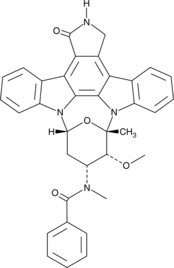
Description
A cell-permeable, reversible inhibitor of several kinases, including PKCα, PKCβ, PKCγ, Syk, FLK1, Akt,PKA, c-Kit, C-Fgr, c-Src, FLT3, PDFRβ, VEGFR1, and VEGF2, with IC50 values ranging from 80-500 nM
Formal name: N-[(9S,10R,11R,13R)-2,3,10,11,12,13-hexahydro-10-methoxy-9-methyl-1-oxo-9,13-epoxy-1H,9H-diindolo[1,2,3-gh:3′,2′,1′-lm]pyrrolo[3,4-j][1,7]benzodiazonin-11-yl]-N-methyl-benzamide
Synonyms: CGP 41231|CGP 41251|Midostaurin|N-Benzoylstaurosporine
Molecular weight: 570.6
CAS: 120685-11-2
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|PDGFR Family||Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|PKA||Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|PKB/Akt||Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|PKC||Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|SRC Family||Product Type|Biochemicals|Kinase Inhibitors|VEGFR Family||Product Type|Biochemicals|Small Molecule Inhibitors|Kinases||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|Growth Factor Receptor Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling||Research Area|Cancer|Cell Signaling|PKC Signaling||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|cAMP Signaling||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Growth Factor Receptors||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|PI3K/Akt/mTOR Signaling