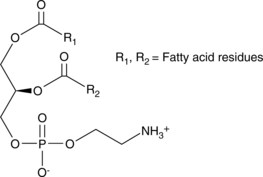
Description
A mixture of phosphatidylethanolamines isolated from bovine brain; comprises approximately 25% of total mammalian phospholipids and almost 50% of brain phospholipids; found mainly in the cell membrane; synthesized mainly in the ER and mitochondrial membranes; acts as a chaperone in E. coli for lactose permease assembly; cofactor for prion propagation that can convert recombinant mammalian proteins into infectious molecules,,
Formal name:
Synonyms: PE (bovine)
Molecular weight: 744
CAS: 90989-93-8
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A solution in chloroform
Product Type|Biochemicals|Lipids|Glycerophospholipids||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cellular Chaperones||Research Area|Lipid Biochemistry|Glycerophospholipids||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Prion Disease