Description
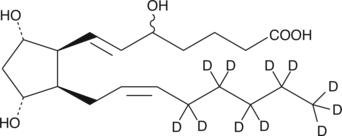
An internal standard for the quantification of (±)5-iPF2α-VI by GC- or LC-MS.
Formal name: (±)5,9α,11α-trihydroxy-(8β)-prosta-6E,14Z-dien-1-oic-16,16,17,17,18,18,19,19,20,20,20-d11 acid
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 365.6
CAS: 936565-17-2
Purity: ≥99% deuterated forms (d1-d11)
Formulation: A solution in ethanol
Application|Mass Spectrometry||Product Type|Biochemicals|Analytical Standards||Product Type|Biochemicals|Isotopically Labeled Standards|Deuterium||Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Isoprostanes||Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Prostaglandins||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|Lipid Peroxidation