}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010638 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)18-HETE is the racemic version of a cytochrome P450 (CYP450) metabolite of arachidonic acid. When formed by the CYP2E1 isoform, 18-HETE is comprised 100% of the (R) isomer.{15766} 18(R)-HETE dose-dependently stimulates vasodilation of the rabbit kidney, whereas 18(S)-HETE does not affect perfusion pressure.{3825} 18-HETE has negligible effects on ATPase activity.{3825} 18(R)-HETE at 1 µM completely blocks 20-HETE-induced vasoconstriction of renal arterioles.{15772}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10010638 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
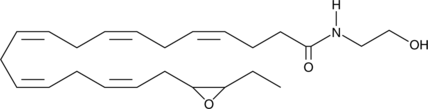
(±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide and cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonist (EC50s = 108 and 280 nM for CB1 and CB2, respectively). It is produced through direct epoxygenation of docosahexaenoyl ethanolamide (DHEA; Item No. 10007534) by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases.{40186,42488} (±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide (25 µM) reduces the viability of 143B metastatic osteosarcoma cells.{42488} It decreases the production of IL-6 and increases the production of IL-10 when used at concentrations ranging from 2.5 to 10 µM in BV-2 microglia stimulated by LPS and decreases LPS-induced cytotoxicity when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 10 µM. It also decreases nitrite production when used at a concentration of 7.5 µM, an effect that can be partially reversed by the CB2 receptor antagonist AM630 (Item No. 10006974) and the PPARγ antagonist GW 9662 (Item No. 70785). (±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide induces vasodilation of isolated preconstricted bovine coronary arteries (ED50 = 1.9 µM) and reduces tube formation by human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs) in a Matrigel™ assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25917 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide and cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonist (EC50s = 108 and 280 nM for CB1 and CB2, respectively). It is produced through direct epoxygenation of docosahexaenoyl ethanolamide (DHEA; Item No. 10007534) by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases.{40186,42488} (±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide (25 µM) reduces the viability of 143B metastatic osteosarcoma cells.{42488} It decreases the production of IL-6 and increases the production of IL-10 when used at concentrations ranging from 2.5 to 10 µM in BV-2 microglia stimulated by LPS and decreases LPS-induced cytotoxicity when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 10 µM. It also decreases nitrite production when used at a concentration of 7.5 µM, an effect that can be partially reversed by the CB2 receptor antagonist AM630 (Item No. 10006974) and the PPARγ antagonist GW 9662 (Item No. 70785). (±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide induces vasodilation of isolated preconstricted bovine coronary arteries (ED50 = 1.9 µM) and reduces tube formation by human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs) in a Matrigel™ assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25917 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide and cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonist (EC50s = 108 and 280 nM for CB1 and CB2, respectively). It is produced through direct epoxygenation of docosahexaenoyl ethanolamide (DHEA; Item No. 10007534) by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases.{40186,42488} (±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide (25 µM) reduces the viability of 143B metastatic osteosarcoma cells.{42488} It decreases the production of IL-6 and increases the production of IL-10 when used at concentrations ranging from 2.5 to 10 µM in BV-2 microglia stimulated by LPS and decreases LPS-induced cytotoxicity when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 10 µM. It also decreases nitrite production when used at a concentration of 7.5 µM, an effect that can be partially reversed by the CB2 receptor antagonist AM630 (Item No. 10006974) and the PPARγ antagonist GW 9662 (Item No. 70785). (±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide induces vasodilation of isolated preconstricted bovine coronary arteries (ED50 = 1.9 µM) and reduces tube formation by human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs) in a Matrigel™ assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25917 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide is an ω-3 endocannabinoid epoxide and cannabinoid (CB) receptor agonist (EC50s = 108 and 280 nM for CB1 and CB2, respectively). It is produced through direct epoxygenation of docosahexaenoyl ethanolamide (DHEA; Item No. 10007534) by cytochrome P450 (CYP) epoxygenases.{40186,42488} (±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide (25 µM) reduces the viability of 143B metastatic osteosarcoma cells.{42488} It decreases the production of IL-6 and increases the production of IL-10 when used at concentrations ranging from 2.5 to 10 µM in BV-2 microglia stimulated by LPS and decreases LPS-induced cytotoxicity when used at concentrations ranging from 5 to 10 µM. It also decreases nitrite production when used at a concentration of 7.5 µM, an effect that can be partially reversed by the CB2 receptor antagonist AM630 (Item No. 10006974) and the PPARγ antagonist GW 9662 (Item No. 70785). (±)19(20)-EDP ethanolamide induces vasodilation of isolated preconstricted bovine coronary arteries (ED50 = 1.9 µM) and reduces tube formation by human microvascular endothelial cells (HMVECs) in a Matrigel™ assay.
Brand:CaymanSKU:25917 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
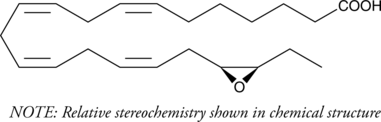
(±)19(20)-EpDTE is an oxylipin and an oxidative metabolite of docosapentaenoic acid (DPA; Item Nos. 90165 | 21907). It is formed via cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolism of DPA and can be further metabolized to (±)19(20)-DiHDTE (Item No. 20336) by epoxide hydrolase.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20331 -Available on backorder
(±)19(20)-EpDTE is an oxylipin and an oxidative metabolite of docosapentaenoic acid (DPA; Item Nos. 90165 | 21907). It is formed via cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolism of DPA and can be further metabolized to (±)19(20)-DiHDTE (Item No. 20336) by epoxide hydrolase.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20331 -Available on backorder
(±)19(20)-EpDTE is an oxylipin and an oxidative metabolite of docosapentaenoic acid (DPA; Item Nos. 90165 | 21907). It is formed via cytochrome P450 (CYP) metabolism of DPA and can be further metabolized to (±)19(20)-DiHDTE (Item No. 20336) by epoxide hydrolase.
