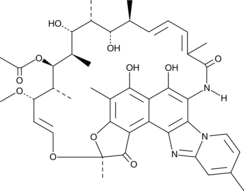
Description
An antibiotic derived from rifamycin SV; inhibits the growth of a variety of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria in vitro, including Staphylococcus, Streptococcus, Enterococcus, H. influenzae, and N. gonorrhoeae (MIC50s = ≤0.015, 50 = ~20 μM); reduces colonic damage, rectal bleeding, and diarrhea in PXR-humanized, but not wild-type or Pxr-null, mice with IBD induced by DSS; exhibits minimal intestinal absorption after oral administration and is, therefore, effective in eliminating bacteria in the gastrointestinal system
Formal name: (2S,18E,28E)-25S-(acetyloxy)-5,6,21S,23R-tetrahydroxy-27S-methoxy-2,4,11,16Z,20S,22R,24R,26R-octamethyl-2,7-(epoxypentadeca[1,11,13]trienimino)benzofuro[4,5-e]pyrido[1,2-a]benzimidazole-1,15(2H)-dione
Synonyms: L 105SV|Rifamycin L 105
Molecular weight: 785.9
CAS: 80621-81-4
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics|Rifamycins||Product Type|Biochemicals|Receptor Pharmacology|Agonists||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases|STDs