Description
An analog of valeric acid; inhibits class I HDACs (IC50s = ~2 mM); the number of axon branches in sensory neurons isolated from newborn rat dorsal root ganglia; inhibits amyloid-β deposition and neuritic plaque formation and decreases escape latency in the Morris water maze test in the APP23 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease; has anticonvulsant activity in the pentylenetetrazol seizure threshold test in mice (ED50 = 0.71 mmol/kg); induces neurotoxicity at ≥1.2 mmol/kg
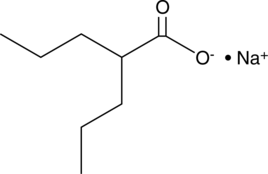
Formal name: 2-propyl-pentanoic acid, monosodium salt
Synonyms: 2-Propylvaleric Acid|Valproate|VPA
Molecular weight: 166.2
CAS: 1069-66-5
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Deacetylases||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Erasers|Histone Deacetylation||Research Area|Neuroscience|Behavioral Neuroscience|Bipolar Disorder||Research Area|Neuroscience|Behavioral Neuroscience|Learning & Memory||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease||Research Area|Neuroscience|Seizure Disorders