Brand:CaymanSKU:20331 -Available on backorder
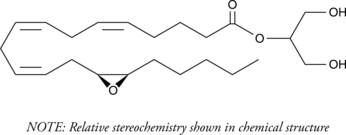
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor agonist that is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system.{7183,7182,6819} 2-AG is hydrolyzed by the enzyme monoacylglycerol lipase, terminating its biological activity, and metabolism by cyclooxygenase-2 and lipoxygenases has been documented.{11364,12168} The related endocannabinoid, 2-arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA), can be metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes in human liver and kidney to a number of epoxy-ethanolamide derivatives.{14767} (±)2-(14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoyl) Glycerol ((±)2-14,15-EG) is a novel CYP450 metabolite of 2-AG in the kidney.{14755} (±)2-14,15-EG is a potent mitogen for renal epithelial cells, increasing DNA synthesis in LLCPKcl4 cells at concentrations as low as 100 nM and doubling cell proliferation rates at 1 µM.{14755} In these cells, (±)2-14,15-EG activates the metalloprotease ADAM17, which cleaves proTGF-α and releases TGF-α as a ligand that initiates the EGFR-ERK signalling pathway.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009962 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor agonist that is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system.{7183,7182,6819} 2-AG is hydrolyzed by the enzyme monoacylglycerol lipase, terminating its biological activity, and metabolism by cyclooxygenase-2 and lipoxygenases has been documented.{11364,12168} The related endocannabinoid, 2-arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA), can be metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes in human liver and kidney to a number of epoxy-ethanolamide derivatives.{14767} (±)2-(14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoyl) Glycerol ((±)2-14,15-EG) is a novel CYP450 metabolite of 2-AG in the kidney.{14755} (±)2-14,15-EG is a potent mitogen for renal epithelial cells, increasing DNA synthesis in LLCPKcl4 cells at concentrations as low as 100 nM and doubling cell proliferation rates at 1 µM.{14755} In these cells, (±)2-14,15-EG activates the metalloprotease ADAM17, which cleaves proTGF-α and releases TGF-α as a ligand that initiates the EGFR-ERK signalling pathway.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor agonist that is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system.{7183,7182,6819} 2-AG is hydrolyzed by the enzyme monoacylglycerol lipase, terminating its biological activity, and metabolism by cyclooxygenase-2 and lipoxygenases has been documented.{11364,12168} The related endocannabinoid, 2-arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA), can be metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes in human liver and kidney to a number of epoxy-ethanolamide derivatives.{14767} (±)2-(14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoyl) Glycerol ((±)2-14,15-EG) is a novel CYP450 metabolite of 2-AG in the kidney.{14755} (±)2-14,15-EG is a potent mitogen for renal epithelial cells, increasing DNA synthesis in LLCPKcl4 cells at concentrations as low as 100 nM and doubling cell proliferation rates at 1 µM.{14755} In these cells, (±)2-14,15-EG activates the metalloprotease ADAM17, which cleaves proTGF-α and releases TGF-α as a ligand that initiates the EGFR-ERK signalling pathway.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009962 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor agonist that is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system.{7183,7182,6819} 2-AG is hydrolyzed by the enzyme monoacylglycerol lipase, terminating its biological activity, and metabolism by cyclooxygenase-2 and lipoxygenases has been documented.{11364,12168} The related endocannabinoid, 2-arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA), can be metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes in human liver and kidney to a number of epoxy-ethanolamide derivatives.{14767} (±)2-(14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoyl) Glycerol ((±)2-14,15-EG) is a novel CYP450 metabolite of 2-AG in the kidney.{14755} (±)2-14,15-EG is a potent mitogen for renal epithelial cells, increasing DNA synthesis in LLCPKcl4 cells at concentrations as low as 100 nM and doubling cell proliferation rates at 1 µM.{14755} In these cells, (±)2-14,15-EG activates the metalloprotease ADAM17, which cleaves proTGF-α and releases TGF-α as a ligand that initiates the EGFR-ERK signalling pathway.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-2-Arachidonoyl glycerol (2-AG) is an endogenous central cannabinoid (CB1) receptor agonist that is present at relatively high levels in the central nervous system.{7183,7182,6819} 2-AG is hydrolyzed by the enzyme monoacylglycerol lipase, terminating its biological activity, and metabolism by cyclooxygenase-2 and lipoxygenases has been documented.{11364,12168} The related endocannabinoid, 2-arachidonoyl ethanolamide (AEA), can be metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes in human liver and kidney to a number of epoxy-ethanolamide derivatives.{14767} (±)2-(14,15-Epoxyeicosatrienoyl) Glycerol ((±)2-14,15-EG) is a novel CYP450 metabolite of 2-AG in the kidney.{14755} (±)2-14,15-EG is a potent mitogen for renal epithelial cells, increasing DNA synthesis in LLCPKcl4 cells at concentrations as low as 100 nM and doubling cell proliferation rates at 1 µM.{14755} In these cells, (±)2-14,15-EG activates the metalloprotease ADAM17, which cleaves proTGF-α and releases TGF-α as a ligand that initiates the EGFR-ERK signalling pathway.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10009962 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)20-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} (±)20-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33750 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)20-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} (±)20-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33750 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)20-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} (±)20-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33750 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)20-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} (±)20-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33750 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)4-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} Enzymatic transformation of DHA by RBL-1 cells also produces 4-HDHA.{7515} However, the enzymatic product is most likely the S-isomer. (±)4-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33200 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)4-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} Enzymatic transformation of DHA by RBL-1 cells also produces 4-HDHA.{7515} However, the enzymatic product is most likely the S-isomer. (±)4-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33200 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)4-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} Enzymatic transformation of DHA by RBL-1 cells also produces 4-HDHA.{7515} However, the enzymatic product is most likely the S-isomer. (±)4-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33200 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)4-HDHA is an autoxidation product of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in vitro.{7479,7491} It is also produced from incubations of DHA in rat liver, brain, and intestinal microsomes.{7480,7490,7492} Enzymatic transformation of DHA by RBL-1 cells also produces 4-HDHA.{7515} However, the enzymatic product is most likely the S-isomer. (±)4-HDHA is a potential marker of oxidative stress in brain and retina where DHA is an abundant polyunsaturated fatty acid.
Brand:CaymanSKU:33200 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)4-Hydroxymephenytoin is a metabolite of (S)-mephenytoin (Item No. 11913), a substrate of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP2C19 with anticonvulsant activities.{23859,23860} It has been used for developing ultra-performance LC tandem mass spectrometry assays for evaluating CYP probe drugs and their relevant metabolites in human urine or plasma samples.{26241}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-(±)4-Hydroxymephenytoin is a metabolite of (S)-mephenytoin (Item No. 11913), a substrate of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP2C19 with anticonvulsant activities.{23859,23860} It has been used for developing ultra-performance LC tandem mass spectrometry assays for evaluating CYP probe drugs and their relevant metabolites in human urine or plasma samples.{26241}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-(±)4-Hydroxymephenytoin is a metabolite of (S)-mephenytoin (Item No. 11913), a substrate of the cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoform CYP2C19 with anticonvulsant activities.{23859,23860} It has been used for developing ultra-performance LC tandem mass spectrometry assays for evaluating CYP probe drugs and their relevant metabolites in human urine or plasma samples.{26241}
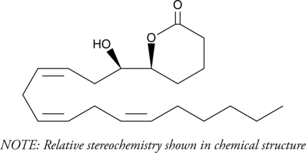
Brand:CaymanSKU:-(±)5(6)-DiHET lactone (Item No. 51212) is a 1,5 cyclic ester derived from (±)5(6)-DiHET (Item No. 51211), which, in turn, is a potential derivative of epoxidation of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) at the α-5 double bond. (±)4(5)-DiHDPA lactone is a derivative of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310) that is analogous to (±)5(6)-DiHET lactone. It is the 1,4 cyclic ester derived from (±)4(5)-DiHDPA, which is produced by epoxidation of DHA at the α-4 double bond. Its biological activity is unknown.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
(±)5(6)-DiHET lactone (Item No. 51212) is a 1,5 cyclic ester derived from (±)5(6)-DiHET (Item No. 51211), which, in turn, is a potential derivative of epoxidation of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) at the α-5 double bond. (±)4(5)-DiHDPA lactone is a derivative of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310) that is analogous to (±)5(6)-DiHET lactone. It is the 1,4 cyclic ester derived from (±)4(5)-DiHDPA, which is produced by epoxidation of DHA at the α-4 double bond. Its biological activity is unknown.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
(±)5(6)-DiHET lactone (Item No. 51212) is a 1,5 cyclic ester derived from (±)5(6)-DiHET (Item No. 51211), which, in turn, is a potential derivative of epoxidation of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) at the α-5 double bond. (±)4(5)-DiHDPA lactone is a derivative of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310) that is analogous to (±)5(6)-DiHET lactone. It is the 1,4 cyclic ester derived from (±)4(5)-DiHDPA, which is produced by epoxidation of DHA at the α-4 double bond. Its biological activity is unknown.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
(±)5(6)-DiHET lactone (Item No. 51212) is a 1,5 cyclic ester derived from (±)5(6)-DiHET (Item No. 51211), which, in turn, is a potential derivative of epoxidation of arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) at the α-5 double bond. (±)4(5)-DiHDPA lactone is a derivative of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA; Item No. 90310) that is analogous to (±)5(6)-DiHET lactone. It is the 1,4 cyclic ester derived from (±)4(5)-DiHDPA, which is produced by epoxidation of DHA at the α-4 double bond. Its biological activity is unknown.
