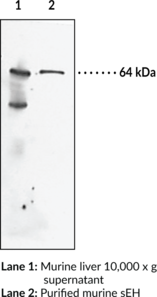
Description
Soluble epoxide hydrolase (sEH) is a member of the α/β-hydrolase fold enzyme family that catalyzes the hydrolysis of bioactive fatty acid epoxides to inactive vicinal diols.{52737} It is a homodimer in which each subunit is composed of two domains, a C-terminal epoxide hydrolase domain and an N-terminal phosphatase domain.{52738,15765} sEH is localized to the cytoplasm or to peroxisomes in a tissue specific manner and is found in various tissues, including skin, lung, uterus, kidney, brain, and myocardium.{52740,52739} sEH is also expressed in the vasculature and inhibition of sEH attenuates pathogenic vascular remodeling and hypertension via preservation of cardioprotective epoxyeicosatrienoic acids (EETs) in rat models of atherosclerosis and hypertension, respectively.{52741} Inhibition of sEH also has a protective role in various diseases including inflammatory bowel disease, osteoarthritis, seizure, stroke, and Alzheimer’s disease, as well as in various chronic pain states.{52737,50771} Cayman’s Soluble Epoxide Hydrolase (FL) Polyclonal Antibody can be used for Western blot applications. The antibody recognizes sEH at 64 kDa from human and murine samples.
Synonyms: Cytosolic Epoxide Hydrolase (CEH)|EPHX2|Epoxide Hydrolase 2|sEH
Immunogen: Recombinant mouse sEH
Formulation: 100 μg of Protein A-purified antibody
Isotype:
Applications: WB
Origin: Animal/Rabbit
Stability: 365 days
Application|Western Blot||Product Type|Antibodies|Polyclonal Antibodies||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Cardiovascular Diseases|Hypertension||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease