Description
A prodrug form of 5-aminosalicylic acid; inhibits TNF-α and LPS-induced NF-κB activation in SW620 colon cancer cells at 0.1-5 mM; inhibits cystine uptake through the system xc- cysteine-glutamate transporter at 0.25 mM and inhibits the growth of U-87MG glioma cells in an NF-κB independent manner at 0.25-1 mM; decreases diarrhea, increases food intake, and reverses body weight decreases in a mouse model of colitis at 100 mg/kg; suppresses antigen-induced arthritis in mice
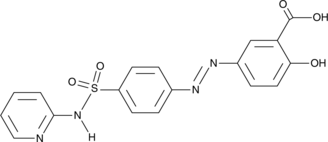
Formal name: 2-hydroxy-5-[2-[4-[(2-pyridinylamino)sulfonyl]phenyl]diazenyl]-benzoic acid
Synonyms: Azopyrin|NSC 203730|NSC 667219
Molecular weight: 398.4
CAS: 599-79-1
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|TNF-α/NF-κB Signaling||Product Type|Biochemicals|Transporter & Exchanger Modulators||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Death|Ferroptosis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|NF-κB Signaling||Research Area|Epigenetics, Transcription, & Translation|Transcription Factors||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Autoimmunity|Rheumatoid Arthritis||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Gastric Disease|Ulcerative Colitis