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Available on backorder
(±)4(5)-EpDPA methyl ester is a derivative of (±)4(5)-EpDPA which is stable enough to ship and handle routinely. The active free acid can be regenerated from the methyl ester by careful base hydrolysis. (±)4(5)EpDPA is a CYP450 metabolite of DHA which can be further metabolized to the diol metabolite.{4334} There are no published reports on the biological activity of (±)4(5)-EpDPA methyl ester at this time.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90314 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)4(5)-EpDPA methyl ester is a derivative of (±)4(5)-EpDPA which is stable enough to ship and handle routinely. The active free acid can be regenerated from the methyl ester by careful base hydrolysis. (±)4(5)EpDPA is a CYP450 metabolite of DHA which can be further metabolized to the diol metabolite.{4334} There are no published reports on the biological activity of (±)4(5)-EpDPA methyl ester at this time.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90314 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)4(5)-EpDPA methyl ester is a derivative of (±)4(5)-EpDPA which is stable enough to ship and handle routinely. The active free acid can be regenerated from the methyl ester by careful base hydrolysis. (±)4(5)EpDPA is a CYP450 metabolite of DHA which can be further metabolized to the diol metabolite.{4334} There are no published reports on the biological activity of (±)4(5)-EpDPA methyl ester at this time.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90314 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)4(5)-EpDPA methyl ester is a derivative of (±)4(5)-EpDPA which is stable enough to ship and handle routinely. The active free acid can be regenerated from the methyl ester by careful base hydrolysis. (±)4(5)EpDPA is a CYP450 metabolite of DHA which can be further metabolized to the diol metabolite.{4334} There are no published reports on the biological activity of (±)4(5)-EpDPA methyl ester at this time.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90314 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 5(S)-HEPE and 5(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)5-HEPE is likely mediated by one of the individual isomers, most commonly the 5(S) isomer in mammalian systems. EPA can be metabolized to 5-HEPE in human and bovine neutrophils, and human eosinophils, which is further metabolized to 5-oxoEPE and LTB5.{11149,11166,11167} The 5-series metabolites of EPA, namely 5-HEPE, 5-oxoEPE, and LTB5, have significantly decreased biological effects compared to the arachidonic acid-derived metabolites.{11167}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32200 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 5(S)-HEPE and 5(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)5-HEPE is likely mediated by one of the individual isomers, most commonly the 5(S) isomer in mammalian systems. EPA can be metabolized to 5-HEPE in human and bovine neutrophils, and human eosinophils, which is further metabolized to 5-oxoEPE and LTB5.{11149,11166,11167} The 5-series metabolites of EPA, namely 5-HEPE, 5-oxoEPE, and LTB5, have significantly decreased biological effects compared to the arachidonic acid-derived metabolites.{11167}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32200 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 5(S)-HEPE and 5(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)5-HEPE is likely mediated by one of the individual isomers, most commonly the 5(S) isomer in mammalian systems. EPA can be metabolized to 5-HEPE in human and bovine neutrophils, and human eosinophils, which is further metabolized to 5-oxoEPE and LTB5.{11149,11166,11167} The 5-series metabolites of EPA, namely 5-HEPE, 5-oxoEPE, and LTB5, have significantly decreased biological effects compared to the arachidonic acid-derived metabolites.{11167}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32200 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HEPE is produced by non-enzymatic oxidation of EPA. It contains equal amounts of 5(S)-HEPE and 5(R)-HEPE. The biological activity of (±)5-HEPE is likely mediated by one of the individual isomers, most commonly the 5(S) isomer in mammalian systems. EPA can be metabolized to 5-HEPE in human and bovine neutrophils, and human eosinophils, which is further metabolized to 5-oxoEPE and LTB5.{11149,11166,11167} The 5-series metabolites of EPA, namely 5-HEPE, 5-oxoEPE, and LTB5, have significantly decreased biological effects compared to the arachidonic acid-derived metabolites.{11167}
Brand:CaymanSKU:32200 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. It contains equal amounts of 5(S)-HETE and 5(R)-HETE. (±)5-HETE induces the aggregation of isolated neutrophils with an IC50 value of 200 nM.{2091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34210 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. It contains equal amounts of 5(S)-HETE and 5(R)-HETE. (±)5-HETE induces the aggregation of isolated neutrophils with an IC50 value of 200 nM.{2091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34210 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. It contains equal amounts of 5(S)-HETE and 5(R)-HETE. (±)5-HETE induces the aggregation of isolated neutrophils with an IC50 value of 200 nM.{2091}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34210 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
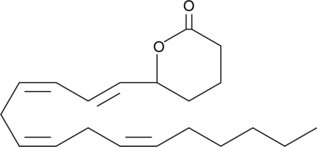
(±)5-HETE lactone is a cyclic ester formed by acid-catalyzed nucleophilic addition of the C-5 hydroxyl to the C-1 carboxyl of (±)5-HETE. (±)5-HETE lactone is an inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase from rat basophilic leukemia cells with an IC50 of 27 µM. The lactone is several times more potent than the linear (±)5-HETE.{690}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34215 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HETE lactone is a cyclic ester formed by acid-catalyzed nucleophilic addition of the C-5 hydroxyl to the C-1 carboxyl of (±)5-HETE. (±)5-HETE lactone is an inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase from rat basophilic leukemia cells with an IC50 of 27 µM. The lactone is several times more potent than the linear (±)5-HETE.{690}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34215 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HETE lactone is a cyclic ester formed by acid-catalyzed nucleophilic addition of the C-5 hydroxyl to the C-1 carboxyl of (±)5-HETE. (±)5-HETE lactone is an inhibitor of 5-lipoxygenase from rat basophilic leukemia cells with an IC50 of 27 µM. The lactone is several times more potent than the linear (±)5-HETE.{690}
Brand:CaymanSKU:34215 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. The methyl ester of (±)5-HETE has no distinguishing biological activity and is supplied as a standard. Oxidatively degraded polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) methyl esters may contain (±)5-HETE methyl ester.
Brand:CaymanSKU:34220 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. The methyl ester of (±)5-HETE has no distinguishing biological activity and is supplied as a standard. Oxidatively degraded polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) methyl esters may contain (±)5-HETE methyl ester.
Brand:CaymanSKU:34220 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. The methyl ester of (±)5-HETE has no distinguishing biological activity and is supplied as a standard. Oxidatively degraded polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) methyl esters may contain (±)5-HETE methyl ester.
Brand:CaymanSKU:34220 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-HETE is one of the six monohydroxy fatty acids produced by the non-enzymatic oxidation of arachidonic acid. The methyl ester of (±)5-HETE has no distinguishing biological activity and is supplied as a standard. Oxidatively degraded polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) methyl esters may contain (±)5-HETE methyl ester.
Brand:CaymanSKU:34220 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
Isoprostanes are prostaglandin (PG)-like products of free-radical induced lipid peroxidation.{320} Although the isoprostanes derived from arachidonic acid are the best characterized, many other polyunsaturated fatty acids can form isoprostanes.{7323} (±)5-iPF2α-VI is one of dozens of possible stereo- and regioisomeric isoprostanes which can be formed from arachidonic acid. To date, the most extensively studied of these is 8-isoprostane (8-epi-PGF2α, iPF2α-III).{3064,5011} However, 8-isoprostane is a minor isoprostane constituent when compared to some of the other isomers which form in natural conditions of oxidative stress.{8367} (±)5-iPF2α-VI is an isoprostane from the unique Type VI class of isoprostanes. This class has been shown to be one of the major isoprostane products, in contrast to 8-isoprostane. In addition to being produced in greater abundance than 8-isoprostane, Type VI isoprostanes form internal lactones, which facilitates their extraction and purification from biological samples.{8367,9408,6910,6390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Isoprostanes are prostaglandin (PG)-like products of free-radical induced lipid peroxidation.{320} Although the isoprostanes derived from arachidonic acid are the best characterized, many other polyunsaturated fatty acids can form isoprostanes.{7323} (±)5-iPF2α-VI is one of dozens of possible stereo- and regioisomeric isoprostanes which can be formed from arachidonic acid. To date, the most extensively studied of these is 8-isoprostane (8-epi-PGF2α, iPF2α-III).{3064,5011} However, 8-isoprostane is a minor isoprostane constituent when compared to some of the other isomers which form in natural conditions of oxidative stress.{8367} (±)5-iPF2α-VI is an isoprostane from the unique Type VI class of isoprostanes. This class has been shown to be one of the major isoprostane products, in contrast to 8-isoprostane. In addition to being produced in greater abundance than 8-isoprostane, Type VI isoprostanes form internal lactones, which facilitates their extraction and purification from biological samples.{8367,9408,6910,6390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Isoprostanes are prostaglandin (PG)-like products of free-radical induced lipid peroxidation.{320} Although the isoprostanes derived from arachidonic acid are the best characterized, many other polyunsaturated fatty acids can form isoprostanes.{7323} (±)5-iPF2α-VI is one of dozens of possible stereo- and regioisomeric isoprostanes which can be formed from arachidonic acid. To date, the most extensively studied of these is 8-isoprostane (8-epi-PGF2α, iPF2α-III).{3064,5011} However, 8-isoprostane is a minor isoprostane constituent when compared to some of the other isomers which form in natural conditions of oxidative stress.{8367} (±)5-iPF2α-VI is an isoprostane from the unique Type VI class of isoprostanes. This class has been shown to be one of the major isoprostane products, in contrast to 8-isoprostane. In addition to being produced in greater abundance than 8-isoprostane, Type VI isoprostanes form internal lactones, which facilitates their extraction and purification from biological samples.{8367,9408,6910,6390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
Isoprostanes are prostaglandin (PG)-like products of free-radical induced lipid peroxidation.{320} Although the isoprostanes derived from arachidonic acid are the best characterized, many other polyunsaturated fatty acids can form isoprostanes.{7323} (±)5-iPF2α-VI is one of dozens of possible stereo- and regioisomeric isoprostanes which can be formed from arachidonic acid. To date, the most extensively studied of these is 8-isoprostane (8-epi-PGF2α, iPF2α-III).{3064,5011} However, 8-isoprostane is a minor isoprostane constituent when compared to some of the other isomers which form in natural conditions of oxidative stress.{8367} (±)5-iPF2α-VI is an isoprostane from the unique Type VI class of isoprostanes. This class has been shown to be one of the major isoprostane products, in contrast to 8-isoprostane. In addition to being produced in greater abundance than 8-isoprostane, Type VI isoprostanes form internal lactones, which facilitates their extraction and purification from biological samples.{8367,9408,6910,6390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:-Out of stock
