Description
An alkaloid with diverse biological activities; inhibits platelet aggregation induced by ADP, arachidonic acid, PAF, and collagen; inhibits norepinephrine-induced contraction of isolated rat thoracic aorta; a non-selective inhibitor of ICa, IK, IK1, and INa in guinea pig ventricular myocytes; inhibits the growth of H. pylori (MIC50 = 100 μg/ml); reduces growth of PC3 and DU145 prostate cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner via induction of mitotic cell cycle arrest; increases latency to first seizure in a pentylenetetrazole-induced mouse model
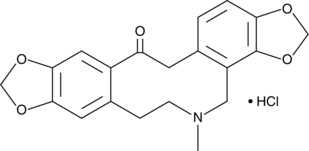
Formal name: 4,6,7,14-tetrahydro-5-methyl-bis[1,3]benzodioxolo[4,5-c:5′,6′-g]azecin-13(5H)-one, monohydrochloride
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 389.8
CAS: 6164-47-2
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Antibiotics||Product Type|Biochemicals|Ion Channel Modulation|Blockers||Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Alkaloids||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Cycle|G2/M||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Blood|Coagulation & Hemostasis||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Blood|Thrombosis||Research Area|Cardiovascular System|Vasculature|Vasodilation||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation||Research Area|Infectious Disease|Bacterial Diseases||Research Area|Neuroscience|Seizure Disorders