Description
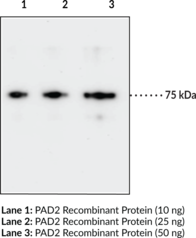
Protein Arginine Deiminases (PADs) are guanidino-modifying enzymes belonging to the amidinotransferase superfamily and are designated PAD1-4 and PAD6. PAD enzymes catalyze the conversion of specific arginine residues to citrulline in a calcium-dependent manner. All enzymes are cytosolic except for PAD4 which is localized in the nucleus.{18141} PAD2 is the most widely expressed member and also the most conserved across mammalian species, implying it is the ancestral homologue of the PADs.{19489} Overexpression of PAD2 results in myelin loss in a transgenic model, potentially linking PAD2 activity to multiple sclerosis.{30727} It has also been shown to modify vimentin and β/γ-actin, potentially aggravating the autoantigen response in rheumatoid arthritis.{30728,30130} PAD2 may also play a role in transcriptional regulation, as it has been shown capable of citrullinating histones, particularly H3 during mammalian reproductive cycles, when it is transcriptionally activated in the nucleus.{30729} The predicted molecular weight of PAD2 is 75.6 kDa and Cayman’s PAD2 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone 9F7) detects a band at 75 kDa by western blot.
Synonyms: Protein-Arginine Deiminase Type-2|PAD-H19|PADI2|Peptidylarginine Deiminase II
Immunogen: Full length recombinant human PAD2 protein
Formulation: 100 µg of protein G-purified antibody
Isotype: IgG1
Applications: ELISA, IHC, and WB
Origin:
Stability: 365 days
Application|ELISA||Application|Immunohistochemistry||Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Monoclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Writers|Citrullination||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity|Rheumatoid Arthritis