(±)5-iPF2α-VI-d11 contains 11 deuterium atoms at the 16, 16, 17, 17, 18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 20, and 20 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of (±)5-iPF2α-VI (Item No. 16300) by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Isoprostanes are prostaglandin-like products of free-radical induced lipid peroxidation.{320} Although the isoprostanes derived from arachidonic acid are the best characterized, many other polyunsaturated fatty acids can form isoprostanes.{7323} iPF2α-VI is one of dozens of possible stereo- and regioisomeric isoprostanes which can be formed from arachidonic acid. To date, the most extensively studied of these is 8-isoprostane (8-epi-PGF2α, iPF2α-III).{3064,5011} However, 8-isoprostane is a minor isoprostane constituent when compared to some of the other isomers which form in natural conditions of oxidative stress,{8367} including iPF2α-VI of the type-VI isoprostanes. This class has been shown to be one of the major isoprostane products, in contrast to 8-isoprostane. In addition to being produced in greater abundance than 8-isoprostane, Type VI isoprostanes form internal lactones which facilitate their extraction and purification from biological samples.{8367,9408,6910,6390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006654 - 10 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5-iPF2α-VI-d11 contains 11 deuterium atoms at the 16, 16, 17, 17, 18, 18, 19, 19, 20, 20, and 20 positions. It is intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of (±)5-iPF2α-VI (Item No. 16300) by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry. Isoprostanes are prostaglandin-like products of free-radical induced lipid peroxidation.{320} Although the isoprostanes derived from arachidonic acid are the best characterized, many other polyunsaturated fatty acids can form isoprostanes.{7323} iPF2α-VI is one of dozens of possible stereo- and regioisomeric isoprostanes which can be formed from arachidonic acid. To date, the most extensively studied of these is 8-isoprostane (8-epi-PGF2α, iPF2α-III).{3064,5011} However, 8-isoprostane is a minor isoprostane constituent when compared to some of the other isomers which form in natural conditions of oxidative stress,{8367} including iPF2α-VI of the type-VI isoprostanes. This class has been shown to be one of the major isoprostane products, in contrast to 8-isoprostane. In addition to being produced in greater abundance than 8-isoprostane, Type VI isoprostanes form internal lactones which facilitate their extraction and purification from biological samples.{8367,9408,6910,6390}
Brand:CaymanSKU:10006654 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
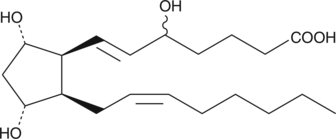
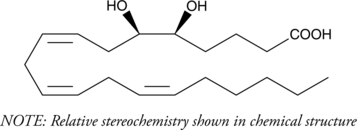
5(6)-DiHET is a fully racemic version of the enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from 5(6)-EET (Item Nos. 50211 | 10007260) by epoxide hydrolases.{729} 5(6)-DiHET can be used to quantify 5(6)-EET due to the conversion of 5(6)-EET to 5(6)-δ-lactone in solution.{39654} 5(6)-DiHET activates large conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels in smooth muscle cells from rat small coronary arteries.{37444} It is a substrate for sheep seminal vesicle COX, producing 5,6-dihydroxy prostaglandin E1 and F1α metabolites in vitro.{461} 5(6)-DiHET levels decrease in plasma in a high-fat diet-induced rat model of hyperlipidemia.{37445}
Brand:CaymanSKU:51211 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
5(6)-DiHET is a fully racemic version of the enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from 5(6)-EET (Item Nos. 50211 | 10007260) by epoxide hydrolases.{729} 5(6)-DiHET can be used to quantify 5(6)-EET due to the conversion of 5(6)-EET to 5(6)-δ-lactone in solution.{39654} 5(6)-DiHET activates large conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels in smooth muscle cells from rat small coronary arteries.{37444} It is a substrate for sheep seminal vesicle COX, producing 5,6-dihydroxy prostaglandin E1 and F1α metabolites in vitro.{461} 5(6)-DiHET levels decrease in plasma in a high-fat diet-induced rat model of hyperlipidemia.{37445}
Brand:CaymanSKU:51211 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
5(6)-DiHET is a fully racemic version of the enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from 5(6)-EET (Item Nos. 50211 | 10007260) by epoxide hydrolases.{729} 5(6)-DiHET can be used to quantify 5(6)-EET due to the conversion of 5(6)-EET to 5(6)-δ-lactone in solution.{39654} 5(6)-DiHET activates large conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels in smooth muscle cells from rat small coronary arteries.{37444} It is a substrate for sheep seminal vesicle COX, producing 5,6-dihydroxy prostaglandin E1 and F1α metabolites in vitro.{461} 5(6)-DiHET levels decrease in plasma in a high-fat diet-induced rat model of hyperlipidemia.{37445}
Brand:CaymanSKU:51211 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
5(6)-DiHET is a fully racemic version of the enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from 5(6)-EET (Item Nos. 50211 | 10007260) by epoxide hydrolases.{729} 5(6)-DiHET can be used to quantify 5(6)-EET due to the conversion of 5(6)-EET to 5(6)-δ-lactone in solution.{39654} 5(6)-DiHET activates large conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels in smooth muscle cells from rat small coronary arteries.{37444} It is a substrate for sheep seminal vesicle COX, producing 5,6-dihydroxy prostaglandin E1 and F1α metabolites in vitro.{461} 5(6)-DiHET levels decrease in plasma in a high-fat diet-induced rat model of hyperlipidemia.{37445}
Brand:CaymanSKU:51211 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
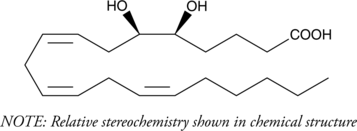
5,6-DiHET lactone is a lactonized form of 5,6-EET and 5,6-DiHET. In solution, 5(6)-EET degrades into 5(6)-DiHET and 5(6)-δ-lactone, which can be converted to 5(6)-DiHET and quantified by GC-MS.{39654} 5,6-DiHET potently induces vasodilation of isolated canine coronary arterioles, with 41 and 100% inhibition occurring at 0.01 and 100 pM, respectively.{12606} It also induces vasodilation in isolated human microvessels and increases intracellular calcium levels in a dose-dependent manner, an effect that can be blocked by the nitric oxide scavenger L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{43011}
Brand:CaymanSKU:51212 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
5,6-DiHET lactone is a lactonized form of 5,6-EET and 5,6-DiHET. In solution, 5(6)-EET degrades into 5(6)-DiHET and 5(6)-δ-lactone, which can be converted to 5(6)-DiHET and quantified by GC-MS.{39654} 5,6-DiHET potently induces vasodilation of isolated canine coronary arterioles, with 41 and 100% inhibition occurring at 0.01 and 100 pM, respectively.{12606} It also induces vasodilation in isolated human microvessels and increases intracellular calcium levels in a dose-dependent manner, an effect that can be blocked by the nitric oxide scavenger L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{43011}
Brand:CaymanSKU:51212 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
5,6-DiHET lactone is a lactonized form of 5,6-EET and 5,6-DiHET. In solution, 5(6)-EET degrades into 5(6)-DiHET and 5(6)-δ-lactone, which can be converted to 5(6)-DiHET and quantified by GC-MS.{39654} 5,6-DiHET potently induces vasodilation of isolated canine coronary arterioles, with 41 and 100% inhibition occurring at 0.01 and 100 pM, respectively.{12606} It also induces vasodilation in isolated human microvessels and increases intracellular calcium levels in a dose-dependent manner, an effect that can be blocked by the nitric oxide scavenger L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{43011}
Brand:CaymanSKU:51212 - 250 µgAvailable on backorder
5,6-DiHET lactone is a lactonized form of 5,6-EET and 5,6-DiHET. In solution, 5(6)-EET degrades into 5(6)-DiHET and 5(6)-δ-lactone, which can be converted to 5(6)-DiHET and quantified by GC-MS.{39654} 5,6-DiHET potently induces vasodilation of isolated canine coronary arterioles, with 41 and 100% inhibition occurring at 0.01 and 100 pM, respectively.{12606} It also induces vasodilation in isolated human microvessels and increases intracellular calcium levels in a dose-dependent manner, an effect that can be blocked by the nitric oxide scavenger L-NAME (Item No. 80210).{43011}
Brand:CaymanSKU:51212 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
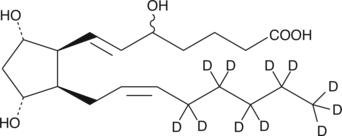
5(6)-DiHET is a fully racemic version of the enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from 5(6)-EET (Item Nos. 50211 | 10007260) by epoxide hydrolases.{729} 5(6)-DiHET can be used to quantify 5(6)-EET due to the conversion of 5(6)-EET to 5(6)-δ-lactone in solution.{39654} 5(6)-DiHET activates large conductance calcium-activated potassium (BK) channels in smooth muscle cells from rat small coronary arteries.{37444} It is a substrate for sheep seminal vesicle COX, producing 5,6-dihydroxy prostaglandin E1 and F1α metabolites in vitro.{461} 5(6)-DiHET levels decrease in plasma in a high-fat diet-induced rat model of hyperlipidemia.{37445} (±)5(6)-DiHET MaxSpec® standard is a quantitative grade standard of (±)5(6)-DiHET (Item No. 51211) that has been prepared specifically for mass spectrometry and related applications where quantitative reproducibility is required. The solution has been prepared gravimetrically and is supplied in a deactivated glass ampule sealed under argon. The concentration was verified by comparison to an independently prepared calibration standard. This (±)5(6)-DiHET MaxSpec® standard is guaranteed to meet identity, purity, stability, and concentration specifications and is provided with a batch-specific certificate of analysis. Ongoing stability testing is performed to ensure the concentration remains accurate throughout the shelf life of the product. Note: The amount of solution added to the vial is in excess of the listed amount. Therefore, it is necessary to accurately measure volumes for preparation of calibration standards. Follow recommended storage and handling conditions to maintain product quality.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10007264 - 10 µgAvailable on backorder
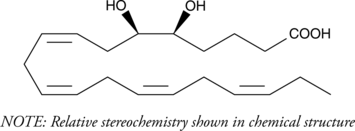
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item No. 90110) is an ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid that is abundant in marine organisms and fish oils. EPA is metabolized, in part, through cytochrome P450-catalyzed epoxidation followed by conversion to the vicinal diols by epoxide hydrolases.{13149,13151,5625} (±)5(6)-DiHETE is a possible metabolite produced from EPA following epoxidation of the α-5 double bond. The biological activity of (±)5(6)-DiHETE has not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10467 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item No. 90110) is an ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid that is abundant in marine organisms and fish oils. EPA is metabolized, in part, through cytochrome P450-catalyzed epoxidation followed by conversion to the vicinal diols by epoxide hydrolases.{13149,13151,5625} (±)5(6)-DiHETE is a possible metabolite produced from EPA following epoxidation of the α-5 double bond. The biological activity of (±)5(6)-DiHETE has not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10467 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
Eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA; Item No. 90110) is an ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid that is abundant in marine organisms and fish oils. EPA is metabolized, in part, through cytochrome P450-catalyzed epoxidation followed by conversion to the vicinal diols by epoxide hydrolases.{13149,13151,5625} (±)5(6)-DiHETE is a possible metabolite produced from EPA following epoxidation of the α-5 double bond. The biological activity of (±)5(6)-DiHETE has not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:10467 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
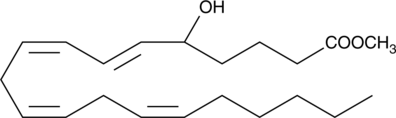
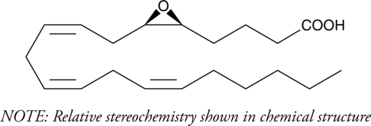
5(6)-EET is a fully racemic version of the enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) by cytochrome P450 enzymes.{463,729} In solution, 5(6)-EET degrades into 5,6-DiHET and 5(6)-δ-lactone, which can be converted to 5(6)-DiHET and quantified by GC-MS.{39654} In neuroendocrine cells, such as the anterior pituitary and pancreatic islets, 5(6)-EET has been implicated in the mobilization of calcium and hormone secretion.{462,460} 5(6)-EET is an inhibitor of T-type voltage-gated calcium channels (Cav3) that inhibits isoforms Cav3.1, Cav3.2 (IC50 = 0.54 µM), and Cav3.3 and decreases nifedipine-resistant phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction in isolated mouse mesenteric arteries via Cav3.2 blockade when used at a concentration of 3 µM.{42110} In addition, it is a substrate of COX-1 and COX-2, as measured by oxygen consumption and product formation assays when used at a concentration of 50 µM.{34481} (±)5(6)-EET is provided as a mixture of the free acid and lactone.
