Description
Activates the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (Ki = 5.4 µM), inducing the expression of both detoxifying enzymes, resulting in pyocyanin degradation, and cytokines that facilitate the clearance of bacteria; accelerates neutrophil apoptosis, resulting in resolution of acute inflammation
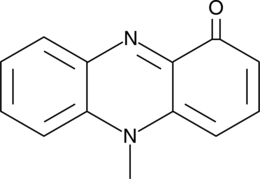
Formal name: 5-methyl-1(5H)-phenazinone
Synonyms: Pyocyanine|Sanasin|Sanazin
Molecular weight: 210.2
CAS: 85-66-5
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Microbial Metabolites||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Activators||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases