Description
Isoxyl is a thiourea derivative that was used in the 1960s to successfully treat tuberculosis (TB). It has considerable antimycobacterial activity in vitro and is effective against multi-drug resistant strains of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in the range of 1-10 µg/ml.{13370,13371} At concentrations of 10 µM, isoxyl inhibits the synthesis of M. bovis during six hours of exposure which is similar to isoniazid (INH) and ethionamide (ETH), two other predominant anti-TB drugs. Unlike INH and ETH, isoxyl also partially inhibits the synthesis of fatty acids. Isoxyl shows no acute toxicity against primary macrophage cell cultures as demonstrated by diminution of redox activity.{13371}
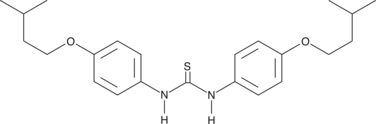
Formal name: N,N’-bis[4-(3-methylbutoxy)phenyl]-thiourea
Synonyms: Isoxyl
Molecular weight: 400.6
CAS: 910-86-1
Purity: >98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|Tuberculosis