Brand:CaymanSKU:50211 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder
5(6)-EET is a fully racemic version of the enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) by cytochrome P450 enzymes.{463,729} In solution, 5(6)-EET degrades into 5,6-DiHET and 5(6)-δ-lactone, which can be converted to 5(6)-DiHET and quantified by GC-MS.{39654} In neuroendocrine cells, such as the anterior pituitary and pancreatic islets, 5(6)-EET has been implicated in the mobilization of calcium and hormone secretion.{462,460} 5(6)-EET is an inhibitor of T-type voltage-gated calcium channels (Cav3) that inhibits isoforms Cav3.1, Cav3.2 (IC50 = 0.54 µM), and Cav3.3 and decreases nifedipine-resistant phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction in isolated mouse mesenteric arteries via Cav3.2 blockade when used at a concentration of 3 µM.{42110} In addition, it is a substrate of COX-1 and COX-2, as measured by oxygen consumption and product formation assays when used at a concentration of 50 µM.{34481} (±)5(6)-EET is provided as a mixture of the free acid and lactone.
Brand:CaymanSKU:50211 - 25 µgAvailable on backorder
5(6)-EET is a fully racemic version of the enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) by cytochrome P450 enzymes.{463,729} In solution, 5(6)-EET degrades into 5,6-DiHET and 5(6)-δ-lactone, which can be converted to 5(6)-DiHET and quantified by GC-MS.{39654} In neuroendocrine cells, such as the anterior pituitary and pancreatic islets, 5(6)-EET has been implicated in the mobilization of calcium and hormone secretion.{462,460} 5(6)-EET is an inhibitor of T-type voltage-gated calcium channels (Cav3) that inhibits isoforms Cav3.1, Cav3.2 (IC50 = 0.54 µM), and Cav3.3 and decreases nifedipine-resistant phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction in isolated mouse mesenteric arteries via Cav3.2 blockade when used at a concentration of 3 µM.{42110} In addition, it is a substrate of COX-1 and COX-2, as measured by oxygen consumption and product formation assays when used at a concentration of 50 µM.{34481} (±)5(6)-EET is provided as a mixture of the free acid and lactone.
Brand:CaymanSKU:50211 - 50 µgAvailable on backorder
5(6)-EET is a fully racemic version of the enantiomeric forms biosynthesized from arachidonic acid (Item No. 90010) by cytochrome P450 enzymes.{463,729} In solution, 5(6)-EET degrades into 5,6-DiHET and 5(6)-δ-lactone, which can be converted to 5(6)-DiHET and quantified by GC-MS.{39654} In neuroendocrine cells, such as the anterior pituitary and pancreatic islets, 5(6)-EET has been implicated in the mobilization of calcium and hormone secretion.{462,460} 5(6)-EET is an inhibitor of T-type voltage-gated calcium channels (Cav3) that inhibits isoforms Cav3.1, Cav3.2 (IC50 = 0.54 µM), and Cav3.3 and decreases nifedipine-resistant phenylephrine-induced vasoconstriction in isolated mouse mesenteric arteries via Cav3.2 blockade when used at a concentration of 3 µM.{42110} In addition, it is a substrate of COX-1 and COX-2, as measured by oxygen consumption and product formation assays when used at a concentration of 50 µM.{34481} (±)5(6)-EET is provided as a mixture of the free acid and lactone.
Brand:CaymanSKU:50211 - 500 µgAvailable on backorder
(±)5(6)-EpETE methyl ester is a derivative of 5(6)-EpETE which is stable enough to ship and handle routinely.(±) 5(6)-EpETE methyl ester is a chemically less reactive derivative of 5(6)-EpETE. The active free acid can be generated from the methyl ester by careful base hydrolysis. Epoxy eicosatetraenoic acids (EpETEs) are the epoxygenase metabolites of EPA. A number of vicinal diol metabolites of EpETEs have been detected in the plasma of patients on marine oil dietary supplementation, while in subjects on a typical western diet these compounds are generally not detected.{996} The specific biologic activity of 5(6)-EpETE and its methyl ester have not been documented.
Brand:CaymanSKU:90114 - 100 µgAvailable on backorder