Description
An anthocyanidin with diverse biological activities; scavenges superoxide anions in cell-free assays (IC50 = 130 µg/ml); inhibits hydrogen peroxide-induced lipid peroxidation in rat brain homogenates (IC50 = 85 µM); reduces serum levels of ALT and AST, hepatocyte apoptosis, and hepatic levels of IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, and TGF-β in a mouse model of acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity at 3 mg/kg; increases survival and reduces pulmonary fibrosis and leukocyte infiltration in a mouse model of LPS-induced endotoxemia; reduces serum levels of NO, TNF-α, and IL-6 and increases renal MPO, SOD, and CAT activities, as well as increases survival, in a mouse model of cecal ligation and puncture-induced sepsis from 0.04-0.4 mg/kg; decreases escape latency in the Morris water maze, reduces hippocampal MDA levels, and increases hippocampal AChE activity in a rat model of Aβ (25-35)-induced Alzheimer’s disease
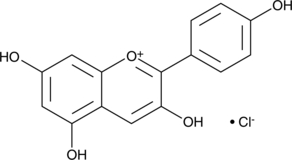
Formal name: 3,5,7-trihydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1-benzopyrylium, monochloride
Synonyms:
Molecular weight: 306.7
CAS: 134-04-3
Purity: ≥98%
Formulation: A crystalline solid
Product Type|Biochemicals|Natural Products|Flavonoids||Product Type|Biochemicals|Ox Stress Reagents|Antioxidants||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Death|Apoptosis||Research Area|Cell Biology|Cell Signaling|Nitric Oxide Signaling||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Innate Immunity|Sepsis/Shock||Research Area|Immunology & Inflammation|Pulmonary Diseases||Research Area|Neuroscience|Behavioral Neuroscience|Learning & Memory||Research Area|Neuroscience|Neurodegenerative Disorders|Alzheimer’s Disease||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|Antioxidant Activity||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|Lipid Peroxidation||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|Reactive Nitrogen||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|Reactive Oxygen|Catalase||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|Reactive Oxygen|Myeloperoxidase||Research Area|Oxidative Stress & Reactive Species|Reactive Oxygen|Superoxide Dismutase