Description
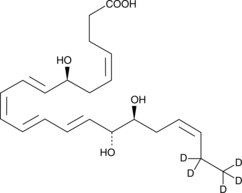
An internal standard for the quantification of RvD2 by GC- or LC-MS
Formal name: 7S,16R,17S-trihydroxy-4Z,8E,10Z,12E,14E,19Z-21,21’,22,22,22-d5 docosahexaenoic acid
Synonyms: 7(S),16(R),17(S)-Resolvin D2-d5|RvD2-d5
Molecular weight: 381.5
CAS: 1881277-33-3
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A solution in ethanol
Application|Mass Spectrometry||Product Type|Biochemicals|Isotopically Labeled Standards|Deuterium||Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Docosanoids||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Inflammatory Lipid Mediators|Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Phagocytosis||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Sepsis/Shock||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Fatty Acids||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Lipoxygenase Pathways