Description
A sulfonamide antibiotic that inhibits the growth of Gram-negative bacteria and other microorganisms; inhibits recombinant P. carinii DHPS (IC50 = 17 nM); inhibits folate biosynthesis in P. carinii by 75% at 50 nM; inhibits any visible growth in culture tubes of 378 out of 530 E. coli isolates from necropsied animals and poultry at 0.25 mg/ml; decreases the number of viable amoxicillin-induced B. burgdorferi round body forms to 30% of control at 50 μM; decreases the number of P. carinii trophozoite and cyst lesions in lung tissue in a mouse model of pneumonia infection (ED50s = 0.06 and 0.08 mg/kg per day, respectively)
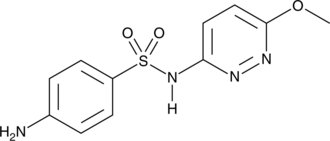
Formal name: 4-amino-N-(6-methoxy-3-pyridazinyl)-benzenesulfonamide
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 280.3
CAS: 80-35-3
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics|Sulfonamides||Product Type|Biochemicals|Antifungals||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Nucleic Acid Turnover/Signaling||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|Pneumonia||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Fungal Diseases|Pneumonia