Description
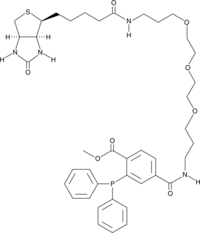
A labeling reagent that selectively reacts with azido groups on modified proteins through the Staudinger ligation reaction; can be used in common avidin-based biochemical techniques in whole cells or by blotting experiments following SDS-PAGE; has been used successfully in conjunction with Daz-1 or Daz-2 to label and detect sulfenic acid sites in proteins
Formal name: 2-(diphenylphosphino)-4-[21-[(3aS,4S,6aR)-hexahydro-2-oxo-1H-thieno[3,4-d]imidazol-4-yl]-1,17-dioxo-6,9,12-trioxa-2,16-diazaheneicos-1-yl]-benzoic acid, methyl ester
Synonyms: Click Tag™ Phosphine-biotin
Molecular weight: 792.9
CAS: 608514-42-7
Purity: ≥95%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Application|Click Chemistry||Product Type|Biochemicals|Labeling & Detection|Reactive Probes||Research Area